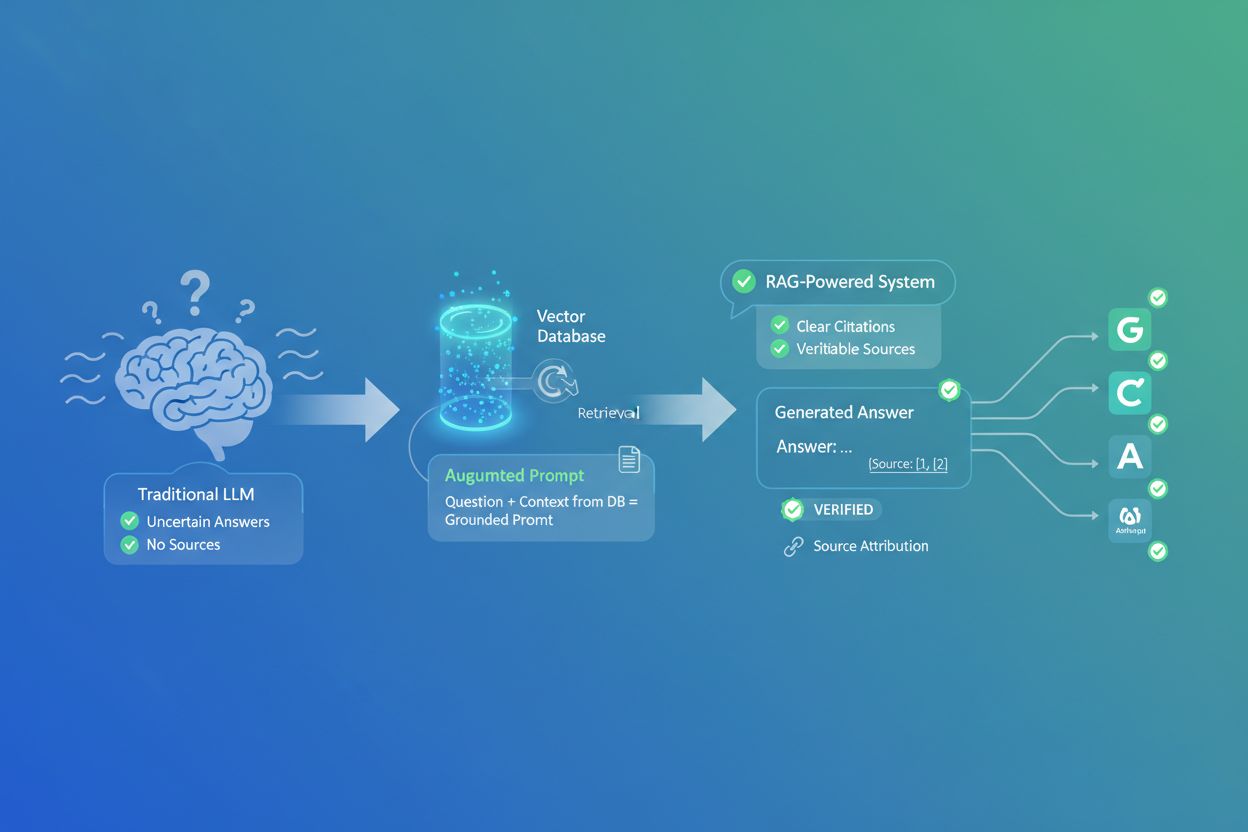
How RAG Changes AI Citations
Discover how Retrieval-Augmented Generation transforms AI citations, enabling accurate source attribution and grounded answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and G...

Discover how AI models cite visual data and charts. Learn why data visualization matters for AI citations and how to track your visual content with AmICited.
Visual data presents a fundamental bottleneck for modern large language models, which were primarily trained on text-based information and struggle to process, interpret, and cite charts with the same precision they apply to written content. Current LLMs face significant limitations when encountering data visualizations—they must first convert visual elements into textual descriptions, a process that often loses critical nuances, precise values, and contextual relationships embedded within the original chart. The inability to accurately process visual data LLM systems means that charts, graphs, and infographics frequently go uncited or are cited incorrectly, creating a credibility gap for content creators who invest time in producing high-quality visualizations. This challenge matters profoundly for researchers, analysts, and organizations that rely on AI chart processing to synthesize information, as the lack of proper attribution undermines both the original creator’s work and the reliability of AI-generated summaries. Understanding these limitations is essential for anyone creating visual content in an increasingly AI-driven information landscape.

Different AI systems approach visual content citation with varying degrees of sophistication, reflecting their underlying architecture and training methodologies. The following table illustrates how major AI platforms handle visual citations:
| AI Model | Visual Citation Capability | Citation Format | Accuracy Level | Multimodal Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT (GPT-4V) | Moderate | Descriptive text | 65-75% | Yes (image input) |
| Claude 3 | High | Detailed attribution | 80-85% | Yes (vision-enabled) |
| Perplexity AI | High | Source + visual reference | 85-90% | Yes (web-integrated) |
| Google AI Overviews | Moderate-High | Inline citations | 75-80% | Yes (image search) |
| Gemini Pro Vision | Moderate | Contextual reference | 70-78% | Yes (multimodal) |
Claude demonstrates superior performance in visual content attribution, often providing detailed source information and visual context when referencing charts, while Perplexity AI excels at integrating visual citations with web sources, creating a more comprehensive attribution trail. ChatGPT’s GPT-4V can process images but frequently defaults to generic descriptions rather than precise citations, particularly when dealing with complex financial charts or scientific visualizations. Google AI Overviews attempts to maintain inline citations for visual content but sometimes conflates the chart creator with the data source, creating ambiguity about proper attribution. For content creators, this variance means that the same visualization may receive dramatically different treatment depending on which AI system processes it—a chart might be properly cited in Claude but completely unattributed in ChatGPT, highlighting the critical need for standardized visual citation protocols across the AI ecosystem.
Data visualization plays a surprisingly influential role in shaping how AI models understand and represent information, as charts and graphs embedded in training datasets teach models to recognize patterns, relationships, and hierarchies within complex data. The quality and diversity of visual data in training sets directly impact how well AI systems can later interpret and cite similar visualizations, meaning that models trained on comprehensive visual datasets demonstrate significantly better performance in visual content attribution. Visual patterns learned during training influence model outputs in subtle but measurable ways—a model trained extensively on properly-labeled scientific charts will more likely generate accurate citations for similar visualizations than one trained primarily on text. The challenge intensifies because most large language models were trained on internet-scale data where visual content often lacks proper metadata, alt-text, or source attribution, perpetuating a cycle where AI systems learn to process charts without learning to cite them. Organizations investing in high-quality, well-documented data visualization datasets are essentially building better foundations for future AI systems, though this investment remains underutilized in the industry.
Monitoring how AI systems cite visual content requires a multi-layered approach that combines automated detection with manual verification. Key tracking methods include:
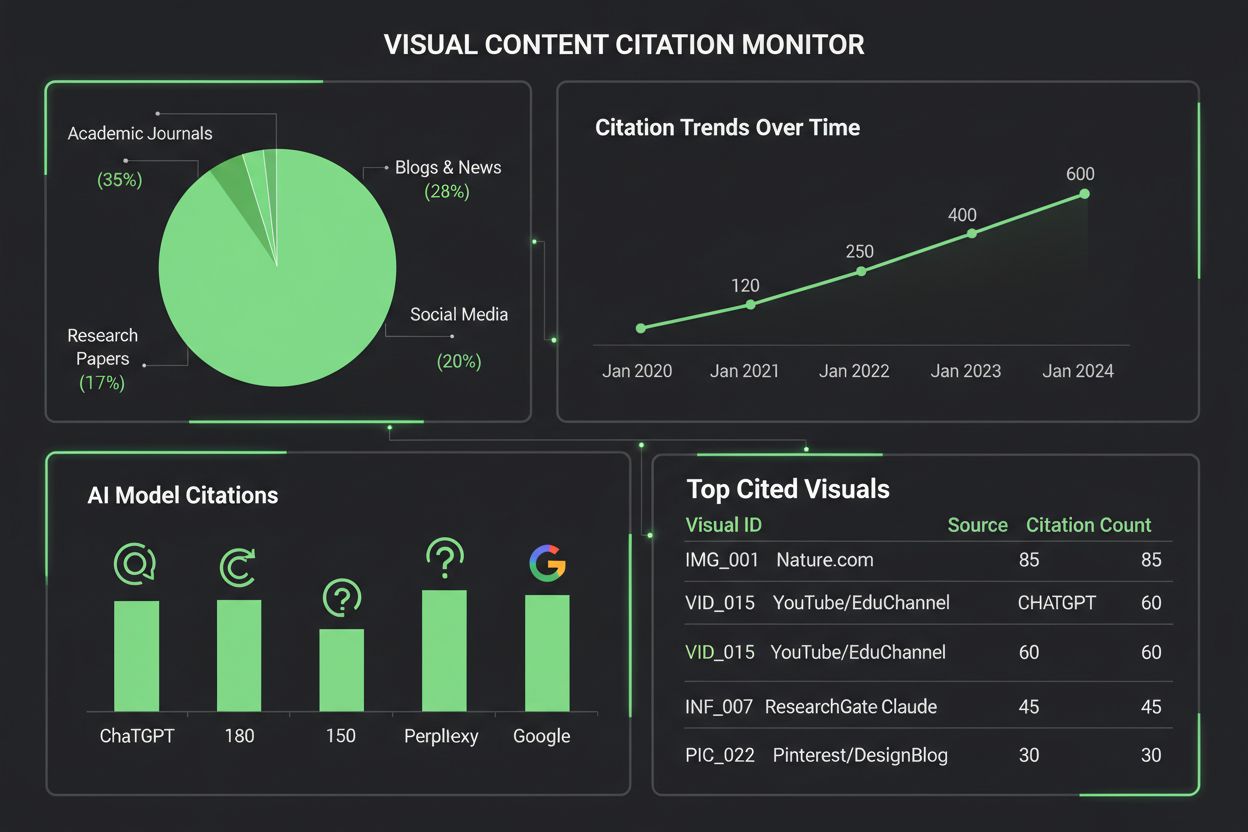
AmICited.com specializes in tracking visual content citations across multiple AI platforms, providing content creators with detailed reports on how their charts are being referenced, attributed, or overlooked by ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Google AI, and other systems. The importance of monitoring visual citations cannot be overstated—without proper tracking, creators lose visibility into how their work influences AI-generated content, making it impossible to advocate for better attribution practices or understand the true reach of their visualizations. AmICited’s visual content monitoring tools fill this critical gap by offering creators real-time alerts when their charts are cited, detailed analytics on citation accuracy, and actionable insights for improving visual content discoverability in AI systems.
Creating visualizations that are more likely to be cited by AI systems requires intentional design choices that prioritize clarity, metadata richness, and machine readability. Bold, high-contrast color schemes and clear labeling significantly improve AI chart processing, as models struggle with subtle gradients, overlapping elements, and ambiguous legends that humans can easily interpret. Include comprehensive alt-text descriptions that capture not just what the chart shows but the underlying data relationships, key insights, and source information—this metadata becomes the foundation for accurate AI citations. Embed structured data within your visualizations using standards like JSON-LD or microdata markup, which allows AI systems to extract precise values and relationships rather than relying on visual interpretation alone. Ensure that chart titles are descriptive and specific rather than generic, as AI models use titles as primary anchors for understanding and citing visual content. Provide source attribution directly within the visualization through footnotes, watermarks, or integrated source labels, making it impossible for AI systems to separate the chart from its origin. Organizations that implement these practices consistently see measurable improvements in how their visual content is cited across AI platforms, translating to better attribution, increased visibility, and stronger professional credibility.
The landscape of visual citation monitoring tools continues to expand as organizations recognize the importance of tracking how AI systems reference visual content. AmICited.com stands out as a comprehensive solution specifically designed for monitoring visual content citations across multiple AI platforms, offering creators detailed dashboards that show exactly when and how their charts are cited by ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and emerging AI systems. Traditional citation tracking platforms like Google Scholar and Scopus focus primarily on academic papers and text-based citations, leaving visual content largely unmonitored and unattributed. Specialized tools like Tinybird and similar data visualization platforms now integrate citation tracking capabilities, allowing organizations to monitor how their real-time data visualizations are consumed and referenced by AI systems. AmICited’s visual analytics capabilities provide metrics on citation frequency, accuracy rates, and platform-specific patterns, enabling content creators to understand which AI systems properly attribute their work and which ones require intervention. For organizations serious about protecting their visual intellectual property and understanding their content’s influence in the AI-driven information ecosystem, implementing a dedicated visual citation monitoring solution like AmICited.com has become essential—it transforms citation tracking from a passive observation into an active management practice that drives better attribution outcomes.
Current AI models have varying capabilities when it comes to citing visual content. While advanced models like Claude and Perplexity can reference charts with reasonable accuracy, many systems struggle with proper attribution. Most LLMs were trained primarily on text data, making visual citation less reliable than text citations. This is why monitoring tools like AmICited are essential for tracking how your visualizations are actually being cited.
AmICited.com provides comprehensive visual content monitoring across multiple AI platforms including ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. The platform uses automated visual fingerprinting and metadata analysis to identify when your charts appear in AI-generated content, providing real-time alerts and detailed analytics on citation accuracy and frequency.
AI systems cite charts more accurately when they feature bold, high-contrast colors, clear labeling, descriptive titles, and comprehensive alt-text. Including structured data markup, source attribution within the visualization, and well-organized legends significantly improves AI chart processing and citation likelihood. Creating multiple versions of complex visualizations—simplified for AI and detailed for humans—also enhances discoverability.
Based on current capabilities, Claude 3 and Perplexity AI demonstrate the highest accuracy in visual content attribution, with citation accuracy rates of 80-90%. Google AI Overviews and Gemini Pro Vision perform moderately well at 75-80%, while ChatGPT's GPT-4V, despite having vision capabilities, often defaults to generic descriptions rather than precise citations. These capabilities continue to evolve as models are updated.
Visual citation tracking is crucial for brand visibility, content value assessment, and intellectual property protection. When your charts are properly cited by AI systems, it increases your brand's visibility in AI-generated content, validates your content's influence, and helps you understand how your work shapes AI-driven information synthesis. Without tracking, you lose visibility into your content's reach and impact.
AmICited specializes in tracking visual content citations across multiple AI platforms, providing detailed dashboards showing when and how your charts are cited. The platform offers real-time alerts, citation accuracy metrics, platform-specific analytics, and actionable insights for improving visual content discoverability. It transforms citation tracking from passive observation into active management of your visual intellectual property.
Text citations in AI systems are generally more reliable because LLMs were trained primarily on text data. Visual citations require additional processing steps—AI must first convert visual elements into text descriptions, which often loses nuances and precise values. This conversion process introduces more opportunities for errors, making visual citations less accurate and less consistent than text citations across different AI platforms.
Absolutely. Implement best practices like using bold, high-contrast colors, creating descriptive titles and alt-text, embedding structured data markup, and including source attribution directly in visualizations. Avoid subtle gradients, overlapping elements, and ambiguous legends. Consider creating simplified versions of complex charts specifically for AI processing. These improvements make your visualizations more discoverable and citable by AI systems.
Track how AI systems cite your charts and visualizations across ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google AI. Get real-time alerts and detailed analytics on visual content attribution.

Discover how Retrieval-Augmented Generation transforms AI citations, enabling accurate source attribution and grounded answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and G...
Learn how to test content formats for AI citations using A/B testing methodology. Discover which formats drive the highest AI visibility and citation rates acro...

Community discussion on how data visualizations and visual content perform in AI search. Strategies for optimizing charts, infographics, and images for AI visib...