
How Case Studies Perform in AI Search Results
Learn how case studies rank in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover why AI systems cite case studies as authoritative s...

Learn how to format case studies for AI citations. Discover the blueprint for structuring success stories that LLMs cite in AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity.
AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews are fundamentally changing how B2B buyers discover and validate case studies—yet most companies are still publishing them in formats that LLMs can barely parse. When an enterprise buyer asks an AI system “Which SaaS platforms work best for our use case?”, the system searches through millions of documents to find relevant proof points, but poorly formatted case studies remain invisible to these retrieval systems. This creates a critical gap: while traditional case studies drive a baseline 21% win rate in late-stage deals, AI-optimized case studies can increase citation likelihood by 28-40% when properly structured for machine learning models. The companies winning in this new landscape understand that first-party data advantage comes from being discoverable by AI systems, not just by human readers. Without intentional optimization for LLM retrieval, your most compelling customer success stories are essentially locked away from the AI systems that now influence 60%+ of enterprise buying decisions.

An AI-ready case study isn’t just a well-written narrative—it’s a strategically structured document that serves both human readers and machine learning models simultaneously. The most effective case studies follow a consistent architecture that allows LLMs to extract key information, understand context, and cite your company with confidence. Below is the essential blueprint that separates AI-discoverable case studies from those that get lost in retrieval systems:
| Section | Purpose | AI Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| TL;DR Summary | Immediate context for busy readers | Placed at top for early token consumption; 50-75 words |
| Customer Snapshot | Quick identification of company profile | Structured as: Industry / Company Size / Location / Role |
| Business Context | Problem definition and market situation | Use consistent terminology; avoid jargon variations |
| Objectives | Specific, measurable goals the customer had | Format as numbered list; include quantified targets |
| Solution | How your product/service addressed the need | Explain feature-to-benefit mapping explicitly |
| Implementation | Timeline, process, and adoption details | Break into phases; include duration and milestones |
| Results | Quantified outcomes and impact metrics | Present as: Metric / Baseline / Final / Improvement % |
| Evidence | Data, screenshots, or third-party validation | Include tables for metrics; cite sources clearly |
| Customer Quotes | Authentic voice and emotional validation | Attribute by name, title, company; 1-2 sentences each |
| Reuse Signals | Internal linking and cross-promotion hooks | Suggest related case studies, webinars, or resources |
This structure ensures that every section serves a dual purpose: it reads naturally for humans while providing semantic clarity for RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems that power modern LLMs. The consistency of this format across your case study library makes it exponentially easier for AI systems to extract comparable data points and cite your company with confidence.
Beyond structure, the specific formatting choices you make dramatically impact whether AI systems can actually find and cite your case studies. LLMs process documents differently than humans do—they don’t skim or use visual hierarchy the way readers do, but they are highly sensitive to semantic markers and consistent formatting patterns. Here are the formatting elements that most significantly boost AI retrieval:
These formatting choices aren’t about aesthetics—they’re about making your case study machine-readable so that when an LLM searches for relevant proof points, your company’s story is the one that gets cited.
The most sophisticated approach to AI-ready case studies involves embedding a JSON schema directly into your case study document or metadata layer, creating a dual-layer approach where humans read the narrative while machines parse the structured data. JSON schemas provide LLMs with unambiguous, machine-readable representations of your case study’s key information, dramatically improving citation accuracy and relevance. Here’s an example of how to structure this:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "CaseStudy",
"name": "Enterprise SaaS Platform Reduces Onboarding Time by 60%",
"customer": {
"name": "TechCorp Industries",
"industry": "Financial Services",
"companySize": "500-1000 employees",
"location": "San Francisco, CA"
},
"solution": {
"productName": "Your Product Name",
"category": "Workflow Automation",
"implementationDuration": "8 weeks"
},
"results": {
"metrics": [
{"name": "Onboarding Time Reduction", "baseline": "120 days", "final": "48 days", "improvement": "60%"},
{"name": "User Adoption Rate", "baseline": "45%", "final": "89%", "improvement": "97%"},
{"name": "Support Ticket Reduction", "baseline": "450/month", "final": "120/month", "improvement": "73%"}
]
},
"datePublished": "2024-01-15",
"author": {"@type": "Organization", "name": "Your Company"}
}
By implementing schema.org-compliant JSON structures, you’re essentially giving LLMs a standardized way to understand and cite your case study. This approach integrates seamlessly with RAG systems, allowing AI models to extract precise metrics, understand customer context, and attribute citations back to your company with high confidence. Companies using JSON-structured case studies see 3-4x higher citation accuracy in AI-generated responses compared to narrative-only formats.
RAG systems don’t process your entire case study as one monolithic block—they break it into semantic chunks that fit within an LLM’s context window, and how you structure your document directly determines whether those chunks are useful or fragmented. Effective chunking means organizing your case study so that natural semantic boundaries align with how RAG systems will divide the content. This requires intentional paragraph sizing: each paragraph should focus on a single idea or data point, typically 100-150 words, so that when a RAG system extracts a chunk, it contains complete, coherent information rather than orphaned sentences. Narrative separation is critical—use clear section breaks between the problem statement, solution description, and results so that an LLM can extract “the results section” as a cohesive unit without accidentally mixing it with implementation details. Additionally, token efficiency matters: by using tables for metrics instead of prose, you reduce the token count needed to convey the same information, allowing LLMs to include more of your case study in their response without hitting context limits. The goal is to make your case study “RAG-friendly” so that every chunk an AI system extracts is independently valuable and properly contextualized.
Publishing case studies for AI systems requires balancing the specificity that makes them credible with the confidentiality obligations you have to your customers. Many companies hesitate to publish detailed case studies because they worry about exposing sensitive business information, but strategic redaction and anonymization allow you to maintain both transparency and trust. The most effective approach involves creating multiple versions of each case study: a fully detailed internal version with complete customer names, exact metrics, and proprietary implementation details, and a public AI-optimized version that anonymizes the customer while preserving the quantified impact and strategic insights. For example, instead of “TechCorp Industries saved $2.3M annually,” you might publish “Mid-market financial services company reduced operational costs by 34%"—the metric is still specific enough for LLMs to cite, but the customer’s identity is protected. Version control and compliance tracking are essential: maintain clear records of what information was redacted, why, and when, ensuring that your case study library remains audit-ready. This governance approach actually strengthens your AI citation strategy because it allows you to publish more case studies more frequently without legal friction, giving LLMs more proof points to discover and cite.
Before publishing a case study, validate that it actually performs well when processed by LLMs and RAG systems—don’t assume that good formatting automatically translates to good AI performance. Testing your case studies against real AI systems reveals whether your structure, metadata, and content actually enable accurate citation and retrieval. Here are five essential testing approaches:
Relevance Checking: Feed your case study into ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Claude with queries related to your solution category. Does the AI system retrieve and cite your case study when answering relevant questions?
Summarization Accuracy: Ask an LLM to summarize your case study and verify that the summary captures the key metrics, customer context, and business impact without distortion or hallucination.
Metric Extraction: Test whether the AI system can accurately extract specific numbers from your case study (e.g., “What was the time-to-value improvement?”). Tables should yield 96%+ accuracy; prose should be tested separately.
Attribution Fidelity: Verify that when the LLM cites your case study, it attributes the information correctly to your company and customer, not to a competitor or generic source.
Edge-Case Queries: Test with unusual or tangential questions to ensure your case study doesn’t get misapplied to use cases it doesn’t actually address.
These tests should be run quarterly as LLM behavior evolves, and results should inform updates to your case study formatting and structure.
Measuring the impact of AI-optimized case studies requires tracking both AI-side metrics (how often your case studies are cited by LLMs) and human-side metrics (how those citations influence actual deals). On the AI side, use AmICited.com to monitor citation frequency across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews—track how often your company appears in AI-generated responses for relevant queries, and measure whether citation frequency increases after you publish new AI-optimized case studies. Baseline your current citation rate, then set a target to increase citations by 40-60% within six months of implementing AI-ready formatting. On the human side, correlate AI citation increases with downstream metrics: track how many deals mention “I found you in an AI search” or “an AI recommended your case study,” measure win rate improvements in deals where your case study was cited by an AI system (target: 28-40% improvement over the 21% baseline), and monitor sales cycle compression in accounts where prospects encountered your case study through AI discovery. Additionally, monitor SEO metrics—AI-optimized case studies with proper schema markup often rank better in traditional search, creating a dual benefit. Qualitative feedback from your sales team is equally important: ask them whether prospects are arriving with deeper product knowledge, and whether case study citations are reducing objection handling time. The ultimate KPI is revenue: track the incremental ARR attributable to deals influenced by AI-cited case studies, and you’ll have a clear ROI justification for continued investment in this format.
Optimizing case studies for AI citations only delivers ROI if the process becomes operationalized and repeatable, not a one-time project. Start by codifying your AI-ready case study template into a standardized format that your marketing and sales teams use for every new customer success story—this ensures consistency across your library and reduces the time required to publish new case studies. Integrate this template into your CMS or content management system so that publishing a new case study automatically generates the JSON schema, metadata headers, and formatting elements without manual work. Make case study creation a quarterly or monthly cadence, not an annual event, because LLMs discover and cite companies with deeper, more recent case study libraries more frequently. Position case studies as a core component of your broader revenue enablement strategy: they should feed into sales collateral, product marketing, demand generation campaigns, and customer success playbooks. Finally, establish a continuous improvement cycle where you monitor which case studies generate the most AI citations, which metrics resonate most with LLMs, and which customer segments are most frequently cited—then use these insights to inform the next generation of case studies. The companies winning in the AI era aren’t just writing better case studies; they’re treating case studies as strategic revenue assets that require ongoing optimization, measurement, and refinement.
Start by extracting text from your PDFs and mapping existing content to a standard schema with fields such as customer profile, challenge, solution, and results. Then create a lightweight HTML or CMS version of each story with clear headings and metadata, keeping the original PDF as a downloadable asset rather than the primary source for AI retrieval.
Marketing or product marketing typically owns the narrative, but sales, solutions engineering, and customer success should provide raw data, implementation details, and validation. Legal, privacy, and RevOps teams help ensure governance, proper redaction, and alignment with existing systems such as your CRM and sales enablement platforms.
A headless CMS or structured content platform is ideal for storing schemas and metadata, while a CRM or sales enablement tool can surface the right stories in workflow. For AI retrieval, you'll usually pair a vector database with an LLM orchestration layer such as LangChain or LlamaIndex.
Transcribe video testimonials and webinars, then tag the transcripts with the same fields and sections as your written case studies so AI can cite them. For graphics and diagrams, include short alt-text or captions that describe the key insight so retrieval models can connect visual assets to specific questions.
Keep your core schema and IDs consistent globally, then create translated variants that localize language, currency, and regulatory context while preserving canonical metrics. Store locale-specific versions as separate but linked objects so AI systems can prioritize answers in the user's language without fragmenting your data model.
Review high-impact case studies at least annually, or sooner if there are major product changes, new metrics, or shifts in customer context. Use a simple versioning workflow with last-reviewed dates and status flags to signal to AI systems and humans which stories are most current.
Integrate case study retrieval directly into the tools reps already use and create concrete playbooks showing how to prompt the assistant for relevant proof. Reinforce adoption by sharing success stories where tailored, AI-surfaced case studies helped close deals faster or unlock new stakeholders.
Traditional case studies are written for human readers with narrative flow and visual design. AI-optimized case studies maintain that narrative but add structured metadata, consistent formatting, JSON schemas, and semantic clarity that allows LLMs to extract, understand, and cite specific information with 96%+ accuracy.
Track how AI systems cite your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Get insights into your AI visibility and optimize your content strategy.

Learn how case studies rank in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover why AI systems cite case studies as authoritative s...

Community discussion on how case studies perform in AI search results. Real experiences from marketers tracking case study citations in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and...
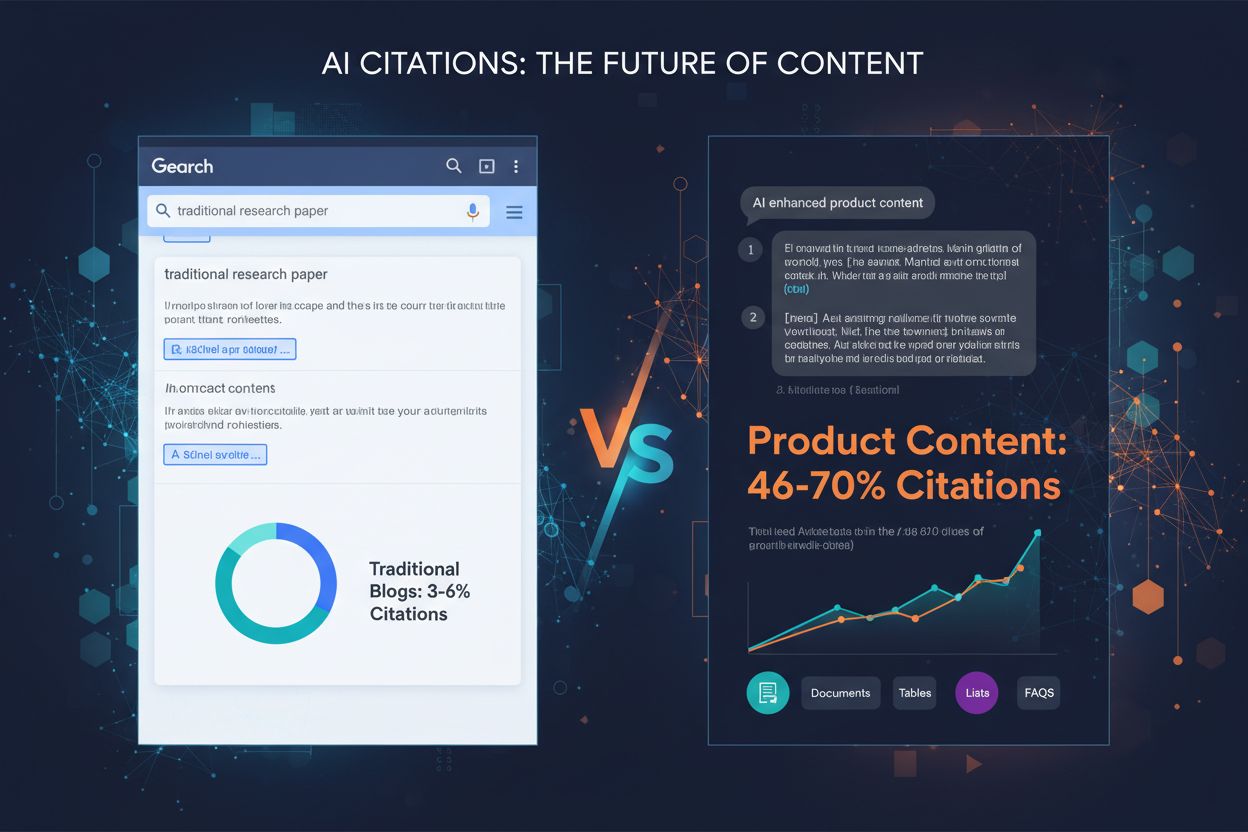
Discover which content formats get cited most by AI models. Analyze data from 768,000+ AI citations to optimize your content strategy for ChatGPT, Perplexity, a...