How Do Images Affect AI Search Visibility? Complete Guide for 2025
Learn how images impact your brand's visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover optimization strategies for AI-powered answe...

Learn how to optimize images for AI systems, LLMs, and visual search. Master alt text, captions, schema markup, and technical optimization to improve AI visibility and citations.
The landscape of search has fundamentally shifted. While traditional SEO focused on text-based ranking factors, AI-powered search engines and answer platforms now evaluate visual content with the same rigor they apply to written words. According to recent research, LLM visitors are 4.4x more valuable than traditional organic visitors in terms of conversion rates, and AI search is projected to overtake traditional search entirely. Multimodal search—where AI systems combine text, images, and data to deliver richer answers—is becoming the dominant discovery mechanism. If your images aren’t optimized for AI systems, you’re invisible in the fastest-growing search channel.
Contrary to popular belief, large language models and AI answer engines don’t “see” images the way humans do. They don’t access pixel data directly from your website. Instead, when tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Perplexity receive a query that requires visual content, they perform real-time web searches using integrated search APIs (typically powered by Bing or Google). These systems then evaluate images based on metadata, structured data, and precomputed embeddings—mathematical representations that capture visual meaning. Vision APIs from providers like Google Vision, OpenAI, and AWS Rekognition analyze images and generate descriptions, labels, and safety scores. Multimodal models create a shared embedding space where visual and textual information can be compared and matched, allowing AI to understand that a photo of a “blue running shoe” relates to the text “athletic footwear” even though the words differ completely.

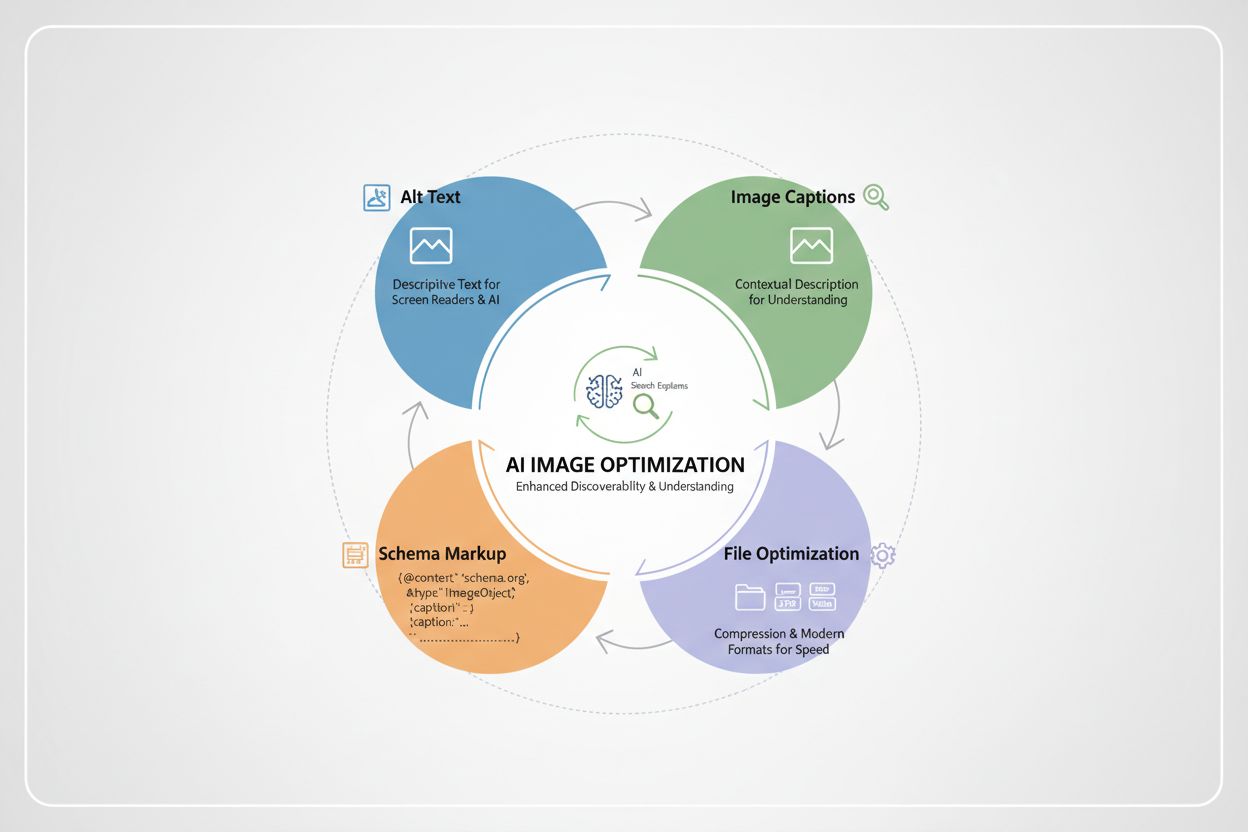
Alt text is the foundation of image optimization for AI systems. It serves a dual purpose: making images accessible to screen reader users and providing AI systems with explicit, human-readable descriptions of visual content. Strong alt text helps LLMs understand image context more accurately, improving relevance in search results and enhancing performance in visual and multimodal search. Effective alt text should be concise (80–125 characters), descriptive, and contextual—explaining not just what the image shows, but why it matters to the surrounding content. Avoid keyword stuffing; instead, write naturally as if describing the image to someone who can’t see it. Here’s how weak and strong alt text compare:
| Weak Alt Text | Strong Alt Text | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| “chart” | “Bar chart showing Q4 SaaS revenue growth of 25% year-over-year” | Provides specificity, context, and measurable data |
| “image of woman” | “Woman using laptop for remote work productivity training” | Adds intent and relevance to the surrounding topic |
| “product photo” | “Blue running shoe with cushioned sole design, front view” | Descriptive, specific, and helps AI understand product details |
| “screenshot” | “HubSpot dashboard displaying customer relationship management pipeline” | Identifies the tool and its function for AI systems |
When alt text is vague or generic, AI systems struggle to understand the image’s relevance to your content, reducing the likelihood of inclusion in AI-generated answers.
Structured data acts as a signal to AI systems about the importance and context of your images. By implementing ImageObject schema markup, you explicitly tell search engines and AI systems that an image is significant and should be prioritized. This markup should include properties like contentUrl (the image URL), caption (a brief description), description (more detailed context), and representativeOfPage (indicating if this is the primary image for the page). Here’s an example in JSON-LD format:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "ImageObject",
"contentUrl": "https://example.com/dashboard-screenshot.jpg",
"caption": "HubSpot CRM dashboard showing sales pipeline",
"description": "Screenshot of HubSpot's customer relationship management interface displaying active deals, pipeline stages, and revenue forecasting",
"representativeOfPage": true,
"name": "CRM Dashboard Interface"
}
When properly implemented, schema markup increases the likelihood of your images appearing in rich snippets, AI Overviews, and featured content sections. Early adopters of ImageObject schema reported a 13% lift in click-through rates from AI-generated answer placements within weeks of implementation.
Captions and surrounding text provide crucial context that helps AI systems understand why an image matters. A well-written caption (40–80 words) should explain the insight or takeaway the image provides, reinforcing the same topic or keyword family as the nearby copy. AI systems analyze not just the image itself, but the entire content ecosystem around it—headings, paragraphs, lists, and captions all contribute to how the system interprets visual relevance. When an image appears immediately after a heading about “remote work productivity” and is accompanied by a caption explaining how the tool improves team collaboration, AI systems can confidently associate that visual with the intended topic. Placement matters too; images buried in sidebars or carousels receive less weight than those positioned near primary content. By treating captions as part of your SEO strategy rather than optional decoration, you significantly improve how AI systems understand and surface your visual content.
Beyond metadata, the technical properties of your images directly impact AI visibility and page performance. Modern image formats like WebP and AVIF reduce file sizes by 15–21% compared to traditional JPEG, improving Core Web Vitals—a ranking factor for both traditional search and AI systems. Compress images using tools like TinyJPG or Google Squoosh without sacrificing quality. Always set explicit width and height attributes in your HTML to prevent layout shifts, which negatively impact user experience and AI evaluation. Ensure high contrast and readable on-image text for accessibility and OCR (optical character recognition) accuracy. Mobile responsiveness is non-negotiable; test images on various devices to confirm they display correctly and remain legible on small screens.
Key technical optimization steps:
Not all images are created equal in the eyes of AI systems. Charts with clear labels are highly favored because they distill complex data into machine-readable formats. Infographics that summarize key statistics or processes are frequently cited in AI-generated answers because they organize information visually in ways that align with how AI systems extract and present data. Annotated product photos—images with labels, arrows, or overlays highlighting specific features—help AI systems understand product details and variations. Custom diagrams with branded elements outperform generic stock images because they’re unique and easier for AI to associate with your brand and content. Screenshots of dashboards, interfaces, or tools are particularly valuable for SaaS and software companies, as they provide concrete evidence of functionality. The common thread: AI systems prefer visuals that communicate information clearly and efficiently, without requiring interpretation or guesswork.
Most brands still treat image optimization as an afterthought, leading to preventable visibility losses. Stuffed or generic alt text like “image of marketing dashboard” or “AI trends infographic 2025” provides no meaningful context to AI systems. Reusing the same image and identical alt text across multiple pages confuses crawlers about which page should rank for that visual. Background images hidden in CSS or lazy-loaded without fallback code are never indexed. Missing captions or weak surrounding text waste opportunities to reinforce relevance. Lack of schema markup means AI systems must guess at image importance. Poor file handling—huge uncompressed PNGs, missing width/height attributes, or outdated formats—slows pages and hurts Core Web Vitals. Perhaps most critically, treating visuals as filler content signals to both humans and machines that your content isn’t serious.
Here’s how to fix these mistakes:
<img> tags for important visuals instead of CSS backgroundsOptimizing images one at a time doesn’t scale. Instead, build systems that make optimization automatic and consistent. Template-based design ensures every new image includes metadata slots for alt text, captions, and filenames before creation. AI-assisted workflows can generate baseline alt text and captions in bulk, which human editors then review and refine—balancing speed with accuracy. For large image libraries, export your image inventory (URLs, filenames, alt text, captions) from your CMS or DAM, then use spreadsheets or BI tools to identify gaps and prioritize high-value pages for remediation. Implement quality control checklists that verify alt text presence, schema markup, compression, and mobile responsiveness before publishing. Automation tools and APIs can sync improved metadata back into your CMS, ensuring consistency across your entire content ecosystem. The goal is to make optimization a default behavior, not an optional extra step.
Image optimization only matters if it drives measurable results. Start by tracking AI Overview citations—how often your images appear in AI-generated answers—using tools like AmICited.com, which monitors how AI systems reference your visual content across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Monitor image search impressions in Google Search Console to see if optimization efforts increase visibility. Measure organic click-through rate (CTR) changes on pages with optimized images compared to control groups. Link these metrics to business outcomes: track conversion rates, average order value, and revenue from pages with upgraded visuals. Use UTM parameters to tag traffic from AI platforms so you can isolate the impact in Google Analytics. Over time, you’ll identify which image types, formats, and optimization approaches drive the most value for your specific audience and business model. This feedback loop transforms image optimization from a checklist item into a data-driven growth lever.
Alt text should be between 80-125 characters, descriptive and contextual. Write naturally as if describing the image to someone who can't see it. Avoid keyword stuffing; instead, focus on clarity and relevance to the surrounding content. AI systems prefer concise, meaningful descriptions over generic labels.
Alt text is an HTML attribute that describes the image for accessibility and AI understanding, typically 80-125 characters. Captions are visible text below or near the image (40-80 words) that explains why the image matters. Both serve different purposes: alt text helps AI parse the image, while captions help both humans and AI understand its relevance to the content.
AI tools can generate baseline alt text quickly, but human review is essential. AI-generated descriptions are often too simplistic or lack context. Use AI to speed up the process, then have editors refine the text to ensure it captures the full meaning and purpose of the image. This hybrid approach balances efficiency with quality.
Image optimization affects both traditional and AI search, but in different ways. For traditional SEO, images help with rankings through alt text and schema markup. For AI search, images are directly cited in AI-generated answers when properly optimized. AI systems are 4.4x more valuable than traditional organic visitors, making image optimization critical for visibility in answer engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Modern formats like WebP and AVIF are preferred because they reduce file sizes by 15-21% compared to JPEG, improving Core Web Vitals and page load speed. AI systems favor fast-loading pages, and these formats help. Use WebP as a primary format with JPEG fallbacks for older browsers. AVIF offers even better compression but has less browser support. Always prioritize performance alongside format choice.
Conduct a comprehensive audit at least quarterly, focusing on high-traffic pages and key landing pages first. For ongoing maintenance, implement quality control checklists before publishing new content to ensure alt text, captions, schema markup, and file optimization are always included. Use tools like Lighthouse or Screaming Frog to detect missing metadata or performance issues automatically.
Yes, significantly. Uncompressed images, missing width/height attributes, and outdated formats slow pages and hurt Core Web Vitals—a ranking factor for both traditional and AI search. Optimized images with proper dimensions, modern formats (WebP/AVIF), and compression improve load times. This creates a win-win: better user experience and improved AI visibility.
Use AmICited.com to monitor how often your images appear in AI-generated answers across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Track image search impressions in Google Search Console, measure organic CTR changes on optimized pages, and link these metrics to business outcomes like conversions and revenue. Use UTM parameters to isolate traffic from AI platforms in Google Analytics.
Track image citations in AI overviews, GPTs, and Perplexity with AmICited. Measure the impact of your image optimization efforts and identify which visuals drive AI visibility.
Learn how images impact your brand's visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover optimization strategies for AI-powered answe...
Learn how technology companies optimize content for AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover strategies for AI visibility, structured da...
Learn how to optimize keywords for AI search engines. Discover strategies to get your brand cited in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI answers with actionable ...