
How to Strengthen Your Brand Entity for AI Search Visibility
Learn how to strengthen your brand entity for AI search visibility. Optimize for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude with entity SEO strategies...

Learn how to build and optimize your brand entity for AI recognition. Implement schema markup, entity linking, and structured data to improve visibility in LLM responses and AI Overviews.
In the era of artificial intelligence and large language models (LLMs), a brand entity represents a distinct, recognizable object—your company, product, or service—that AI systems can identify, understand, and reference independently of keyword matching. Unlike traditional search engine optimization that relies on keyword density and placement, entity-based AI recognition focuses on establishing your brand as a clearly defined concept with specific attributes, relationships, and contextual meaning that LLMs can comprehend and utilize. When you search Google for “Apple,” the search engine matches keywords; when you ask ChatGPT about Apple, the LLM understands Apple as a distinct entity with multiple dimensions—a technology company, a brand identity, a set of products, and a collection of relationships with other entities like Steve Jobs, innovation, and consumer electronics. This fundamental shift from keyword-centric to entity-centric understanding represents a paradigm change in how brands must optimize their digital presence for AI recognition.
LLMs interpret entities through semantic understanding and relational mapping, recognizing not just what your brand is called, but what it represents, who it serves, what problems it solves, and how it connects to other concepts in the knowledge graph. Traditional search engines treat each keyword occurrence as a signal; LLMs treat your brand entity as a node in a vast network of interconnected information, understanding its properties, associations, and contextual relevance. For example, when Tesla is mentioned in an article about electric vehicles, sustainable energy, or Elon Musk, LLMs recognize these as entity relationships that reinforce Tesla’s identity and relevance across multiple domains. This entity-based approach means that building AI recognition requires establishing clear, consistent, and comprehensive information about your brand across multiple dimensions—not just optimizing for specific keywords, but ensuring your brand entity is well-defined, properly attributed, and meaningfully connected to relevant concepts and other entities.
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | Entity-Based AI |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Keyword matching and density | Entity recognition and semantic relationships |
| Understanding | Literal text matching and relevance signals | Contextual meaning and entity attributes |
| Optimization | Meta tags, content keywords, backlinks | Entity attributes, knowledge graphs, relational data |
| Brand Visibility | Ranking for specific search queries | Recognition across diverse AI contexts and conversations |
| Measurement | Click-through rates and rankings | Entity mentions, relationship accuracy, and contextual relevance |
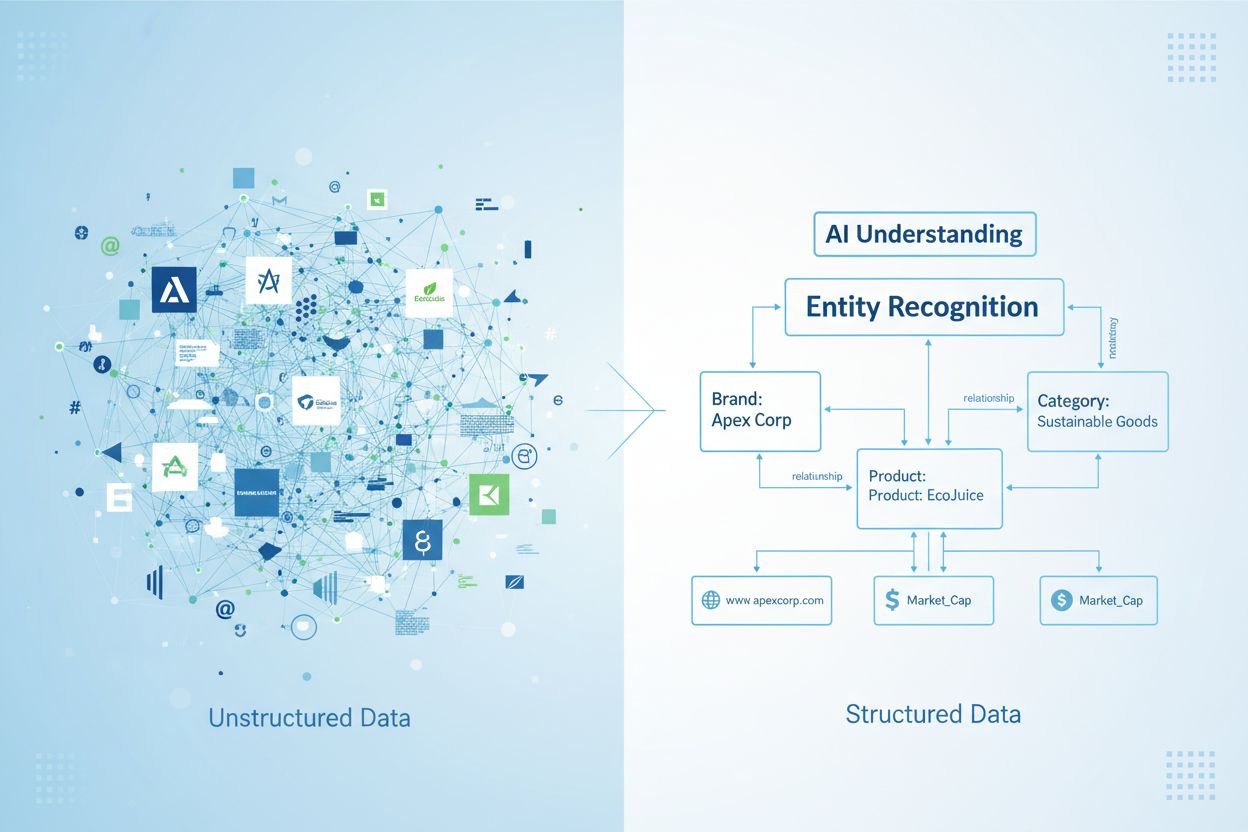
As AI systems become increasingly sophisticated in generating answers and recommendations, they rely heavily on structured data and entity recognition to understand context and provide accurate information. Unlike traditional search engines that match keywords, modern AI systems—including large language models and AI Overviews—need to recognize your brand as a distinct, authoritative entity with clear relationships to your industry, products, and expertise. When your brand entity is poorly defined or fragmented across the web, AI systems struggle to understand what you represent, leading to incorrect citations, omissions from relevant answers, or worse, attribution of your expertise to competitors. This ambiguity directly impacts your visibility: studies show that brands with well-structured entity data appear in AI-generated responses up to 3x more frequently than those without clear entity definitions.
The technical foundation for this visibility lies in semantic authority—the degree to which AI systems recognize your brand as a credible source within your domain. Clear brand entities establish trust signals that align with EEAT principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), which are critical ranking factors for both traditional search and AI systems. When your brand entity is properly defined with consistent information across structured data, knowledge graphs, and authoritative sources, AI systems can confidently cite your content and recommendations.
Key reasons why AI systems need clear brand entities:
By investing in clear brand entity definition, you’re not just optimizing for today’s search landscape—you’re building the semantic foundation that determines your visibility and credibility in an AI-driven future.
A complete brand entity functions as a comprehensive digital profile that consolidates all critical information about your organization into a structured, machine-readable format. This unified representation ensures that AI systems can accurately identify, understand, and associate your brand across multiple platforms and contexts. The foundation of an effective brand entity consists of several interconnected components that work together to create a complete picture of your organization.
Organization and Company Information forms the cornerstone of your brand entity, including your official business name, detailed company description, logo URLs, and primary website. This section establishes the basic identity and legitimacy of your organization in the eyes of AI systems. Products and Services should be comprehensively documented with specific names, detailed descriptions, relevant categories, and any associated SKUs or product identifiers that help AI systems understand your market offerings. Key People such as founders, C-suite executives, and notable team members should be listed with their roles and professional profiles, as these human connections add credibility and context to your brand narrative.
Your geographic presence and locations matter significantly for AI recognition, particularly for businesses operating across multiple regions or with physical storefronts. Document headquarters, office locations, distribution centers, and service areas to help AI systems understand your operational scope. Industry classifications and relationships provide essential context by specifying your primary industry, relevant sub-sectors, and competitive positioning within your market landscape. Unique identifiers are critical for AI disambiguation—these include your official website URL, social media profiles (LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook), Wikidata identifiers, and any industry-specific registration numbers or certifications.
Finally, brand attributes and values capture the intangible qualities that define your organization, including your mission statement, core values, brand voice, and key differentiators. Here’s a practical JSON schema example that demonstrates how these components integrate into a structured brand entity:
{
"brandEntity": {
"organization": {
"name": "TechVision Solutions",
"description": "Leading provider of AI-powered business intelligence platforms",
"logo": "https://example.com/logo.png",
"website": "https://www.techvisionsolutions.com"
},
"productsServices": [
{
"name": "InsightPro Analytics",
"description": "Real-time data analytics platform",
"category": "Business Intelligence"
}
],
"keyPeople": [
{
"name": "Jane Smith",
"role": "CEO & Founder",
"linkedinProfile": "https://linkedin.com/in/janesmith"
}
],
"locations": [
{
"type": "headquarters",
"city": "San Francisco",
"country": "United States"
}
],
"industryClassifications": ["Software", "Artificial Intelligence", "Business Services"],
"uniqueIdentifiers": {
"wikidata": "Q12345678",
"socialProfiles": {
"linkedin": "https://linkedin.com/company/techvisionsolutions",
"twitter": "@TechVisionSol"
}
},
"brandAttributes": {
"mission": "Democratizing AI-powered insights for businesses",
"coreValues": ["Innovation", "Transparency", "Customer Success"]
}
}
}
By systematically documenting each of these components, you create a robust brand entity that AI systems can reliably recognize, verify, and reference across the digital ecosystem.
Schema.org is a collaborative vocabulary of structured data markup that search engines and AI systems use to better understand your brand’s identity and offerings. By implementing schema markup on your website, you provide explicit context about your business, products, and services, making it significantly easier for AI algorithms to recognize and categorize your brand entity. This structured data acts as a bridge between human-readable content and machine-readable information, enabling search engines and AI systems to extract meaningful insights about your organization.
The most critical schema types for brand recognition include Organization, which defines your company’s fundamental information such as name, logo, contact details, and social profiles; Product, which describes the specific items or solutions you offer with pricing and availability; Person, which establishes profiles for key team members and executives; and Service, which outlines the services your business provides with detailed descriptions and pricing structures. Each schema type serves a distinct purpose in building a comprehensive entity profile that AI systems can reference and trust.
Implementing schema markup involves adding JSON-LD code to your website’s HTML header or body sections. Here’s a practical example of basic Organization schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Your Brand Name",
"url": "https://www.yourbrand.com",
"logo": "https://www.yourbrand.com/logo.png",
"description": "Brief description of your organization",
"sameAs": [
"https://www.facebook.com/yourbrand",
"https://www.twitter.com/yourbrand",
"https://www.linkedin.com/company/yourbrand"
],
"contactPoint": {
"@type": "ContactPoint",
"contactType": "Customer Service",
"telephone": "+1-XXX-XXX-XXXX",
"email": "contact@yourbrand.com"
}
}
To validate your schema implementation, use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool or Schema.org’s validation resources to ensure your markup is correctly formatted and recognized. Common mistakes to avoid include providing incomplete data fields, using inconsistent naming conventions across different pages, failing to establish relationships between related entities, and neglecting to update schema markup when your business information changes. By carefully implementing comprehensive schema markup and regularly validating your structured data, you significantly enhance your brand’s visibility to AI systems and improve your entity recognition across the digital landscape.
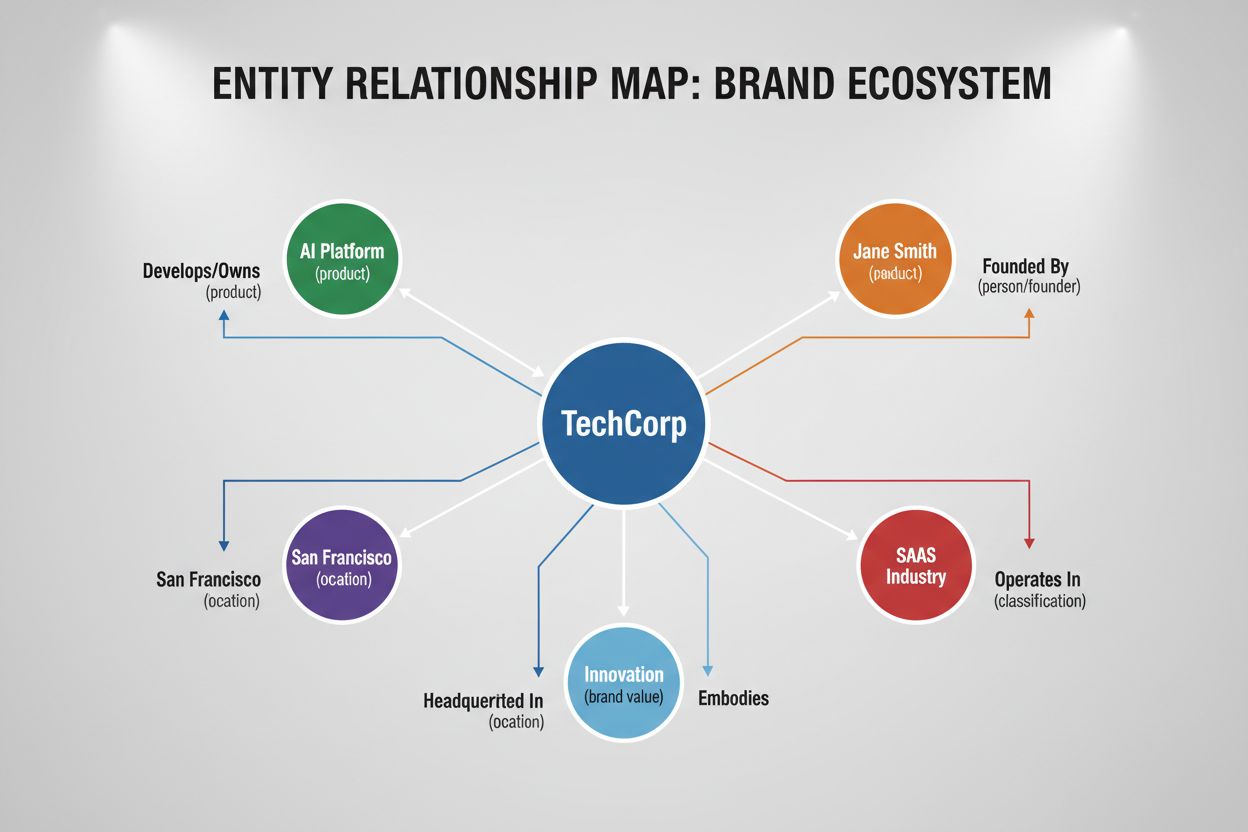
Entity relationships form the backbone of how AI systems understand your brand’s authority and relevance within your industry. When you strategically link your brand entity to other recognized entities—such as industry associations, complementary services, geographic locations, and thought leaders—you create a web of semantic connections that signals expertise to search algorithms and AI systems. Entity linking, the process of connecting your content to established entities in knowledge graphs, tells AI that your brand operates within a legitimate ecosystem of related concepts and organizations. This interconnected approach is far more powerful than isolated mentions, as it demonstrates that your brand doesn’t exist in a vacuum but rather plays a meaningful role within a broader industry context.
Topic clusters amplify this effect by organizing your content around core themes and their related subtopics, each reinforced by consistent entity references. When Brightview Senior Living restructured their content strategy around entity relationships—connecting their brand to specific senior care specialties, geographic service areas, and affiliated healthcare providers—they saw significant improvements in local search visibility and AI-driven recommendations. This wasn’t just about mentioning these entities once; it was about building consistent, contextual relationships that demonstrated deep expertise. Semantic authority emerges naturally from this approach, as AI systems recognize that your content thoroughly explores topics from multiple angles while maintaining clear connections to established, trustworthy entities.
The way AI systems process entity relationships has evolved significantly with advances in natural language processing and knowledge graphs. Rather than simply counting keyword mentions, modern AI understands the quality and context of entity connections—whether your brand is meaningfully related to other entities or merely name-dropping them. By building credibility through related entities, you’re essentially creating a network effect where each connection reinforces your overall authority. This means consistently referencing industry partners, citing relevant research from recognized institutions, and establishing clear geographic or categorical relationships that make sense within your industry. The result is a brand entity that AI systems recognize as authoritative, well-connected, and genuinely embedded within its professional ecosystem, ultimately driving better visibility across search results, recommendations, and AI-powered applications.
Maintaining entity consistency across multiple domains presents one of the most significant challenges in brand AI recognition. When your marketing domain emphasizes innovation, your support domain focuses on reliability, and your careers domain highlights company culture, AI systems attempting to synthesize this information often produce averaged, vague responses that fail to capture your authentic brand voice. Different domains naturally prioritize different aspects of your brand identity, but without explicit coordination, these variations create conflicting signals that confuse both AI systems and your audience. The solution lies in establishing unified brand specifications that transcend individual domains while allowing contextual flexibility. Organizations should develop machine-readable brand guidelines in JSON or YAML format that define core entity attributes, approved terminology, tone parameters, and domain-specific variations in a structured way that AI systems can reliably parse and apply. This requires implementing cross-functional governance where marketing, customer support, HR, and product teams collaborate to define consistent entity representations while documenting legitimate domain-specific adaptations. Regular consistency audits using automated tools can monitor how your brand entity appears across subdomains, social channels, and customer touchpoints, flagging discrepancies before they reach your audience. When your brand entity maintains consistency across domains, AI systems generate more coherent, trustworthy responses that strengthen customer relationships and reinforce brand recognition, directly impacting both customer experience and long-term brand equity.
Optimizing your brand entity requires leveraging specialized tools designed to monitor, analyze, and enhance how AI systems recognize and cite your organization. The landscape of entity optimization solutions has evolved significantly, offering marketers and brand managers unprecedented control over their digital presence in AI-generated content. AmICited.com stands out as the premier solution for monitoring AI citations, providing real-time tracking of how your brand appears in answers generated by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other major AI platforms. This tool is essential for understanding your entity’s visibility in AI responses and identifying opportunities to improve your presence across these critical channels. Beyond citation monitoring, a comprehensive toolkit should include Schema App for structured data management, Google’s NLP API for entity analysis and recognition capabilities, and integration with Wikidata to ensure your entity is properly linked within the global knowledge base. Understanding how your entity connects within Google’s Knowledge Graph provides invaluable insights into relationship mapping and entity authority signals that influence AI recognition. These platforms work synergistically to create a complete entity optimization strategy that addresses monitoring, analysis, and continuous improvement.
| Tool Name | Primary Function | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| AmICited.com | AI citation monitoring and tracking | Real-time visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews |
| Schema App | Structured data and schema optimization | Entity markup and semantic clarity |
| Google NLP API | Entity analysis and recognition | Understanding how AI systems identify entities |
| Wikidata | Knowledge base entity linking | Global entity standardization and relationships |
| Google Knowledge Graph | Entity relationship mapping | Authority signals and entity connections |
| Monitoring Platforms | Analytics and performance tracking | Measuring entity optimization ROI |
Implementing these tools creates a data-driven approach to entity optimization, allowing you to track performance metrics, identify gaps in your entity presence, and make informed decisions about where to invest your optimization efforts. The combination of AmICited.com’s citation monitoring with Schema App’s technical implementation and Google’s analytical tools provides a complete feedback loop for continuous entity improvement. By systematically using these platforms, brands can ensure their entities are not only recognized by AI systems but prominently featured in the most valuable AI-generated responses.
Implementing a comprehensive brand entity strategy requires a structured approach that builds momentum while establishing a solid foundation for AI recognition. Begin with Step 1: Audit Your Current Entity Presence (1-2 weeks), where you’ll conduct a thorough inventory of all existing brand mentions, structured data, and entity references across your digital properties. Use tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, and Ahrefs to identify how search engines currently perceive your brand, then document gaps between your desired entity profile and current reality. This audit requires minimal resources—primarily your marketing team’s time and access to existing analytics platforms—but provides invaluable baseline data for measuring future progress.
Step 2: Define Your Core Brand Entities (1-2 weeks) involves identifying the 5-10 primary entities that represent your brand’s essence and competitive positioning. Work cross-functionally with marketing, product, and leadership teams to establish clear definitions for each entity, including its attributes, relationships to other entities, and strategic importance. Document these definitions in a centralized entity database or spreadsheet, ensuring consistency across all team members who’ll reference them during implementation. This step requires minimal budget but demands significant strategic thinking and cross-departmental alignment.
Step 3: Map Entity Relationships (1-2 weeks) focuses on visualizing how your core entities connect to each other and to external entities in your industry ecosystem. Create relationship diagrams showing how your brand entity relates to product entities, service entities, location entities, and person entities (founders, executives, thought leaders). This mapping exercise often reveals opportunities for deeper entity connections and helps identify which relationships deserve emphasis in your schema markup and content strategy. Tools like Lucidchart or even detailed spreadsheets can facilitate this process without significant expense.
Step 4: Implement Schema Markup (2-4 weeks) is where your strategy becomes technically tangible across your website, content management system, and digital properties. Begin with high-priority pages—your homepage, about page, and key service/product pages—implementing Organization, LocalBusiness, Product, or Person schema as appropriate. Work with your development team to integrate schema markup into your CMS templates, ensuring consistency across all pages and reducing manual implementation burden. This phase requires technical resources and may involve hiring a schema markup specialist if your team lacks expertise, but the investment pays dividends through improved search visibility and AI comprehension.
Step 5: Monitor and Optimize (Ongoing) establishes continuous improvement processes using tools like Google Search Console, Rich Results Test, and structured data testing tools to verify proper implementation and identify errors. Track how search engines and AI systems recognize your entities through monitoring SERP features, featured snippets, knowledge panels, and AI-generated summaries that reference your brand. Set up monthly reviews to analyze performance metrics, identify optimization opportunities, and adjust your entity strategy based on emerging trends and algorithm updates. This ongoing phase requires minimal budget but demands consistent attention and quarterly strategy refinement.
Step 6: Maintain Consistency (Ongoing) ensures your entity information remains accurate and synchronized across all platforms, from your website to business directories, social media profiles, and industry databases. Implement governance processes that require entity information updates to flow through a centralized approval system before publication, preventing conflicting information that confuses AI systems. Assign clear ownership for entity maintenance, establish quarterly audits to catch inconsistencies, and create documentation that guides new team members in maintaining entity standards. This final step protects your investment and ensures sustained AI recognition as your brand evolves.
Tracking the impact of your entity optimization efforts is essential to demonstrate value and refine your strategy over time. The most critical metrics to monitor include entity recognition rate (how often AI systems correctly identify your brand), AI citation frequency (mentions in AI-generated responses), and visibility in AI Overviews and similar AI-powered search features. Tools like Google Search Console, Semrush, Ahrefs, and specialized AI monitoring platforms can help you measure these KPIs, while Google Analytics 4 tracks traffic originating from AI-generated content and AI Overviews. You should expect to see measurable improvements within 3-6 months of consistent optimization, including increased brand mentions in AI responses, higher click-through rates from AI Overviews, and improved EEAT (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals across your digital properties.
Key metrics to track:
The long-term benefits extend far beyond immediate traffic gains. As your entity becomes more established in AI knowledge bases, you’ll experience compounding returns through improved brand recall, stronger competitive positioning, and increased customer trust. Organizations that invest in entity optimization early gain significant advantages as AI systems become more sophisticated and influential in consumer decision-making. By measuring these metrics consistently and adjusting your approach based on data, you transform entity optimization from a theoretical exercise into a measurable business driver that directly impacts revenue, customer acquisition, and brand equity.
Keywords are search terms that match text; entities are distinct, recognizable objects that AI systems understand contextually. Entities provide semantic meaning that helps AI understand relationships and context, making them essential for AI recognition rather than just search engine visibility.
Initial implementation takes 2-4 weeks; visibility improvements typically appear within 1-3 months as AI systems crawl and index your structured data. However, long-term benefits compound over time as your entity becomes more established in AI knowledge bases.
Start with Organization, Product, and Person schemas most relevant to your business. You can expand gradually as you see results and understand which entity types drive the most value for your specific industry and audience.
Entity optimization complements traditional SEO perfectly. Better structured data improves both search engine understanding and AI system recognition, creating a synergistic effect that enhances visibility across all search and AI platforms.
Clear, consistent entities signal expertise and trustworthiness to AI systems, which improves your EEAT signals and brand authority. This creates a positive feedback loop where better entity definition leads to stronger authority signals and improved visibility.
Use tools like AmICited.com to track AI citations, Google Search Console for structured data reports, and entity-specific analytics platforms. These tools provide real-time insights into how AI systems are recognizing and referencing your brand.
Yes, entity optimization is particularly powerful for multi-location brands. You can define location-specific entities while maintaining brand consistency, helping AI systems understand your geographic presence and local relevance.
Inconsistent naming and descriptions across domains is the most common mistake. Ensure your brand name, product names, and descriptions are identical everywhere to prevent AI systems from treating them as separate entities.
Track how AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity reference your brand with AmICited. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and optimize your entity recognition strategy.

Learn how to strengthen your brand entity for AI search visibility. Optimize for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude with entity SEO strategies...
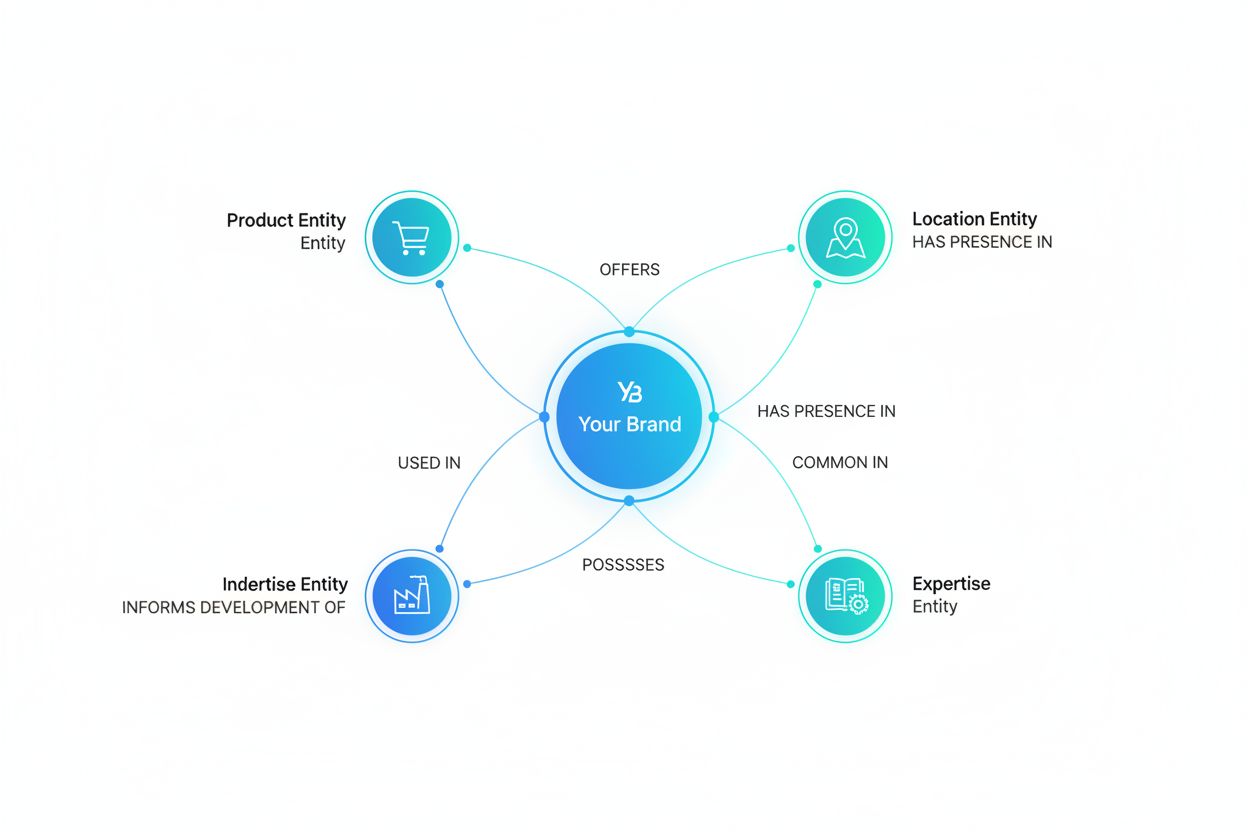
Learn how entity optimization helps your brand become recognizable to LLMs. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity strategies for AI vis...

Learn how to build entity visibility in AI search. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity SEO strategies to increase brand presence in C...