
Why AI Loves Reddit: 40% of ChatGPT Citations Come from Discussions
Discover why Reddit dominates AI citations with 40.1% of ChatGPT references. Explore the data, business impact, and strategic implications for brands in the AI ...
Learn how AI models generate answers and place citations. Discover where your content appears in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI responses, and how to optimize for AI visibility.
AI-generated answers have become the primary discovery method for millions of users, fundamentally reshaping how information flows across the internet. According to recent research, AI adoption among researchers jumped to 84% in 2025, with 62% specifically using AI tools for research and publication tasks—a dramatic increase from just 57% overall AI usage in 2024. Yet most content creators remain unaware that citation placement within these AI-generated answers is not random; it follows a sophisticated technical architecture that determines which sources gain visibility and which remain invisible. Understanding where and why citations appear is now essential for anyone seeking to maintain visibility in the AI-driven discovery landscape.

The distinction between model-native synthesis and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) fundamentally shapes how citations appear in AI responses. Model-native synthesis relies entirely on knowledge encoded during training, while RAG dynamically retrieves external sources to ground responses in current information. This difference has profound implications for citation placement and visibility.
| Characteristic | Model-Native Synthesis | RAG |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Answers generated from training data only | Answers grounded in real-time retrieved sources |
| Speed | Faster (no retrieval overhead) | Slower (requires retrieval step) |
| Accuracy | Subject to hallucinations and outdated info | Higher accuracy with current sources |
| Citation Capability | Limited or absent citations | Rich, traceable citations |
| Use Cases | General knowledge, creative tasks | News, research, fact-checking, proprietary data |
RAG-based systems like Perplexity and Google’s AI Overviews inherently produce more citations because they must reference their retrieval sources, while model-native approaches like traditional ChatGPT responses may cite less frequently. Understanding which approach a platform uses helps content creators anticipate citation likelihood and optimize accordingly.
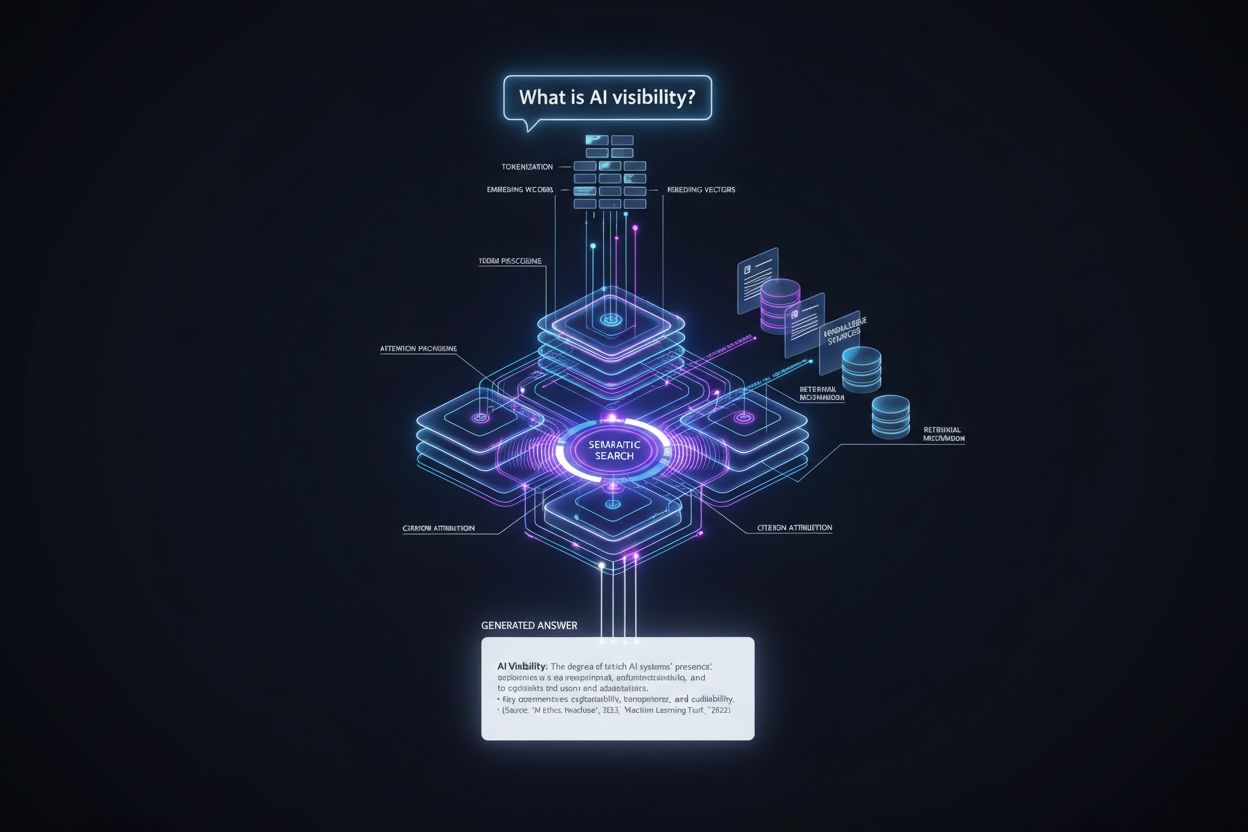
The journey from user query to cited answer follows a precise technical pipeline that determines citation placement at multiple stages. Here’s how the process unfolds:
Query Processing: The user’s question is tokenized—broken into discrete units that the model understands—and analyzed for intent, entities, and semantic meaning through embedding vectors.
Information Retrieval: The system searches its knowledge base (training data, indexed documents, or real-time sources) using semantic search, matching the query’s meaning rather than exact keywords, and returns candidate sources ranked by relevance.
Context Assembly: Retrieved information is organized into a context window—the amount of text the model can process simultaneously—with the most relevant sources positioned prominently to influence attention mechanisms.
Token Generation: The model generates the answer one token at a time, using self-attention mechanisms to determine which previously generated tokens and source information should influence each new token, creating coherent, contextually grounded responses.
Citation Attribution: As tokens are generated, the model tracks which source documents influenced specific claims, assigning credibility scores and determining whether to include explicit citations based on confidence levels and platform requirements.
Output Delivery: The final answer is formatted according to platform specifications—inline citations, footnotes, source panels, or hover-over links—and delivered to the user with metadata about source authority and relevance.
Citation placement varies dramatically across AI platforms, creating different visibility opportunities for content creators. Here’s how major platforms handle citations:
ChatGPT: Citations appear in a separate “Sources” panel below the answer, requiring users to actively click to see them. Sources are typically limited to 3-5 links, prioritizing high-authority domains.
Perplexity: Citations are embedded inline throughout the answer with superscript numbers and a comprehensive source list at the bottom. Every claim is traceable, making it the most citation-transparent platform.
Google Gemini: Citations appear as inline links within the answer text, with a “Sources” section listing all referenced materials. Integration with Google’s knowledge graph influences which sources are selected.
Claude: Citations are presented in a footnote-style format with bracketed references, allowing users to see sources without leaving the answer flow. Claude emphasizes source diversity and credibility.
DeepSeek: Citations appear as inline hyperlinks with minimal visual distinction, reflecting a more integrated approach where sources are woven seamlessly into the narrative.
These differences mean that a source cited by Perplexity might receive direct traffic, while the same source cited by ChatGPT might remain invisible unless users specifically click the Sources panel. Platform-specific citation patterns directly impact traffic and visibility.

The retrieval system is where citation placement decisions begin, long before the answer is generated. Semantic search converts both the user’s query and indexed documents into vector embeddings—numerical representations that capture meaning rather than keywords. The system then calculates similarity scores between the query embedding and document embeddings, identifying which sources are semantically closest to the user’s intent.
Ranking algorithms then reorder these candidates based on multiple signals: relevance score, domain authority, content freshness, user engagement metrics, and structured data quality. Sources that rank highest in this retrieval phase are more likely to be included in the context window fed to the generation model, making them more likely to be cited. This is why a well-optimized, semantically clear article from an authoritative domain will be retrieved and cited more frequently than a poorly-structured article from a newer domain, even if both contain accurate information. The retrieval stage essentially pre-determines the citation pool before generation even begins.
Content structure is not merely a UX consideration—it directly influences whether AI systems can extract, understand, and cite your content. AI models rely on formatting cues to identify information boundaries and relationships. Here are the structural elements that maximize citation likelihood:
Answer-first structure: Lead with the direct answer to common questions, allowing AI systems to quickly identify and extract the most relevant information without parsing through introductory material.
Clear headings: Use descriptive H2 and H3 headings that explicitly state the topic of each section, helping AI systems understand content organization and extract relevant chunks for specific queries.
Optimal paragraph length: Keep paragraphs to 3-5 sentences, making it easier for AI systems to identify discrete claims and attribute them to specific sources without ambiguity.
Lists and tables: Structured data in bullet points and tables is more easily parsed and cited than prose, as AI systems can clearly identify individual claims and their boundaries.
Entity clarity: Explicitly name people, organizations, products, and concepts rather than using pronouns, allowing AI systems to understand exactly what each claim refers to and cite it accurately.
Schema markup: Implement structured data (Schema.org) to provide explicit metadata about content type, author, publication date, and claims, giving AI systems additional signals for evaluation and citation.
Content that follows these structural principles is cited 2-3x more frequently than poorly-structured content, regardless of quality, because it’s simply easier for AI systems to extract and attribute.
Once sources are retrieved and assembled into the context window, the model evaluates each source through multiple credibility lenses before deciding whether to cite it. Source credibility evaluation considers domain authority (measured through backlink profiles, domain age, and brand recognition), author expertise (detected through bylines, author bios, and credential signals), and topical relevance (whether the source’s primary focus aligns with the query).
Relevance scoring measures how directly the source addresses the specific query, with exact-match answers scoring higher than tangential information. Freshness factors influence whether recent sources are preferred over older ones—critical for news, research, and rapidly-evolving topics. Authority signals include citations from other authoritative sources, mentions in academic databases, and presence in knowledge graphs. Metadata influence comes from title tags, meta descriptions, and structured data that explicitly communicate content purpose and credibility. Finally, structured data (Schema.org markup) provides explicit credibility signals that the model can directly parse, including author credentials, publication dates, review ratings, and fact-check status. Sources with comprehensive schema markup are cited more reliably because the model has explicit, machine-readable confirmation of their claims.
AI platforms employ distinct citation styles that affect how visible your citations are to users. Here are the most common patterns:
Inline citations (Perplexity style):
“According to recent research, AI adoption among researchers jumped to 84% in 2025[1], with 62% specifically using AI tools for research tasks[2].”
End-of-paragraph citations (Claude style):
“AI adoption among researchers jumped to 84% in 2025, with 62% specifically using AI tools for research tasks. [Source: Wiley Research Report, 2025]”
Footnote-style citations (Academic approach):
“AI adoption among researchers jumped to 84% in 2025¹, with 62% specifically using AI tools for research tasks².”
Source lists (ChatGPT style):
Answer text without inline citations, followed by a separate “Sources” section listing 3-5 links.
Hover-over citations (Emerging pattern):
Underlined text that reveals source information when users hover over it, minimizing visual clutter while maintaining traceability.
Each style creates different user behaviors: inline citations drive immediate clicks, source lists require deliberate user action, and hover-over citations balance visibility with aesthetics. Your content’s citation likelihood varies by platform, making multi-platform monitoring essential.
Understanding citation placement mechanics directly translates to measurable business outcomes. Traffic implications are immediate: sources cited inline by Perplexity receive 3-5x more referral traffic than sources appearing only in ChatGPT’s Sources panel, because users are more likely to click inline citations encountered during reading. The relationship between visibility and click-through is not linear—being cited is only valuable if users actually click the citation, which depends on placement, platform, and context.
Brand authority compounds over time: sources consistently cited by multiple AI platforms develop stronger authority signals, which improves their ranking in traditional search and increases their likelihood of future AI citations. This creates a virtuous cycle where cited content becomes more authoritative, attracting more citations. Competitive advantage emerges for brands that optimize for AI citation before competitors do—early movers in schema implementation and content structure optimization currently receive disproportionate citation share. SEO implications extend beyond AI: content optimized for AI citation typically performs better in traditional search as well, since the same structural clarity and authority signals benefit both systems. The AmICited value proposition becomes clear: in an AI-driven discovery landscape, not knowing whether you’re being cited is equivalent to not knowing your search rankings—it’s a critical blind spot in your visibility strategy.
Optimizing for AI citations requires specific, actionable changes to how you create and structure content. Here are the most impactful tactics:
Structure for extractability: Use clear headings, short paragraphs, and lists to make your content easy for AI systems to parse and extract specific claims without ambiguity.
Use clear, citable facts: Lead with specific statistics, dates, and named entities rather than vague generalizations. AI systems cite concrete claims more readily than abstract statements.
Implement schema markup: Add Schema.org markup for Article, NewsArticle, or ScholarlyArticle types, including author, publication date, and claim-specific metadata that AI systems can directly parse.
Maintain entity consistency: Use the same names for people, organizations, and concepts throughout your content, avoiding pronouns and abbreviations that create ambiguity for AI systems.
Cite your sources: When you cite other sources within your content, you signal to AI systems that your content is well-researched and credible, increasing your own citation likelihood.
Test with AI tools: Regularly query your target topics in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude to see whether your content is being cited and how it’s being presented.
Monitor performance: Track which pieces of your content are cited, by which platforms, and in what context, using this data to refine your optimization strategy.
Content creators who implement these tactics see citation rates increase by 40-60% within 3-6 months, with corresponding increases in referral traffic and brand authority.
Citation monitoring is no longer optional—it’s essential infrastructure for understanding your visibility in the AI-driven discovery landscape. Why monitoring matters is straightforward: you cannot optimize what you don’t measure, and citation patterns change as AI systems evolve and new platforms emerge. What metrics to track includes citation frequency (how often you’re cited), citation placement (inline vs. source list), platform distribution (which platforms cite you most), query context (what topics trigger your citations), and traffic attribution (how much referral traffic comes from AI citations).
Identifying opportunities requires analyzing citation gaps: topics where competitors are cited but you aren’t, platforms where you’re underrepresented, and content types that underperform. This analysis reveals specific optimization targets—perhaps your how-to guides aren’t being cited because they lack schema markup, or your research content isn’t appearing in Perplexity because it’s not structured for inline extraction.
AmICited solves the monitoring challenge by tracking your citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, and other major AI platforms in real-time. Rather than manually querying your topics repeatedly, AmICited automatically monitors citation patterns, alerts you to new citations, and provides competitive benchmarking data showing how your citation performance compares to competitors. For content creators, marketers, and SEO professionals, AmICited transforms citation monitoring from a manual, time-consuming process into an automated system that surfaces actionable insights. In an AI-driven discovery landscape, having visibility into where your content is cited is as essential as having visibility into your search rankings—and AmICited makes that visibility achievable at scale.
Model-native answers come from patterns learned during training, while RAG retrieves live data before generating answers. RAG typically provides better citations because it grounds responses in specific sources, making it more transparent and traceable for users and content creators.
Different platforms use different architectures. Perplexity and Gemini prioritize RAG with citations, while ChatGPT defaults to model-native generation unless browsing is enabled. The choice reflects each platform's design philosophy and approach to transparency.
Clear, well-structured content with direct answers, proper headings, and schema markup is more extractable by AI systems. Content that leads with answers and uses lists and tables is more likely to be cited because it's easier for AI to parse and attribute.
Schema markup helps AI systems understand content structure and entity relationships, making it easier to correctly attribute and cite your content. Proper schema implementation increases citation likelihood and helps AI systems verify your content's credibility.
Yes. Focus on answer-first structure, clear formatting, factual accuracy, credible sourcing, and proper schema implementation. Monitor your citations and iterate based on performance data to continuously improve your AI visibility.
Tools like AmICited monitor your brand mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other platforms, showing exactly where and how you're cited in AI responses. This provides actionable insights for optimization.
While AI citations don't directly impact Google rankings, they increase brand visibility and authority signals. Being cited by AI can drive traffic and strengthen your overall online presence, creating indirect SEO benefits.
They're complementary. Traditional SEO focuses on ranking in search results, while AI citation optimization focuses on appearing in AI-generated answers. Both are important for comprehensive visibility in the modern discovery landscape.
Understand exactly where your brand appears in AI-generated answers. Track citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and more with AmICited.

Discover why Reddit dominates AI citations with 40.1% of ChatGPT references. Explore the data, business impact, and strategic implications for brands in the AI ...
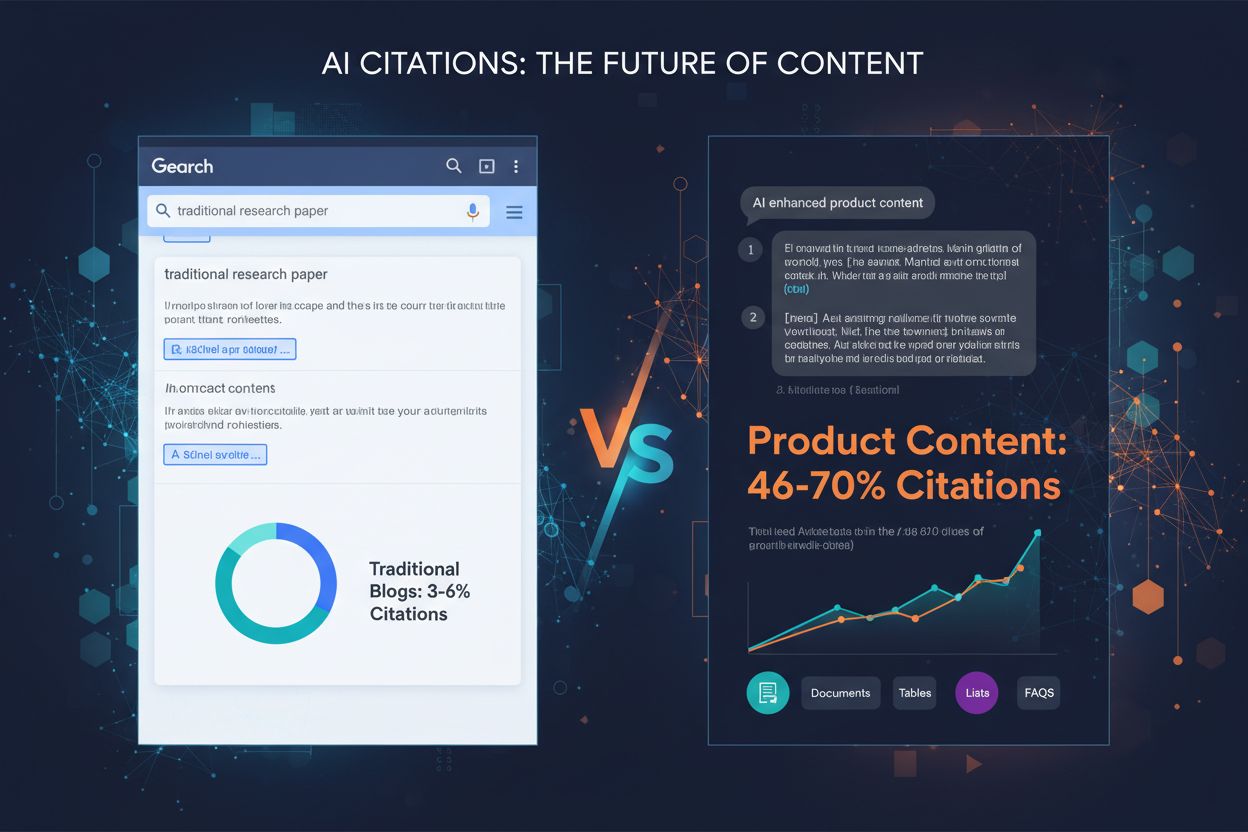
Discover which content formats get cited most by AI models. Analyze data from 768,000+ AI citations to optimize your content strategy for ChatGPT, Perplexity, a...
Learn how to reverse-engineer competitor AI citations and discover what content AI models prefer to cite. Strategic guide to competitive advantage in AI search.