Why Free ChatGPT Users Show as Direct Traffic
Discover why ChatGPT traffic appears as direct traffic in GA4, how to identify hidden AI traffic, and proven methods to track and optimize for AI-driven visitor...
Discover why AI chatbots like ChatGPT and Perplexity are sending traffic that appears as ‘direct’ in your analytics. Learn how to detect and measure unattributed AI traffic with practical attribution strategies.
Your analytics dashboard shows a mysterious surge in direct traffic, but you didn’t launch any campaigns. The culprit? AI applications like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews are sending users to your site without passing referrer information, making them appear as direct traffic in your analytics. With ChatGPT alone boasting over 46 million downloads, this attribution gap represents a massive blind spot in how you understand your traffic sources. The problem isn’t just cosmetic—it’s fundamentally distorting your understanding of which channels drive real business value. When AI-generated traffic gets lumped into “direct,” you lose visibility into one of the fastest-growing traffic sources. This misattribution cascades through your entire marketing strategy, from budget allocation to channel optimization.

To understand why AI traffic disappears from your attribution model, you need to understand how referrer data works. When you click a link in a web browser, the HTTP request includes a referrer header that tells the destination website where you came from. This is the foundation of traditional attribution—Google Analytics reads this header and credits the appropriate channel. However, mobile applications operate differently. When an app opens a link, it often uses a webview or native browser that doesn’t automatically pass referrer information to the destination server. This is a deliberate design choice for privacy and security, but it creates an attribution nightmare. ChatGPT’s mobile app, Perplexity’s app, and Google’s mobile search all exhibit this behavior. The contrast is stark: click a ChatGPT link in a web browser and you might see referral attribution; click the same link in the ChatGPT mobile app and it appears as direct traffic.
The attribution gap exists because different AI platforms handle referrer data inconsistently, and most mobile implementations strip this information entirely. Understanding which sources pass referrer data and which don’t is critical for building an accurate picture of your traffic. Here’s how the major AI traffic sources behave:
| Traffic Source | Referrer Passed | Attribution Result | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search (web) | Yes | organic/google | Organic traffic |
| ChatGPT Web Browser | Sometimes | referral/chatgpt | Referral traffic |
| ChatGPT Mobile App | No | direct/(none) | Direct traffic |
| Perplexity App | No | direct/(none) | Direct traffic |
| Google AI Overviews | No | direct/(none) | Direct traffic |
This table reveals the core problem: the most popular AI applications—particularly their mobile versions—don’t pass referrer information. When a user taps a link in the ChatGPT mobile app and lands on your site, your analytics system has no way to know the traffic came from ChatGPT. The referrer header is empty, so Google Analytics defaults to classifying it as direct traffic. This isn’t a bug in your analytics setup; it’s a fundamental limitation of how mobile apps communicate with web servers. The result is that your direct traffic bucket becomes a catch-all for all unattributed sources, making it impossible to distinguish between users who typed your URL directly and users who came from AI applications. As AI traffic grows, this misattribution becomes increasingly problematic.
The consequences of AI traffic misattribution extend far beyond vanity metrics. Your direct traffic numbers are artificially inflated, making it appear that more users are coming directly to your site than actually are. Simultaneously, you’re systematically underestimating the impact of AI as a traffic source, which means you’re likely underinvesting in AI optimization and visibility. This creates a vicious cycle: because you can’t see AI traffic’s true value, you don’t optimize for it, which means you capture less of it. Budget allocation decisions become distorted—you might cut spending on channels that appear underperforming while over-investing in channels that seem to drive direct traffic. Conversion rate analysis becomes unreliable because you’re mixing high-intent AI-referred traffic with true direct traffic, which may have different conversion characteristics. Perhaps most critically, you’re flying blind when it comes to understanding which AI platforms send the highest-quality traffic to your site.
Many marketers attempt to solve the AI attribution problem using existing tools, but these approaches have significant limitations. UTM parameters require users to click links that you’ve manually tagged, but AI applications generate their own links without your UTM codes, making this approach ineffective for AI traffic. Server-side tagging and enhanced ecommerce tracking can capture some additional signals, but they can’t retroactively identify traffic that’s already been classified as direct. Google Analytics 4’s modeled data attempts to fill attribution gaps using machine learning, but it’s designed for first-party data gaps, not for systematically missing entire traffic sources. Privacy-focused browsers and ad blockers further complicate the picture by stripping additional tracking signals. The fundamental issue is that all these solutions assume you have some data to work with—but with AI traffic, you often have nothing but a direct traffic classification and a user session.
Since AI traffic masquerades as direct traffic, you need to develop detective skills to identify it. The key is looking for patterns that distinguish AI-referred traffic from genuine direct traffic. Here are six signals that suggest hidden AI traffic in your direct traffic bucket:
By analyzing these signals together, you can build a profile of what AI traffic looks like in your data. Once you understand these patterns, you can estimate how much of your direct traffic is actually AI-referred.
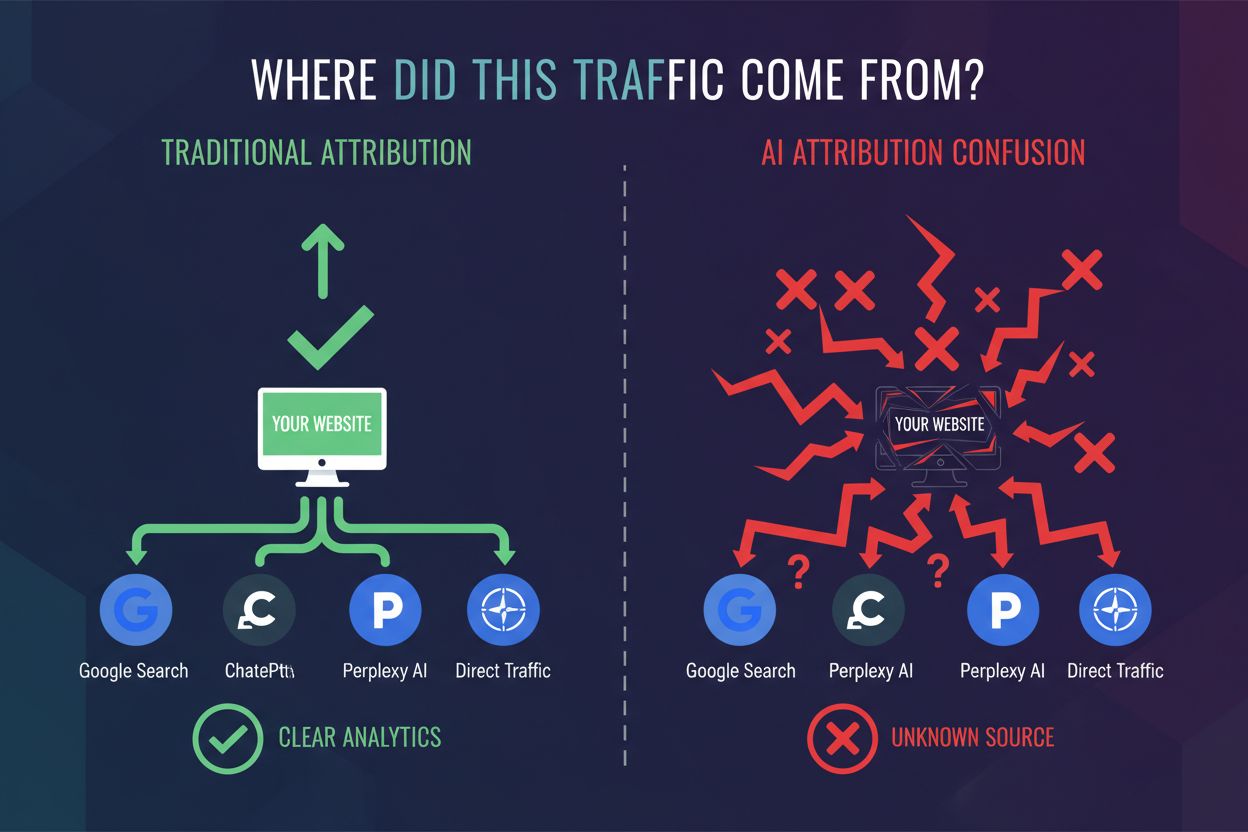
Rather than relying on a single attribution signal, the most effective approach is multi-signal attribution that combines multiple independent indicators of AI traffic. This framework draws from marketing measurement best practices and applies them to the AI attribution problem. The first principle is inclusion—cast a wide net and look for all possible signals that might indicate AI traffic, from referrer patterns to user behavior to device characteristics. The second is framing—understand the context of each signal and what it tells you about traffic quality and source. The third is freshness—continuously update your understanding as AI platforms evolve and new sources emerge. The fourth is corroboration—look for multiple signals pointing to the same conclusion rather than relying on any single indicator. The fifth is demand lift—measure whether your visibility in AI applications correlates with traffic increases. The sixth is sales evidence—ultimately, track whether AI-referred traffic converts and contributes to business outcomes. By combining these six elements, you can build a robust understanding of your AI traffic even without perfect referrer data.
Start by auditing your current direct traffic to establish a baseline. Segment your direct traffic by device type, operating system, and landing page to identify patterns that might indicate AI traffic. Set up custom events in Google Analytics 4 to track specific behaviors associated with AI users—for example, users who land on comparison pages or informational content without a referrer. Create a separate view or data stream dedicated to analyzing direct traffic patterns, allowing you to dig deeper without contaminating your main analytics setup. Implement server-side tracking to capture additional context about direct traffic sessions, such as user agent strings that might reveal mobile app traffic. Most importantly, establish a regular review cadence—weekly or monthly—to monitor direct traffic trends and identify anomalies. Document your findings and share them with your marketing team so everyone understands that direct traffic includes a significant AI component. This foundation will allow you to make more informed decisions about AI visibility and optimization.
The AI attribution landscape is evolving rapidly, and solutions are emerging. Google has announced plans to add referrer information to AI Mode traffic, which would solve the attribution problem for Google’s own AI Overviews. Other AI platforms may follow suit as the business importance of attribution becomes clear. Industry standards bodies are beginning to develop guidelines for how AI applications should handle referrer data, balancing privacy concerns with the legitimate need for attribution. We’re also seeing the emergence of specialized tools designed specifically to measure AI traffic and its impact on business outcomes. As AI becomes a more significant traffic source, the pressure on platforms to provide attribution data will only increase. The companies that solve this problem first will gain a competitive advantage in understanding their traffic sources. In the meantime, the multi-signal attribution approach outlined in this post represents the most practical path forward.
AmICited is purpose-built to solve the AI attribution mystery by continuously monitoring your traffic for signs of AI-referred visitors and quantifying their impact on your business. Rather than waiting for AI platforms to pass referrer data, AmICited uses the multi-signal attribution framework described in this post to identify AI traffic in real-time. The platform tracks which AI applications mention your brand, correlates those mentions with traffic spikes, and attributes conversions to AI sources with confidence scoring. AmICited integrates directly with your existing analytics stack, layering AI attribution insights on top of your Google Analytics data without requiring any changes to your tracking implementation. By using AmICited, you gain visibility into the true value of AI traffic, allowing you to optimize your content for AI applications and make smarter budget allocation decisions. The platform transforms the direct traffic mystery into actionable intelligence, ensuring that you never again underestimate the impact of AI on your business.
AI mobile apps like ChatGPT and Perplexity don't pass referrer information when users click links. Without referrer data, Google Analytics defaults to classifying the traffic as 'direct' instead of from the AI source. This is a technical limitation of how mobile applications communicate with web servers, not a bug in your analytics setup.
The percentage varies by industry and audience, but for many websites, 15-40% of direct traffic may actually be AI-referred. You can estimate this by analyzing patterns in your direct traffic: mobile-only spikes, specific landing pages, and conversion rate differences compared to true direct traffic.
UTM parameters are ineffective for AI traffic because AI applications generate their own links without your custom UTM codes. AI platforms don't use your tagged links; they create their own citations. You need a different approach, such as multi-signal attribution that combines device patterns, landing page analysis, and behavioral signals.
Google has already announced plans to add referrer information to AI Mode traffic, which would solve attribution for Google's own AI Overviews. However, other AI platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity may take longer to implement similar changes. In the meantime, you need tools designed specifically to measure AI traffic.
True direct traffic comes from users who typed your URL directly or used a bookmark. AI-referred traffic comes from users who clicked a link in an AI application. AI traffic typically has higher intent, better conversion rates, and different landing page patterns than true direct traffic.
Look for patterns in your direct traffic: unexplained mobile spikes, specific landing pages (comparison or informational content), higher conversion rates, and correlation with branded search volume. Segment by device type and OS to identify AI app signatures. These signals together indicate hidden AI traffic.
Multi-signal attribution combines multiple independent indicators to identify AI traffic: inclusion (is your brand cited?), framing (how are you described?), freshness (crawler revisit rates), corroboration (third-party mentions), demand lift (traffic spikes), and sales evidence (customer feedback). Together, these signals reveal AI traffic's true impact.
No, AmICited complements Google Analytics by adding a specialized layer of AI traffic attribution. It integrates with your existing analytics stack and provides insights specifically designed to measure AI-driven traffic and its business impact, filling the gap that traditional analytics tools leave.
AmICited monitors how AI applications reference your brand and attributes traffic accurately. Get real-time visibility into AI-driven visitors and their impact on your business.

Discover why ChatGPT traffic appears as direct traffic in GA4, how to identify hidden AI traffic, and proven methods to track and optimize for AI-driven visitor...
Master regex patterns to track AI traffic from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms in Google Analytics 4. Complete technical guide with step-by-step imp...
Learn how to track AI referrals from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Step-by-step technical implementation guide for GA4 and specialized monitorin...