
The Truth About LLMs.txt: Overhyped or Essential?
Critical analysis of LLMs.txt effectiveness. Discover whether this AI content standard is essential for your site or just hype. Real data on adoption, platform ...

Learn what LLMs.txt is, whether it actually works, and if you should implement it on your website. Honest analysis of this emerging AI SEO standard.
LLMs.txt is a proposed web standard designed to give website owners a way to communicate directly with artificial intelligence systems about how their content should be used and interpreted. Introduced by Jeremy Howard of Answer.AI in September 2024, it functions similarly to robots.txt but is specifically tailored for AI applications rather than search engine crawlers. The file is written in Markdown format and placed at the root of a website’s domain, making it easily discoverable by AI systems that choose to respect it. The core problem LLMs.txt attempts to solve is the lack of standardized communication between content creators and AI platforms—website owners currently have no reliable mechanism to specify preferences about how their content is processed, cited, or used in AI training and inference. Unlike robots.txt, which has been widely adopted and respected for decades, LLMs.txt represents an emerging attempt to establish similar conventions in the AI era. This standard reflects growing concerns from content creators about AI systems using their work without clear attribution or permission frameworks.
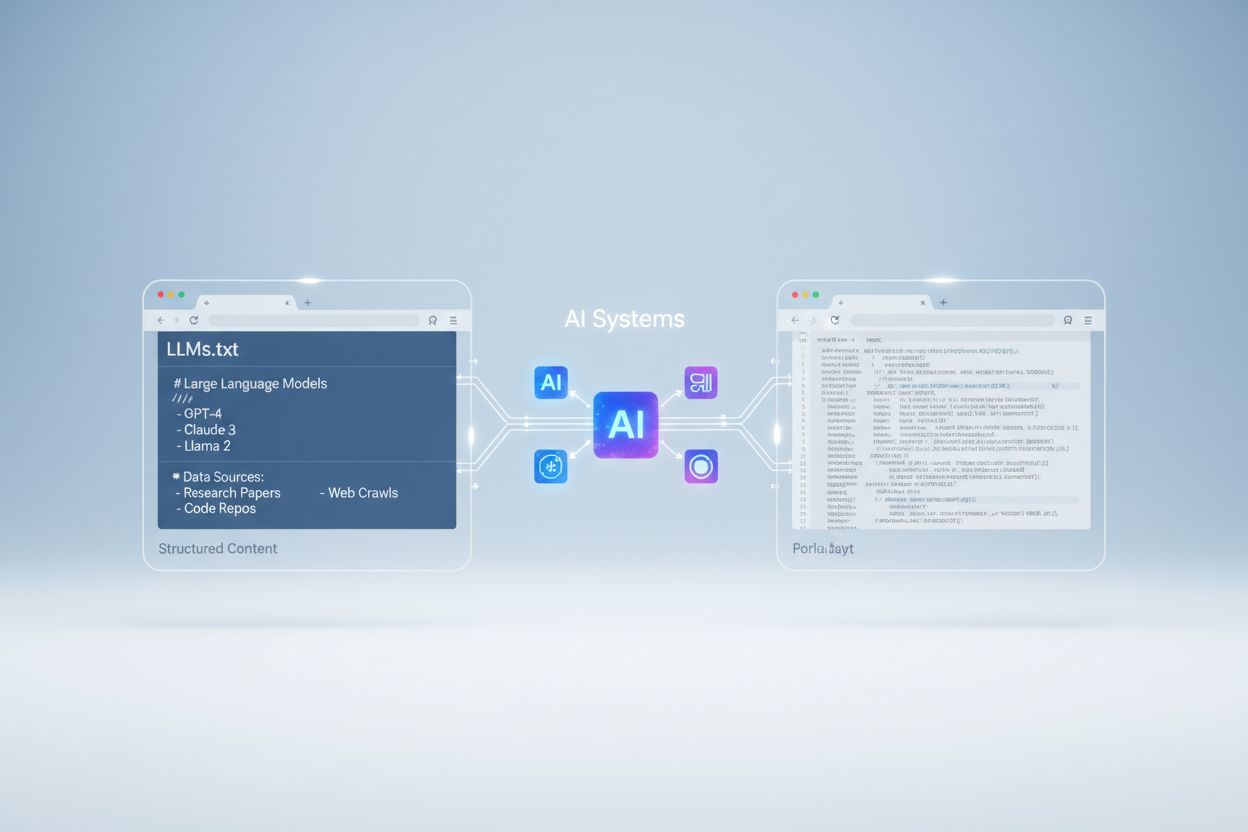
LLMs.txt is placed at the root directory of a website (e.g., example.com/llms.txt) and uses a structured Markdown format to communicate preferences to AI systems. The file typically includes an H1 title, a blockquote summary of its purpose, and detailed sections organized with H2 headers that specify different content categories and usage guidelines. Unlike robots.txt, which uses a simple text-based syntax with specific rules and directives, LLMs.txt leverages Markdown’s flexibility to allow more nuanced and human-readable instructions. It also differs from XML sitemaps, which are primarily designed to help search engines discover and prioritize content for indexing. The key distinction is that LLMs.txt is meant to communicate intent and preferences rather than simply listing available content or blocking access. Website owners can specify which content should be prioritized for AI training, which should be excluded, and how their work should be attributed when used by AI systems.
| File Type | Purpose | Audience | Format | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLMs.txt | Communicate AI usage preferences | AI systems & LLMs | Markdown | Voluntary compliance |
| robots.txt | Control crawler access & indexing | Search engines | Text-based directives | Widely respected standard |
| XML Sitemaps | Prioritize content discovery | Search engines | XML structure | Improves indexing efficiency |
Despite its introduction over a year ago, no major AI platform—including OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, or Meta—has implemented support for LLMs.txt in their systems. Google’s John Mueller confirmed that the company does not consider LLMs.txt necessary for its operations, suggesting that established AI platforms see limited incentive to adopt the standard. This lack of adoption has created a misinformation loop where some SEO tools and content creators promote LLMs.txt as an essential practice, while the reality remains that it has virtually no practical impact on how AI systems currently process content. The reasons why major AI platforms may avoid implementing LLMs.txt support include:
This disconnect between promotion and reality underscores the challenges of establishing new web standards without broad industry consensus.
If major AI platforms were to adopt and respect LLMs.txt standards, the benefits for content creators could be substantial. Website owners would gain greater control over how their content is interpreted and used by AI systems, potentially leading to better attribution practices and more accurate representation of their work in AI-generated outputs. From an AI system perspective, respecting LLMs.txt could improve content comprehension by providing explicit context about a website’s purpose, structure, and intended use cases, potentially leading to more accurate and relevant AI responses. Resource optimization would also improve, as AI systems could prioritize high-quality, explicitly-approved content over scraping indiscriminately across the web. Additionally, implementing LLMs.txt could serve as a form of future-proofing for digital presence, establishing clear preferences before more sophisticated AI systems emerge that might respect such standards. For organizations concerned about AI usage of their content, having a standardized mechanism to communicate preferences—even if currently unenforced—represents a step toward more transparent AI practices.
Creating an LLMs.txt file is straightforward and requires no technical expertise beyond basic file creation. Several popular SEO tools now offer built-in LLMs.txt generators, including AIOSEO, Rank Math, Yoast, and Squirrly, making the process accessible to website owners using these platforms. For those implementing manually, the basic structure involves creating a Markdown file with an H1 title (typically “# LLMs.txt”), a blockquote explaining the file’s purpose, and H2-organized sections that detail content categories and usage preferences. The file should be saved as “llms.txt” and uploaded to the root directory of your domain, making it accessible at yourdomain.com/llms.txt. For developers preferring command-line tools, the llms_txt2ctx CLI tool provides an alternative method for generating and managing LLMs.txt files. Best practices for implementation include being specific about which content types should be prioritized, clearly stating attribution requirements, and regularly reviewing and updating the file as your content strategy evolves. While implementation is simple, remember that effectiveness depends entirely on AI platforms choosing to respect the standard.
The question of whether to implement LLMs.txt has sparked genuine debate within the SEO and content creation communities, with thoughtful perspectives on both sides. Squirrly takes a cautious, honest approach—acknowledging that while LLMs.txt is easy to implement, it currently provides no measurable benefits since no major AI platforms respect it. Rank Math, conversely, takes a more optimistic stance, positioning LLMs.txt as a forward-looking best practice that content creators should adopt in anticipation of future adoption. The practical reality is that implementing LLMs.txt won’t hurt your website or SEO performance, but it also won’t provide immediate, tangible benefits in how AI systems currently process your content. For most website owners, time and resources are better spent on proven SEO fundamentals—quality content creation, technical SEO optimization, proper internal linking, and mobile responsiveness—which have demonstrated, measurable impacts on visibility and traffic. That said, LLMs.txt represents a reasonable hedge for organizations deeply concerned about AI usage of their content, offering a way to document preferences even if those preferences aren’t currently enforced. The balanced perspective is to implement it if you have the tools and time, but not to prioritize it over core SEO and content strategies.
AmICited.com serves as a verification and monitoring platform for how AI systems cite and use content across the web, making it a natural complement to LLMs.txt implementation. While LLMs.txt allows you to communicate preferences to AI systems, AmICited enables you to monitor whether those preferences are being respected and how your content is actually being used in AI-generated outputs. The platform helps content creators track citations, verify attribution accuracy, and understand the broader landscape of AI content usage—providing data-driven insights into whether your LLMs.txt guidelines are having any practical effect. By using AmICited.com alongside LLMs.txt, organizations can establish a complete monitoring framework: setting preferences through LLMs.txt while simultaneously tracking real-world AI citation patterns through AmICited’s verification tools. This combination allows you to measure the effectiveness of your LLMs.txt implementation and adjust your strategy based on actual AI behavior rather than assumptions. As AI platforms potentially evolve to respect LLMs.txt standards, AmICited will become increasingly valuable for verifying compliance and ensuring your content preferences are being honored.
The trajectory of LLMs.txt remains uncertain, but the underlying conversation it represents—about AI systems’ responsibility to respect content creators’ preferences—will likely continue evolving. Community efforts to refine and promote the standard are ongoing, with various stakeholders working to demonstrate its value and encourage adoption among major AI platforms. The next critical milestone will be whether any significant AI company implements LLMs.txt support, which could trigger broader adoption across the industry. Until that happens, LLMs.txt exists in a liminal space: technically sound and easy to implement, but practically ineffective due to lack of platform support. Content creators should monitor official sources and industry developments to stay informed about any shifts in AI platform adoption, as the landscape could change relatively quickly if major players decide the standard serves their interests. For now, LLMs.txt is best viewed as an emerging standard with potential future relevance rather than an immediately essential practice. The honest assessment is to keep it on your radar, implement it if convenient, but remain focused on proven strategies while the AI and content creation landscape continues to mature and stabilize.
LLMs.txt is a proposed web standard file placed at the root of a website (example.com/llms.txt) that allows website owners to communicate preferences to AI systems about how their content should be used and interpreted. Introduced in September 2024 by Jeremy Howard of Answer.AI, it functions similarly to robots.txt but is specifically designed for AI applications rather than search engine crawlers.
No. Despite being proposed over a year ago, no major AI platform—including OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, or Meta—has implemented support for LLMs.txt. Google's John Mueller confirmed that the company does not consider it necessary. This lack of adoption means LLMs.txt currently has no practical impact on how AI systems process your content.
No, implementing LLMs.txt will not directly improve your SEO rankings. Since no major AI platforms currently respect the standard, it has no measurable impact on search visibility or AI-powered search results. However, it could become valuable in the future if major AI platforms decide to adopt and respect the standard.
Creating an LLMs.txt file is straightforward and requires no technical expertise. Several popular SEO tools including AIOSEO, Rank Math, Yoast, and Squirrly offer built-in LLMs.txt generators that can create the file with just a few clicks. You can also create one manually using a simple Markdown format and upload it to your website's root directory.
No. Time and resources are better spent on proven SEO fundamentals like quality content creation, technical SEO optimization, proper internal linking, and mobile responsiveness. These have demonstrated, measurable impacts on visibility and traffic. Implement LLMs.txt only if you have the tools and time available after addressing core SEO priorities.
Use tools like AmICited.com to track how AI systems cite and use your content across the web. AmICited monitors AI citations and provides data-driven insights into whether your LLMs.txt guidelines are having any practical effect on how AI systems represent your content.
These three files serve different purposes: robots.txt controls crawler access and indexing for search engines, XML sitemaps list URLs for search engines to discover and prioritize, and LLMs.txt communicates preferences to AI systems about content usage. They complement each other in managing how different automated systems interact with your website.
It depends on your perspective. Implementing LLMs.txt won't hurt and is easy with modern tools, but it currently provides no measurable benefits since no major AI platforms respect it. It's best viewed as a low-effort hedge for future-proofing your digital presence, but not as an immediately essential practice.
Track how AI systems cite and use your content across the web. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and content attribution.

Critical analysis of LLMs.txt effectiveness. Discover whether this AI content standard is essential for your site or just hype. Real data on adoption, platform ...
Learn how to implement LLMs.txt on your website to help AI systems understand your content better. Complete step-by-step guide for all platforms including WordP...

Learn how to configure robots.txt to control AI crawler access including GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and Perplexity. Manage your brand visibility in AI-generated answers...