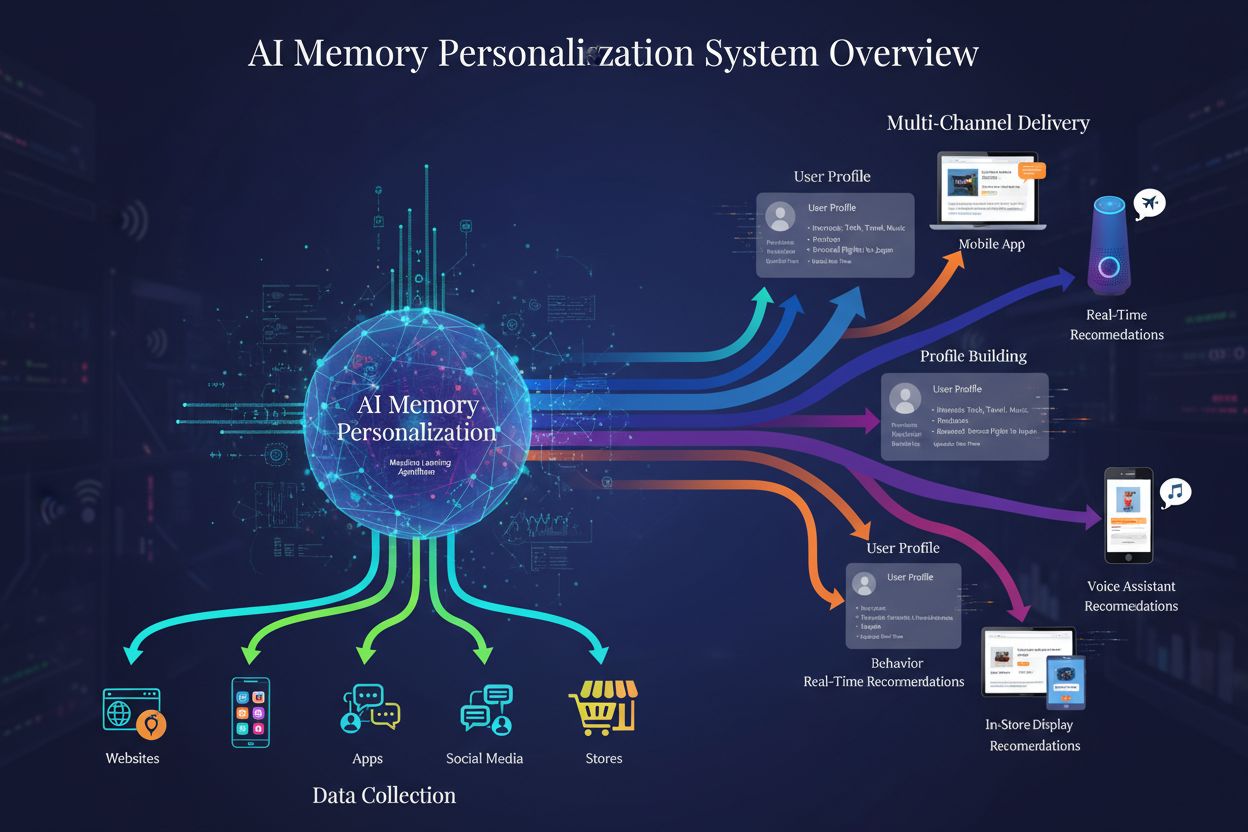
AI Memory Personalization
Learn how AI memory personalization systems build detailed user profiles to deliver personalized brand recommendations. Understand the technology, benefits, pri...

Discover how AI memory systems create lasting brand relationships through recurring, personalized recommendations that evolve over time. Learn about persistent personalization and customer loyalty.
The evolution from stateless AI to memory-enabled AI represents one of the most significant shifts in how brands can build lasting customer relationships. Traditional AI systems operated like a goldfish, processing each interaction independently without retaining any context from previous conversations—a limitation that fundamentally undermined personalization efforts. Today’s advanced language models are transitioning into “elephants,” capable of remembering user preferences, purchase history, communication style, and behavioral patterns across multiple sessions. AI memory in the context of brand relationships refers to the system’s ability to store, retrieve, and apply customer context to deliver increasingly relevant interactions over time. This transformation directly impacts customer experience by enabling brands to recognize returning customers, anticipate needs, and provide recommendations that feel genuinely personalized rather than generic. The shift from stateless to memory-enabled systems means that each interaction builds upon previous ones, creating a cumulative understanding of the customer that deepens with every touchpoint. For brands, this evolution opens unprecedented opportunities to create customer context that drives loyalty and lifetime value.
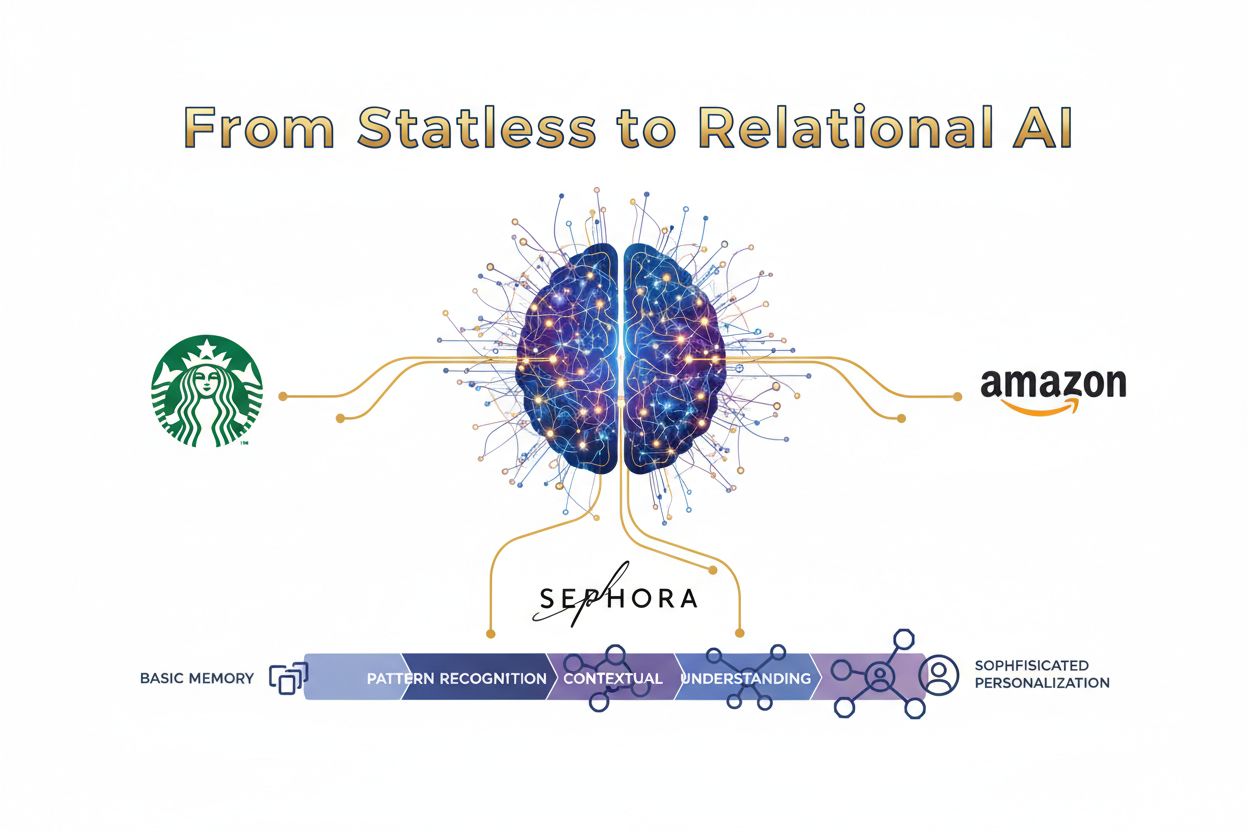
AI memory powers recurring recommendations through a sophisticated process of pattern recognition, preference storage, and contextual retrieval that operates across multiple dimensions of customer behavior. When a customer interacts with an AI system, the system captures explicit preferences (stated likes and dislikes), implicit signals (browsing patterns, purchase frequency, time spent on products), and behavioral metadata (device type, location, time of day) that collectively inform future recommendations. Over time, this accumulated context creates a rich profile that enables the AI to recognize patterns invisible to traditional recommendation engines—such as seasonal preferences, life-stage transitions, or evolving taste profiles. Real-world implementations demonstrate this power: Starbucks uses AI memory to recognize that a customer orders cold brew every summer but switches to hot lattes in winter, while Sephora remembers skin type, previous product reactions, and beauty trend interests to suggest new launches aligned with individual preferences. Amazon’s recommendation engine leverages years of browsing and purchase history to surface products with remarkable accuracy. Research shows that 72% of consumers say fast, personalized service earns their loyalty, while two-thirds of customers stick with brands that offer personalized experiences. The compounding effect of recurring recommendations creates a virtuous cycle where each interaction makes the next recommendation more valuable, strengthening the customer-brand relationship incrementally.
| Aspect | Traditional Recommendations | AI Memory-Powered Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Data Source | Single session/recent history | Complete interaction history |
| Update Frequency | Weekly or monthly | Real-time |
| Personalization Depth | Demographic segments | Individual-level with emotional context |
| Adaptation | Static | Dynamic and evolving |
| Context Retention | Lost between sessions | Persistent across time |
| Pattern Recognition | Basic behavioral signals | Complex multi-dimensional patterns |
AI memory operates across three distinct layers, each serving a critical function in building and maintaining brand relationships over time. Short-term memory, implemented through context windows, holds the current conversation and recent interactions—typically ranging from a few thousand to over a million tokens in modern systems, representing a 250x increase in capacity over just three years (from 4K tokens to 1M tokens). Long-term memory involves persistent storage systems that retain customer data across sessions, including purchase history, preferences, communication preferences, and interaction logs that can span months or years. Semantic memory captures the relationships and meaning behind data points—understanding not just that a customer bought running shoes, but that they’re a marathon enthusiast who values sustainability and prefers minimalist designs. These three layers work in concert to create comprehensive brand relationships: short-term memory provides immediate context for the current conversation, long-term memory ensures consistency and personalization across sessions, and semantic memory enables the AI to understand the deeper significance of customer behaviors and preferences. Together, they transform isolated transactions into a coherent narrative of customer identity and needs that brands can leverage for increasingly sophisticated personalization.
Different AI platforms implement memory systems with distinct architectural approaches that significantly impact how brands can leverage recurring recommendations. ChatGPT’s approach relies on context stuffing, where the system automatically saves conversation summaries and user metadata, then retrieves relevant historical context to include in the current conversation window—creating a seamless experience where the AI appears to remember previous interactions without explicit user intervention. Claude’s approach uses dynamic search capabilities, allowing the system to query conversation history and retrieve specific relevant memories on-demand, providing more precise context retrieval while maintaining transparency about what information is being accessed. ChatGPT’s automatic memory saving means customers don’t need to explicitly request that preferences be remembered; the system proactively captures and applies context across sessions. Claude’s search-based approach gives users more control and visibility into what memories are being used, though it requires more deliberate memory management. Both approaches have profound implications for brand interactions: ChatGPT’s seamless memory creates a more natural, conversational experience that feels like talking to someone who genuinely knows you, while Claude’s explicit approach builds trust through transparency about data usage. For brands implementing AI-driven customer experiences, understanding these architectural differences is crucial for selecting the right platform and setting appropriate customer expectations about personalization capabilities.
AI memory creates emotional connections that transcend transactional relationships by enabling brands to demonstrate genuine understanding of individual customer needs and preferences over extended periods. When an AI system remembers that a customer has a nut allergy, prefers sustainable packaging, or celebrates their birthday in March, and proactively incorporates these details into recommendations, it signals that the brand values them as an individual rather than a transaction. Recurring recommendations serve as powerful loyalty drivers because they reduce friction in the decision-making process—customers appreciate when a system suggests products aligned with their established preferences without requiring them to re-explain their needs. Behavioral pattern recognition allows AI to identify when customers are likely to need replenishment (detecting that someone orders coffee beans every 28 days) or when they might be ready to upgrade (recognizing that a customer has used the same phone model for three years). Sentiment analysis of past interactions helps AI understand not just what customers bought, but how they felt about those purchases, enabling more emotionally intelligent recommendations. Successful implementations like Starbucks’ personalized app and Sephora’s beauty advisor AI demonstrate that customers actively seek out and return to brands that remember their preferences. Notably, the shift in ChatGPT usage patterns—from 47% work-related messages in June 2024 to just 27% by June 2025—reveals that users increasingly rely on AI for personal, relationship-building interactions, suggesting that memory-enabled personalization is becoming a primary driver of customer engagement.
The business impact of AI memory extends far beyond improved customer satisfaction, delivering measurable improvements across critical business metrics that directly affect profitability and competitive positioning. Customer lifetime value increases substantially when AI systems can deliver recurring recommendations that keep customers engaged and purchasing over extended periods—customers who receive personalized recommendations spend more per transaction and maintain longer relationships with brands. Conversion rates from AI-powered recommendations consistently outperform generic suggestions by 20-40%, as memory-enabled systems understand individual purchase triggers and optimal timing for recommendations. Customer churn decreases when AI demonstrates understanding of individual preferences and proactively addresses needs before customers consider switching to competitors. Customer satisfaction metrics improve measurably because personalized experiences reduce decision fatigue and increase the likelihood that customers find exactly what they need. The ROI of memory-enabled systems is compelling: brands report that implementing persistent AI memory increases repeat purchase rates by 15-30% and reduces customer acquisition costs by enabling more efficient retention strategies. Starbucks has seen significant increases in app engagement and repeat visits since implementing AI-powered personalization, while Sephora’s AI beauty advisor drives higher average order values and increased customer lifetime value. For brands competing in saturated markets, AI memory represents a defensible competitive advantage that compounds over time as the system’s understanding of each customer deepens.
The implementation of AI memory systems requires careful attention to privacy, ethics, and trust—considerations that are equally important as the technological capabilities themselves for building sustainable brand relationships. Data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA impose strict requirements on how customer data can be collected, stored, and used, meaning brands must implement robust consent mechanisms and provide clear opt-out options for customers who prefer not to have their data retained. Transparency in memory systems is essential; customers should understand what data is being remembered, how it’s being used, and have visibility into the memories that inform their personalized experiences. User control over stored memories empowers customers to edit, delete, or correct information that the AI system has retained, preventing outdated or inaccurate data from degrading the personalization experience. The risks of false memories and hallucinations—where AI systems confidently assert preferences or past interactions that never occurred—can severely damage trust if not actively mitigated through verification mechanisms and human oversight. Building trust through ethical implementation means prioritizing customer privacy over aggressive personalization, being transparent about AI involvement in recommendations, and maintaining human oversight of critical decisions. The balance between personalization and privacy is delicate; customers want relevant recommendations but increasingly expect brands to respect their data and provide control over how their information is used. Brands that implement memory systems with privacy-first approaches, clear communication, and genuine user control will build stronger, more resilient customer relationships than those that prioritize aggressive personalization at the expense of trust.
The future of AI memory and brand relationships is being shaped by emerging platforms and architectural innovations that will fundamentally transform how brands interact with customers at scale. Memory-as-a-service platforms like Mem0 and Zep are abstracting memory management away from individual AI applications, creating standardized infrastructure for storing, retrieving, and managing customer context across multiple touchpoints and AI systems. Integration with agentic AI systems—where AI agents autonomously take actions on behalf of customers based on remembered preferences and patterns—will enable brands to deliver proactive, anticipatory service that feels almost prescient. Predictive personalization powered by memory systems will move beyond reactive recommendations to anticipatory suggestions, where AI predicts customer needs before they’re explicitly expressed based on historical patterns and contextual signals. Omnichannel memory integration will ensure that customer context flows seamlessly across websites, mobile apps, physical stores, and customer service channels, creating a unified experience regardless of where the interaction occurs. As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated in remembering and applying customer context, the importance of monitoring how AI systems cite and recommend brands becomes critical—ensuring that recommendations are accurate, unbiased, and genuinely serve customer interests rather than hidden commercial agendas. By 2026, industry analysts predict that 50% of transactions will involve AI agents, making memory-enabled personalization a fundamental expectation rather than a competitive differentiator. For brands preparing for this future, understanding and implementing robust AI memory systems today will determine whether they lead or lag in the next generation of customer relationships.
AI memory refers to a system's ability to store, retrieve, and apply customer context across multiple sessions and interactions. Unlike traditional systems that treat each interaction independently, memory-enabled AI builds a cumulative understanding of customer preferences, behaviors, and needs over time, enabling increasingly personalized recommendations that improve with every interaction.
Starbucks uses AI memory to recognize seasonal preference changes—remembering that customers order cold brew in summer but switch to hot lattes in winter. Sephora remembers skin type, previous product reactions, and beauty trend interests to suggest new launches. Both leverage accumulated customer context to deliver recommendations that feel genuinely personalized rather than generic.
Short-term memory (context windows) holds current conversations and recent interactions, typically ranging from thousands to over a million tokens. Long-term memory involves persistent storage of customer data across sessions, including purchase history and preferences. Semantic memory captures relationships and meaning behind data points, enabling AI to understand the deeper significance of customer behaviors.
ChatGPT uses context stuffing, automatically saving conversation summaries and user metadata, then retrieving relevant historical context to include in current conversations. Claude uses dynamic search, allowing the system to query conversation history on-demand for more precise context retrieval. ChatGPT's approach feels more seamless, while Claude's approach provides more transparency and user control.
Key considerations include GDPR and CCPA compliance, transparency about what data is remembered, user control over stored memories, and preventing false memories or hallucinations. Brands must balance personalization with privacy, provide clear opt-out options, and maintain human oversight. Building trust through ethical implementation is essential for sustainable customer relationships.
AI memory increases customer lifetime value by delivering personalized recommendations that keep customers engaged over extended periods. Conversion rates from memory-enabled recommendations typically outperform generic suggestions by 20-40%. Customer churn decreases when AI demonstrates understanding of individual preferences, and repeat purchase rates increase by 15-30% with persistent personalization.
Memory-as-a-service platforms like Mem0 and Zep abstract memory management away from individual AI applications, creating standardized infrastructure for storing and managing customer context across multiple touchpoints. They enable brands to implement sophisticated memory systems without building custom infrastructure, accelerating the adoption of memory-enabled personalization.
By 2026, industry analysts predict that 50% of transactions will involve AI agents. Agentic AI systems will autonomously take actions based on remembered preferences, enabling proactive, anticipatory service. This shift will make memory-enabled personalization a fundamental expectation rather than a competitive differentiator, requiring brands to implement robust memory systems now.
Track how AI systems cite and recommend your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. Understand your presence in AI-generated answers.

Learn how AI memory personalization systems build detailed user profiles to deliver personalized brand recommendations. Understand the technology, benefits, pri...

Understand post-purchase AI search behavior, how customers use AI tools after buying, and why monitoring your brand mentions in AI answers is critical for custo...

Discover how AI-powered search engines improve customer retention through personalization, predictive analytics, and real-time engagement. Learn the impact on c...