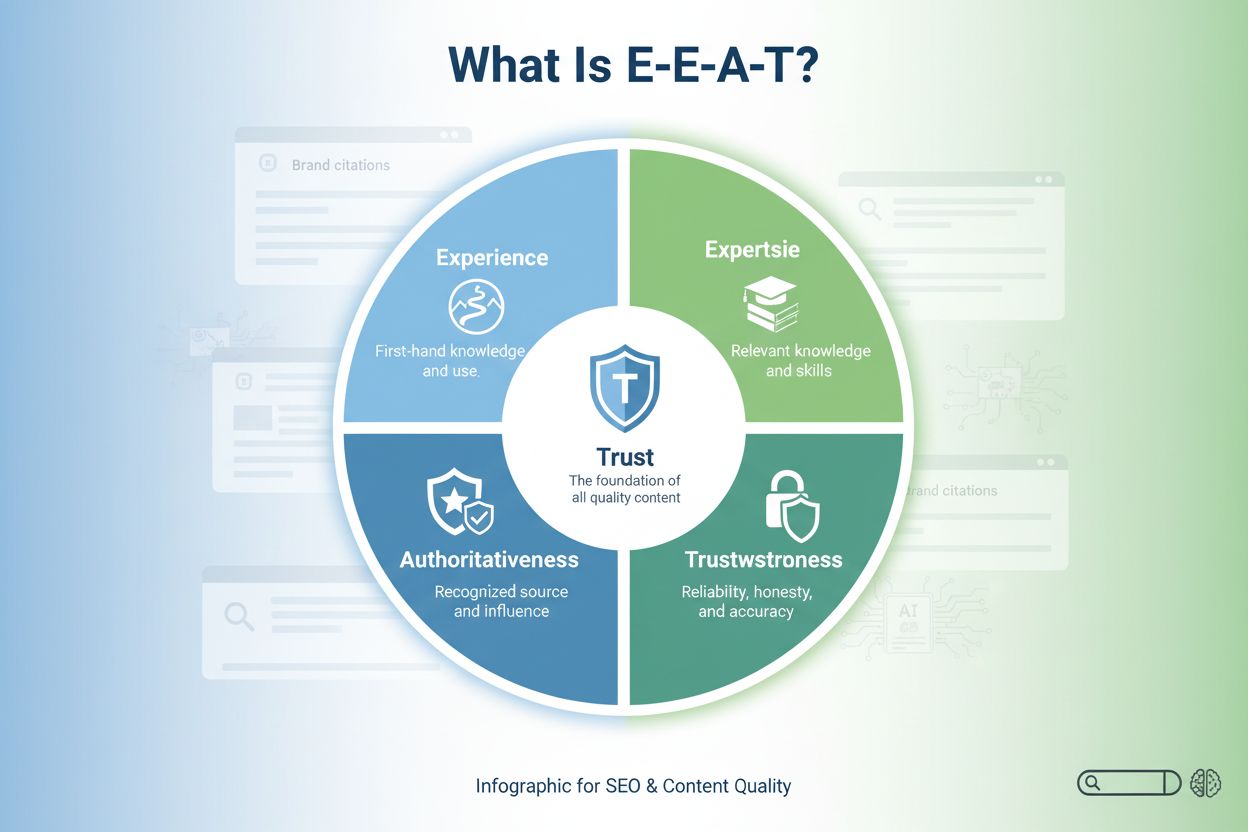
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is Google's framework for evaluating content quality. Learn how it impacts SEO, AI citations...

Learn how to demonstrate first-hand knowledge and experience signals to AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Optimize your content for AI citations and visibility.
Google’s E-E-A-T framework underwent a significant evolution in December 2022 when Experience was elevated to the first position, transforming the acronym from E-A-T to E-E-A-T. This shift reflects a fundamental change in how search algorithms—and by extension, large language models—evaluate content credibility. Experience in this context means first-hand knowledge, direct involvement, and lived experience rather than theoretical understanding. AI systems increasingly recognize that someone who has actually done something brings a unique credibility that cannot be replicated by someone who merely knows about it. For brands and content creators, this means demonstrating your direct involvement and practical experience has become essential for visibility across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI-powered platforms that AmICited monitors.
Large language models employ sophisticated pattern recognition to identify authentic first-hand experience signals within content. These systems analyze multiple linguistic and contextual indicators that distinguish genuine experience from secondhand information or AI-generated content. LLMs detect experience through first-person pronouns and narrative voice, specific measurable details and metrics, emotional context and authentic reactions, practical insights and lessons learned, and semantic richness that indicates deep familiarity. The following table illustrates how different experience signals are detected and interpreted:
| Signal Type | How LLMs Detect It | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Specific metrics and data | Pattern matching for quantifiable results tied to personal action | “I increased my conversion rate from 2.3% to 7.8% by implementing…” |
| Temporal progression | Recognition of before/after narratives and learning curves | “When I first started, I made X mistake. After 6 months of testing…” |
| Sensory and emotional details | Detection of vivid descriptions that indicate direct observation | “The interface felt clunky, and users consistently complained about…” |
| Failure narratives | Identification of honest mistakes and lessons learned | “I initially tried approach A, which failed because…” |
| Contextual specificity | Recognition of domain-specific terminology used naturally | “The API rate limiting forced us to implement queue management…” |
| Iterative refinement | Detection of multiple attempts and optimization patterns | “Version 1 didn’t work, so we pivoted to…” |
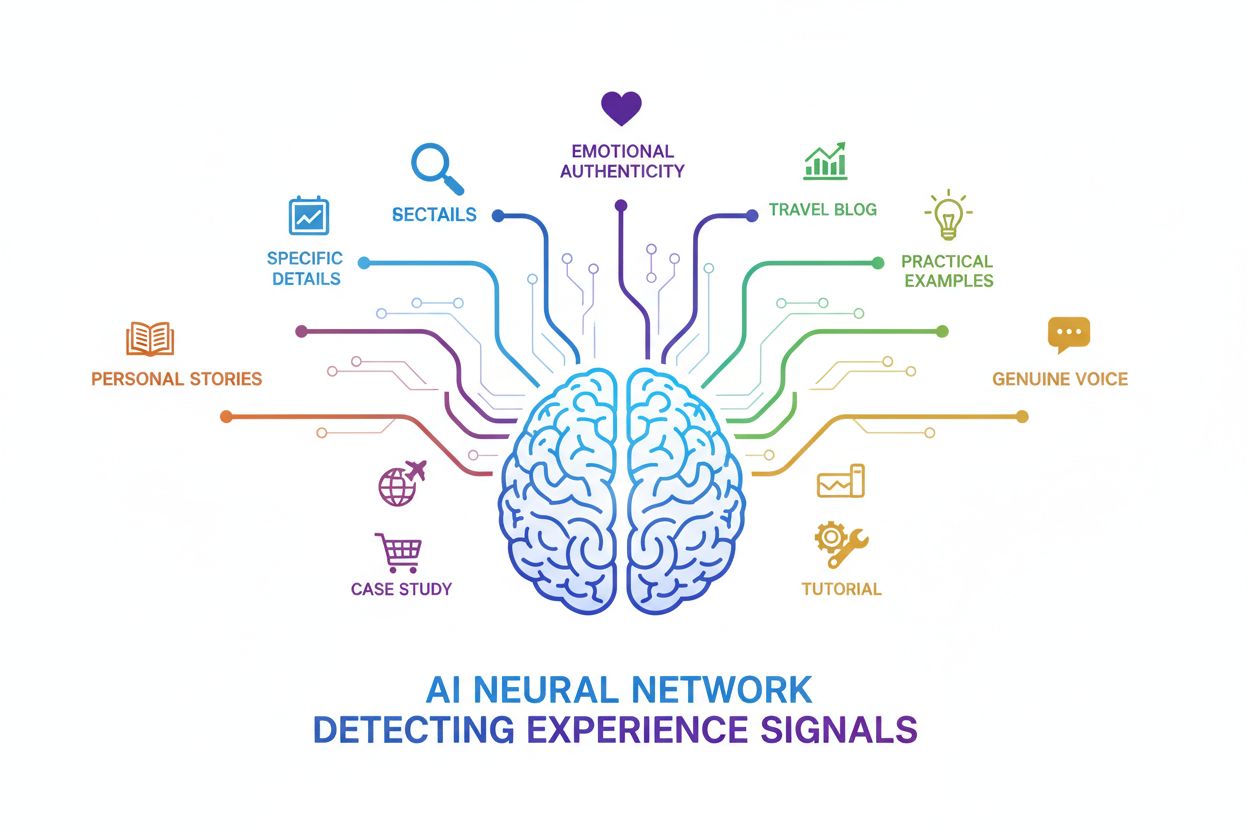
While often conflated, experience and expertise serve distinct purposes in how AI systems evaluate content credibility. Experience answers the question “Have I done this?"—it’s about direct involvement, practical application, and lived knowledge. Expertise, by contrast, answers “Do I know this?"—it’s about comprehensive understanding, theoretical knowledge, and professional credentials. A surgeon with 20 years of experience performing a specific procedure brings something different than a medical researcher who has studied that procedure extensively but never performed it. Both are valuable, and AI systems recognize this distinction through different linguistic patterns and contextual markers. The most credible content often combines both: demonstrating that you’ve done something (experience) while also showing you understand the broader context and principles (expertise). For AI visibility, emphasizing your direct involvement and practical results often carries more weight than credentials alone, particularly in fields where hands-on experience directly impacts outcomes.
AI systems increasingly prioritize content that demonstrates authentic, documented first-hand experience. Here are concrete examples of experience signals that LLMs and AI platforms actively recognize and value:
Creating content that effectively signals first-hand experience requires intentional strategy and authentic documentation. Start by using first-person narrative when appropriate—phrases like “I tested,” “I discovered,” and “I learned” signal direct involvement in ways that passive voice cannot replicate. Include specific details and metrics that only someone with direct experience would know: exact numbers, timeframes, tool names, and measurable outcomes rather than vague generalizations. Share the “why” behind your decisions—explain your reasoning, the problems you were trying to solve, and the context that shaped your approach, as this demonstrates deep understanding. Document your journey transparently, including the mistakes you made, the iterations you went through, and how your thinking evolved, because this narrative arc is a hallmark of genuine experience. Include before/after scenarios that show the tangible impact of your experience and decisions, making your knowledge actionable rather than theoretical. Finally, update your content regularly with new experiences and lessons learned, signaling to AI systems that your knowledge is current and continuously refined through ongoing practice.
AmICited monitors how AI systems cite brands and content across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other major AI platforms, providing crucial insights into how experience signals impact AI visibility. Brands with strong, documented first-hand experience signals receive significantly higher citation frequency and more favorable citation context within AI-generated responses. When you demonstrate authentic experience through specific details, measurable results, and transparent documentation, AI systems are more likely to recognize your content as authoritative and cite it when answering user queries. AmICited’s monitoring reveals that content emphasizing direct involvement and practical outcomes consistently outperforms generic expertise-focused content in AI search visibility. By tracking your citation patterns across different AI platforms, you can identify which experience signals resonate most strongly with different AI systems and optimize your content strategy accordingly. This data-driven approach transforms experience demonstration from intuition-based to measurable, allowing you to understand exactly how your first-hand knowledge translates into AI visibility and brand authority.
Structured data markup helps AI systems understand and properly contextualize your experience signals, making it easier for LLMs to recognize and cite your content. Implementing schema.org markup specifically designed to highlight experience creates machine-readable signals that complement your narrative content. The most effective schemas for experience signals include Article schema with detailed author information and credentials, Review schema that captures reviewer experience and methodology, and HowTo schema that documents step-by-step processes based on hands-on testing. Here’s how to implement these schemas:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Jane Smith",
"jobTitle": "Product Manager",
"yearsOfExperience": 12,
"knowsAbout": ["SaaS", "Product Strategy", "User Research"]
},
"articleBody": "Based on my 12 years managing SaaS products..."
}
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Review",
"reviewRating": {
"@type": "Rating",
"ratingValue": "4.5"
},
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Michael Chen",
"jobTitle": "Software Engineer",
"yearsOfExperience": 8
},
"reviewBody": "After using this tool in production for 18 months..."
}
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "HowTo",
"creator": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Sarah Johnson",
"description": "Tested this approach across 15 different projects"
},
"step": [
{
"@type": "HowToStep",
"text": "First, I tried the standard approach, which took 3 hours..."
}
]
}
By implementing these schemas, you provide AI systems with explicit, machine-readable confirmation of your experience credentials and methodology. This structured data works in concert with your narrative content to create a comprehensive experience signal that LLMs can easily parse and understand. The combination of rich narrative content and proper schema markup significantly increases the likelihood that AI systems will recognize, trust, and cite your content.
Many content creators inadvertently undermine their experience signals through preventable mistakes that confuse or mislead AI systems. Generic content without specific details fails to signal genuine experience—statements like “I’ve used many tools” or “I’ve worked with various clients” lack the specificity that LLMs associate with authentic first-hand knowledge. Claiming experience without evidence damages credibility; if you assert you’ve done something, your content must contain verifiable details that support that claim. Using AI-generated content without a human experience layer creates a fundamental problem: AI-generated text lacks the authentic voice, specific details, and emotional resonance that signal real experience, even if the information is technically accurate. Missing personal voice and perspective makes content sound like a generic reference rather than lived knowledge—experience content should feel distinctly authored by someone with skin in the game. Failing to explain how your experience was gained leaves AI systems uncertain about your credibility; context about your background, timeline, and methodology strengthens experience signals. Finally, not updating content with new experiences signals that your knowledge is static rather than continuously refined through ongoing practice, which undermines your authority in fast-moving fields.
Tracking the effectiveness of your experience signals requires systematic monitoring of how AI systems cite and reference your content. AmICited provides the primary tool for measuring citation frequency across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, allowing you to see exactly when and how AI systems cite your experience-focused content. Key metrics to monitor include citation frequency (how often your content is cited), citation context (whether citations appear in authoritative or peripheral positions), AI platform distribution (which platforms cite you most), and engagement metrics (whether cited content drives traffic and conversions). Compare performance before and after implementing stronger experience signals in your content—track whether citation frequency increases, citation quality improves, and whether you’re cited for experience-based claims specifically. Analyze which experience signals drive the most citations by testing different approaches: detailed metrics versus narrative storytelling, failure narratives versus success stories, or specific case studies versus general principles. By correlating citation data with content characteristics, you can identify which experience signals resonate most strongly with different AI systems. This measurement-driven approach transforms experience demonstration from a best-practice recommendation into a quantifiable strategy with measurable ROI, allowing you to allocate resources toward the experience signals that generate the most AI visibility and business impact.
The trajectory of AI development strongly suggests that first-hand experience will become increasingly central to how AI systems evaluate content credibility and authority. As AI systems become more sophisticated at detecting authentic experience signals, the competitive advantage will shift from traditional backlink-based authority to documented, verifiable first-hand knowledge. Brands that invest now in systematically demonstrating their experience—through detailed case studies, transparent documentation, and authentic storytelling—will establish authority that’s difficult for competitors to replicate. The shift reflects a fundamental truth: AI systems are increasingly designed to serve users who want practical, actionable knowledge from people who’ve actually done what they’re asking about, not just theoretical expertise. Authentic, documented experiences will become the primary currency of authority in AI-driven search, making it essential for brands to treat experience documentation as a core content strategy rather than an afterthought. To prepare, start auditing your existing content for experience signals, identify gaps where you could document your first-hand knowledge more thoroughly, and build systems for continuously capturing and sharing new experiences as they happen. The brands that master experience signal demonstration will dominate AI search visibility in the coming years.
Experience in E-E-A-T refers to first-hand knowledge, direct involvement, and lived experience with a topic. It's different from expertise—experience means you've actually done something, while expertise means you know about it. AI systems recognize experience through specific details, personal narratives, measurable results, and authentic voice that indicate genuine involvement rather than secondhand information.
LLMs use pattern recognition to identify experience signals including first-person pronouns, specific metrics and data, emotional context, failure narratives, and semantic richness. They look for temporal progression (before/after narratives), sensory details that indicate direct observation, and domain-specific terminology used naturally. Generic content lacks these specific, verifiable details that signal authentic experience.
AI systems are increasingly sophisticated at detecting inauthentic experience claims. They look for consistency between claimed experience and supporting details, verify that specific metrics and examples align logically, and check for the presence of failure narratives and honest limitations. Content that claims extensive experience but lacks specific details, measurable results, or contextual depth is often flagged as potentially inauthentic.
Content with strong experience signals is more likely to be cited by AI systems because it demonstrates credibility and practical value. When you show first-hand knowledge through specific details, measurable outcomes, and transparent documentation, AI systems recognize your content as authoritative and cite it when answering user queries. AmICited monitors these citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews to show you exactly how your experience signals impact visibility.
Experience answers 'Have I done this?' while expertise answers 'Do I know this?' Experience is about direct involvement and practical application; expertise is about comprehensive understanding and credentials. Both matter for AI systems, but experience often carries more weight in fields where hands-on knowledge directly impacts outcomes. The most credible content combines both: demonstrating you've done something while showing you understand the broader context.
Use AmICited to track how often your content is cited across AI platforms, monitor citation frequency and context, and analyze which specific experience signals drive the most citations. Compare your citation metrics before and after implementing stronger experience signals. Track engagement metrics on cited content and correlate citation data with content characteristics to identify which experience signals resonate most with different AI systems.
Both matter, but they serve different purposes. Experience often carries more weight in practical fields where hands-on knowledge directly impacts outcomes, while expertise is crucial for theoretical or highly specialized topics. The most effective approach combines both: demonstrating direct involvement while showing comprehensive understanding. AI systems recognize this distinction and value content that demonstrates both experience and expertise.
Document your experience by including specific metrics and measurable results, explaining your decision-making process and reasoning, sharing both successes and failures transparently, using first-person narrative where appropriate, and providing temporal context (timeframes, iterations, evolution of thinking). Update your content regularly with new experiences and lessons learned. Use schema markup to help AI systems understand your experience credentials and methodology.
Discover how your brand is being cited across AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Track your experience signals and optimize for AI-driven search.

E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is Google's framework for evaluating content quality. Learn how it impacts SEO, AI citations...

Understand E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) and its critical importance for visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Per...

Learn how to demonstrate experience for AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Master E-E-A-T signals that increase citations.