
How AI Agents Change Search Behavior: Impact on User Queries and Discovery
Discover how AI agents reshape search behavior, from conversational queries to zero-click results. Learn the impact on user habits, brand visibility, and search...

Explore the complete timeline of AI search algorithm updates from Google, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. Learn how AI search evolved and what it means for your brand visibility in AI-powered answers.
The history of search algorithms reveals a fundamental transformation in how information is discovered and delivered online. For over two decades, Google’s algorithm updates shaped the digital landscape—from the Florida update in 2003 that targeted keyword stuffing to the Panda update in 2011 that penalized low-quality content. These traditional algorithms ranked websites based on links, content quality, and relevance signals, requiring users to click through to find answers. However, the emergence of AI-powered search platforms beginning in 2022 fundamentally changed this paradigm. Today, platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s own AI Overviews generate direct answers to user queries without requiring clicks to external websites. This shift from ranking-based search to citation-based AI answers represents the most significant evolution in search since Google’s inception, requiring brands to rethink their visibility strategy entirely.
Google’s algorithm evolution laid the foundation for modern search understanding. The Florida update (2003) was the first major algorithm change, targeting keyword stuffing and manipulative SEO tactics that had plagued search results. The Panda update (2011) marked a watershed moment by introducing quality signals that penalized thin, low-value content and rewarded comprehensive, authoritative pages—impacting 11.8% of U.S. search results. The Penguin update (2012) shifted focus to link quality, neutralizing the impact of spammy backlinks and paid link schemes that had artificially inflated rankings. The Hummingbird update (2013) represented a conceptual leap, moving Google from matching keywords to understanding semantic meaning and user intent behind search queries. The RankBrain system (2015) introduced machine learning to interpret unfamiliar queries by analyzing patterns in search behavior, becoming one of Google’s three most important ranking signals. Finally, BERT (2019) enhanced Google’s ability to understand context within search queries and webpage content using bidirectional neural networks, improving results for complex, conversational searches. Together, these updates demonstrate Google’s progression from simple keyword matching to sophisticated understanding of user intent and content quality.
| Year | Algorithm | Primary Focus | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | Florida | Keyword stuffing prevention | Penalized manipulative SEO |
| 2011 | Panda | Content quality | 11.8% of results affected |
| 2012 | Penguin | Link quality | Neutralized spammy links |
| 2013 | Hummingbird | Semantic understanding | Intent-based ranking |
| 2015 | RankBrain | Machine learning | 15% of new queries handled |
| 2019 | BERT | Neural networks | Context understanding |
The introduction of RankBrain in 2015 marked the beginning of machine learning’s dominance in search. RankBrain was designed to handle the 15% of Google searches that had never been seen before by analyzing patterns in historical search data and understanding semantic relationships between concepts. Rather than relying solely on explicit signals like keywords and links, RankBrain could infer meaning and predict relevant results for novel queries. This represented a fundamental shift in how search engines processed information—moving from rule-based systems to learning systems that improved over time. BERT (2019) accelerated this evolution by introducing transformer-based neural networks that could understand the bidirectional context of words in sentences, dramatically improving Google’s ability to comprehend natural language. These machine learning systems didn’t just improve ranking; they changed the nature of search itself:
The emergence of generative AI fundamentally disrupted the search landscape beginning in late 2022. ChatGPT, launched by OpenAI in November 2022, rapidly became the fastest-growing application in history, reaching 800 million weekly active users by September 2025 and processing 2 billion queries daily. Perplexity, launched in December 2022, positioned itself as a citation-focused alternative, emphasizing source transparency and real-time information retrieval. Google AI Overviews, introduced in May 2024, brought AI-generated summaries directly into Google’s search results, now appearing in 18% of global searches and reaching 2 billion monthly users. Google’s AI Mode, also launched in May 2024, created a separate search experience powered by Gemini that restructures the entire SERP around conversational AI answers, with 100 million monthly active users in the U.S. and India. These platforms represent a complete departure from traditional ranking-based search. Rather than presenting a list of ranked websites, they generate synthesized answers by pulling information from multiple sources and presenting it in a conversational format. ChatGPT dominates with an 81% share of the AI chatbot market, while other platforms like Microsoft Copilot (33 million users), Claude (18.9 million users), and DeepSeek (125 million users) continue to grow rapidly, creating a fragmented but expanding AI search ecosystem.
The differences between AI search and traditional Google search are profound and require fundamentally different optimization strategies. Zero-click behavior illustrates this shift dramatically: while 34% of traditional Google searches end without a click, this rises to 43% when AI Overviews are present, and reaches 93% in Google’s AI Mode—meaning users get their answers directly without visiting any website. Citation-based ranking replaces traditional ranking factors; instead of optimizing for position in search results, brands must focus on being cited as a source in AI-generated answers. Research shows that branded web mentions have a 0.664 correlation with appearing in AI Overviews, far stronger than backlinks (0.218 correlation), fundamentally shifting the importance of brand visibility and mentions. Content freshness matters more in AI search, with AI platforms preferring content that is 25.7% fresher than traditional search prefers, meaning regular content updates become critical. Additionally, 40% of sources cited in AI Overviews rank lower than position 10 in traditional Google search, indicating that AI platforms discover and value sources that traditional SEO would overlook. This means your visibility in AI search is largely independent of your Google rankings—you could rank well in Google but be invisible in AI, or vice versa.
Succeeding in AI search requires rethinking content strategy from the ground up. Listicles and comparison content perform exceptionally well, with listicles achieving a 25% citation rate compared to 11% for traditional blog posts, making “best of,” “top,” and “vs” content formats highly valuable. Schema markup implementation directly improves AI citations by 30%, making structured data essential rather than optional—properly marked-up content is significantly more likely to be cited by AI platforms. Brand mentions across the web have become a primary visibility driver, with 86% of AI citations coming from brand-managed sources like your website and business listings, emphasizing the importance of consistent brand presence and mentions. Content freshness requires regular updates; AI platforms show a strong preference for recently updated content, making a content maintenance schedule as important as creating new content. Specific, actionable information performs better than general overviews—AI systems prefer content that directly answers questions with concrete details, examples, and data rather than broad introductions. These changes mean that traditional SEO strategies focused on keyword optimization and link building must be supplemented with AI-specific tactics centered on brand mentions, fresh content, and structured data.
The history of Google’s algorithm updates provides valuable lessons that remain relevant in the AI search era. The Panda update’s emphasis on quality taught us that thin, low-value content will always be penalized—this principle applies equally to AI search, where platforms prioritize authoritative, comprehensive sources. The Hummingbird and RankBrain updates’ focus on user intent demonstrated that understanding what users actually want matters more than matching keywords—AI platforms take this further by generating answers that directly address intent rather than ranking pages. The Medic update’s emphasis on E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) showed that credibility matters, especially for topics affecting user well-being—this remains critical in AI search, where platforms must cite trustworthy sources. The fundamental lesson across all these updates is that search engines consistently reward content created for users first, not for algorithms. This principle holds true in AI search: platforms cite sources that provide genuine value, answer questions comprehensively, and demonstrate expertise. AmICited.com helps brands apply these lessons by monitoring how AI platforms cite and reference your content, providing visibility into whether your brand is being recognized as an authoritative source in AI-generated answers. By tracking your AI citations, you can identify which content resonates with AI platforms and adjust your strategy accordingly.
The trajectory of AI search points toward increasingly sophisticated, personalized, and integrated experiences. Multimodal search will become standard, with AI platforms processing and synthesizing information from text, images, videos, and audio to provide richer, more comprehensive answers. Personalization will deepen as AI systems learn individual user preferences, search history, and context, delivering increasingly tailored results—this means the same query could generate different answers for different users based on their profile. Commerce integration is accelerating, with platforms like ChatGPT introducing Agent Mode and Instant Checkout, allowing users to complete purchases directly within AI interfaces without visiting external websites. Real-time information will become more critical as AI platforms compete to provide current, accurate answers, making content freshness and real-time data feeds increasingly important. The competitive landscape will likely consolidate around a few dominant platforms while niche players serve specific use cases, similar to how Google dominates traditional search. For brands, the key to thriving in this future is continuous monitoring of AI visibility through tools like AmICited.com, which tracks how your brand appears across multiple AI platforms. By understanding your current AI citation patterns and staying informed about algorithm changes, you can adapt your content strategy proactively rather than reactively, ensuring your brand remains visible and cited as AI search continues to evolve and capture an increasing share of search traffic.
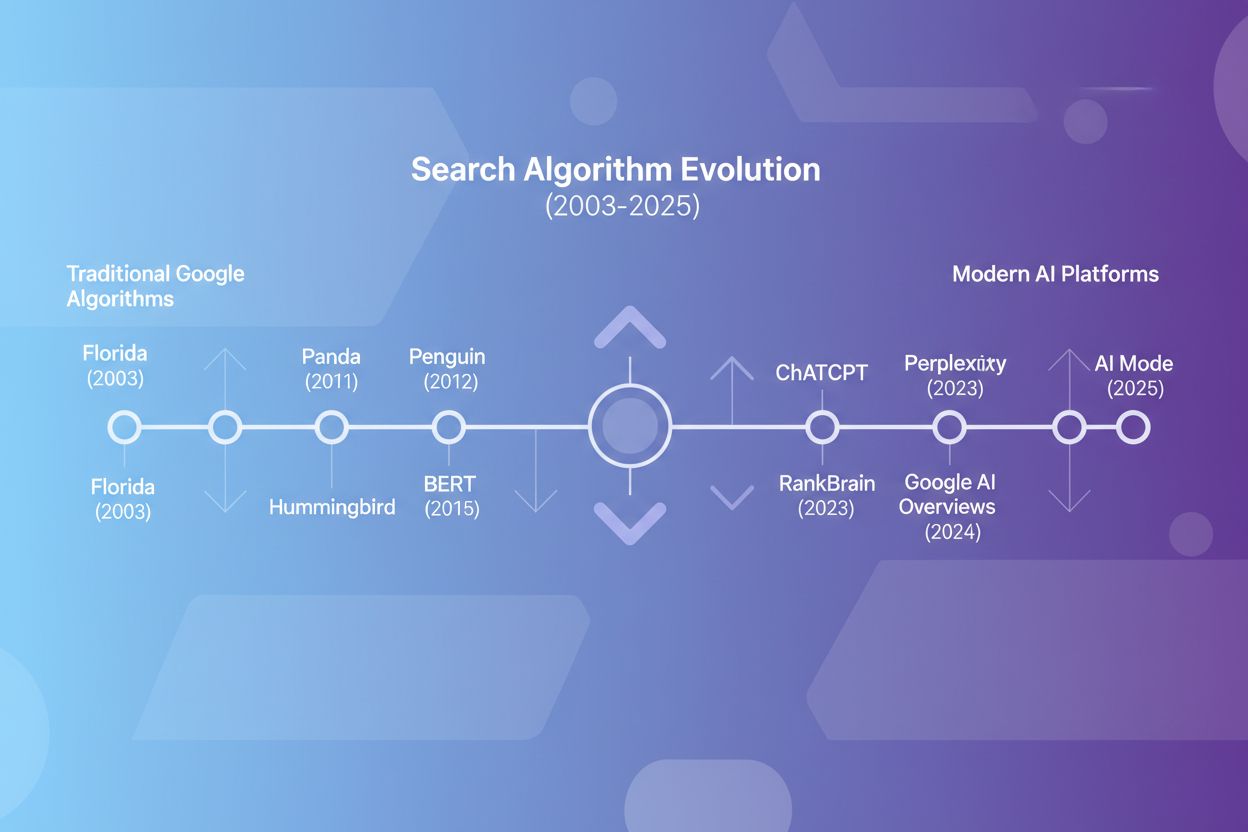
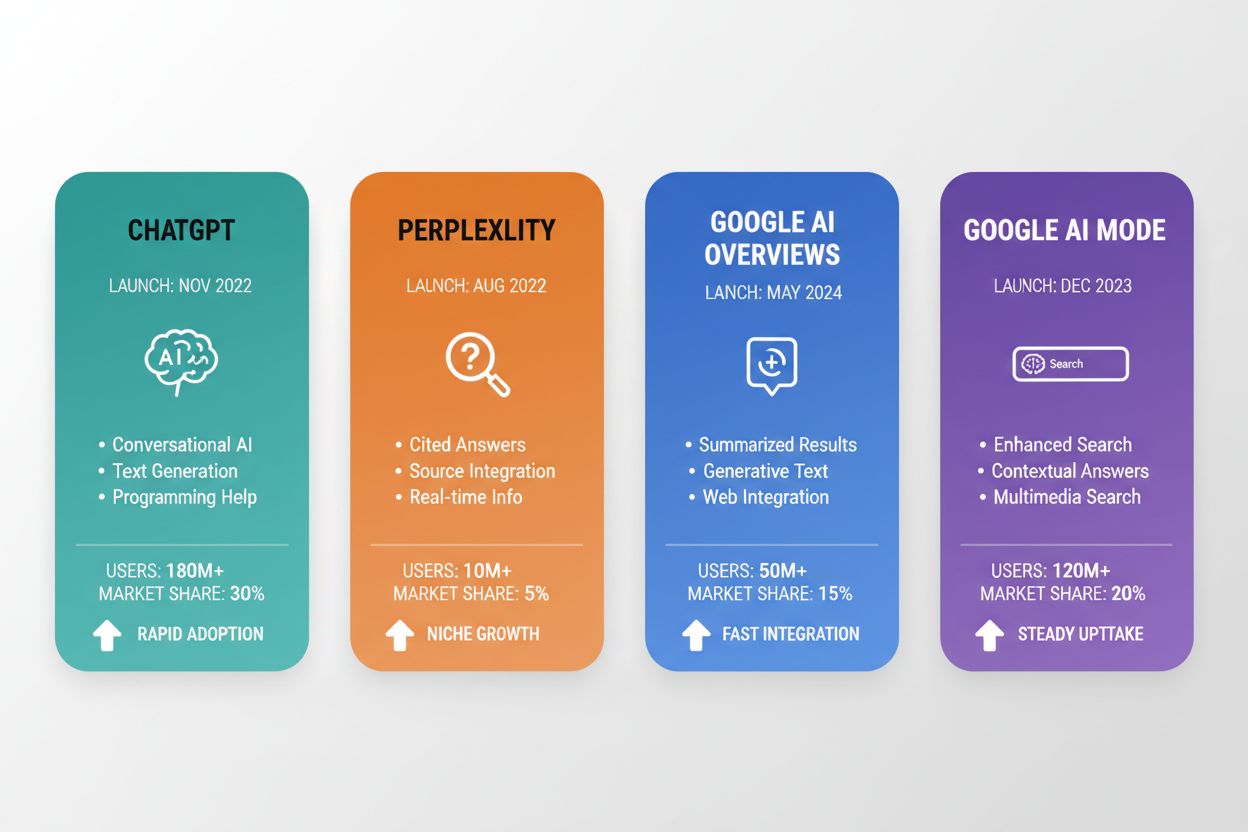
Traditional Google algorithms like Panda and Penguin focused on ranking websites based on links and content quality. AI search algorithms, introduced by platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity, generate answers directly from multiple sources without requiring users to click through to websites. This fundamental shift means brands need to focus on being cited in AI-generated responses rather than just ranking in search results.
RankBrain, introduced in 2015, was Google's first machine learning system that helped understand search intent for unfamiliar queries. Modern AI platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity go much further by generating complete answers using neural networks and large language models. While RankBrain improved ranking, AI platforms fundamentally changed how search results are delivered—moving from ranked lists to conversational answers with citations.
AI platforms use different ranking criteria than traditional Google search. They prioritize fresh content (25.7% fresher than traditional search), brand mentions (0.664 correlation), and specific content formats like listicles (25% citation rate). Additionally, 40% of sources cited in AI Overviews rank lower than position 10 in traditional Google search, meaning your visibility in AI depends on different optimization strategies.
Listicles and comparison content perform exceptionally well in AI search, with listicles achieving a 25% citation rate compared to 11% for traditional blogs. Content that is fresh, includes schema markup (which improves citations by 30%), and contains strong brand mentions tends to be cited more frequently. AI platforms also prefer content that directly answers questions with specific, actionable information.
Tools like AmICited.com allow you to track how AI platforms cite and reference your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI search engines. These monitoring platforms provide real-time insights into your AI citations, citation sources, and competitive positioning. This data helps you understand your AI visibility and optimize your content strategy accordingly.
Key lessons include: quality content matters (from Panda), user intent is critical (from Hummingbird and RankBrain), and expertise and trustworthiness are essential (from the Medic update). These principles remain relevant in AI search, but the execution differs. Instead of optimizing for rankings, focus on creating authoritative, fresh content that directly answers user questions and earns brand mentions across the web.
While AI search is growing rapidly, traditional Google search will likely coexist with AI platforms for the foreseeable future. Google itself is integrating AI features like AI Overviews and AI Mode into its search experience. The future of search will likely be hybrid, with users choosing between traditional ranked results and AI-generated answers depending on their needs. Brands should optimize for both to maintain visibility.
AI platforms update their algorithms continuously as part of their machine learning processes, rather than announcing major updates like Google does. Google makes thousands of changes to its algorithms annually, but AI platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity update their models and ranking systems on an ongoing basis. This means AI visibility can fluctuate more frequently, making continuous monitoring essential for brands.
Track how AI platforms cite and reference your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and more. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and stay ahead of the competition.

Discover how AI agents reshape search behavior, from conversational queries to zero-click results. Learn the impact on user habits, brand visibility, and search...

Explore AI Visibility Futures - forward-looking analysis of emerging trends in AI-driven brand discovery. Learn how brands will be discovered by AI systems and ...
Master AI search optimization with proven tactics to outrank competitors in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Learn brand visibility strategies that...