
AI Visibility Futures
Explore AI Visibility Futures - forward-looking analysis of emerging trends in AI-driven brand discovery. Learn how brands will be discovered by AI systems and ...
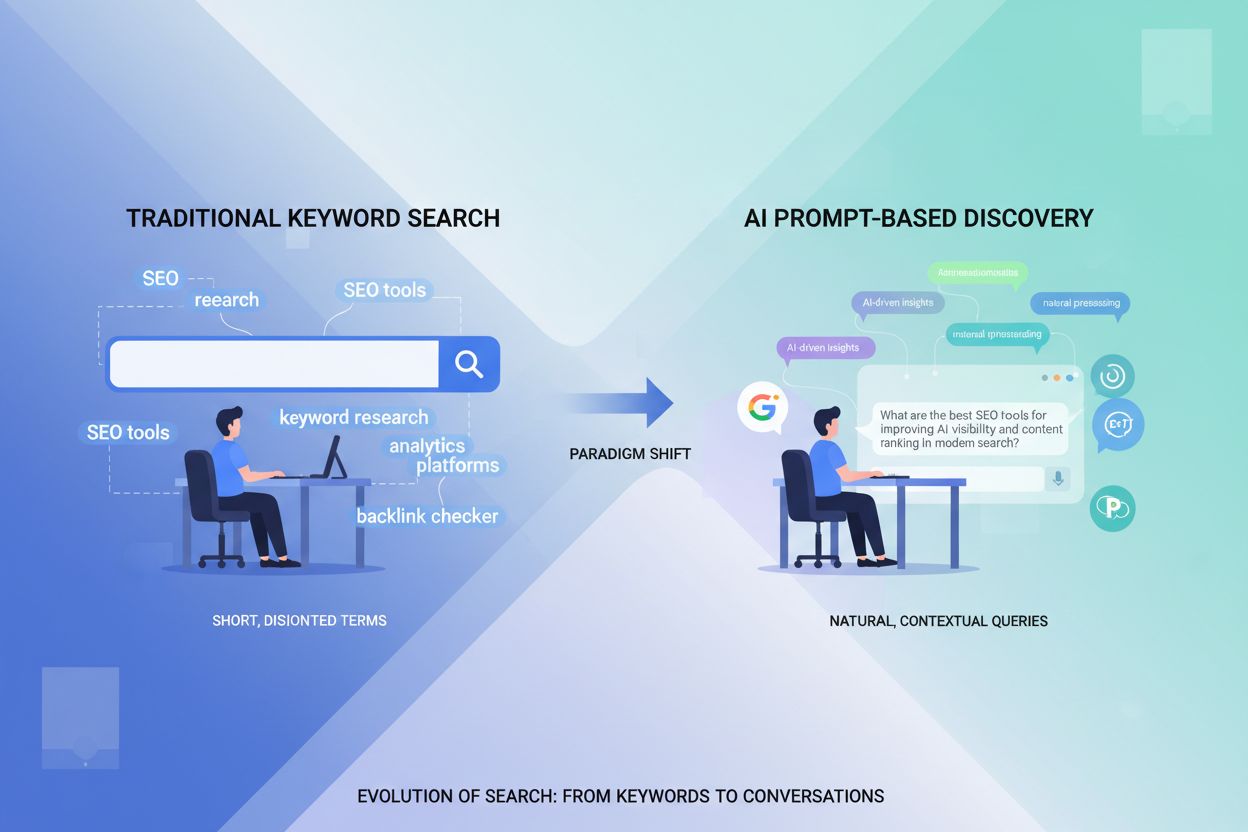
Discover how prompt research is replacing traditional keyword research in AI-driven search. Learn the methodology differences and optimize your content for generative engines like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
The way people discover information online is undergoing a seismic transformation. 13.14% of Google queries now trigger AI Overviews, fundamentally changing how search results are generated and presented. Meanwhile, ChatGPT has exploded from 100 million users in October 2023 to 800 million users by April 2025—an 8x increase in just 18 months—signaling that generative AI has moved from novelty to mainstream discovery tool. Consider the difference: a decade ago, someone searching for marketing advice might type “content marketing tips,” but today they’re more likely to ask ChatGPT, “I’m a B2B SaaS company with a $50K monthly marketing budget and no brand awareness. What’s the most cost-effective content strategy to generate qualified leads in the next 90 days?” This shift from fragmented keywords to detailed, conversational prompts represents a fundamental change in how discovery works, and brands that don’t adapt their content strategy will find themselves invisible in the AI-driven search landscape.

Keywords and prompts are fundamentally different tools for different discovery mechanisms. Keywords are short phrases—typically 2 to 5 words—that are fragmented and list-like, with minimal context provided to the search engine. They’re optimized for traditional search algorithms that match keywords to indexed pages. Prompts, by contrast, are longer, conversational inputs (often 10–25 words or more) written in natural language with detailed context and explicit intent. A user doesn’t just type “AI monitoring”; they ask, “How can I track whether my company’s research is being cited in ChatGPT responses?” The distinction matters because each is optimized for a different system: keywords for search engines, prompts for large language models. Here’s how they compare across key dimensions:
| Dimension | Keywords | Prompts |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 2–5 words | 10–25 words |
| Style | Fragmented, list-like | Conversational, full-sentence |
| Context | Minimal or implied | Detailed and explicit |
| Intent | Often inferred | Clearly stated |
| User Behavior | Search-focused | Conversational or task-based |
| Optimized For | Search engine algorithms | LLMs and AI interfaces |
| Goal | Match pages to queries | Generate answers or complete tasks |
Understanding this distinction is critical for modern content strategy, as the same piece of content may need to perform well for both keyword searches and prompt-based discovery.
Large language models don’t process prompts the way search engines process keywords—they read them more like a narrative, weighing context, flow, and explicit instructions. Understanding how LLMs interpret prompts is essential for optimizing content visibility in generative AI systems. Here are the eight key interpretation methods that drive how AI systems understand and respond to user input:
Compare a vague prompt (“Tell me about SEO”) with a clear one (“I’m optimizing a B2B SaaS website for AI search visibility. What are the top 5 on-page SEO factors that help content get cited in ChatGPT responses?”). The second prompt gives the AI explicit context, clear intent, and specific constraints—all of which produce dramatically better, more actionable responses.
Prompts have become the dominant discovery mechanism in generative AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity because they fundamentally align with how these systems are designed to work. Unlike traditional search engines that return a list of links, generative engines synthesize information into answers, and prompts are the ideal input format for that synthesis. Here’s why prompts outperform keywords in AI-driven discovery:
The result is that content optimized for prompt-based discovery—content that answers detailed, contextual questions—will increasingly dominate visibility in generative AI systems.
Optimizing content for prompt-based discovery requires a fundamentally different approach than traditional keyword SEO. Instead of targeting short phrases, you’re now creating content that answers the detailed, contextual questions users ask AI systems. Here are ten actionable strategies to optimize your content for prompt-first discovery:
Create Content That Mirrors Real Prompts — Write content that directly answers the kinds of detailed, multi-part questions users ask AI. If users ask “What’s the best AI monitoring tool for tracking brand citations?”, create content that comprehensively answers that exact question.
Add Context Everywhere — Don’t assume readers know your industry, company stage, or use case. Provide context upfront: “For B2B SaaS companies with $50K+ annual marketing budgets…” This helps AI systems match your content to specific user scenarios.
Use Clear Structure (HTML + Schema) — Use semantic HTML and schema markup to make content structure explicit. H2s, H3s, lists, and tables help both AI systems and users navigate your content.
Focus on Explicit Intent, Not Implied Topics — Instead of writing about “AI tools,” write about “How to monitor whether your research is cited in ChatGPT responses.” Explicit intent matches how users phrase prompts.
Seed with Real-Life Scenarios — Start sections with realistic user scenarios. “Imagine you’re a marketing director who just launched a new product…” helps AI systems understand the context and intent behind your content.
Strengthen Internal Signals — Link related content with descriptive anchor text. “Learn how to track AI citations across multiple platforms” is better than “read more.” This helps AI systems understand content relationships.
Quote Experts or Trusted Sources — Include direct quotes from industry experts and cite authoritative sources. AI systems weight expert opinions heavily when generating responses.
Include Useful, Shareable Stats — Data points and statistics are frequently cited in AI-generated responses. Include original research, benchmarks, and statistics that AI systems will want to reference.
Think in Snippets — Structure content so key insights can stand alone. AI systems often extract snippets from longer content, so make sure your most important points are clear and concise.
Keep Testing with AI Tools — Regularly test your content by asking ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity questions related to your topic. See if your content gets cited, and if not, identify what’s missing.

While prompts have become the dominant discovery mechanism, keywords haven’t become obsolete—they’ve simply evolved into a different role. Keywords now function as anchors within prompts, helping AI systems focus on the most relevant information. Rather than being the primary discovery mechanism, keywords are now embedded within longer, more contextual prompts. Here’s how keywords continue to matter:
The key insight is that keywords are still important—they’re just used differently. Instead of being the primary optimization target, they’re now supporting elements within a larger, prompt-optimized content strategy.
The difference between keyword and prompt optimization becomes clear when you compare how the same topic performs across different discovery mechanisms. Consider the keyword “SEO tools” versus the prompt “What are the best SEO tools for improving AI search visibility?” The keyword is broad and competitive, while the prompt is specific and intent-driven. Here’s how they differ across key dimensions:
| Dimension | “SEO tools” (Keyword) | “What are the best SEO tools for improving AI search visibility?” (Prompt) |
|---|---|---|
| Search Intent | Broad, informational intent | Specific, decision-oriented intent |
| Competition & Search Volume | High volume, high competition | Lower volume but higher conversion |
| Content Strategy | Requires broad coverage of all SEO tools | Focus on AI-specific SEO factors and tool comparisons |
| User Engagement | Attracts early-stage researchers | Engages high-intent users ready to make decisions |
| AI Search Visibility | Ranked via keyword match | Recognized by generative engines as directly answering the prompt |
The keyword “SEO tools” might rank well in traditional search, but it attracts a broad audience with varying needs. The prompt-based query attracts users with specific intent—they want to improve AI visibility—and content optimized for that prompt will be cited directly in AI-generated responses. Long-form, prompt-optimized content performs better in generative engines because it provides the detailed context and explicit intent that AI systems need to generate accurate, relevant answers. A single piece of content that comprehensively answers the prompt-based query will be cited more frequently in AI responses than a generic “SEO tools” article, even if the latter ranks higher in traditional search.
As content discovery shifts from keywords to prompts, tracking your brand’s visibility in AI-generated responses becomes critical. AmICited.com specializes in monitoring how your content and research are cited across generative AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity—the exact systems where prompt-based discovery is happening. By using AmICited, you can identify visibility gaps in AI search, understand which of your content pieces are being cited most frequently, and discover the specific prompts that trigger your citations. This insight is invaluable for refining your content strategy: if certain topics consistently get cited while others don’t, you can adjust your approach to match what AI systems are actually surfacing. Rather than guessing whether your content is visible in the AI-driven discovery landscape, AmICited gives you concrete data on how your brand performs across generative engines—enabling you to optimize for prompt-based discovery with confidence and precision.
Keyword research focuses on short phrases (2-5 words) that users type into search engines, while prompt research analyzes longer, conversational queries (10-25+ words) that users submit to AI systems like ChatGPT and Gemini. Keywords are fragmented and minimal in context, whereas prompts are detailed and explicit about user intent. Prompt research is essential for optimizing content visibility in generative AI platforms.
Prompts are becoming dominant because AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity are designed to synthesize answers from detailed context, not match keywords to pages. Prompts provide the full story, explicit intent, and detailed constraints that LLMs need to generate accurate, relevant responses. As AI-driven discovery grows (13.14% of Google queries now trigger AI Overviews), optimizing for prompts is critical for visibility.
Optimize for prompts by creating content that mirrors real user questions, adding context throughout, using clear HTML structure and schema markup, focusing on explicit intent rather than implied topics, seeding content with real-life scenarios, strengthening internal signals with descriptive links, quoting experts, including shareable statistics, thinking in snippets, and continuously testing your content in ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Yes, keywords still matter—they've just evolved into a different role. Keywords now function as anchors within longer prompts, helping AI systems focus on relevant information. They guide AI focus, reduce ambiguity, enhance contextual relevance, and improve traditional search visibility. The key is embedding keywords within detailed, prompt-optimized content rather than treating them as the primary optimization target.
Use AmICited.com to monitor how your content and research are cited across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other generative AI platforms. AmICited provides concrete data on which of your content pieces are being cited, the specific prompts that trigger your citations, and visibility gaps in AI search. This insight helps you refine your content strategy based on actual AI performance.
Effective prompts include: explicit role framing (who the AI should act as), clear context and background (who is asking, why, what stage they're at), explicit intent (not just topic), formatting instructions (desired output format), constraints (limits that force conciseness), narrative flow (logical progression), and examples (few-shot prompting). Structure your content to answer these detailed, multi-part prompts directly.
AmICited specializes in tracking how your content performs across generative AI platforms. It shows you which prompts trigger your citations, how frequently your content appears in AI responses, and which topics get cited most. This data reveals what AI systems are actually surfacing, enabling you to optimize your content strategy with precision and confidence.
Track citation frequency (how often your content appears in AI responses), citation sources (which AI platforms cite you), prompt patterns (what types of questions trigger your citations), engagement metrics (time on page, scroll depth), and competitive positioning (how you compare to competitors in AI responses). AmICited provides dashboards for all these metrics, helping you measure and improve your AI search visibility.
Track how your content and research are cited across ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and other AI platforms. Get real-time insights into your AI search visibility and identify optimization opportunities.

Explore AI Visibility Futures - forward-looking analysis of emerging trends in AI-driven brand discovery. Learn how brands will be discovered by AI systems and ...
Discover how AI visibility is reshaping marketing success. Learn why citations matter more than clicks, how to measure AI visibility, and why your brand's prese...
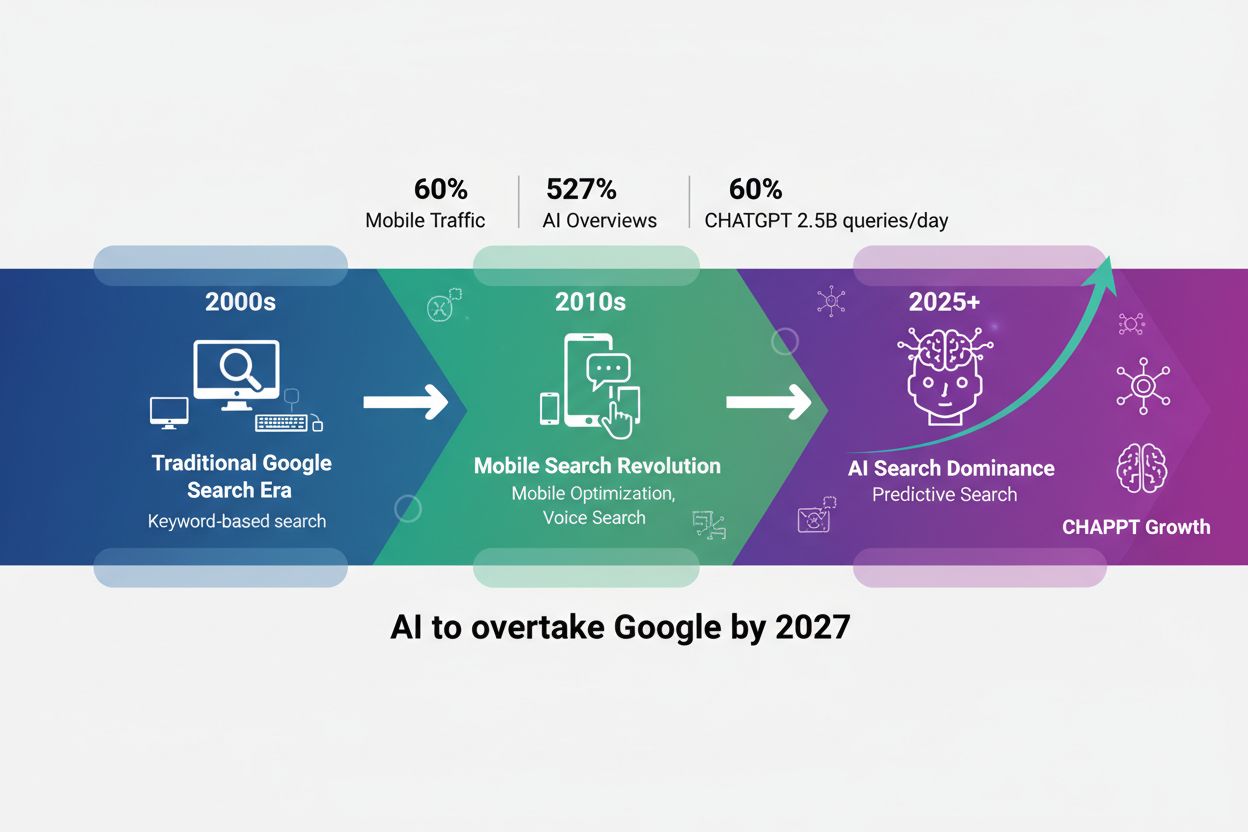
Discover how AI search is reshaping SEO. Learn the key differences between AI platforms like ChatGPT and traditional Google search, and how to optimize your con...