
Matching Content to Prompts: Optimization Based on Query Intent
Learn how to align your content with AI query intent to increase citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Master content-prompt matching strategies ...

Learn how conversational intent shapes AI dialogue. Discover strategies to match your content to how users interact with AI systems and monitor brand visibility across AI platforms.
Conversational intent refers to the underlying purpose or goal that a user has when engaging in a dialogue with an AI system, chatbot, or voice assistant. Unlike traditional search queries that often consist of a few keywords, conversational intent encompasses the broader context, nuance, and desired outcome of a multi-turn interaction. Understanding conversational intent is crucial for AI dialogue systems because it enables them to provide more relevant, contextually appropriate, and helpful responses. When AI systems can accurately identify what a user truly wants to accomplish—whether that’s learning something new, making a purchase decision, solving a problem, or simply having a casual conversation—they can tailor their responses accordingly and create more satisfying user experiences.
The distinction between conversational intent and traditional SEO intent represents a fundamental shift in how we think about user needs in the age of AI. Traditional search intent, developed for keyword-based search engines, focuses on categorizing queries into broad buckets like “navigational,” “informational,” or “transactional.” These categories assume relatively simple, single-turn interactions where a user enters a query and receives a ranked list of results. Conversational intent, by contrast, acknowledges that modern AI interactions are dynamic, multi-turn exchanges where user needs may evolve, clarifications may be needed, and the context of previous messages shapes the interpretation of new ones. This shift reflects how people naturally communicate—with nuance, follow-up questions, and evolving requirements that can’t be captured in a simple keyword phrase.
| Aspect | Traditional Search Intent | Conversational Intent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Categorization of keyword queries into navigational, informational, or transactional buckets | The underlying purpose and desired outcome of a multi-turn dialogue with an AI system |
| Focus | Keywords and query structure; what the user is searching for | Context, nuance, and user goals; what the user is trying to accomplish |
| Flexibility | Static and predetermined; limited ability to adapt based on user feedback | Dynamic and evolving; adapts based on conversation history and clarifications |
| Use Case | Optimizing web pages for search engine rankings | Improving AI response quality, relevance, and user satisfaction in dialogue systems |
The practical implications of understanding conversational intent are significant for both AI developers and businesses. When an AI system misidentifies intent, it may provide irrelevant information, miss opportunities to assist the user, or fail to recognize when a user needs human intervention. For example, a user asking “How do I fix my printer?” might have informational intent (wanting to learn troubleshooting steps) or commercial intent (considering whether to buy a new printer). The AI’s ability to recognize which intent applies—perhaps through follow-up questions or context clues—determines whether the response will be genuinely helpful. This becomes even more critical in business contexts where conversational AI systems interact with customers, as misaligned intent recognition can lead to poor customer experiences and missed sales opportunities.
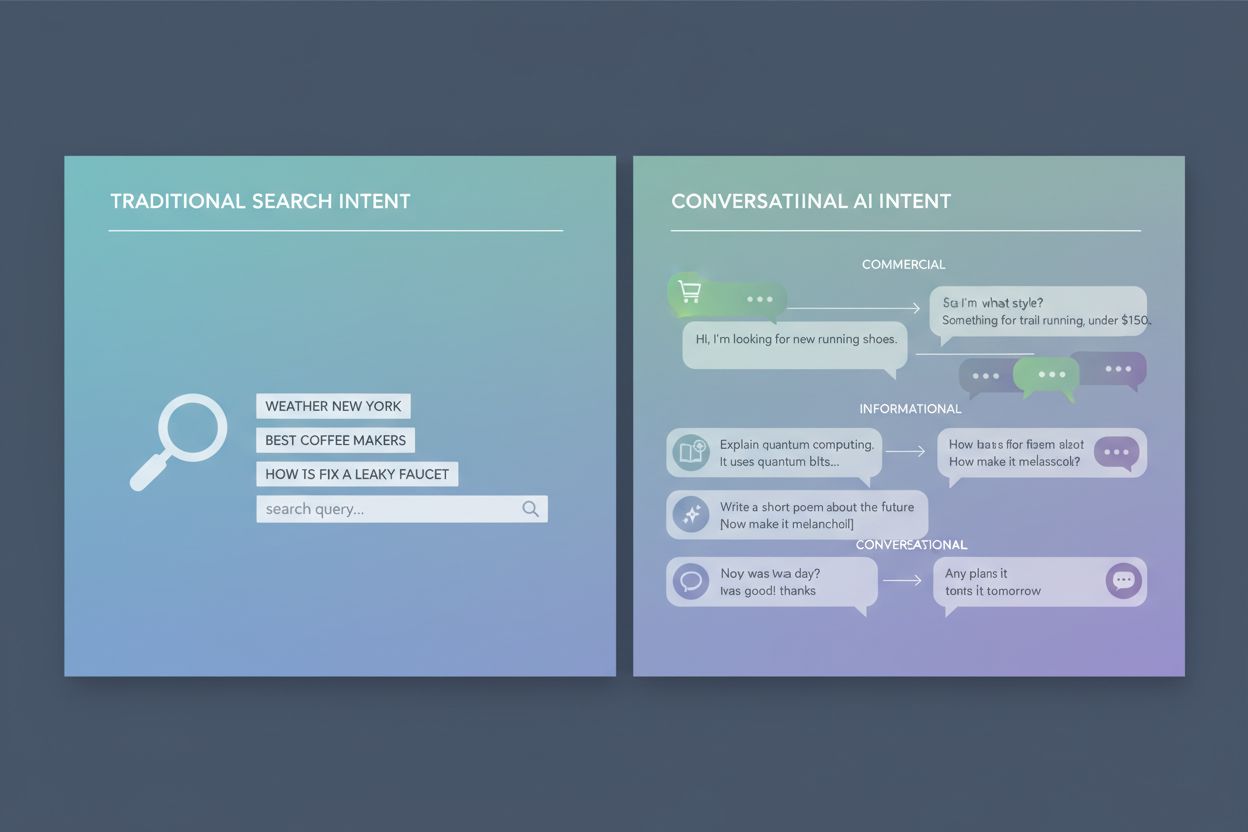
Commercial Intent encompasses interactions where users are engaged in some stage of a purchasing or business decision-making process. This category includes awareness-stage conversations where users are exploring options and learning about products or services, consideration-stage discussions where they’re comparing alternatives and evaluating features, purchase-stage interactions where they’re ready to buy and need final information or support, and post-purchase support conversations where they need help using or troubleshooting a product. Examples include a user asking “What’s the best project management tool for remote teams?” (awareness), “How does Asana compare to Monday.com?” (consideration), “Can I get a discount if I commit to an annual plan?” (purchase), and “Why isn’t my integration working?” (support).
Informational Intent represents conversations where users are primarily seeking knowledge, facts, or procedural guidance. This includes learning-focused queries where users want to understand concepts or develop new skills, fact-based questions where they need specific information or data, and how-to requests where they’re looking for step-by-step instructions. A user asking “What is machine learning?” demonstrates learning intent, “What was the GDP of Japan in 2023?” shows fact-seeking intent, and “How do I make sourdough bread?” exemplifies how-to intent. These conversations are typically straightforward and focused on knowledge transfer rather than decision-making.
Generative Intent refers to interactions where users want AI systems to create, produce, or synthesize new content or solutions. This category includes content creation requests where users ask AI to write articles, emails, or social media posts; code generation where developers request help writing or debugging code; and strategy development where users seek AI assistance in planning approaches or solutions. Examples include “Write a professional email requesting a meeting,” “Help me debug this Python function,” and “What’s a good go-to-market strategy for a B2B SaaS startup?” These interactions leverage AI’s creative and analytical capabilities to produce original outputs.
Conversational/Other Intent encompasses interactions that don’t fit neatly into the previous categories, including casual chat where users engage in friendly conversation without a specific goal, unclear or ambiguous requests where the user’s true intent isn’t immediately apparent, and exploratory conversations where users are testing the AI’s capabilities or having open-ended discussions. Examples include “Tell me a joke,” “I’m not sure what I’m looking for,” and “What can you help me with?” These interactions often require the AI to ask clarifying questions or engage in more open-ended dialogue to understand what the user actually needs.
Intent matching has become a critical component of AI monitoring and brand tracking because how AI systems reference brands varies dramatically based on the conversational intent driving the interaction. When a user has commercial intent and is actively considering a purchase, they’re likely to ask direct questions about specific brands, and the AI’s response—whether it mentions your brand, competitors, or neither—directly impacts your visibility in the decision-making process. In informational contexts, brands may be referenced as examples or case studies, but the mention carries different weight than in a commercial context. Understanding these distinctions is essential for companies trying to track how their brand appears in AI-generated responses across different user scenarios.
The impact on brand visibility in AI answers is substantial and often underestimated by traditional marketing teams. A brand that appears prominently in commercial intent conversations may be invisible in informational ones, or vice versa. For instance, a software company might be mentioned frequently when users ask “What project management tools should I buy?” but rarely appear when users ask “What is project management?” This fragmentation means that simple metrics counting total brand mentions across all AI conversations can be misleading. Companies need to understand not just whether they’re mentioned, but in what contexts and with what intent their brand appears in AI-generated content.
Platforms like AmICited and similar AI monitoring tools address this gap by tracking brand references within the context of conversational intent. These platforms recognize that a mention in a commercial intent conversation—where a user is actively making a decision—carries more business value than a mention in a casual or informational context. By categorizing AI references by intent type, these monitoring solutions provide more actionable insights into brand visibility and competitive positioning. This allows marketing and product teams to understand not just how often they’re mentioned, but how effectively they’re being positioned in the moments that matter most for business outcomes.
The business implications of intent-aware AI monitoring are profound. Companies can identify gaps in their visibility during critical decision-making moments, understand how competitors are being positioned relative to them in different intent contexts, and adjust their strategies accordingly. A brand might discover that while they’re mentioned frequently in informational contexts, they’re rarely recommended in commercial intent conversations—a clear signal that their positioning or messaging needs adjustment. Additionally, understanding intent patterns helps companies anticipate how their brand will appear as AI systems become more prevalent in customer decision-making, allowing them to proactively shape their presence in these new channels before they become dominant. This shift from traditional search monitoring to intent-aware AI monitoring represents a fundamental evolution in how brands must track and manage their visibility in the digital landscape.
Intent recognition is the foundational process by which AI systems identify what a user wants to accomplish through their input. When a user types “What’s the best laptop for video editing?” the system must recognize that this is an informational intent rather than a transactional one. This classification happens through sophisticated pattern matching and machine learning algorithms that analyze linguistic features, context clues, and historical data. The accuracy of intent recognition directly impacts the quality of responses and the overall user experience, making it one of the most critical components in dialogue systems. Modern AI systems employ multiple approaches simultaneously to ensure robust intent classification across diverse user inputs and conversational contexts.
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Large Language Models (LLMs) represent two distinct paradigms for intent recognition, each with unique strengths and limitations. Traditional NLU systems use rule-based and machine learning approaches, relying on labeled training data and predefined intent categories to classify user inputs with high precision. These systems excel at handling structured conversations with well-defined intents and typically require less computational resources. Conversely, LLM-based approaches leverage transformer architectures and vast pre-training datasets to understand intent through contextual reasoning and semantic similarity, enabling them to handle novel intents and complex conversational nuances without explicit training. While LLMs demonstrate superior flexibility and generalization capabilities, they may require more computational resources and can sometimes produce less predictable results compared to traditional NLU systems.
Intent classification techniques vary in sophistication, ranging from simple keyword matching to advanced neural network architectures. Basic systems use keyword spotting, identifying specific words or phrases that signal particular intents—for example, “buy,” “purchase,” or “checkout” indicating commercial intent. More advanced techniques employ supervised learning with labeled datasets, training classifiers like Support Vector Machines (SVMs) or neural networks to recognize intent patterns. Deep learning approaches using recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformers can capture sequential dependencies and long-range contextual relationships within user inputs. Multi-intent detection systems can identify when users express multiple intents simultaneously, such as asking for product information while also wanting to make a purchase. Ensemble methods combining multiple classifiers often outperform single-model approaches by leveraging diverse perspectives on the same classification problem.
Context awareness and slot filling enhance intent recognition by capturing the specific details and parameters relevant to user requests. Context awareness involves maintaining information about previous turns in a conversation, user history, and environmental factors that influence intent interpretation. For instance, if a user previously asked about running shoes and then says “show me reviews,” the system recognizes this as a request for reviews specifically about running shoes. Slot filling is the process of extracting key entities and parameters from user input—if someone says “I want to book a flight to New York next Tuesday,” the system identifies “New York” as the destination slot and “next Tuesday” as the date slot. These techniques work synergistically with intent recognition to create comprehensive understanding of user needs and enable more precise, personalized responses.
Intent recognition faces several significant challenges that impact real-world deployment and performance. Ambiguity is a primary challenge, as many user inputs can reasonably map to multiple intents; “I’m looking for a new phone” could indicate informational, commercial, or research intent depending on context. Out-of-domain inputs that fall outside predefined intent categories can confuse systems trained on limited datasets, requiring robust fallback mechanisms. Sarcasm, idioms, and cultural references present linguistic challenges that even advanced systems struggle to interpret correctly. Intent drift occurs when user intent evolves during a conversation, requiring systems to dynamically update their understanding rather than relying on initial classifications. Additionally, data scarcity for specialized domains and class imbalance in training datasets can significantly degrade intent recognition performance.
Monitoring tools track intent recognition performance through multiple metrics and analytical approaches that provide visibility into system behavior and accuracy. These platforms capture intent classification confidence scores, allowing teams to identify low-confidence predictions that may require human review or system retraining. Intent distribution analysis reveals which intents users most frequently express, informing product development and content strategy priorities. Monitoring systems track intent misclassification patterns, identifying specific user input types or contexts where the system consistently fails. Real-time dashboards display intent recognition metrics alongside user satisfaction scores, enabling teams to correlate intent accuracy with overall user experience. Advanced monitoring platforms integrate feedback loops where human reviewers can correct misclassified intents, creating continuous improvement cycles that enhance system performance over time.
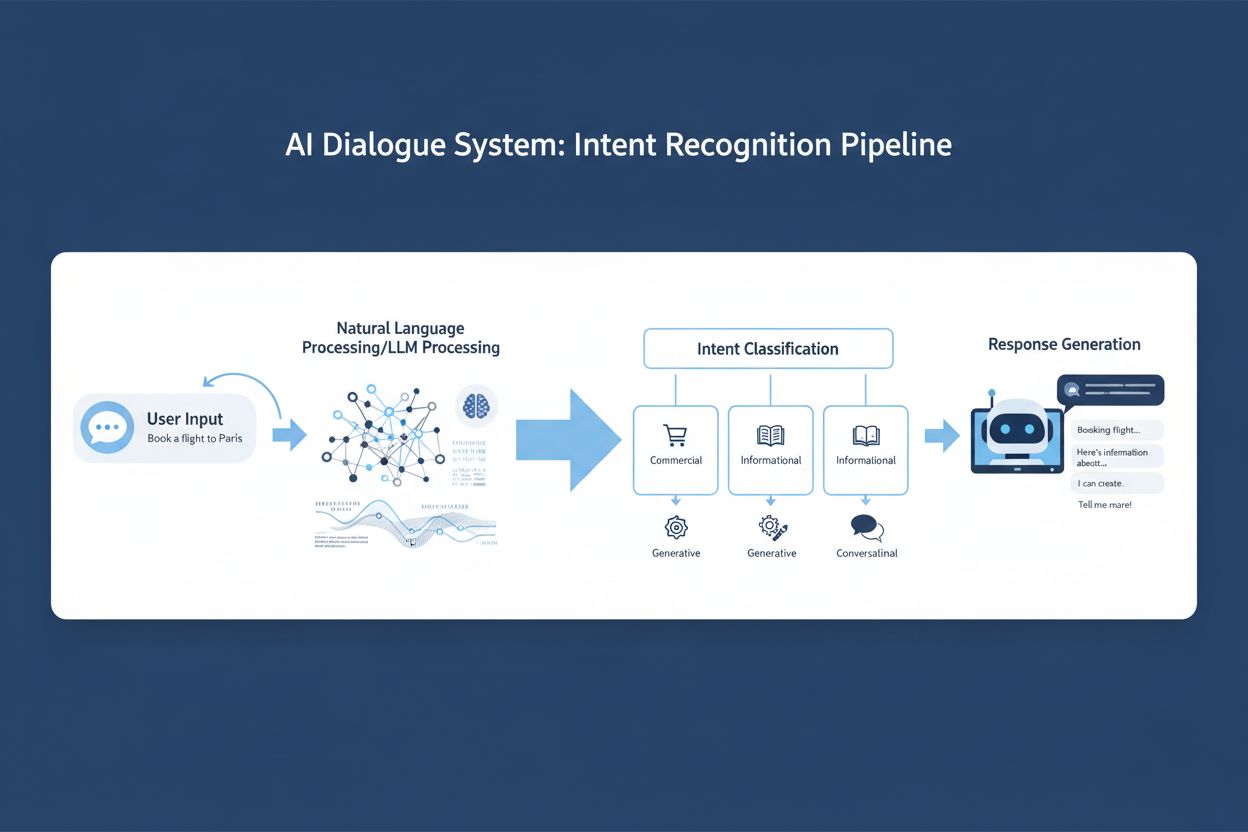
Aligning content strategy with conversation intent is essential for delivering relevant, valuable responses that meet user needs and drive desired business outcomes. Different intents require fundamentally different content approaches, messaging strategies, and engagement tactics. A user with commercial intent needs persuasive, benefit-focused content that addresses objections and facilitates purchase decisions, while a user with informational intent requires educational, comprehensive content that builds understanding and establishes authority. By tailoring content to match detected intent, organizations can dramatically improve engagement metrics, conversion rates, and user satisfaction. The most sophisticated dialogue systems employ dynamic content selection mechanisms that choose from multiple content variants based on real-time intent classification, ensuring optimal relevance for each interaction.
Commercial intent content strategy focuses on conversion optimization through persuasive messaging, social proof, and clear calls-to-action. When users express intent to purchase or compare products, content should emphasize unique value propositions, competitive advantages, and customer testimonials that build confidence in the purchase decision. Product comparison tables, pricing transparency, and limited-time offers create urgency and facilitate decision-making. For example, when a user asks “What’s the difference between your Pro and Enterprise plans?” the system should deliver a detailed comparison highlighting features most relevant to their use case, supported by customer success stories from similar organizations. Objection-handling content addresses common concerns like pricing, implementation complexity, or integration challenges, removing friction from the conversion path. Effective commercial content includes clear next steps—whether scheduling a demo, starting a free trial, or completing a purchase—with minimal friction and maximum clarity.
Informational intent content strategy prioritizes educational value, accuracy, and comprehensive coverage that establishes the brand as a trusted authority. Users seeking information want detailed explanations, context, and background that help them understand complex topics or make informed decisions. Content should be well-structured with clear headings, bullet points, and visual aids that facilitate scanning and comprehension. For instance, when someone asks “How does machine learning differ from traditional programming?” the response should provide clear definitions, concrete examples, and practical implications rather than sales-focused messaging. Educational frameworks like problem-solution-benefit structures help organize information logically and guide users toward understanding. Informational content often includes links to deeper resources, related topics, and expert perspectives, positioning the brand as a comprehensive knowledge resource. This approach builds long-term trust and authority, creating opportunities for future engagement when users are ready to make purchasing decisions.
Generative intent content requires templates and frameworks that enable users to create, customize, and produce original outputs aligned with their specific needs. When users want to generate content—whether writing product descriptions, creating marketing copy, or developing technical documentation—the system should provide structured templates that guide the generation process while allowing customization. Prompt templates that include placeholders for key variables (product name, target audience, tone, length) enable consistent, high-quality outputs. For example, a template for generating product descriptions might include sections for key features, benefits, use cases, and technical specifications, with guidance on optimal length and tone for different platforms. Framework-based generation uses established structures like the AIDA model (Attention, Interest, Desire, Action) or the Problem-Agitate-Solve framework to organize generated content logically. Providing examples of high-quality outputs helps users understand expectations and refine their requests, creating iterative improvement cycles that enhance content quality.
Optimization strategies for each intent type involve continuous testing, measurement, and refinement based on performance data and user feedback. For commercial intent, A/B testing different value propositions, pricing presentations, and call-to-action placements reveals which approaches drive highest conversion rates. Conversion rate optimization focuses on reducing friction, clarifying benefits, and building trust through social proof and guarantees. For informational intent, optimization involves measuring engagement metrics like time-on-page, scroll depth, and return visits to understand which content formats and structures resonate most effectively. Content performance analysis identifies which topics, explanations, and examples generate highest engagement and satisfaction. For generative intent, optimization focuses on output quality, customization flexibility, and user satisfaction with generated content. Iterative refinement based on user feedback and performance metrics ensures continuous improvement across all intent types.
Intent data provides invaluable guidance for content creation strategy, informing decisions about topics, formats, messaging, and resource allocation. Intent analytics reveal which questions users most frequently ask, which topics generate highest engagement, and which content gaps exist in current offerings. By analyzing intent distribution, content teams can prioritize creating resources for high-volume intents that currently lack adequate coverage. For example, if monitoring reveals that 40% of user queries express informational intent about a specific feature, but only 10% of content addresses that topic, this represents a clear opportunity for content expansion. Intent-driven content calendars align editorial planning with user needs, ensuring that content creation efforts address the most impactful intents. Seasonal intent patterns inform timing decisions, helping teams publish relevant content when user interest peaks. Competitive intent analysis reveals which topics competitors address effectively, identifying opportunities to differentiate through superior content quality or unique perspectives.
Monitoring intent in AI-generated answers is critical for brands seeking to maintain quality, relevance, and alignment with business objectives across all customer interactions. When AI systems generate responses without proper intent monitoring, they risk providing irrelevant information, missing sales opportunities, or delivering educational content when users seek to make purchases. Intent monitoring ensures that AI responses match user needs, maintain brand voice consistency, and drive desired business outcomes. For organizations deploying AI across customer service, sales, and support functions, intent monitoring provides essential visibility into system performance and user satisfaction. The stakes are particularly high in customer-facing applications where poor intent alignment can damage brand reputation and reduce customer lifetime value.
Intent monitoring platforms track how well AI systems recognize and respond to user intent through sophisticated analytical frameworks and real-time dashboards. These platforms capture intent classification confidence scores, allowing teams to identify uncertain predictions that may require human review or system retraining. Response relevance scoring measures whether generated answers actually address the detected intent, using both automated metrics and human evaluation. For example, if a user expresses commercial intent but receives purely informational content, the monitoring system flags this mismatch as a quality issue. Intent fulfillment tracking measures whether responses include appropriate calls-to-action, product recommendations, or next steps aligned with the detected intent. Advanced platforms integrate multi-turn conversation analysis, examining how intent evolves across dialogue sequences and whether the system adapts its responses accordingly. Real-time dashboards provide visibility into intent recognition accuracy, response relevance, and user satisfaction metrics, enabling rapid identification and resolution of performance issues.
Key metrics for measuring intent-based performance provide quantifiable indicators of system effectiveness and areas requiring improvement. Intent classification accuracy measures the percentage of user inputs correctly classified into appropriate intent categories, with separate metrics for each intent type. Intent-response alignment measures whether generated responses match the detected intent, calculated as the percentage of responses that appropriately address user needs. Conversion rate by intent tracks how effectively the system drives desired outcomes for commercial intent conversations, comparing conversion rates across different intent types and user segments. User satisfaction by intent measures whether users find responses helpful and relevant, often captured through post-interaction surveys or implicit signals like follow-up questions. Intent coverage measures the percentage of user inputs that the system can confidently classify, identifying gaps where the system lacks adequate intent recognition capabilities. Response latency by intent tracks whether the system responds quickly across different intent types, as some intents may require more complex processing. Fallback rate measures how frequently the system fails to recognize intent and defaults to generic responses, indicating areas requiring system improvement.
Tools and platforms for intent monitoring range from specialized dialogue analytics solutions to comprehensive AI governance platforms that integrate intent tracking with broader quality assurance functions. AmICited provides sophisticated intent monitoring capabilities specifically designed for AI-generated content, tracking how well responses align with detected user intent and measuring impact on business outcomes. Dedicated dialogue analytics platforms like Dashbot, Botanalytics, and Conversica offer intent-specific dashboards, conversation analysis, and performance benchmarking. Customer data platforms (CDPs) integrate intent data with broader customer profiles, enabling sophisticated segmentation and personalization based on intent patterns. Natural language processing (NLP) monitoring tools provide detailed linguistic analysis of both user inputs and AI responses, identifying intent mismatches and content quality issues. Business intelligence platforms like Tableau and Looker enable custom intent monitoring dashboards that integrate with existing analytics infrastructure. Human-in-the-loop platforms combine automated intent monitoring with human review workflows, enabling quality assurance teams to validate system performance and provide training data for continuous improvement.
Actionable insights from intent data guide strategic decisions about content, product development, and customer experience optimization. Intent distribution analysis reveals which user needs are most prevalent, informing product roadmap priorities and content creation strategies. For example, if monitoring reveals that 60% of user queries express informational intent while only 20% express commercial intent, this suggests opportunities to develop more educational content and improve conversion optimization. Intent-based segmentation enables personalized experiences where different user segments receive tailored content based on their typical intent patterns. Users who frequently express commercial intent might receive product recommendations and special offers, while those with informational intent receive educational resources and expert perspectives. Intent trend analysis identifies emerging user needs and shifting priorities, enabling proactive content development and product innovation. Competitive intent benchmarking compares your system’s intent recognition and response quality against competitors, identifying areas where superior performance creates competitive advantage. Intent-driven optimization uses performance data to prioritize improvements, focusing resources on high-impact intents that significantly influence user satisfaction and business outcomes.
Practical examples demonstrate how intent monitoring drives real-world improvements in AI system performance and business results. A SaaS company monitoring intent in customer support conversations discovered that 35% of users expressing commercial intent received purely informational responses, resulting in missed upsell opportunities. By retraining the system to recognize commercial intent more accurately and adjusting response templates to include relevant product recommendations, the company increased conversion rates by 18% within three months. An e-commerce retailer used intent monitoring to identify that users asking about product durability (informational intent) had significantly higher purchase rates when provided with warranty information and customer reviews. By automatically including this content in responses to durability-related questions, the retailer improved conversion rates by 12% while simultaneously increasing customer satisfaction scores. A financial services firm discovered through intent monitoring that users expressing research intent (comparing investment options) had higher lifetime value than those with transactional intent, prompting a strategic shift toward more educational content and thought leadership positioning. These examples illustrate how systematic intent monitoring translates into measurable business value through improved relevance, higher conversion rates, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Segment Your Content by Intent Type to maximize relevance and engagement across your audience. Begin by categorizing your existing content into informational, navigational, commercial, and transactional buckets based on user search intent. This segmentation allows you to tailor messaging, tone, and calls-to-action to match what users are actually seeking at each stage of their journey. Create separate content strategies for each intent category, ensuring that informational content educates without aggressive selling, while commercial content highlights competitive advantages and social proof. By aligning content with intent, you’ll see improved click-through rates, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates across your digital properties. Document your intent categories in a content audit spreadsheet to maintain consistency and enable team-wide understanding of your segmentation strategy.
Implement Rigorous Testing and Optimization Protocols to continuously improve content performance based on user behavior and intent signals. Conduct A/B testing on headlines, meta descriptions, and calls-to-action to determine which variations resonate best with different intent-driven audiences. Use heat mapping and session recording tools to understand how users interact with your content and whether it satisfies their underlying intent. Establish baseline metrics for each intent category, then systematically test variations to improve performance. Create a testing calendar that prioritizes high-traffic, high-value content pieces first, allowing you to generate quick wins while building momentum for broader optimization efforts. Document all test results and learnings in a centralized repository to avoid duplicating efforts and to build institutional knowledge about what works for your specific audience.
Maintain Consistency Across All Channels while adapting content to platform-specific intent signals and user behaviors. Develop brand guidelines that specify how core messages should be communicated across search, social media, email, and paid advertising channels. Ensure that users encountering your brand through different touchpoints receive a cohesive experience that acknowledges their intent at each stage. Use consistent terminology, visual branding, and value propositions across channels, while allowing flexibility in format and tone to match platform norms. Create channel-specific content calendars that reference your master intent-driven strategy, ensuring alignment while respecting each platform’s unique characteristics. Regular audits of cross-channel messaging help identify gaps and opportunities for reinforcing your intent-driven approach.
Measure Success Through Intent-Aligned Metrics that go beyond vanity metrics to reveal true business impact. Define specific KPIs for each intent category: informational content might track engagement time and shares, while transactional content focuses on conversion rates and revenue per visitor. Implement UTM parameters and custom event tracking to attribute conversions back to specific intent-driven content pieces. Create dashboards that visualize performance across intent categories, making it easy to identify which segments are thriving and which need attention. Establish monthly review cycles where you analyze intent-based metrics alongside traditional analytics to understand the complete picture of content performance.
Embrace Continuous Improvement as a Core Operating Principle by building feedback loops into your content strategy. Collect qualitative feedback through surveys, user interviews, and customer support interactions to understand whether your content truly satisfies user intent. Use this feedback to refine your intent categories, update content, and identify gaps in your content library. Schedule quarterly strategy reviews to assess whether your intent segmentation remains accurate as market conditions and user behaviors evolve. Foster a culture of experimentation where team members are encouraged to test new approaches to intent-driven content, learning from both successes and failures to drive ongoing optimization.
Conversational intent refers to the underlying purpose or goal that a user has when engaging in dialogue with an AI system. Unlike traditional search queries, conversational intent encompasses the broader context, nuance, and desired outcome of multi-turn interactions, enabling AI systems to provide more relevant and contextually appropriate responses.
Traditional search intent focuses on categorizing keyword queries into buckets like navigational, informational, or transactional. Conversational intent, by contrast, acknowledges that modern AI interactions are dynamic, multi-turn exchanges where user needs may evolve and context shapes interpretation. This shift reflects how people naturally communicate with nuance and follow-up questions.
Monitoring conversational intent provides critical visibility into how your brand appears in AI-generated responses across different user scenarios. Understanding intent patterns helps you identify gaps in visibility during decision-making moments, understand competitive positioning, and adjust strategies to improve brand presence where it matters most for business outcomes.
The four core intent categories are: Commercial Intent (awareness, consideration, purchase, support), Informational Intent (learning, facts, how-to), Generative Intent (content creation, code, strategies), and Conversational/Other Intent (casual chat, unclear requests). Each requires different content strategies and engagement approaches.
Tailor your content strategy to match each intent type: commercial content should emphasize value propositions and social proof, informational content should prioritize educational value and accuracy, generative content should provide templates and frameworks, and conversational content should be engaging and exploratory. Use intent data to guide content creation priorities and resource allocation.
Specialized platforms like AmICited provide sophisticated intent monitoring capabilities designed for AI-generated content. Other tools include dialogue analytics platforms like Dashbot and Botanalytics, customer data platforms, NLP monitoring tools, and business intelligence platforms like Tableau. These tools track intent classification accuracy, response relevance, and business impact metrics.
AI systems recognize intent through Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Large Language Models (LLMs). Traditional NLU uses rule-based and machine learning approaches with predefined intent categories, while LLM-based approaches leverage transformer architectures to understand intent through contextual reasoning. Both approaches analyze linguistic features, context clues, and historical data to classify user inputs.
Key metrics include intent classification accuracy, intent-response alignment, conversion rate by intent, user satisfaction by intent, intent coverage, response latency by intent, and fallback rate. These metrics provide quantifiable indicators of system effectiveness and reveal areas requiring improvement in your dialogue systems.
Understand how your brand appears in AI conversations. Track conversational intent patterns and optimize your content strategy with AmICited's AI monitoring platform.

Learn how to align your content with AI query intent to increase citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Master content-prompt matching strategies ...
Conversational AI is a collection of AI technologies enabling natural dialogue between humans and machines. Learn how NLP, machine learning, and dialogue manage...

Learn how to identify and optimize for search intent in AI search engines. Discover methods to classify user queries, analyze AI SERPs, and structure content fo...