Entity Optimization for AI: Making Your Brand Recognizable to LLMs
Learn how entity optimization helps your brand become recognizable to LLMs. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity strategies for AI vis...

Learn how to build entity visibility in AI search. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity SEO strategies to increase brand presence in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Entities are the fundamental building blocks of how AI systems understand and interpret information. Rather than simply matching keywords on a page, modern AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews recognize entities—distinct “things” such as brands, products, people, concepts, and their relationships—and use these to generate contextually relevant answers. When you search “best project management tool for remote teams,” the AI doesn’t just look for pages containing those exact words; it identifies entities like “Asana,” “ClickUp,” and “Notion,” understands their attributes (features, pricing, integrations), and retrieves the ones most relevant to your query. This shift from keyword-matching to entity-based understanding means your visibility in AI search depends less on optimizing specific phrases and more on how clearly AI systems can identify and categorize your brand as a distinct, authoritative entity within their knowledge frameworks.
Traditional SEO focused on keyword density and page authority, but AI systems use dense retrieval—a method that prioritizes semantic meaning and contextual relationships over exact word matches. When an AI system processes a query, it doesn’t search for keywords in isolation; instead, it expands the query into multiple related searches simultaneously, exploring different semantic angles and entity relationships. For example, a question like “best email marketing for Shopify stores” might internally decompose into searches about “Shopify integrations,” “abandoned cart recovery,” “email automation,” and “ecommerce marketing tools”—allowing your brand to surface through any of these entity-based pathways, even if you never optimized for the original query. This means a Reddit comment stating “We switched from Klaviyo to Omnisend because the Shopify integration actually works” carries more weight than a keyword-stuffed landing page, because it establishes authentic entity relationships (Klaviyo → Omnisend → Shopify integration) with real context.
| Aspect | Traditional SEO | Entity SEO |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Keyword density and matching | Semantic meaning and entity relationships |
| Ranking Signal | Backlinks and page authority | Entity clarity and authentic mentions |
| Content Strategy | Optimize for specific keywords | Build entity presence across platforms |
| Visibility | Depends on ranking position | Depends on entity recognition in AI systems |
| Measurement | Rankings and click-through rates | Entity citations and AI mentions |
AI systems recognize entities through multiple interconnected mechanisms that work at massive scale. Google’s Knowledge Graph and similar entity databases maintained by other AI platforms contain billions of structured records mapping entities (companies, products, people, concepts) to their attributes and relationships—when Nike releases the Pegasus 41 running shoe, it doesn’t just become a product page; it becomes an entity in Google’s Shopping Graph, automatically connected to “running shoes,” “Nike,” “marathon training,” and hundreds of other semantic nodes. Beyond structured databases, human conversation serves as training data: when an Outdoor Gear Lab review compares Patagonia’s Torrentshell 3L to Arc’teryx’s Beta SL, or when a podcast guest mentions switching from Asana to Notion for task management, these authentic discussions get encoded into AI training data as entity relationships and competitive signals. AI systems also extract entities from multimodal sources—they transcribe audio from podcasts and YouTube videos, process visual content, and convert all of this into structured entity data; a 10-minute YouTube review of project management tools becomes structured data comparing ClickUp, Notion, and Asana with feature comparisons and use case mappings. This multi-source entity recognition means your brand’s visibility depends not just on your website, but on how consistently and authentically it appears across Reddit threads, podcast transcripts, YouTube reviews, and industry discussions.
For two decades, SEO professionals obsessed over backlinks as the currency of authority, but AI systems now recognize that authentic mentions without links still count. When Patagonia appears in climate change articles without a hyperlink, when Notion gets name-dropped in productivity discussions on Reddit, or when your brand is mentioned in a podcast transcript—these all strengthen your entity in AI’s understanding. Reddit and Quora have become unexpectedly powerful for entity recognition because they capture what websites struggle to do: real people sharing real decisions with real context, and Google has explicitly stated they’re prioritizing “authentic discussion forums” in their ranking systems. A single comment explaining why someone chose Obsidian over Notion for knowledge management carries more semantic weight than optimized comparison content, because it establishes genuine entity relationships grounded in authentic user experience. YouTube reviews and podcast discussions function similarly—when a creator demonstrates multiple tools side-by-side or discusses switching between platforms, they’re creating dense entity relationships that AI systems extract and use to understand competitive positioning. The key insight is that you can’t manufacture authentic mentions the way you could game PageRank; the system rewards genuine presence in genuine conversations, making your PR strategy, community participation, and customer advocacy as important to entity visibility as your technical SEO.
Schema markup is your machine-readable handshake with AI systems and Knowledge Graphs, translating your content into structured data that search engines and AI models can reliably interpret. Using formats like JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), you explicitly define what entities your page represents, their attributes, and their relationships to other entities. Here’s a practical example of how to mark up an article about email marketing platforms:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"@id": "https://example.com/guide/best-email-marketing-platforms#article",
"headline": "Best Email Marketing Platforms for Ecommerce",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "Thing",
"@id": "https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q123456",
"name": "Email Marketing Platform"
},
"about": [
{
"@type": "SoftwareApplication",
"name": "Omnisend",
"sameAs": "https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q789012"
},
{
"@type": "SoftwareApplication",
"name": "Klaviyo",
"sameAs": "https://www.wikidata.org/entity/Q345678"
}
]
}
The mainEntityOfPage attribute tells AI systems what primary entity your page is about, while sameAs links your entities to authoritative external sources like Wikidata or Wikipedia, proving legitimacy and helping AI systems disambiguate (distinguishing “Apple” the company from “apple” the fruit). After implementing schema markup, validate it using Google’s Rich Results Test or the Knowledge Graph API to ensure your structured data is correctly recognized and that entity relationships remain intact. Proper schema implementation acts like citations for machines, strengthening how AI systems understand and recall your brand as an authoritative source.
Before optimizing for entity visibility, you need a baseline understanding of how AI systems currently categorize your brand relative to competitors. Start by verifying schema markup across your key pages using the Schema Markup Validator—check whether your homepage, product pages, and service pages include Organization, Product, or Service schema with complete attributes. Next, assess your entity presence in major knowledge sources like Wikidata and Crunchbase; search for your brand and note what information is present, what’s missing, and how it compares to competitors. For example, if your competitor has detailed Wikidata entries with multiple industry classifications, partnerships, and product offerings while your entry is minimal, that’s a clear opportunity to expand your entity definition. Create or update your Wikidata profile with comprehensive information including your industry, founding date, key products, social media profiles, and notable relationships. Finally, run your top-traffic pages through Google’s Natural Language API to see which entities the system currently recognizes in your content—this reveals whether your entity presence is clear or scattered across multiple interpretations. This foundation-building phase transforms your entity presence from accidental to intentional, ensuring AI systems have accurate, complete information about who you are and what you offer.
Understanding when and how AI systems group your brand with competitors reveals strategic opportunities for entity positioning. Test query decomposition by running variations of your target queries through ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews while logged out and using a VPN to minimize personalization bias—track which brands consistently appear together and in what order. For instance, if you run 15 variations of “best email marketing for ecommerce” queries, you might find that Klaviyo appears first in 5 of 5 ecommerce-specific queries while your brand ranks second or third, suggesting you’re part of the conversation but not at the forefront of that specific entity cluster. Create a co-citation testing tracker documenting which competitors appear alongside you in different query contexts—you might discover that you dominate general email marketing discussions but disappear from deliverability-focused queries, revealing that your entity relationships are contextually fragmented. This analysis shows that entity relationships are radically contextual: being the leader in ecommerce email doesn’t guarantee presence in deliverability conversations, so your entity optimization strategy must account for multiple competitive clusters rather than assuming one-size-fits-all positioning. By mapping these relationships, you identify which entity associations are strong, which are weak, and where you have opportunities to build new semantic connections that expand your visibility across different AI search contexts.
AI systems extract and understand information more effectively when it’s presented in entity-rich passages with clear contextual density. Compare these two descriptions: “Our automation features help ecommerce businesses increase revenue through targeted campaigns” versus “Omnisend’s SMS automation integrates with Shopify’s abandoned cart data to trigger personalized recovery messages within 2 hours of cart abandonment, without requiring manual workflow setup.” The second version establishes multiple extractable entity relationships (Omnisend → SMS automation → Shopify integration → abandoned cart recovery) within a single passage, making it far easier for AI systems to understand your product’s specific positioning and capabilities. Entity density matters: pages with strong entity relationships and contextual clarity tend to get cited more often in AI responses than pages requiring additional context or inference. To optimize your content, run key passages through Google’s Natural Language API to see what entities get recognized and how confidently—this reveals whether your content is establishing the entity relationships you intend or whether it’s ambiguous. Focus on writing passages that explicitly connect your brand to relevant entities (products, features, use cases, integrations, competitors) rather than generic descriptions, and ensure each major claim includes specific entity references that AI systems can extract and relate to other content. This approach reduces friction for both AI systems trying to understand your content and human readers seeking specific information.
Entity authority builds through consistent, contextual mention alongside relevant entities in trusted sources—this moves your focus from link building to building relationships where natural comparisons happen. Reddit threads comparing tools for specific use cases carry different entity weight than appearing in generic “best tools” content; a discussion titled “Klaviyo vs Omnisend for Shopify stores” creates dense entity relationships (Klaviyo → Omnisend → Shopify integration → ecommerce email) grounded in authentic decision-making. YouTube reviews demonstrating multiple platforms side-by-side establish competitive entity relationships that AI systems extract and use to understand market positioning. Industry roundups grouping tools by specialization (e.g., “Best Email Marketing Platforms for B2B vs B2C”) create contextual entity clusters that strengthen your association with specific use cases. Podcast discussions of marketing technology stacks where hosts and guests mention your product alongside competitors build entity relationships through authentic conversation. The most valuable co-citations happen in platforms where real users make real decisions—not in content created primarily for search engines. This approach emphasizes genuine participation in your category’s authentic discussions rather than manufacturing mentions; when your brand appears naturally in Reddit threads, YouTube reviews, and podcast conversations where people are genuinely evaluating solutions, you’re building entity relationships that AI systems recognize as credible and contextually relevant.
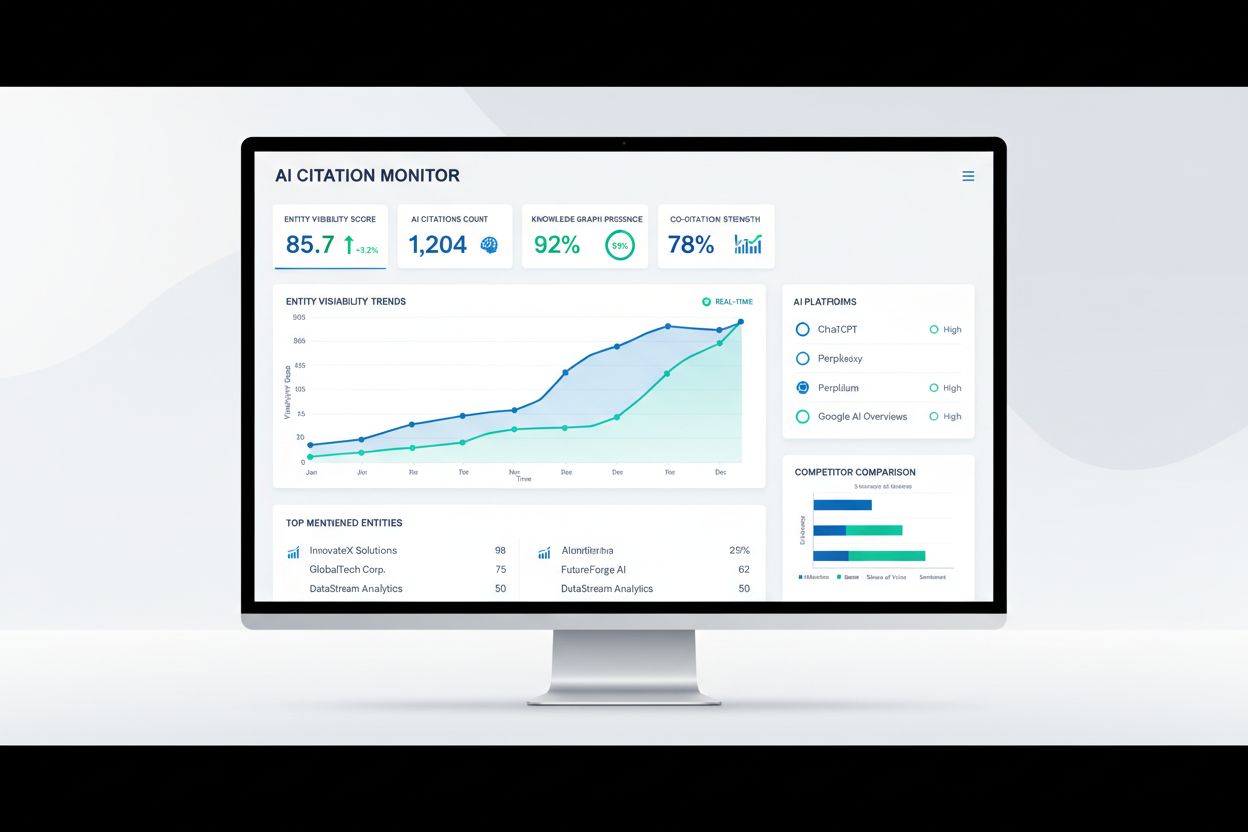
Tracking your entity visibility across AI search platforms is essential for understanding how clearly AI systems recognize and cite your brand. AmICited.com is purpose-built for this exact challenge—it monitors how your brand appears as an entity across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI-powered search platforms, tracking not just mentions but the context and authority with which your brand is cited. Rather than relying on traditional SEO metrics like rankings and click-through rates, AmICited measures entity-level visibility: how often your brand appears in AI-generated answers, which entities it’s mentioned alongside, and how your entity presence compares to competitors. The platform reveals critical insights like whether your brand is cited as a primary recommendation or a secondary mention, which AI platforms recognize your entity most strongly, and how your entity relationships shift across different query contexts. With AmICited, you can monitor entity visibility trends over time, identifying whether your co-citation strength is improving, which competitive entity relationships are strengthening or weakening, and where your entity presence is growing or declining. This data-driven approach to entity monitoring transforms entity SEO from a theoretical concept into a measurable, optimizable strategy—you can see exactly how your entity optimization efforts translate into increased visibility across the AI search platforms that now drive discovery for millions of users. By tracking these metrics continuously, you ensure your entity strategy remains aligned with how AI systems actually recognize and cite your brand.
Implementing entity SEO requires a systematic approach that prioritizes clarity, consistency, and continuous measurement. Start with your highest-priority product or service line—the entity that drives the most business value—and work through these implementation phases:
mainEntityOfPage, sameAs, and relationship attributes are correctly implemented and validatedAfter establishing this foundation with your primary entity, expand to secondary entities (related products, features, use cases) and measure progress using AmICited to track how your entity visibility changes across AI platforms. The key is treating entity optimization as an ongoing process rather than a one-time project—continuously monitor your entity relationships, identify gaps in your entity coverage, and refine your strategy based on how AI systems actually recognize and cite your brand. This systematic approach ensures that entity SEO becomes embedded in your content strategy, technical implementation, and measurement practices, creating sustainable visibility across the AI search platforms that increasingly drive discovery and decision-making.
Traditional SEO focuses on matching keywords on pages and building backlinks, while entity SEO focuses on how clearly AI systems understand and recognize your brand as a distinct entity. Entity SEO uses semantic understanding and structured data to help AI systems identify your brand's attributes, relationships, and context across the entire web, not just your website.
You can check your entity presence by searching for your brand in Google's Knowledge Graph, Wikidata, and Crunchbase. Use Google's Natural Language API to see what entities are recognized in your content. Tools like AmICited.com specifically monitor how your brand appears as an entity across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Schema markup translates your content into structured data that AI systems can reliably interpret. Using JSON-LD format, you explicitly define what entities your page represents, their attributes, and relationships. This helps AI systems understand your brand more clearly and improves your chances of appearing in AI-generated answers and knowledge panels.
Yes. While backlinks still matter, AI systems now recognize authentic mentions across platforms like Reddit, YouTube, podcasts, and reviews. Genuine discussions where people mention your brand alongside competitors, customer testimonials, and industry coverage all strengthen your entity visibility without requiring traditional backlinks.
Entity visibility should be monitored continuously, ideally weekly or monthly, to track trends and identify changes in how AI systems recognize your brand. Platforms like AmICited.com provide real-time monitoring, allowing you to see how your entity presence evolves and respond quickly to competitive changes.
Focus on platforms where authentic discussions happen: Reddit for tool comparisons and user experiences, YouTube for product reviews and demonstrations, podcasts for industry discussions, and review sites for customer feedback. These platforms generate training data that AI systems use to understand entity relationships and competitive positioning.
AmICited.com tracks how your brand appears as an entity across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. It monitors entity citations, co-citation strength, competitive positioning, and visibility trends, providing data-driven insights into how clearly AI systems recognize and cite your brand.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) signals are strengthened through entity SEO. When your entity is clearly defined, properly structured with schema markup, and consistently mentioned in authoritative sources, you build stronger E-E-A-T signals that help both traditional search and AI systems recognize your brand as a trusted authority.
Track how your brand appears across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. Get real-time insights into your entity presence and competitive positioning.

Learn how entity optimization helps your brand become recognizable to LLMs. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity strategies for AI vis...

Learn what entity optimization for AI is, how it works, and why it's critical for visibility in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Complete techn...

Learn how to strengthen your brand entity for AI search visibility. Optimize for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude with entity SEO strategies...