
Wikipedia Citations as AI Training Data: The Ripple Effect
Discover how Wikipedia citations shape AI training data and create a ripple effect across LLMs. Learn why your Wikipedia presence matters for AI mentions and br...

Discover where ChatGPT gets its training data, how it cites sources, knowledge cutoff dates, and why monitoring AI citations matters for your brand.
ChatGPT’s knowledge base is built from a diverse collection of publicly available internet data, combined with licensed datasets and human feedback refinement. The model was trained on three primary sources: publicly available internet data (websites, articles, and online content), licensed datasets (including books and academic publications), and human feedback from trainers who helped refine responses. This training data encompasses an extraordinarily broad range of sources including news websites, academic journals, books, technical documentation, forums like Reddit and Stack Overflow, Wikipedia articles, and countless other publicly accessible web pages. The sheer volume and diversity of these sources—spanning multiple languages, domains, and perspectives—creates a comprehensive knowledge base that allows ChatGPT to discuss topics ranging from quantum physics to medieval history to contemporary pop culture. However, it’s crucial to understand that ChatGPT doesn’t have access to real-time information or proprietary databases; it can only draw from what was available during its training period.
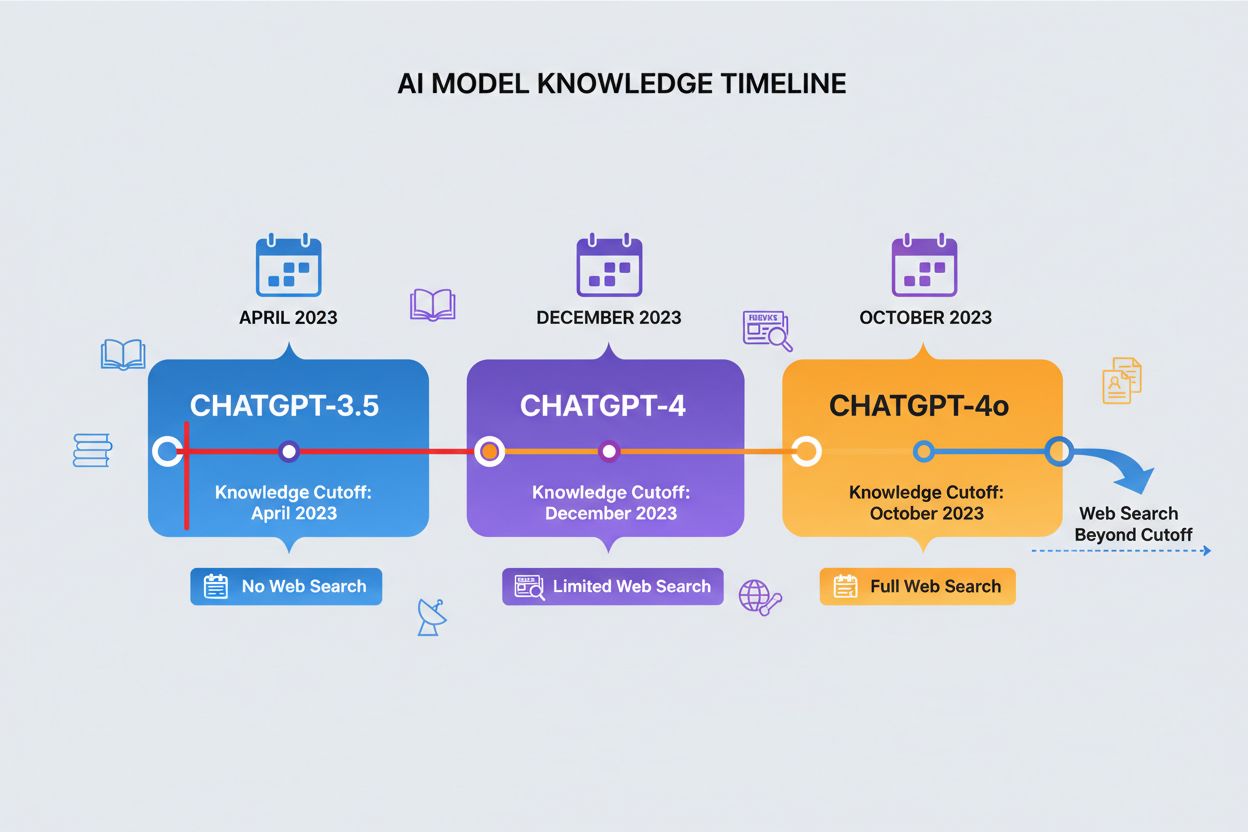
A knowledge cutoff date represents the point in time after which ChatGPT has no training data, creating a hard boundary for the information it can access. Different versions of ChatGPT have different cutoff dates: ChatGPT-4 was trained on data through December 2023, while ChatGPT-4o (the optimized version) has a knowledge cutoff of October 2023. These cutoff dates significantly impact the accuracy and relevance of responses, particularly for recent events, newly published research, or current statistics that may have changed since the training data was collected. Some newer versions of ChatGPT can perform web searches to retrieve current information beyond their cutoff dates, though this feature is not available in all versions or contexts. Understanding your model’s cutoff date is essential for users who need current information, as ChatGPT cannot provide accurate answers about events or developments that occurred after its training period ended. This limitation is one of the most important factors to consider when evaluating ChatGPT’s reliability for time-sensitive queries.
| ChatGPT Version | Knowledge Cutoff Date | Web Search Capability | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT-4 | December 2023 | Limited | General knowledge, analysis, reasoning |
| ChatGPT-4o | October 2023 | Available | Optimized performance, multimodal tasks |
| ChatGPT-3.5 | April 2023 | No | Basic queries, cost-effective option |
| ChatGPT with Browsing | Real-time | Yes | Current events, recent research |
Unlike search engines that retrieve specific documents or web pages in response to queries, ChatGPT generates responses by synthesizing patterns learned during training—a fundamentally different process. When you ask ChatGPT a question, it doesn’t search through a database or index; instead, it uses statistical patterns from its training data to predict the most likely sequence of words that would constitute a helpful answer. This generation-based approach means ChatGPT combines information from multiple sources in its training data to create novel responses that may not exist verbatim anywhere in its source material. The model essentially learns the relationships between concepts, facts, and ideas, then reconstructs this knowledge in response to your specific query. However, this process has a significant drawback: when the model is uncertain about information or when patterns in its training data are contradictory or sparse, it may generate plausible-sounding but false information, a phenomenon known as “hallucination.” Newer versions of ChatGPT that integrate web search functionality can supplement this generation process by retrieving current information from the internet, though this feature requires explicit activation and isn’t available across all platforms.
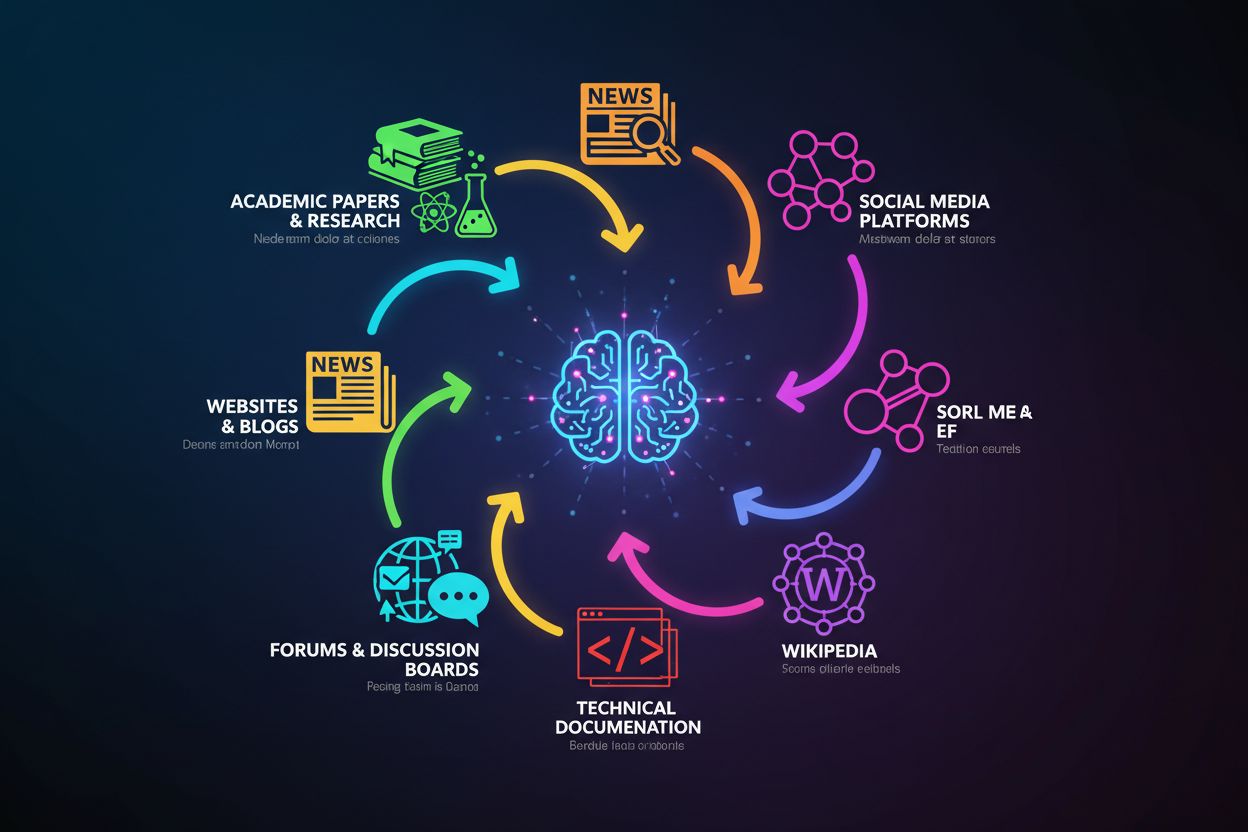
ChatGPT’s training data draws from several major source categories, each contributing unique value to its knowledge base:
The importance of these diverse sources lies in their complementary strengths: academic papers provide rigor, news articles provide timeliness, books provide depth, and forums provide practical application. However, source quality varies significantly—a peer-reviewed academic paper carries more weight than a random blog post, yet ChatGPT’s training process doesn’t explicitly distinguish between them. This means ChatGPT’s knowledge reflects both high-quality authoritative sources and lower-quality or potentially misleading content, which is why verification remains essential when using the model for important decisions.
After the initial training on vast amounts of text data, OpenAI employed a technique called Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) to refine ChatGPT’s responses. In this process, human trainers evaluated model outputs and provided feedback, helping the system learn which responses were more helpful, accurate, and aligned with human values. These human trainers didn’t fact-check every statement; rather, they assessed overall response quality, helpfulness, and safety, which indirectly shaped how the model prioritizes and presents information. The RLHF process significantly influences which information gets emphasized in responses and how different topics are framed, introducing human judgment into what would otherwise be a purely statistical model. However, this human feedback process has inherent limitations: trainers have their own biases, knowledge gaps, and limitations, and they cannot possibly evaluate the accuracy of every claim across all domains. Additionally, the feedback process is resource-intensive and can only be applied to a fraction of the model’s possible outputs, meaning much of ChatGPT’s behavior still reflects the raw patterns in its training data rather than explicit human curation.
Citing ChatGPT is important for academic integrity and transparency, allowing readers to understand where information came from and potentially reproduce or verify your findings. The citation format depends on your required style guide, but here are the most common approaches:
MLA Format Example:
OpenAI. "ChatGPT." Accessed [Date], https://chat.openai.com.
In MLA style, you cite ChatGPT as a website, including the access date since the content is dynamic and may change. If you’re citing a specific response, you should note the date you accessed it and ideally include the prompt or question you asked.
APA Format Example:
OpenAI. (2024). ChatGPT (Version 4) [Large language model].
Retrieved from https://chat.openai.com
APA format treats ChatGPT as a software tool or application, including the version number and retrieval date. Some APA guidelines recommend including the specific prompt in your citation or in a supplementary note.
When to cite ChatGPT: You should cite the tool whenever you use its output in academic work, professional reports, or any context where attribution matters. Document the exact prompt you used, the date of access, and ideally the version of ChatGPT, as these details affect reproducibility. The key difference between citing ChatGPT and traditional sources is that ChatGPT responses are generated dynamically—the same prompt may produce slightly different outputs on different occasions—so including the prompt itself becomes part of proper citation practice. Many institutions are still developing formal guidelines for AI citation, so check with your specific organization or publication for their preferred format.
While ChatGPT is remarkably capable, it has significant limitations that affect the reliability of its information. ChatGPT can confidently state false information, a problem known as hallucination, particularly when asked about obscure topics, recent events beyond its knowledge cutoff, or when it encounters contradictory information in its training data. The model’s training data contains inherent biases reflecting the perspectives, demographics, and viewpoints present in its source material, which means responses may inadvertently favor certain viewpoints or contain stereotypes. Information in ChatGPT’s training data becomes progressively more outdated as time passes, making it unreliable for current statistics, recent research findings, or evolving situations. For these reasons, fact-checking ChatGPT’s claims is essential, particularly for important decisions—you should verify key facts against primary sources, recent publications, and authoritative databases. To verify ChatGPT’s claims, cross-reference its statements with multiple independent sources, check dates and statistics against current data, and be especially skeptical of specific numbers, names, or recent events. Finally, remember that ChatGPT is not a primary source; it’s a secondary source that synthesizes information from other sources, so for academic or professional work, you should cite the original sources ChatGPT references rather than ChatGPT itself.
As ChatGPT and other AI systems become increasingly integrated into how people discover information, monitoring how these systems cite and reference your brand or organization has become crucial. AmICited is an AI answers monitoring platform designed specifically to track how ChatGPT, Claude, and other large language models mention, cite, or reference your company, products, or brand across their responses. The platform helps you understand when and how your brand appears in AI-generated answers, providing visibility into a new and growing channel of information discovery that traditional web monitoring tools often miss. This monitoring capability is essential because AI citations operate differently from traditional web citations—they’re embedded in conversational responses that millions of users interact with daily, yet most brands have no visibility into how they’re being represented. By using AmICited to track AI mentions and citations, you gain insights into brand perception in AI systems, can identify inaccuracies or outdated information that needs correction, and understand how your brand compares to competitors in AI-generated responses. In an era where AI systems are becoming primary information sources for many users, monitoring your presence in these systems is as important as monitoring traditional search results, making tools like AmICited essential for modern brand management and AI transparency.
ChatGPT was trained on three primary sources: publicly available internet data (websites, articles, forums), licensed datasets (books and academic publications), and human feedback from trainers. The training data encompasses news websites, academic journals, technical documentation, Wikipedia, Reddit, Stack Overflow, and countless other publicly accessible web pages collected up to its knowledge cutoff date.
A knowledge cutoff date is the point in time after which ChatGPT has no training data. ChatGPT-4 has a December 2023 cutoff, while ChatGPT-4o has an October 2023 cutoff. This matters because ChatGPT cannot provide accurate information about events, research, or developments that occurred after its training period ended, making it unreliable for time-sensitive queries.
ChatGPT cannot access real-time information from its training data alone. However, newer versions of ChatGPT can perform web searches to retrieve current information beyond their knowledge cutoff dates, though this feature is not available in all versions or contexts and requires explicit activation.
In MLA format, cite ChatGPT as a website with the access date. In APA format, treat it as software and include the version number. Both formats require documenting the exact prompt you used, the date of access, and ideally the ChatGPT version, since the same prompt may produce different outputs on different occasions.
No. ChatGPT can confidently state false information (hallucination), especially about obscure topics, recent events beyond its knowledge cutoff, or contradictory information. Its training data contains inherent biases, and information becomes progressively more outdated. Always fact-check important claims against primary sources and authoritative databases.
ChatGPT's training data is not continuously updated. New versions are released periodically with updated knowledge cutoff dates, but there is no real-time updating of the base model. OpenAI releases new versions (like GPT-4o) with more recent training data, but the exact update schedule is not publicly disclosed.
ChatGPT doesn't cite specific sources for individual claims because it synthesizes information from patterns in its training data rather than retrieving specific documents. It cannot point you to the exact source of a fact. For academic work, you should verify ChatGPT's claims and cite the original sources you find, not ChatGPT itself.
AmICited tracks how ChatGPT, Claude, and other AI systems mention, cite, or reference your brand across their responses. It provides visibility into how your company appears in AI-generated answers, helps identify inaccuracies, and shows how your brand compares to competitors in AI systems—essential for modern brand management in the AI era.
Track ChatGPT citations and AI mentions in real-time with AmICited. Understand how AI systems reference your brand and stay ahead of AI-driven information discovery.

Discover how Wikipedia citations shape AI training data and create a ripple effect across LLMs. Learn why your Wikipedia presence matters for AI mentions and br...
Learn how to optimize your Reddit presence for AI citations. Master Reddit LLM seeding strategies to increase brand visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Googl...

Discover how Wikipedia serves as a critical AI training dataset, its impact on model accuracy, licensing agreements, and why AI companies depend on it for train...