Thin Content Definition and AI Penalties: Complete Guide
Learn what thin content is, how AI systems detect it, and whether ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI penalize low-quality pages. Expert guide with detection met...
Learn how to create content deep enough for AI systems to cite. Discover why semantic completeness matters more than word count for ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Thin content in the AI era has taken on new meaning as language models and AI systems become increasingly sophisticated in evaluating information quality. Unlike traditional search engine optimization where thin content simply meant low word count, AI systems now assess semantic completeness—whether content fully addresses user intent and provides genuine value. The rise of AI Overviews, ChatGPT citations, and Perplexity answers has fundamentally changed how content visibility works, making it critical to understand what constitutes truly thin content versus what represents legitimate, focused information. Research shows that 65% of AI citations come from content less than one year old, indicating that freshness and relevance matter significantly in AI evaluation algorithms. However, this doesn’t mean every piece of content needs to be exhaustive; rather, it must be purposeful and complete within its scope. The challenge for content creators and brands is distinguishing between content that’s appropriately concise and content that’s genuinely inadequate for AI systems. Tools like AmICited.com help monitor how your content appears in AI systems, providing visibility into whether your depth strategy is working effectively.
| Aspect | Thin Content | Comprehensive Content |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose Clarity | Vague or unclear intent; doesn’t fully address the topic | Crystal clear purpose; completely addresses user intent |
| Information Completeness | Missing key details, context, or supporting evidence | Includes all necessary information, examples, and evidence |
| Structural Organization | Minimal structure; difficult to navigate | Well-organized with clear sections, headers, and logical flow |
| Supporting Evidence | Few or no citations, statistics, or examples | Rich with data, quotes, case studies, and credible sources |
| Semantic Depth | Surface-level coverage; lacks nuance | Explores multiple angles, acknowledges complexity |
| User Satisfaction | Leaves readers with unanswered questions | Provides comprehensive answers and actionable insights |
| AI Citation Likelihood | Low probability of being selected by AI systems | High probability of being cited in AI Overviews and ChatGPT |
| Freshness Factor | Often outdated or stale information | Regularly updated with current data and trends |
| Topical Authority | Isolated content with no supporting cluster | Part of a comprehensive content cluster on the topic |
Content depth directly impacts your visibility in AI systems because these algorithms evaluate whether your content provides sufficient information to be useful in AI-generated responses. When AI systems like Google’s AI Overviews or ChatGPT need to cite sources, they prioritize content that comprehensively addresses the query, reducing the need for multiple citations. Research demonstrates that 81.10% of top-10 SERP results have at least one citation in AI Overviews, but not all of these citations are equal—deeper, more authoritative content receives preferential treatment. The 0.334 correlation between brand search volume and AI citations reveals that established brands with comprehensive content strategies dominate AI visibility, suggesting that depth is part of a broader authority signal. AI systems use content chunking and extraction to pull relevant information, meaning your content must be structured in ways that allow these systems to easily identify and utilize your most valuable insights. Without sufficient depth, your content may be overlooked entirely, even if it ranks well in traditional search results. This distinction is crucial: traditional SEO and AI visibility require different optimization approaches, with depth being far more critical for the latter.
Not all thin content is bad—some focused, concise pieces serve legitimate purposes and deserve protection from being replaced by AI-generated summaries. Here’s how to identify thin content worth keeping:
Genuinely thin content—material that fails to adequately address its topic—faces increasing risk in an AI-driven search landscape. Unlike traditional search engines that could rank thin content based on backlinks or domain authority, AI systems evaluate actual information quality and completeness. When AI systems encounter thin content, they’re more likely to either skip it entirely or combine it with multiple other sources, diluting your brand’s visibility and authority. The problem compounds because AI systems prioritize content that can stand alone as a complete answer, meaning thin content that requires readers to visit multiple sources is inherently disadvantaged. Additionally, thin content often lacks the statistical evidence and quotations that improve AI visibility by 22% and 37% respectively, making it even less likely to be selected for AI citations. Brands that rely on thin content strategies find themselves increasingly invisible in AI Overviews and ChatGPT responses, losing traffic to competitors with more comprehensive approaches. The competitive pressure is real: as more brands invest in depth, thin content becomes progressively less viable for maintaining visibility.
| Content Type | Minimum Depth Requirement | Key Depth Elements | Citation Probability |
|---|---|---|---|
| How-To Guides | 1,500-2,500 words | Step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting, examples, tools needed | High |
| Product Reviews | 1,200-2,000 words | Specifications, pros/cons, comparisons, user feedback, pricing | High |
| Industry Analysis | 2,000-3,500 words | Statistics, expert quotes, trend analysis, case studies | Very High |
| Listicles | 1,000-1,800 words | Detailed descriptions per item, comparisons, use cases | Very High (32.5% of AI citations) |
| News Articles | 500-1,000 words | Context, quotes, multiple sources, implications | Medium-High |
| Definitions | 300-600 words | Clear explanation, examples, related concepts, use cases | Medium |
| Quick Tips | 200-400 words | Actionable advice, brief explanation, immediate value | Low-Medium |
| Comparison Articles | 1,500-2,500 words | Feature comparison, pros/cons, use cases, pricing | Very High |
| Case Studies | 1,500-3,000 words | Background, methodology, results, metrics, lessons learned | Very High |
| Glossary Entries | 150-400 words | Definition, context, examples, related terms | Low |
Strategic structure can dramatically increase perceived and actual depth without requiring excessive word count. Using subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists helps AI systems understand your content’s organization and extract key information more effectively. Data visualization through tables, charts, and infographics adds depth by presenting information in multiple formats, which AI systems can process and reference. Callout boxes and highlighted sections emphasize key insights, making your content more scannable while maintaining depth. Internal linking to related content creates topical clusters that signal expertise to AI systems—research shows that brands appearing on 4+ platforms are 2.8x more likely to appear in ChatGPT, and similar principles apply to content interconnection. Structured data markup (schema.org) helps AI systems understand your content’s context and relationships, improving both comprehension and citation likelihood. Blockquotes and expert attributions add credibility and depth simultaneously, particularly since quotations improve AI visibility by 37%. Finally, clear introductions and summaries at the beginning and end of sections help AI systems quickly identify your most valuable insights without requiring them to parse through dense paragraphs.
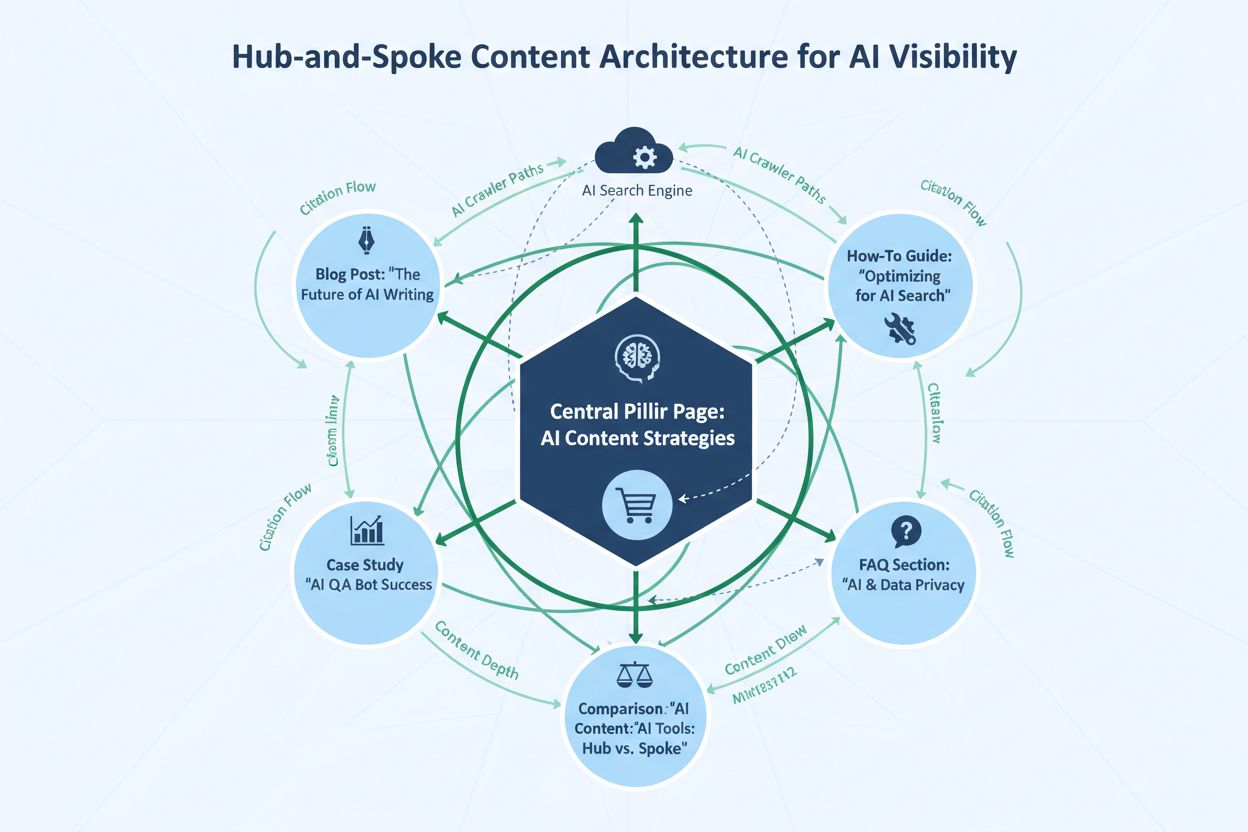
Topical depth extends beyond individual pieces of content to encompass how comprehensively you cover an entire subject area across your content ecosystem. AI systems evaluate not just whether a single article is deep, but whether your brand demonstrates topical authority through multiple interconnected pieces addressing different angles of the same subject. A content cluster strategy—where a pillar article covers a topic broadly and supporting articles explore specific subtopics—signals to AI systems that you have comprehensive expertise. This approach is particularly effective because AI systems can draw from multiple pieces of your content when generating responses, increasing your overall visibility and citation frequency. Comparative listicles, which account for 32.5% of AI citations, work especially well within content clusters because they naturally reference and link to deeper explorations of each item. The interconnection between cluster pieces helps AI systems understand relationships between concepts and identify your content as authoritative. Brands that invest in topical depth across content clusters see significantly higher AI citation rates than those with isolated, standalone pieces, regardless of individual article length.
Measuring content depth requires moving beyond traditional metrics like word count and bounce rate to assess how AI systems actually evaluate your content. Start by analyzing your current AI visibility using tools like AmICited.com, which shows exactly how your content appears in AI Overviews, ChatGPT responses, and Perplexity answers. Compare your cited content against non-cited content to identify patterns—do your cited pieces include statistics, quotations, or specific structural elements? Track whether your content appears in comparative listicles and content clusters, as these formats show 32.5% citation rates. Monitor the freshness of your cited content, keeping in mind that 65% of AI citations come from content less than one year old, suggesting that regular updates significantly impact visibility. Evaluate your brand search volume correlation, understanding that the 0.334 correlation between brand searches and AI citations means building brand authority through multiple platforms and consistent messaging. Assess your semantic completeness by asking whether your content fully answers the query without requiring readers to visit other sources. Finally, measure the extractability of your content—can AI systems easily identify and pull your key insights, or is valuable information buried in dense paragraphs?
Transforming thin content into AI-visible content requires strategic enhancement rather than simply adding filler words. Start by adding supporting evidence: if your content lacks statistics, research the topic and incorporate relevant data points that strengthen your claims—remember that statistics improve AI visibility by 22%. Integrate expert quotations and attributions to add credibility and depth; quotations boost AI visibility by 37%, making them one of the highest-impact additions you can make. Restructure your content to improve scannability and AI comprehension by adding descriptive subheadings, bullet points, and numbered lists that break up dense paragraphs. Expand your content cluster by creating supporting pieces that explore related subtopics, helping AI systems understand your topical authority—this is particularly important since comparative listicles generate 32.5% of AI citations. Update your content regularly to maintain freshness, as 65% of AI citations come from content less than one year old, meaning stale content loses visibility over time. Add structured data markup to help AI systems understand your content’s context and relationships. Implement internal linking to connect related pieces and create topical clusters that signal expertise. Finally, monitor your AI visibility through AmICited.com to track whether your optimization efforts are translating into actual AI citations and visibility improvements.
There's no universal minimum, but research shows content under 500 words rarely gets cited by AI systems. Most comprehensive content ranges from 1,500-3,000+ words depending on topic complexity. However, word count alone doesn't matter—semantic completeness and answer-level usefulness are more important. A well-structured 800-word article with clear sections and citations can outperform a 2,000-word rambling post.
No. 'Thin but useful' content serves legitimate purposes—login pages, FAQs, micro-features, and legal disclaimers should remain concise. The problem is genuinely thin content: auto-generated pages, spun articles, and low-value duplicates. Protect necessary thin content with structured data and strong internal linking, but eliminate wasteful thin content.
Traditional SEO rewards depth through engagement signals and backlink potential. AI systems evaluate depth differently—they assess semantic completeness, answer-level usefulness, and extractability for synthesis. Deep content performs well in both, but AI is more forgiving of shorter content if it's semantically complete and well-structured.
Add FAQ sections, statistics, citations, and expert quotes. These elements increase AI visibility by 22-37% without requiring complete rewrites. Improve heading hierarchy, add internal links to supporting content, and implement structured data. Update publication dates to signal freshness (65% of AI citations target recent content).
Evaluate semantic completeness: Does it answer the main question and likely follow-up questions? Check coverage: Are all important subtopics addressed? Assess structure: Are there clear headings, sections, and extractable chunks? Use LLM evaluation tools to score usefulness, depth, and originality. Compare against top-performing content in your niche.
Mostly yes, but with variations. ChatGPT relies heavily on training data (favors Wikipedia and authoritative sources), Perplexity emphasizes real-time retrieval (favors recent, detailed content), Google AI Overviews favor diverse sources. Deep, well-structured content performs well across all platforms, but platform-specific optimization can improve visibility.
Unlikely for AI visibility, but yes for user experience. Extremely long, unfocused content can hurt readability and engagement. The sweet spot is comprehensive coverage with clear structure—deep enough to be authoritative, organized enough to be scannable. Use subheadings, bullet points, and tables to maintain readability while adding depth.
Both matter significantly. 65% of AI citations target content from the past year. Deep, outdated content underperforms compared to moderately deep, recent content. The best strategy: create comprehensive content and update it regularly. Add new statistics, refresh examples, and update timestamps to signal freshness while maintaining depth.
See exactly how your content appears in AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. Track which pieces get cited and optimize based on real AI visibility data.
Learn what thin content is, how AI systems detect it, and whether ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI penalize low-quality pages. Expert guide with detection met...
Learn the optimal content depth, structure, and detail requirements for getting cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Discover what makes content citatio...
Community discussion on how AI systems treat thin content compared to Google. Real experiences from content marketers on content quality requirements for AI vis...