GPTBot
Learn what GPTBot is, how it works, and whether you should block it from your website. Understand the impact on SEO, server load, and brand visibility in AI sea...
Learn the key differences between GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot crawlers. Understand their purposes, crawl behaviors, and how to manage them for optimal content visibility in AI search results.
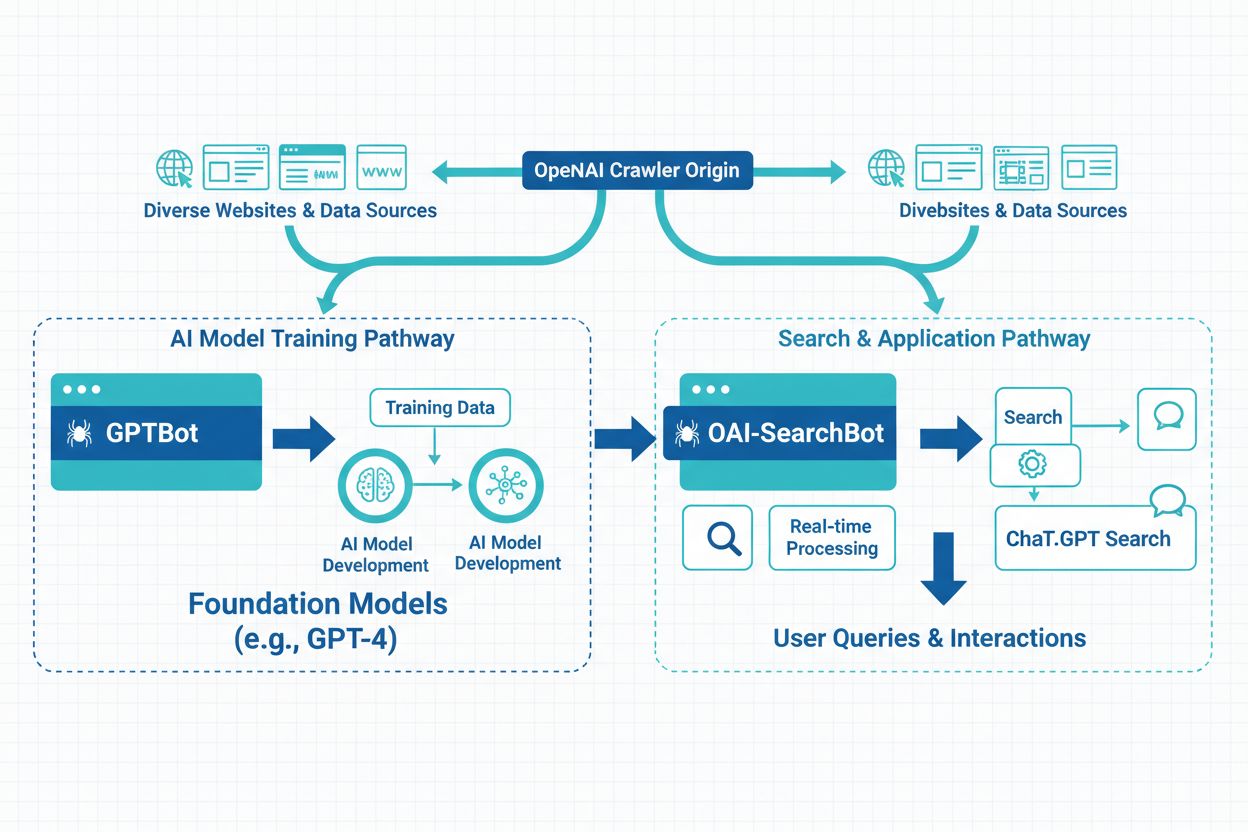
OpenAI operates two distinct web crawlers that serve different purposes in their ecosystem, and understanding the difference between them is crucial for content creators and website owners. GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot represent different approaches to data collection, with one focused on training AI models and the other dedicated to powering search functionality. These crawlers have different behaviors, access patterns, and implications for your website’s visibility and data usage. Knowing which crawler is accessing your site and how to manage them can significantly impact your content strategy.

GPTBot is OpenAI’s primary web crawler designed to collect training data for their large language models, including ChatGPT and other AI systems. Launched to help improve the quality and breadth of training data, GPTBot systematically crawls websites to gather text content that helps train and refine OpenAI’s AI models. This crawler operates under the user-agent identifier “GPTBot” and respects the robots.txt file, allowing website owners to opt out of data collection. GPTBot’s primary mission is to enhance AI model capabilities by learning from diverse, high-quality content across the internet. The crawler is designed to be respectful of server resources while comprehensively gathering information that contributes to AI training datasets. Website owners who want their content included in future AI model training can allow GPTBot access, while those concerned about data usage can block it entirely.
OAI-SearchBot is OpenAI’s specialized crawler dedicated to powering the search functionality within ChatGPT, enabling users to search the web directly from the ChatGPT interface. This crawler was introduced as part of ChatGPT’s search capabilities, allowing the AI to retrieve real-time information and provide current, relevant results to users. Unlike GPTBot, OAI-SearchBot focuses on indexing content for immediate retrieval rather than long-term model training. The crawler operates under the user-agent identifier “OAI-SearchBot” and also respects robots.txt directives, giving website owners control over whether their content appears in ChatGPT search results. OAI-SearchBot’s crawl patterns are typically more frequent and targeted, as it needs to maintain current indexes for real-time search functionality. This crawler is essential for websites that want their content to be discoverable and cited when users perform searches within ChatGPT.
While both crawlers serve OpenAI’s ecosystem, they have distinct purposes, behaviors, and implications for content creators. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about which crawlers to allow or block on your website. Here’s a comprehensive comparison of the two crawlers:
| Feature | GPTBot | OAI-SearchBot |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Training data collection for AI models | Real-time search indexing for ChatGPT |
| User-Agent String | GPTBot | OAI-SearchBot |
| Crawl Frequency | Periodic, less frequent | More frequent, continuous updates |
| Data Usage | Long-term model training and improvement | Immediate search result retrieval |
| Content Visibility | Influences future AI model capabilities | Affects ChatGPT search result rankings |
| Robots.txt Support | Yes, fully respects directives | Yes, fully respects directives |
| Real-Time Requirements | No, batch processing acceptable | Yes, requires current indexes |
The fundamental difference between these crawlers lies in their operational objectives and how they utilize collected data. GPTBot is designed with a long-term vision, collecting diverse content to improve AI model training over months and years, contributing to better language understanding and generation capabilities. OAI-SearchBot, conversely, operates on a real-time basis, maintaining fresh indexes that enable ChatGPT users to get current information when they search for recent news, events, or time-sensitive topics. GPTBot’s data collection is more comprehensive and exploratory, aiming to capture the breadth of human knowledge and writing styles. OAI-SearchBot’s approach is more targeted and efficiency-focused, prioritizing content relevance and freshness for search queries. The implications are significant: allowing GPTBot means your content contributes to AI model development, while allowing OAI-SearchBot ensures your content can be discovered and cited in ChatGPT search results. Many websites choose different strategies for each crawler based on their content type and business objectives.
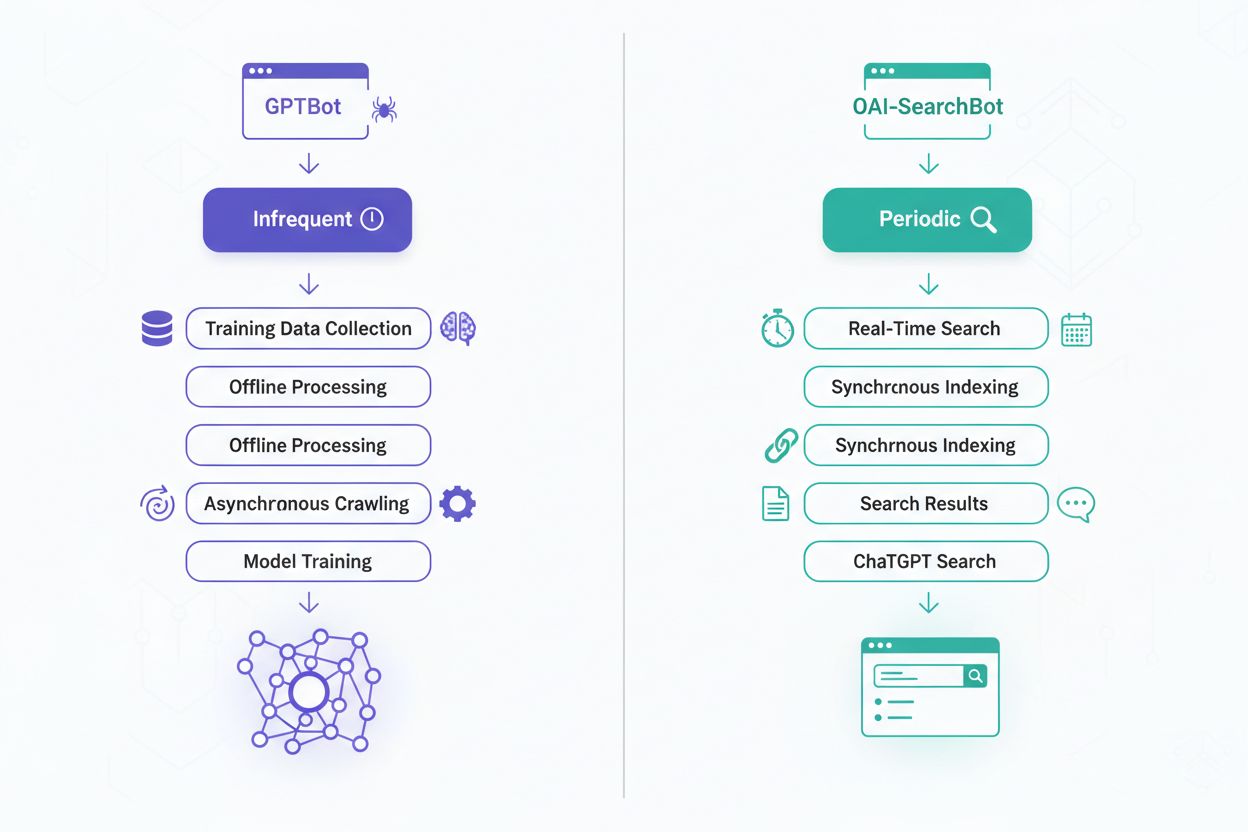
GPTBot operates on a periodic crawl schedule, visiting websites at intervals that may span weeks or months depending on content update frequency and site importance. This crawler is designed to be efficient with bandwidth and server resources, as it doesn’t require real-time data for its training purposes. The crawl depth and breadth are typically comprehensive, as GPTBot aims to capture diverse content types and writing styles for model training. OAI-SearchBot, by contrast, maintains a more aggressive crawl schedule with frequent revisits to ensure search indexes remain current and accurate. This crawler prioritizes recently updated content and trending topics, making multiple passes through popular or frequently-updated websites. The frequency difference reflects their distinct purposes: GPTBot can afford to be patient and thorough, while OAI-SearchBot must stay synchronized with the rapidly changing web to provide relevant search results.
Allowing GPTBot access means your content becomes part of the training data for future AI models, potentially influencing how AI systems understand and generate content related to your topics. This can have long-term benefits as your writing style, expertise, and unique perspectives help shape AI responses in your domain. However, it also means your content is used to train systems that may eventually compete with your original work. OAI-SearchBot access directly impacts your visibility in ChatGPT search results, making your content discoverable to millions of ChatGPT users searching for information. When users find your content through ChatGPT search, it can drive significant traffic and establish your site as an authoritative source. The visibility impact differs significantly: GPTBot affects your influence on AI development, while OAI-SearchBot affects your immediate discoverability and traffic potential. Content creators must weigh these considerations based on their goals, whether they prioritize AI training participation or search visibility.
Both GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot respect the robots.txt file, giving website owners complete control over crawler access through standard web protocols. You can block either or both crawlers by adding specific directives to your robots.txt file, or you can allow them while blocking other crawlers. This flexibility enables nuanced content strategies where you might allow one crawler while blocking the other based on your specific needs and concerns. OpenAI has also provided official documentation and guidelines for managing these crawlers, making it straightforward to implement your preferred access policies. The robots.txt approach is transparent and follows established web standards, ensuring compatibility with other tools and monitoring systems. Here are common robots.txt configurations for managing OpenAI crawlers:
User-agent: GPTBot and User-agent: OAI-SearchBot with Disallow: /User-agent: GPTBot with Disallow: / while allowing OAI-SearchBotUser-agent: OAI-SearchBot with Disallow: / while allowing GPTBotDisallow: /private/ to block crawlers from sensitive sectionsCrawl-delay: 10 to limit crawler frequency and server impactVerifying that OpenAI crawlers are actually accessing your website requires examining server logs and looking for the specific user-agent strings. You can identify GPTBot requests by searching logs for “GPTBot” and OAI-SearchBot requests by searching for “OAI-SearchBot” in your access logs. Many website owners use log analysis tools or web analytics platforms that can filter and report on specific crawler activity. Monitoring crawler behavior helps you understand whether your robots.txt directives are working correctly and whether the crawlers are respecting your access policies. Regular monitoring also reveals crawl patterns and frequency, helping you optimize your server resources and understand the impact on your infrastructure. Additionally, you can verify crawler IP addresses against OpenAI’s published IP ranges to ensure requests are legitimate and not spoofed by malicious actors.
Your decision to allow or block these crawlers should align with your content strategy and business objectives. If your primary goal is to drive traffic and visibility, allowing OAI-SearchBot makes sense as it directly impacts discoverability in ChatGPT search results. If you’re concerned about AI training data usage or prefer to maintain exclusive control over your content, blocking GPTBot protects your intellectual property from being used in model training. Some websites adopt a hybrid approach, allowing OAI-SearchBot for search visibility while blocking GPTBot to prevent training data collection. Consider your content type: news organizations and current-events sites benefit significantly from OAI-SearchBot access, while creators of proprietary or sensitive content may prefer blocking both. The decision isn’t permanent—you can adjust your robots.txt file at any time to change your crawler access policies. Regularly reviewing your crawler strategy ensures it continues to align with your evolving business goals and content priorities.
AmICited provides comprehensive crawler monitoring solutions that help you track both GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot activity on your website with detailed analytics and insights. The platform offers real-time notifications when these crawlers access your content, allowing you to verify compliance with your robots.txt directives and monitor crawl patterns. With AmICited, you gain visibility into how your content is being indexed and used by OpenAI’s systems, enabling data-driven decisions about your crawler access policies. This monitoring solution simplifies the process of understanding your content’s role in AI training and search indexing, giving you the control and transparency you need in the evolving AI landscape.
GPTBot is OpenAI's training crawler that collects data for AI model development, operating on a periodic schedule with long-term goals. OAI-SearchBot is OpenAI's search crawler that maintains real-time indexes for ChatGPT search functionality. While both respect robots.txt, they serve different purposes and have different crawl frequencies and implications for your content visibility.
The decision depends on your content strategy and business goals. Allow OAI-SearchBot if you want your content discoverable in ChatGPT search results and willing to drive traffic. Block GPTBot if you're concerned about your content being used in AI model training. Many websites use a hybrid approach, allowing one while blocking the other based on their specific needs.
Search your server access logs for the user-agent strings 'GPTBot' and 'OAI-SearchBot'. Most web analytics platforms and log analysis tools allow you to filter by user-agent, making it easy to identify and monitor crawler activity. You can also verify crawler IP addresses against OpenAI's published IP ranges to ensure requests are legitimate.
No, blocking GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot are independent actions. You can block both, allow both, or block one while allowing the other using separate robots.txt directives. Each crawler respects its own user-agent rules, so your access policies for one crawler don't automatically apply to the other.
GPTBot operates on a periodic crawl schedule, visiting websites at intervals that may span weeks or months depending on content freshness and site importance. OAI-SearchBot maintains a more frequent crawl schedule to keep search indexes current and accurate. The frequency difference reflects their distinct purposes: GPTBot prioritizes thoroughness while OAI-SearchBot prioritizes freshness.
Allowing OAI-SearchBot can drive traffic to your website when users find and click through from ChatGPT search results. The impact varies based on your content type and relevance to user queries. News, current events, and informational content typically see more traffic from AI search, while niche or specialized content may see less immediate impact.
Yes, you can use robots.txt to block specific directories or file types from GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot. For example, you can use 'Disallow: /private/' to block crawlers from sensitive sections while allowing them to access public content. This granular control lets you protect sensitive information while maintaining visibility in AI search results.
AmICited provides real-time monitoring and analytics for both GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot activity on your website. The platform tracks crawler visits, verifies robots.txt compliance, and provides insights into how your content is being indexed and used by OpenAI's systems. This gives you the transparency and control needed to make informed decisions about your crawler access policies.
Track how GPTBot and OAI-SearchBot access your content with real-time insights and analytics. Understand your content's role in AI training and search indexing.

Learn what GPTBot is, how it works, and whether you should block it from your website. Understand the impact on SEO, server load, and brand visibility in AI sea...

Learn what GPTBot is, how it works, and whether you should allow or block OpenAI's web crawler. Understand the impact on your brand visibility in AI search engi...
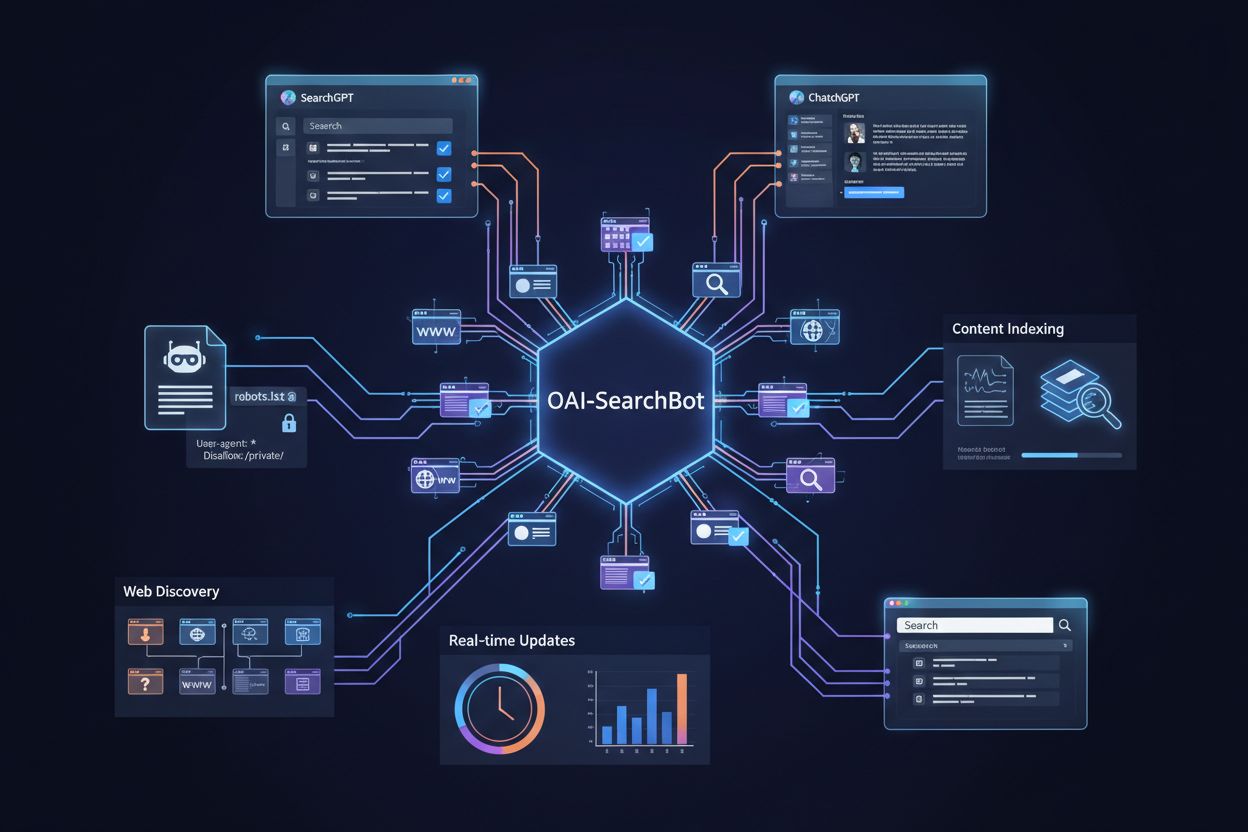
Learn what OAI-SearchBot is, how it works, and how to optimize your website for OpenAI's dedicated search crawler used by SearchGPT and ChatGPT.