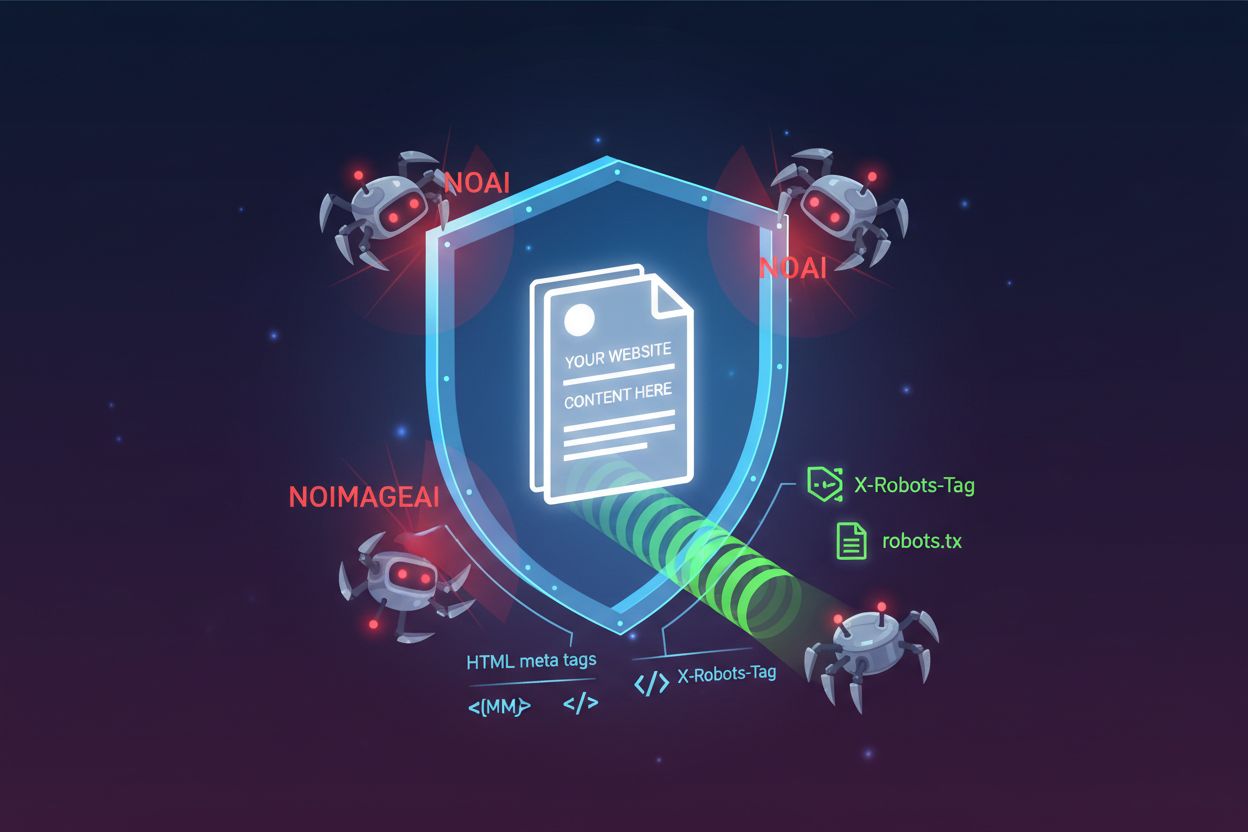
NoAI Meta Tags: Controlling AI Access Through Headers
Learn how to implement noai and noimageai meta tags to control AI crawler access to your website content. Complete guide to AI access control headers and implem...
Discover how meta tags have evolved for AI-driven search. Learn which meta tags matter most for AI optimization, visibility in AI Overviews, and practical strategies to improve your search rankings.
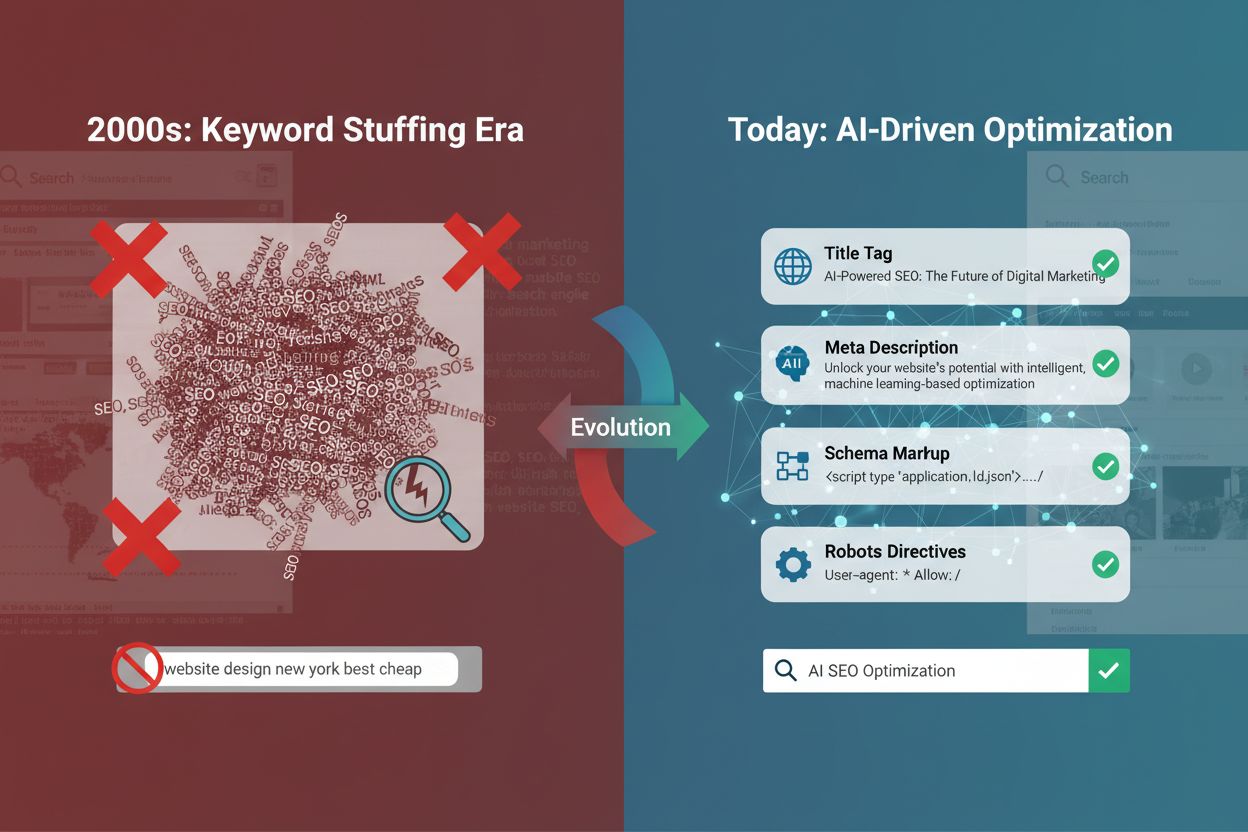
Meta tags have undergone a dramatic transformation over the past two decades, evolving from simple keyword repositories to sophisticated signals that help AI systems understand content context and relevance. In the early days of SEO, keyword stuffing in meta tags was the norm—marketers would cram dozens of keywords into title tags and meta descriptions with little regard for user experience or accuracy. Today’s AI-driven SEO (AIEO) landscape demands a fundamentally different approach, where meta tags serve as bridges between human-readable content and machine learning algorithms that power search engines and AI Overviews. Rather than deceiving search engines, modern meta tags must accurately represent content while being optimized for both human readers and AI systems that increasingly determine search visibility. The shift reflects a broader industry recognition that semantic understanding and entity recognition matter far more than keyword density, fundamentally changing how we approach meta tag optimization.
Every website requires a foundational set of meta tags to function effectively in today’s AI-powered search environment, each serving distinct purposes that impact both visibility and user engagement. The most critical meta tags include the title tag, which appears in search results and browser tabs; the meta description, which provides a preview of your content; the robots meta tag, which controls how search engines and AI systems interact with your pages; and the viewport meta tag, which ensures proper display on mobile devices. Beyond these essentials, canonical tags prevent duplicate content issues, Open Graph tags enhance social sharing, and schema markup provides structured data that AI systems use to better understand your content. Each of these tags plays a specific role in the AI-driven search ecosystem, and neglecting any one of them can result in missed opportunities for visibility and engagement. The following table outlines the key meta tags, their purposes, and their impact on AI systems:
| Meta Tag Type | Purpose | AI Impact | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Title Tag | Appears in search results and browser tabs | Critical for AI understanding of page topic and relevance | 50-60 characters, include primary keyword, brand name at end |
| Meta Description | Provides content preview in search results | Influences CTR and helps AI understand content intent | 150-160 characters, include call-to-action, natural language |
| Robots Meta Tag | Controls search engine and AI crawler behavior | Prevents AI systems from indexing or using content inappropriately | Use noindex for duplicate/thin content, nofollow for untrusted links |
| Viewport Meta Tag | Ensures mobile responsiveness | Critical for mobile-first indexing and AI ranking | width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0 |
| Canonical Tag | Specifies preferred version of duplicate content | Helps AI consolidate ranking signals to correct URL | Point to self for unique pages, to original for duplicates |
| Schema Markup | Provides structured data about content | Essential for AI understanding of entities, products, articles | Use JSON-LD format, implement relevant schemas |
| Open Graph Tags | Controls social media sharing appearance | Impacts social signals and AI understanding of content value | Include og:title, og:description, og:image, og:url |
Title tags remain one of the most important ranking factors in AI-driven search, yet their optimization has shifted from keyword-focused to intent-focused and user-centric approaches. A well-optimized title tag should be between 50-60 characters to display fully in search results, include your primary keyword naturally, and communicate clear value to both users and AI systems. Research shows that optimized title tags can increase click-through rates by up to 27%, particularly when they address user intent and include compelling modifiers like “2024,” “Guide,” or “Best.” Meta descriptions, while not a direct ranking factor, significantly impact CTR and should be 150-160 characters, written in natural language that encourages clicks, and include a subtle call-to-action when appropriate.
Before optimization: “SEO Services | Digital Marketing Agency” After optimization: “Professional SEO Services for Small Businesses | Increase Rankings 2024”
The difference is stark—the optimized version includes the primary keyword, a benefit statement, and a timely modifier that appeals to both users and AI systems. Meta descriptions should accurately summarize page content without misleading users, as AI systems increasingly evaluate whether the description matches the actual content. Including relevant entities and semantic keywords in both title tags and meta descriptions helps AI models understand your content’s context and relationship to broader topics. For e-commerce sites, research demonstrates that including pricing information in title tags can boost CTR by 23%, showing that specific, valuable information resonates with both users and AI algorithms.
The robots meta tag has become increasingly important in the AI era, as it provides explicit instructions about how search engines and AI systems should treat your content. This tag allows you to control whether pages are indexed, whether links are followed, and whether snippets can be displayed in search results—all critical considerations when AI systems are scraping content for training data and generating AI Overviews. Beyond the traditional noindex and nofollow directives, modern robots tags include AI-specific instructions that help you maintain control over how your content is used by large language models and AI systems.
Key robots directives include:
max-snippet:-1 for unlimited, max-snippet:160 for 160 characters)Implementing these directives correctly ensures that your content is used appropriately by AI systems while maintaining your visibility in traditional search results. The noai directive, in particular, is gaining importance as content creators seek to protect their intellectual property from being used to train large language models without permission or compensation.
Schema markup has evolved from a nice-to-have optimization to an essential component of AI-driven SEO, as it provides the structured data that AI systems need to understand your content’s meaning, context, and entities. Structured data in JSON-LD format tells search engines and AI systems exactly what your content is about—whether it’s a product, article, recipe, event, or organization—enabling more accurate indexing and representation in search results and AI Overviews. Without schema markup, AI systems must infer meaning from unstructured text, which is less reliable and can lead to misrepresentation or missed opportunities for visibility.
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Meta Tags for AI: What Still Matters",
"description": "Comprehensive guide to optimizing meta tags for AI-driven search",
"author": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "AmICited"
},
"datePublished": "2024-01-15",
"image": "https://example.com/image.jpg"
}
The most important schemas for modern SEO include Article (for blog posts and news), Product (for e-commerce), Organization (for company information), LocalBusiness (for location-based services), FAQPage (for frequently asked questions), and BreadcrumbList (for site navigation). Implementing these schemas correctly helps AI systems understand your content’s structure and context, improving your chances of appearing in AI Overviews and featured snippets. Schema markup also enables rich snippets in search results, which can increase CTR by providing additional information like ratings, prices, or availability directly in the search listing.
Open Graph tags and other social meta tags have become increasingly important for visibility and engagement, as they control how your content appears when shared on social media platforms and how AI systems evaluate your content’s social signals. When someone shares your article on Facebook, LinkedIn, or Twitter, the Open Graph tags determine what image, title, and description appear in the preview—directly impacting whether people click through to your content. The primary Open Graph tags you should implement include og:title (the title shown in social shares), og:description (the description shown in social shares), og:image (the image displayed in social shares), and og:url (the canonical URL of the page).
Beyond Open Graph, Twitter Card tags (twitter:card, twitter:title, twitter:description, twitter:image) provide similar functionality for Twitter/X, while LinkedIn tags ensure proper formatting on that platform. These social meta tags indirectly impact SEO by increasing social signals—shares, likes, and comments—which AI systems use as indicators of content quality and relevance. Optimizing social meta tags with compelling, click-worthy titles and high-quality images can significantly increase traffic from social platforms, which in turn signals to AI systems that your content is valuable and worth ranking higher.
Canonical tags solve one of the most persistent problems in modern web management: duplicate content that confuses search engines and dilutes ranking signals across multiple URLs. When you have multiple versions of the same content—such as a product page with different parameters, a blog post available in multiple languages, or content syndicated across multiple domains—canonical tags tell search engines which version is the “preferred” or “original” version that should receive ranking credit. Without proper canonical implementation, AI systems may struggle to understand which version is authoritative, potentially fragmenting your ranking signals and reducing visibility.
<!-- On the duplicate page, point to the original -->
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/original-page/">
<!-- On the original page, you can self-reference (optional but recommended) -->
<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/original-page/">
Canonical tags should always point to the version you want to rank, typically the original source or the version with the most complete information. For syndicated content, the original publisher should use a self-referential canonical tag, while syndicated versions should point back to the original. Implementing canonical tags correctly ensures that AI systems consolidate ranking signals to your preferred URL, improving your chances of ranking higher and preventing the dilution of authority across multiple versions of the same content.
Mobile optimization has become non-negotiable in the AI-driven search era, as Google’s mobile-first indexing means that AI systems primarily evaluate the mobile version of your site when determining rankings and generating AI Overviews. The viewport meta tag is the foundation of mobile optimization, telling browsers how to scale and display your content on different screen sizes. Without a properly configured viewport tag, your site may appear zoomed out or unreadable on mobile devices, leading to poor user experience and lower rankings from AI systems that prioritize mobile usability.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
This simple tag ensures that your content scales appropriately to the device width and doesn’t require horizontal scrolling. Beyond the viewport tag, mobile optimization includes responsive design, fast loading times, and touch-friendly navigation—all factors that AI systems evaluate when ranking pages. Mobile optimization also impacts how AI systems crawl and understand your content, as they increasingly use mobile user agents to evaluate pages. Ensuring that your viewport tag is correctly configured and that your site is fully responsive is essential for maintaining visibility in AI-driven search results.
Entity-based SEO represents a fundamental shift in how AI systems understand and rank content, moving beyond keyword matching to semantic understanding of the entities (people, places, things, concepts) mentioned in your content. AI systems like those powering Google’s AI Overviews use knowledge graphs and entity recognition to understand relationships between concepts, and your meta tags should reflect this entity-focused approach. By aligning your title tags, meta descriptions, and schema markup with entity-based SEO principles, you help AI systems understand not just what your content is about, but how it relates to broader topics and entities in your industry.
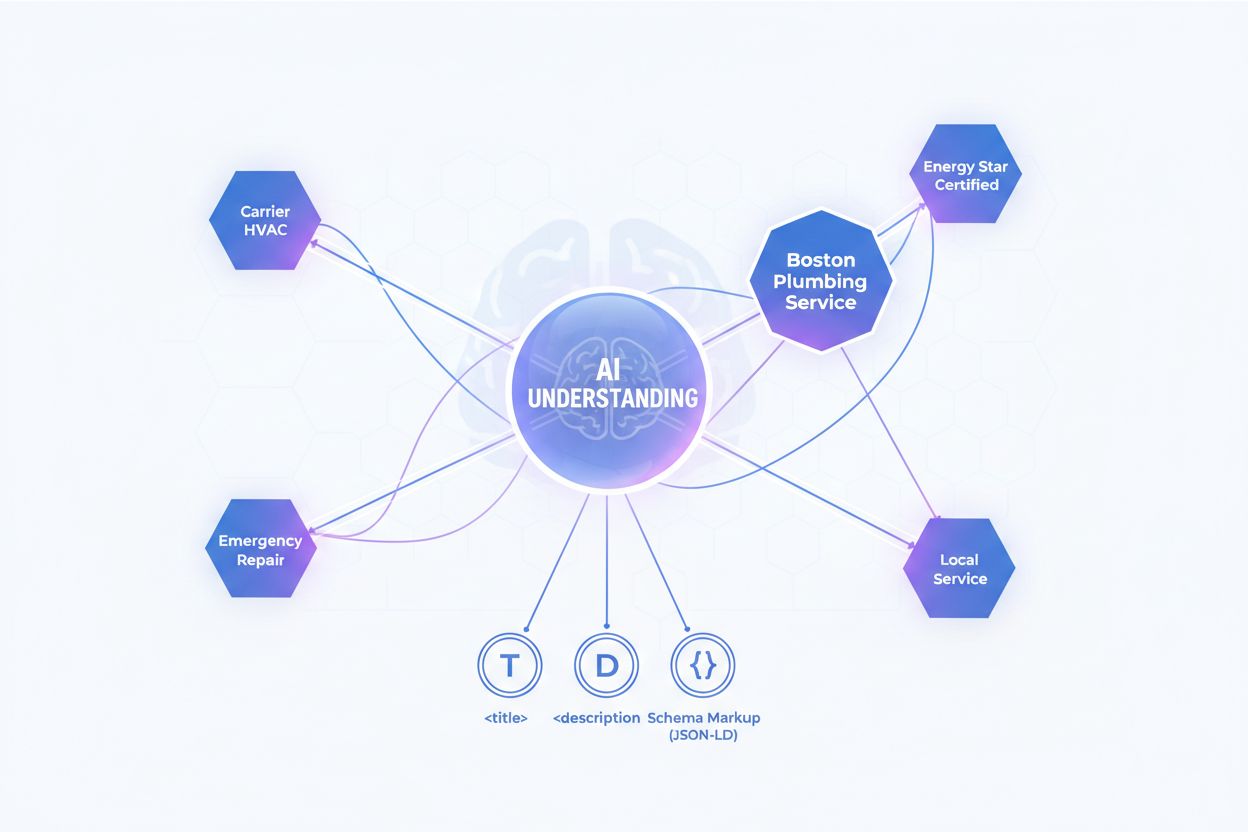
For example, instead of optimizing for the keyword “best running shoes,” an entity-focused approach would optimize for the entity “running shoes” while establishing relationships to related entities like “marathon training,” “foot health,” and specific shoe brands. Your schema markup should include entity information like author, publisher, organization, and mentions to help AI systems understand the entities involved in your content. This approach is particularly important for branded content, as it helps AI systems understand your company’s expertise and authority in specific domains. By implementing entity-based SEO strategies in your meta tags and structured data, you improve your chances of appearing in AI Overviews and being recognized as an authoritative source on specific topics.
Tracking the performance of your meta tag optimizations is essential for understanding their impact and making data-driven improvements to your SEO strategy. The primary metric for evaluating meta tag performance is click-through rate (CTR), which measures the percentage of people who see your page in search results and click through to your site. You can track CTR in Google Search Console by filtering by page, query, or device type, allowing you to identify which meta tags are driving the most clicks and which need improvement.
Key metrics to monitor include CTR by page (identify which pages have low CTR and need meta tag optimization), average position (track how your rankings change after meta tag updates), impressions (monitor whether your visibility in search results is increasing or decreasing), AI Overview citations (track whether your content is being cited in AI Overviews and how often), and social shares (monitor how your Open Graph tags are performing on social platforms). A/B testing is a powerful technique for optimizing meta tags, where you test different title tags or meta descriptions on similar pages to see which versions drive higher CTR. For example, you might test a title tag with a number (“5 Ways to Improve Your SEO”) against one without (“How to Improve Your SEO”) to see which resonates better with your audience. Monitoring these metrics over time helps you understand the impact of your meta tag optimizations and identify patterns that can be applied across your entire site.
Even experienced SEO professionals make meta tag mistakes that can significantly impact visibility and user experience, often without realizing the damage until rankings drop or CTR declines. Understanding these common pitfalls and how to avoid them is essential for maintaining a healthy, AI-optimized website.
Common meta tag mistakes include:
Numerous tools can help you audit, optimize, and monitor your meta tags, making it easier to implement best practices across your entire website. Screaming Frog is an industry-standard crawler that identifies missing or duplicate meta tags, allowing you to audit your entire site and export data for analysis. RankMath is a WordPress plugin that provides real-time meta tag optimization suggestions, including character count warnings and readability scores, making it easy to optimize as you write.
For larger-scale analysis, Semrush and Ahrefs offer comprehensive SEO platforms that include meta tag audits, competitor analysis, and ranking tracking. Google Search Console remains the most important tool for understanding how your meta tags are performing in search results, providing CTR data, impressions, and average position for each page. Additionally, Google’s Rich Results Test allows you to validate your schema markup and see how your rich snippets will appear in search results. By leveraging these tools, you can systematically optimize your meta tags, monitor their performance, and stay ahead of changes in AI-driven search algorithms.
Yes, meta tags remain crucial for SEO, especially with AI-driven search. While they don't directly impact rankings like they did in the past, they influence click-through rates, help AI understand your content, and control how your pages appear in search results and AI Overviews.
Meta tags are HTML snippets that provide basic information about your page (title, description, robots directives). Schema markup is structured data that provides detailed, machine-readable information about specific content types. Both work together to help AI understand your content.
This depends on your business goals. Allowing AI usage gains visibility as a cited source and positions you as an authority. Restricting it preserves direct traffic to your site. Consider using max-snippet directives for a hybrid approach that balances both benefits.
Aim for 150-160 characters on desktop and 120 characters on mobile. However, Google may dynamically adjust descriptions based on search queries, so focus on writing compelling, benefit-driven descriptions rather than hitting exact character counts.
The title tag is the most important. It's your first opportunity to communicate relevance to both AI systems and human searchers. A well-crafted title tag significantly impacts click-through rates and helps AI understand your page's primary topic.
Use Google Search Console to track click-through rates (CTR) for your pages. Pages with lower-than-expected CTR for their ranking position are prime candidates for meta tag optimization. A/B test different title and description variations to measure impact.
No, Google explicitly stated it doesn't use the meta keywords tag. Focus your efforts on title tags, meta descriptions, robots directives, and schema markup instead. These elements have far more impact on your visibility in AI-driven search.
Review and update meta tags quarterly or when you make significant content changes. Monitor performance in Google Search Console and adjust underperforming pages. Keep meta tags fresh and aligned with current search intent and AI capabilities.
Track how AI systems reference your brand across Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other AI search platforms. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and optimize your meta tags accordingly.

Learn how to implement noai and noimageai meta tags to control AI crawler access to your website content. Complete guide to AI access control headers and implem...

Discover how artificial intelligence is transforming SEO strategies, from AI-powered keyword research to personalized search results. Learn what the future of S...

Discover how artificial intelligence is transforming SEO strategies, from AI Overviews to answer engine optimization. Learn what the future of search looks like...