Semantic HTML for AI: Beyond Basic Markup
Learn how semantic HTML improves AI understanding, LLM comprehension, and content attribution. Discover advanced techniques for optimizing markup for AI systems...

Learn how definition lists and semantic HTML markup help AI systems understand your terminology. Improve AI visibility and citations with proper DL, DT, DD implementation.
Definition lists represent one of HTML’s most underutilized semantic elements, yet they’re becoming increasingly important as artificial intelligence systems learn to interpret structured web content. The <dl> element, paired with <dt> (definition term) and <dd> (definition description) tags, creates a machine-readable format that helps both humans and AI understand relationships between concepts and their explanations. In an era where AI systems like Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity are actively parsing web content to generate answers, properly structured definition lists can significantly improve how your terminology is understood and cited by these systems.
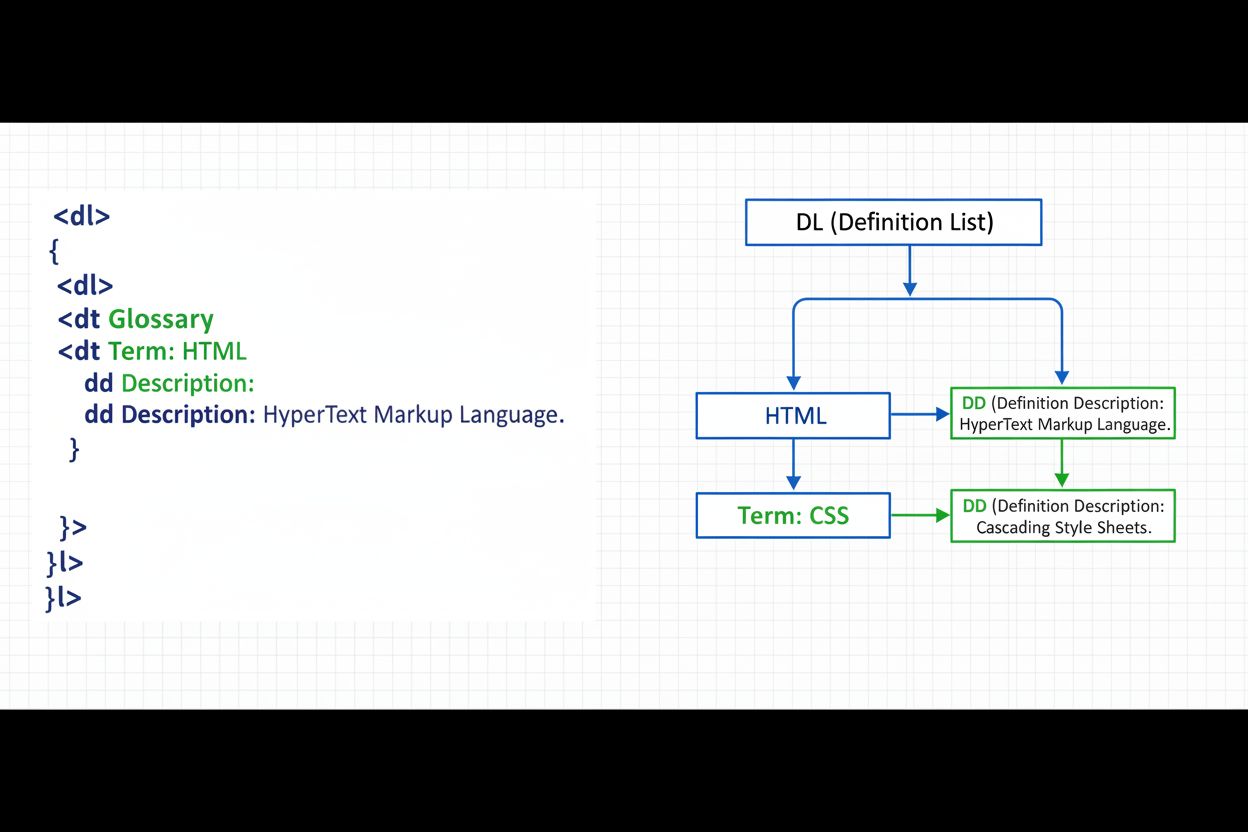
Definition lists consist of three core HTML elements working in concert to create semantic meaning. The <dl> (definition list) element serves as the container, much like <ul> for unordered lists or <ol> for ordered lists. Within this container, the <dt> (definition term) element represents the term or concept being defined, while the <dd> (definition description) element provides the explanation or value associated with that term. This structure creates explicit relationships that machines can parse and understand.
| Element | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
<dl> | Container for the entire definition list | Wraps all terms and descriptions |
<dt> | Marks up a term or concept | “Semantic HTML”, “API”, “Cache” |
<dd> | Provides the definition or description | The explanation following a term |
<div> (optional) | Groups a term with its descriptions for styling | Wraps <dt> and <dd> pairs together |
The flexibility of definition lists allows for multiple configurations: one term with one description, one term with multiple descriptions, or multiple terms sharing a single description. This versatility makes them suitable for glossaries, FAQs, product specifications, and metadata displays. When properly structured, these elements create a semantic layer that AI systems can reliably interpret, making your content more discoverable and citable by intelligent machines.
Artificial intelligence models, particularly large language models (LLMs) and search engines, process vast amounts of web content to generate answers and citations. However, unstructured text presents challenges: the AI must infer relationships between concepts, guess at definitions, and determine which information is most authoritative. Structured terminology, marked up with semantic HTML like definition lists, eliminates this ambiguity. When an AI system encounters a properly formatted definition list, it immediately understands that specific terms have specific meanings, that these relationships are intentional, and that the content creator has explicitly defined these connections.
This structured approach becomes critical when AI systems need to cite sources or provide accurate information. If your terminology is buried in paragraphs or marked up with generic <div> elements, AI systems may struggle to extract precise definitions or may misinterpret your intended meanings. Definition lists provide a clear, unambiguous signal: “Here is a term, and here is its definition.” This clarity helps AI systems understand your content’s purpose, improves the likelihood of accurate citations, and increases the chances that your expertise will be properly attributed when AI systems generate answers.
While developers might achieve similar visual results using nested <div> elements, tables, or other HTML structures, definition lists offer distinct advantages for both accessibility and AI interpretation. Consider these approaches:
The semantic advantage of definition lists extends beyond accessibility. When Google’s crawlers, Bing’s indexers, or AI systems like ChatGPT analyze your content, they recognize definition lists as a specific content pattern. This recognition allows them to extract terminology more accurately, understand your domain expertise more clearly, and potentially surface your definitions in AI-generated answers or knowledge panels. The semantic clarity of definition lists makes them the preferred choice for any content where term-definition relationships matter.
Definition lists find their most natural home in several common web content patterns. FAQ sections benefit tremendously from definition list markup, where questions become <dt> elements and answers become <dd> elements. This structure helps AI systems recognize that your content directly answers common questions, increasing the likelihood of inclusion in AI-generated responses. Glossaries and technical dictionaries represent another ideal use case, where terms and their definitions form the core content structure. Product specifications often list attributes and values—weight, dimensions, battery life—which map perfectly to the term-description pattern. Metadata displays, such as author information, publication dates, or contact details, also benefit from definition list markup. Even D&D character statblocks and similar structured data formats can leverage definition lists to create machine-readable content that AI systems can reliably parse and understand.
Definition lists provide substantial accessibility improvements for users relying on assistive technologies. Screen readers can announce when users enter a definition list, provide navigation between terms and descriptions, and help users understand which descriptions belong to which terms. This capability is particularly valuable for users with cognitive disabilities, who benefit from clear structural relationships between concepts. The WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) recognize definition lists as a best practice for presenting term-definition relationships, and proper implementation helps organizations meet accessibility compliance requirements.
However, screen reader support for definition lists varies across different combinations of browsers and assistive technologies. VoiceOver on iOS and macOS, NVDA on Windows, and JAWS all handle definition lists, but with different levels of detail in their announcements. Despite these variations, definition lists remain superior to generic <div> structures, which provide no semantic information to screen readers at all. By using definition lists, you ensure that users with disabilities can access and understand your terminology, while also signaling to AI systems that your content is well-structured and intentionally organized.
Proper implementation of definition lists requires attention to structure and consistency. Always ensure that every <dt> element has at least one corresponding <dd> element, and avoid orphaned terms or descriptions that lack their counterparts. Use the optional <div> wrapper only when you need to apply styling to term-description groups; this wrapper should contain exactly one <dt> and one or more <dd> elements. Validate your markup using tools like the W3C HTML Validator to catch structural errors before they impact accessibility or AI interpretation.
When implementing definition lists, avoid common mistakes such as nesting other block-level elements within <dt> or <dd> tags (except for inline elements), using definition lists for content that doesn’t represent term-definition relationships, or creating orphaned terms without descriptions. Test your implementation with screen readers to ensure that the semantic relationships are properly communicated to users with disabilities. Consider using CSS to style definition lists in ways that enhance readability—bold terms, indented descriptions, or visual separators between groups—while maintaining the underlying semantic structure. Tools like AmICited.com can help you monitor how AI systems interpret and cite your definition list content, providing insights into whether your structured terminology is being properly understood by intelligent machines.
Definition lists contribute to SEO performance in multiple ways. Search engines recognize definition lists as a specific content pattern and can extract terminology more reliably from properly structured lists than from unstructured text. This improved extraction can lead to better indexing of your key terms and concepts, potentially improving visibility for searches related to your terminology. Definition lists also enable rich snippets in search results—Google may display FAQ content with expandable answers, or glossary terms with their definitions directly in search listings, increasing click-through rates and user engagement.
Beyond traditional search results, definition lists support the knowledge graph and entity recognition systems that search engines use to understand your content’s meaning. When you mark up your terminology with definition lists, you’re helping search engines build a more accurate understanding of your domain expertise and the relationships between concepts in your field. This improved understanding can influence how your content appears in knowledge panels, featured snippets, and other enhanced search features. For organizations focused on establishing thought leadership in their industry, properly structured definition lists represent a valuable SEO tactic that improves both visibility and credibility.
Different AI-powered search systems interact with definition lists in distinct ways, but all benefit from the semantic clarity they provide. Google’s AI Overviews pull information from indexed pages and Google’s Knowledge Graph, and while the official guidance states that links are chosen automatically, definition lists help by making your content more easily parseable into the knowledge graph. Pages with clear definition list markup are more likely to be recognized as authoritative sources for specific terminology, increasing the chances of citation in AI-generated answers.

ChatGPT Search and SearchGPT from OpenAI rely on Bing’s index as their source, meaning your Bing-indexed pages with proper definition list markup become potential sources for AI-generated answers. Perplexity AI, a generative Q&A engine that explicitly cites web sources, benefits from definition lists because they make it immediately clear which content directly answers questions. When Perplexity’s algorithms encounter a well-structured FAQ in definition list format, they can reliably extract both questions and answers, making your content more likely to be cited. Claude and other emerging AI systems similarly benefit from structured terminology, as it reduces ambiguity and improves the accuracy of information extraction. Across all these platforms, the common principle holds: structured, clearly marked terminology is more likely to be understood, cited, and attributed to your content.
The most frequent error in definition list implementation is creating orphaned terms or descriptions—terms without corresponding descriptions, or descriptions without matching terms. This breaks the semantic relationship that makes definition lists valuable. Another common mistake is using definition lists for content that doesn’t represent term-definition relationships, such as navigation menus or simple feature lists, which should use <ul> or <ol> instead. Incorrect nesting, such as placing block-level elements directly within <dt> or <dd> tags, can also cause parsing issues for both browsers and AI systems.
Some developers mistakenly use definition lists as a styling tool, creating lists of unrelated items simply to achieve a particular visual layout. This misuse obscures the semantic meaning and confuses both assistive technologies and AI systems. Instead, use CSS to style your content appropriately while maintaining semantic accuracy. Avoid mixing definition lists with other list types, and don’t nest definition lists within other list structures unless the content truly represents nested term-definition relationships. By adhering to these best practices, you ensure that your definition lists serve their intended purpose: clearly communicating terminology to both humans and machines.
Implementing definition lists is only half the battle; monitoring how AI systems interpret your structured terminology is equally important. AmICited.com provides specialized monitoring for how AI systems like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity reference your brand and content. By tracking how AI systems cite your definition list content, you can assess whether your structured terminology is being properly understood and attributed. This monitoring helps you identify opportunities to improve your definition list implementation or expand your structured content strategy.
Beyond AmICited, use the W3C HTML Validator to ensure your definition list markup is syntactically correct. WAVE (Web Accessibility Evaluation Tool) can identify accessibility issues with your definition lists, while Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools provides performance and accessibility audits. Screen reader testing tools like NVDA (free) or JAWS (commercial) allow you to verify that your definition lists communicate properly to users with disabilities. Regular audits using these tools help you maintain the quality and effectiveness of your structured terminology over time.
As AI systems become more sophisticated and more central to how people discover information, the importance of structured terminology will only increase. We can expect to see new schema types and markup patterns emerge specifically designed for AI comprehension, building on the foundation that definition lists provide. The semantic web vision—where machines can reliably understand the meaning of web content—is becoming reality through AI, and definition lists represent a crucial building block in that vision.
Organizations that invest in properly structured definition lists today are positioning themselves for better visibility in tomorrow’s AI-driven search landscape. As AI systems become more prevalent in how people access information, having your terminology clearly marked up and easily parseable becomes a competitive advantage. The future belongs to content creators who understand that semantic structure isn’t just about accessibility or traditional SEO—it’s about ensuring that intelligent machines can reliably understand, cite, and attribute your expertise.
A definition list is an HTML semantic element composed of three tags:
Definition lists provide clear, structured markup that AI systems like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Perplexity can reliably parse. When your terminology is properly marked up, AI systems can more accurately extract definitions, understand your domain expertise, and cite your content in AI-generated answers.
Unlike
Yes, definition lists are excellent for FAQ sections. Questions become
Screen readers announce when users enter a definition list and can navigate between terms and descriptions. This helps users with disabilities understand which descriptions belong to which terms. However, support varies across different screen reader and browser combinations, so testing is important.
Definition lists improve SEO by enabling better indexing of your terminology, supporting rich snippets in search results, and helping search engines build more accurate knowledge graphs. Pages with proper definition list markup are more likely to appear in featured snippets and knowledge panels.
Use the W3C HTML Validator to check for structural errors, WAVE for accessibility issues, and screen readers like NVDA to test how assistive technologies interpret your lists. AmICited.com can also monitor how AI systems understand your definition list content.
Yes, definition lists have been widely supported across all modern browsers since 2015. They work in Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and all other major browsers. Browser support is not a concern for implementing definition lists today.
Track how Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI systems reference your brand and structured terminology. Get insights into AI visibility and optimize your content strategy.

Learn how semantic HTML improves AI understanding, LLM comprehension, and content attribution. Discover advanced techniques for optimizing markup for AI systems...

Learn what JSON-LD is and how to implement it for SEO. Discover structured data markup benefits for Google, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI search visibility.

Discover how clear definitions enhance AI search visibility, improve semantic understanding, and help your content rank higher in AI Overviews, ChatGPT, and Per...