How Retrieval-Augmented Generation Works: Architecture and Process
Learn how RAG combines LLMs with external data sources to generate accurate AI responses. Understand the five-stage process, components, and why it matters for ...
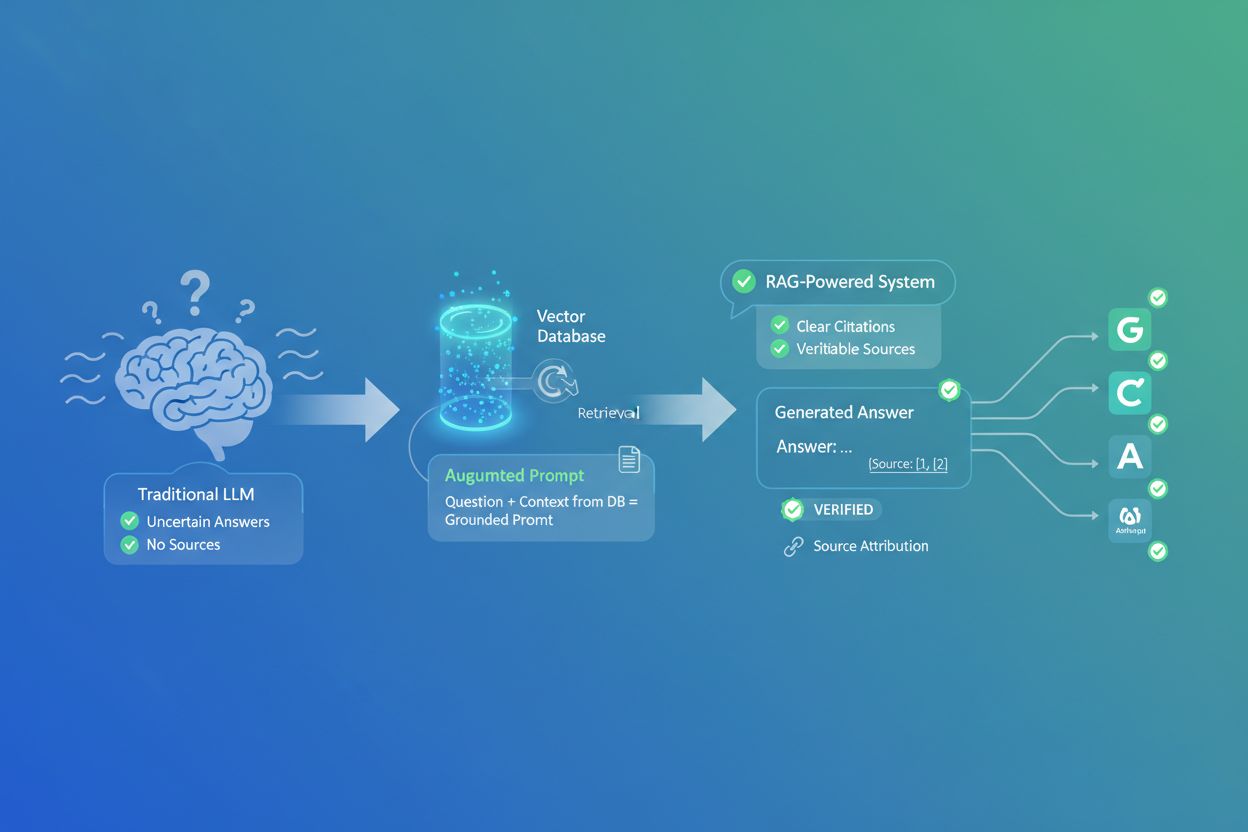
Discover how Retrieval-Augmented Generation transforms AI citations, enabling accurate source attribution and grounded answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Large language models have revolutionized AI, but they come with a critical flaw: knowledge cutoffs. These models are trained on data up to a specific point in time, meaning they can’t access information beyond that date. Beyond staleness, traditional LLMs suffer from hallucinations—confidently generating false information that sounds plausible—and they provide no source attribution for their claims. When a business needs current market data, proprietary research, or verifiable facts, traditional LLMs fall short, leaving users with answers they can’t trust or verify.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a framework that combines the generative power of LLMs with the precision of information retrieval systems. Instead of relying solely on training data, RAG systems fetch relevant information from external sources before generating responses, creating a pipeline that grounds answers in actual data. The four core components work in concert: Ingestion (converting documents into searchable formats), Retrieval (finding the most relevant sources), Augmentation (enriching the prompt with retrieved context), and Generation (creating the final response with citations). Here’s how RAG compares to traditional approaches:
| Aspect | Traditional LLM | RAG System |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Source | Static training data | External indexed sources |
| Citation Capability | None/hallucinated | Traceable to sources |
| Accuracy | Prone to errors | Grounded in facts |
| Real-time Data | No | Yes |
| Hallucination Risk | High | Low |
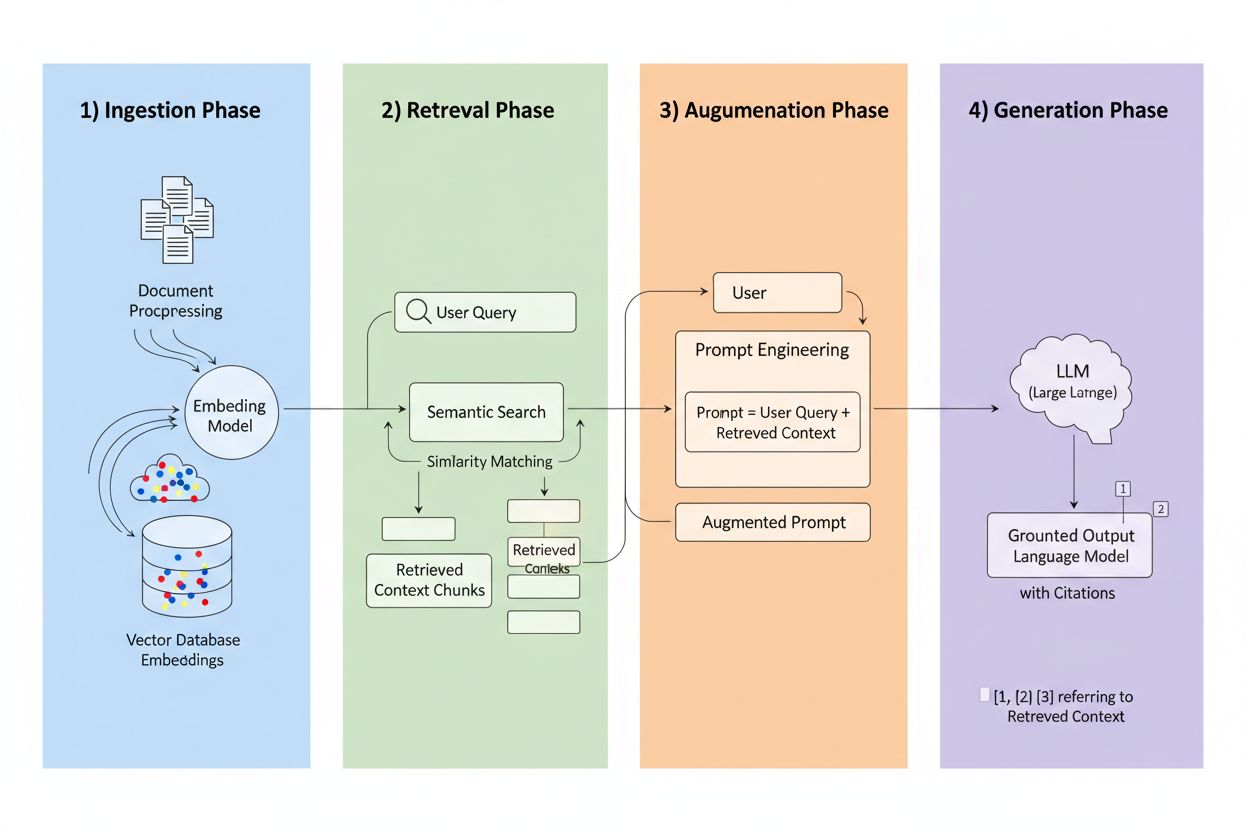
The retrieval engine is RAG’s beating heart, and it’s far more sophisticated than simple keyword matching. Documents are converted into vector embeddings—mathematical representations that capture semantic meaning—allowing the system to find conceptually similar content even when exact words don’t match. The system chunks documents into manageable pieces, typically 256-1024 tokens, balancing context preservation with retrieval precision. Most advanced RAG systems employ hybrid search, combining semantic similarity with traditional keyword matching to catch both conceptual and exact matches. A reranking mechanism then scores these candidates, often using cross-encoder models that evaluate relevance more accurately than initial retrieval. Relevance is calculated through multiple signals: semantic similarity scores, keyword overlap, metadata matching, and domain authority. The entire process happens in milliseconds, ensuring users get fast, accurate responses without noticeable latency.
Here’s where RAG transforms the citation landscape: when a system retrieves information from a specific indexed source, that source becomes traceable and verifiable. Each chunk of text can be mapped back to its original document, URL, or publication, making citation automatic rather than hallucinated. This fundamental shift creates unprecedented transparency in AI decision-making—users can see exactly which sources informed the answer, verify claims independently, and assess source credibility themselves. Unlike traditional LLMs where citations are often invented or generic, RAG citations are grounded in actual retrieval events. This traceability builds user trust dramatically, as people can validate information rather than accepting it on faith. For content creators and publishers, this means their work can be discovered and credited through AI systems, opening entirely new visibility channels.
Not all sources are equal in RAG systems, and several factors determine which content gets cited most frequently:
Each factor compounds the others—a well-structured, frequently-updated article from an authoritative domain with strong backlinks and knowledge graph presence becomes a citation magnet in RAG systems. This creates a new optimization paradigm where visibility depends less on traffic-driving SEO and more on becoming a trusted, structured information source.
Different AI platforms implement RAG with distinct strategies, creating varied citation patterns. ChatGPT heavily weights Wikipedia sources, with studies showing approximately 26-35% of citations come from Wikipedia alone, reflecting its authority and structured format. Google AI Overviews employ more diverse source selection, pulling from news sites, academic papers, and forums, with Reddit appearing in roughly 5% of citations despite lower traditional authority. Perplexity AI typically cites 3-5 sources per response and shows strong preference for industry-specific publications and recent news, optimizing for comprehensiveness and timeliness. These platforms weight domain authority differently—some prioritize traditional markers like backlinks and domain age, while others emphasize content freshness and semantic relevance. Understanding these platform-specific retrieval strategies is crucial for content creators, as optimization for one platform’s RAG system may differ significantly from another’s.
The rise of RAG fundamentally disrupts traditional SEO wisdom. In search engine optimization, citations and visibility correlate directly with traffic—you need clicks to matter. RAG inverts this equation: content can be cited and influence AI answers without driving any traffic. A well-structured, authoritative article might appear in dozens of AI responses daily while receiving zero clicks, as users get their answer directly from the AI summary. This means authority signals matter more than ever, as they’re the primary mechanism RAG systems use to evaluate source quality. Consistency across platforms becomes critical—if your content appears on your website, LinkedIn, industry databases, and knowledge graphs, RAG systems see reinforced authority signals. Knowledge graph presence transforms from a nice-to-have into essential infrastructure, as these structured databases are primary retrieval sources for many RAG implementations. The citation game has fundamentally changed from “drive traffic” to “become a trusted information source.”
To maximize RAG citations, content strategy must shift from traffic optimization to source optimization. Implement update frequency cycles of 48-72 hours for evergreen content, signaling to retrieval systems that your information stays current. Deploy structured data markup (Schema.org, JSON-LD) to help systems parse and understand your content’s meaning and relationships. Align your content semantically with common query patterns—use natural language that matches how people ask questions, not just how they search. Format content with FAQ and Q&A sections, as these directly match the question-answer pattern RAG systems use. Develop or contribute to Wikipedia and knowledge graph entries, as these are primary retrieval sources for most platforms. Build backlink authority through strategic partnerships and citations from other authoritative sources, as link profiles remain strong authority signals. Finally, maintain consistency across platforms—ensure your core claims, data, and messaging align across your website, social profiles, industry databases, and knowledge graphs, creating reinforced signals of reliability.
RAG technology continues evolving rapidly, with several trends reshaping how citations work. More sophisticated retrieval algorithms will move beyond semantic similarity toward deeper understanding of query intent and context, improving citation relevance. Specialized knowledge bases will emerge for specific domains—medical RAG systems using curated medical literature, legal systems using case law and statutes—creating new citation opportunities for authoritative domain sources. Integration with multi-agent systems will enable RAG to orchestrate multiple specialized retrievers, combining insights from different knowledge bases for more comprehensive answers. Real-time data access will improve dramatically, allowing RAG systems to incorporate live information from APIs, databases, and streaming sources. Agentic RAG—where AI agents autonomously decide what to retrieve, how to process it, and when to iterate—will create more dynamic citation patterns, potentially citing sources multiple times as agents refine their reasoning.
As RAG reshapes how AI systems discover and cite sources, understanding your citation performance becomes essential. AmICited monitors AI citations across platforms, tracking which of your sources appear in ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and emerging AI systems. You’ll see which specific sources get cited, how frequently they appear, and in what context—revealing which content resonates with RAG retrieval algorithms. Our platform helps you understand citation patterns across your content portfolio, identifying what makes certain pieces citation-worthy and others invisible. Measure your brand visibility in AI answers with metrics that matter in the RAG era, moving beyond traditional traffic analytics. Conduct competitive analysis of citation performance, seeing how your sources stack up against competitors in AI-generated responses. In a world where AI citations drive visibility and authority, having clear insight into your citation performance isn’t optional—it’s how you stay competitive.
Traditional LLMs rely on static training data with knowledge cutoffs and cannot access real-time information, often resulting in hallucinations and unverifiable claims. RAG systems retrieve information from external indexed sources before generating responses, enabling accurate citations and grounded answers based on current, verifiable data.
RAG traces each piece of retrieved information back to its original source, making citations automatic and verifiable rather than hallucinated. This creates a direct link between the answer and the source material, allowing users to verify claims independently and assess source credibility.
RAG systems evaluate sources based on authority (domain reputation and backlinks), recency (content updated within 48-72 hours), semantic relevance to the query, content structure and clarity, factual density with specific data points, and presence in knowledge graphs like Wikipedia. These factors compound to determine citation likelihood.
Update content every 48-72 hours to maintain freshness signals, implement structured data markup (Schema.org), align content semantically with common queries, use FAQ and Q&A formatting, develop Wikipedia and knowledge graph presence, build backlink authority, and maintain consistency across all platforms.
Knowledge graphs like Wikipedia and Wikidata are primary retrieval sources for most RAG systems. Presence in these structured databases dramatically increases citation likelihood and creates foundational trust signals that AI systems reference repeatedly across diverse queries.
Content should be updated every 48-72 hours to maintain strong recency signals in RAG systems. This doesn't require complete rewrites—adding new data points, updating statistics, or expanding sections with recent developments is sufficient to sustain citation eligibility.
Domain authority functions as a reliability proxy in RAG algorithms, accounting for approximately 5% of citation probability. It's assessed through domain age, SSL certificates, backlink profiles, expert attribution, and presence in knowledge graphs, all of which compound to influence source selection.
AmICited tracks which of your sources appear in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other platforms. You'll see citation frequency, context, and competitive performance, helping you understand what makes content citation-worthy in the RAG era.
Understand how your brand appears in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and more. Track citation patterns, measure visibility, and optimize your presence in the AI-driven search landscape.
Learn how RAG combines LLMs with external data sources to generate accurate AI responses. Understand the five-stage process, components, and why it matters for ...
Learn how Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems manage knowledge base freshness, prevent stale data, and maintain current information through indexing strategi...
Learn what RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is in AI search. Discover how RAG improves accuracy, reduces hallucinations, and powers ChatGPT, Perplexity, and...