
What is Reputation Management for AI Search? Complete Guide
Learn what reputation management for AI search means, why it matters for your brand, and how to monitor your presence across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and ot...
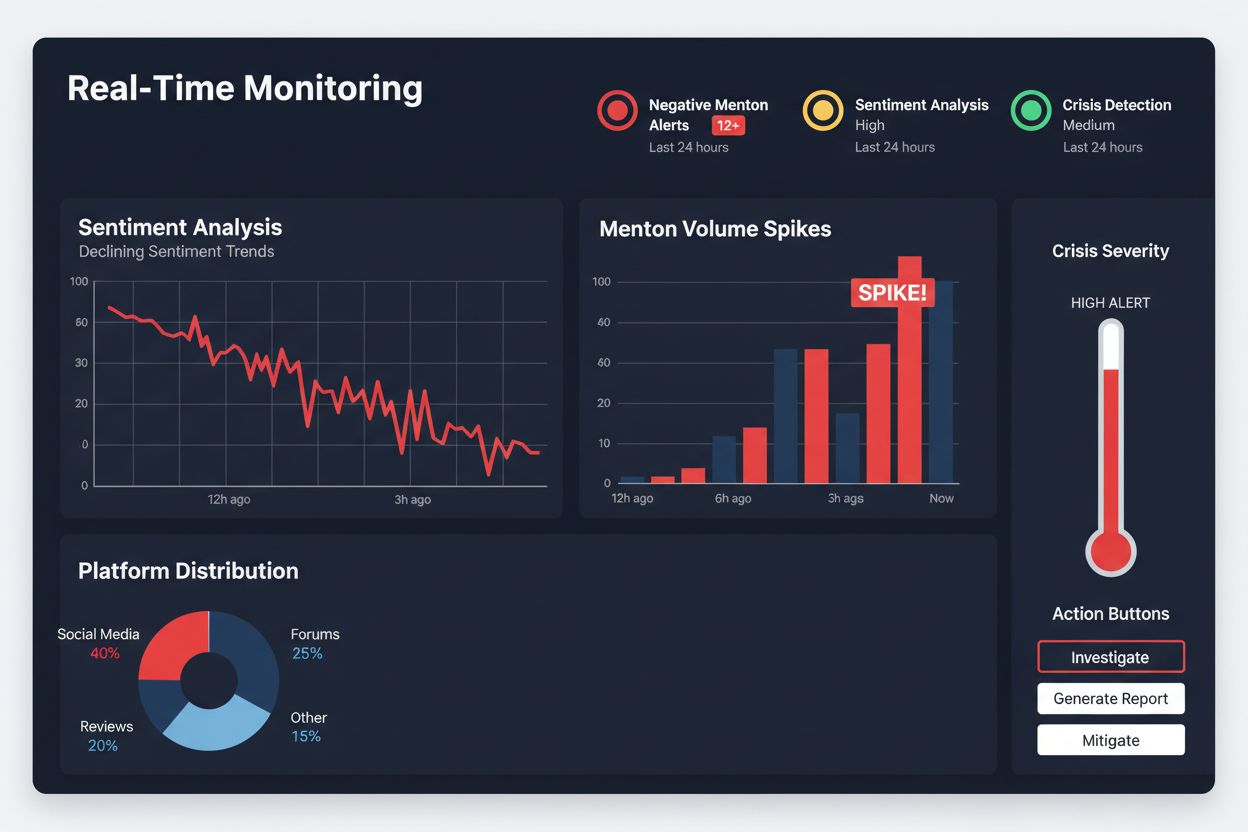
Learn how to detect and respond to negative brand mentions in AI search platforms with real-time alert systems. Protect your reputation before negative content spreads.
The emergence of AI search tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has fundamentally transformed how consumers discover information about brands, creating a dual reputation exposure that traditional monitoring systems were never designed to handle. Over 40% of shopping journeys now begin in AI tools rather than traditional search engines, meaning negative mentions captured and synthesized by these systems reach potential customers before they ever visit your website or social media channels. Unlike traditional search results where negative content appears alongside positive reviews and official company information, AI-generated summaries can amplify and distill negative narratives into authoritative-sounding answers that persist for months or even years. This represents both an immediate crisis—where a single viral complaint can be synthesized into an AI answer within hours—and a long-term amplification problem where outdated negative information becomes embedded in AI model training data and continues influencing customer perception long after the original issue has been resolved.
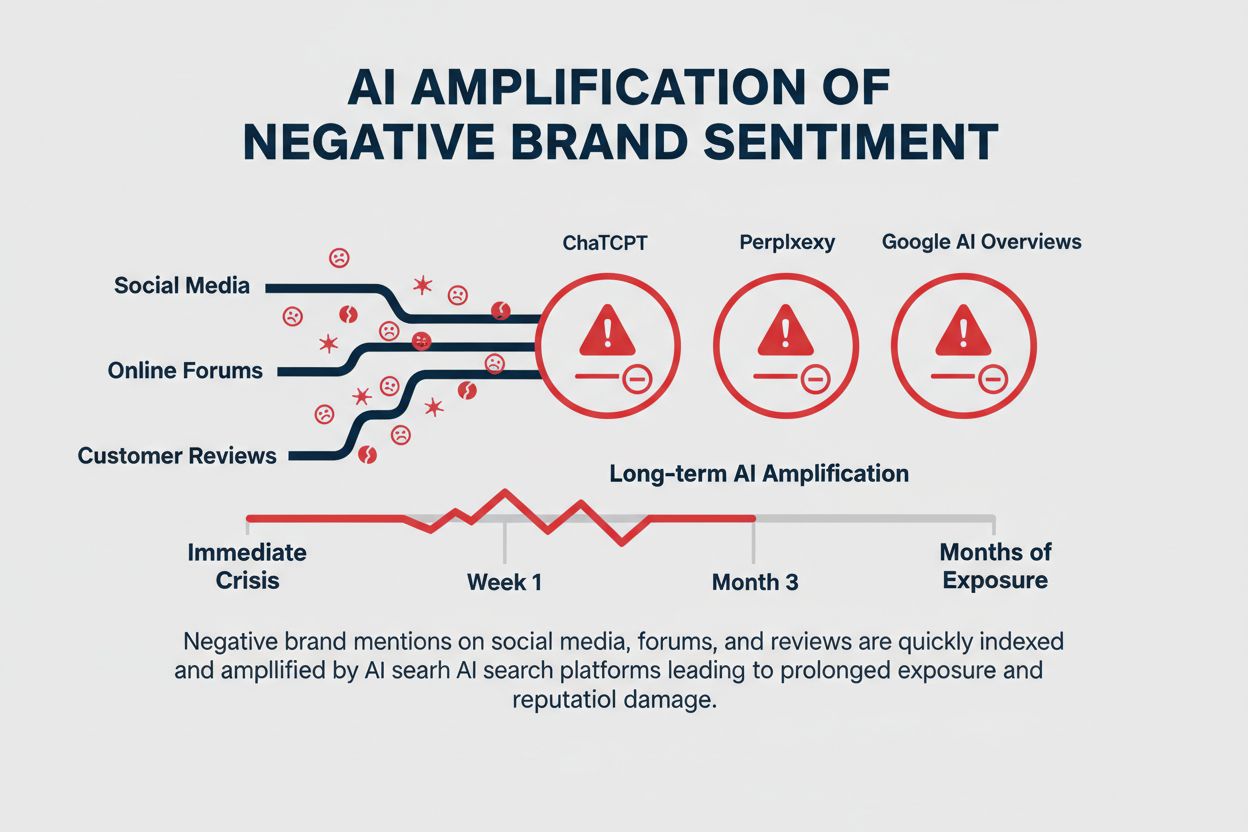
Keyword-based alert systems and manual social media reviews, which dominated reputation management for the past decade, fundamentally fail to capture the nuanced ways negative sentiment emerges and spreads in the AI era. Approximately 60% of customer complaints lack explicitly negative language, instead using sarcasm, subtle criticism, or indirect references that traditional keyword matching completely misses—a customer saying “wow, great customer service” in response to a 6-hour wait time will never trigger a basic alert system despite expressing severe dissatisfaction. The velocity problem compounds this limitation: negative sentiment spreads approximately 4x faster than positive sentiment, yet traditional systems often require manual review before alerts are even generated, creating dangerous delays when minutes matter. Scale presents another insurmountable challenge, as brands now operate across dozens of platforms simultaneously—social media, review sites, forums, news outlets, AI search results, and emerging platforms—making comprehensive manual monitoring practically impossible for any organization without a dedicated team of hundreds.
| Monitoring Approach | Detection Speed | Sentiment Accuracy | Scale Capability | Contextual Understanding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Keyword Alerts | 2-4 hours | 40-50% | Limited to 5-10 platforms | Minimal |
| Manual Social Review | 4-8 hours | 70% | 3-5 platforms max | Good but inconsistent |
| AI-Powered Monitoring | 5-15 minutes | 85-92% | 50+ platforms simultaneously | Contextual and nuanced |
| Hybrid Human-AI System | 15-30 minutes | 90%+ | Unlimited scale | Excellent |
Negative visibility detection in the AI context refers to the systematic identification and measurement of how negative content about your brand appears, spreads, and gets synthesized across AI search platforms and traditional channels—a fundamentally different challenge than simply counting negative mentions. Modern detection systems employ sentiment analysis, which uses natural language processing to understand not just whether text is negative, but the intensity, context, and emotional drivers behind that negativity, allowing systems to distinguish between casual complaints and serious reputation threats. Anomaly detection algorithms work alongside sentiment analysis to identify unusual patterns—sudden spikes in complaint volume, coordinated negative campaigns, or emerging narratives that deviate from baseline conversation patterns—which often signal emerging crises before they reach critical mass. The critical insight that separates effective monitoring from ineffective monitoring is understanding that context matters exponentially more than raw mention counts; a single mention of your brand in a major news outlet discussing a product failure carries vastly different weight than fifty mentions in a niche forum, yet traditional systems treat them identically. Effective negative visibility detection therefore requires systems that can weigh mentions by source authority, audience reach, emotional intensity, and potential for AI synthesis, not simply aggregate raw numbers.
Modern real-time alert systems function as continuous listening networks that process millions of data points across platforms simultaneously, using machine learning models trained to recognize patterns associated with emerging reputation threats before they reach critical visibility. These systems operate on multiple detection layers: velocity thresholds monitor the rate at which negative mentions accelerate (a 300% increase in complaint volume over 2 hours triggers different alerts than steady baseline complaints), while emotional intensity scoring evaluates whether mentions contain language associated with high-impact emotions like anger, betrayal, or fear that correlate with viral spread and customer churn. Advanced systems employ natural language processing specifically trained to detect sarcasm, irony, and cultural references that simpler sentiment analysis completely misses—understanding that “thanks for the amazing 3-hour wait time” is negative requires contextual intelligence that only sophisticated NLP models possess. The practical impact of this sophistication is measurable: organizations using AI-powered monitoring respond to emerging crises 30% faster than those relying on traditional systems, a speed advantage that often determines whether a reputation threat can be contained or spirals into widespread damage. Real-time systems also integrate with escalation workflows, automatically routing high-severity alerts to appropriate teams and triggering pre-planned response protocols without requiring manual triage.
Configuring alert thresholds represents one of the most critical yet frequently mishandled aspects of reputation monitoring, as poorly calibrated thresholds either generate alert fatigue that causes teams to ignore genuine crises or miss emerging threats entirely by setting bars too high. Effective threshold configuration requires analyzing your brand’s baseline conversation patterns—understanding your normal daily mention volume, typical sentiment distribution, and platform-specific dynamics—then establishing alert triggers based on meaningful deviations rather than arbitrary numbers. Organizations should establish multiple alert tiers based on severity and urgency:
Prioritization requires understanding that not all alerts demand immediate response—a single angry customer tweet differs fundamentally from coordinated negative coverage across major news outlets—so effective systems implement severity scoring that routes alerts to appropriate response teams based on potential impact rather than treating all alerts identically.
AI-powered monitoring systems excel at catching false narratives and fabricated content in their earliest stages, before they gain the momentum and credibility that makes them nearly impossible to counter through traditional crisis response. Anomaly detection algorithms identify unusual patterns that often precede misinformation spread: sudden coordinated mentions from new accounts, unusual hashtag combinations, or content that contradicts established facts about your brand or industry—patterns that human monitors would never notice across thousands of daily mentions. The Target satanic-themed clothing hoax provides a instructive example: false claims about intentionally satanic children’s clothing designs spread rapidly through social media and were synthesized into AI search results, damaging brand reputation despite being completely fabricated; modern monitoring systems would have detected the coordinated nature of these claims and the anomalous pattern of new accounts spreading identical narratives, enabling rapid fact-checking and counter-messaging before widespread belief formation. Deepfake detection represents an emerging frontier, as AI-generated images and videos of executives or products can now be created convincingly enough to fool casual observers, yet monitoring systems trained on visual anomaly detection can identify the subtle artifacts and statistical improbabilities that distinguish deepfakes from authentic content. The key advantage of early detection is that misinformation becomes exponentially harder to counter once it achieves widespread belief—detecting false narratives when they involve dozens of mentions rather than thousands or millions enables organizations to deploy fact-checking resources efficiently and prevent false narratives from becoming entrenched in AI model training data.
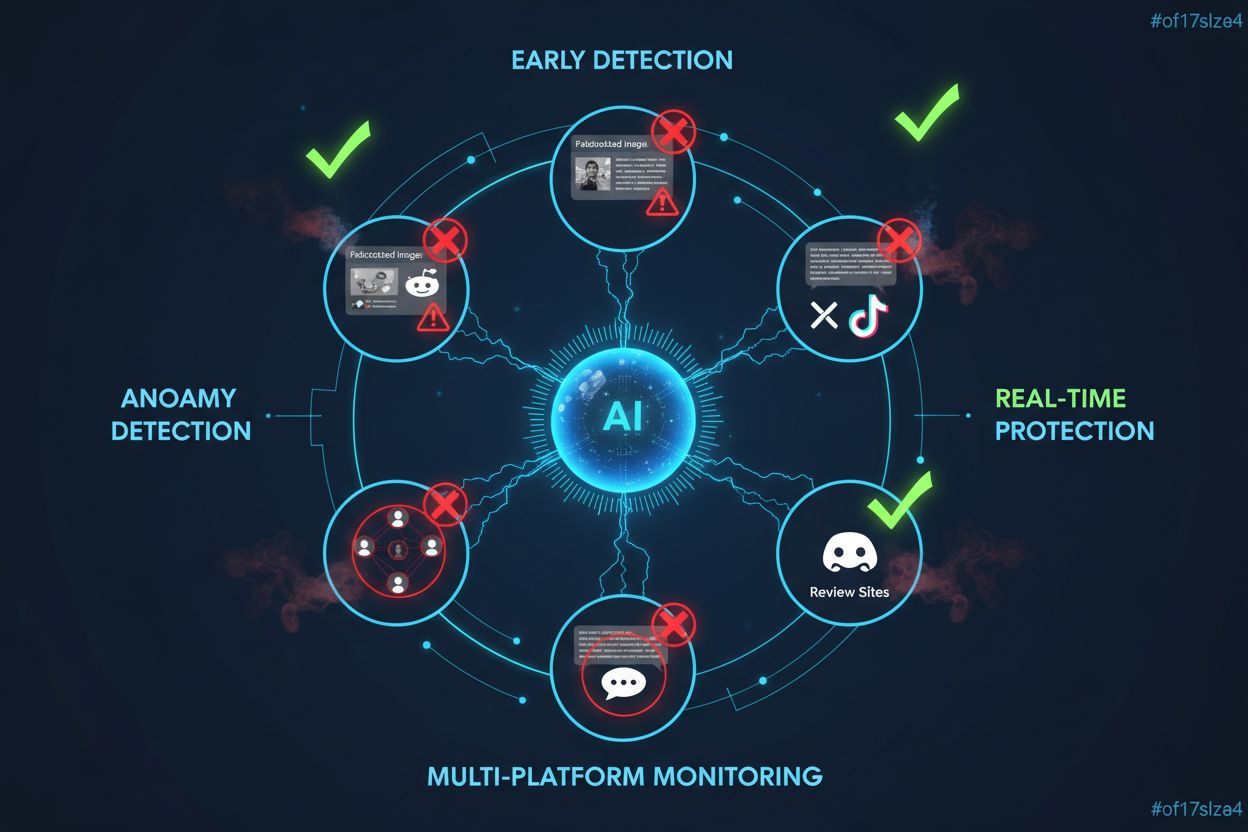
Effective alert systems create value only when connected to clearly defined crisis response workflows that translate detection into action, ensuring that alerts trigger appropriate escalation, cross-functional coordination, and rapid response rather than simply generating notifications that disappear into overwhelmed inboxes. Escalation paths should be predetermined based on alert severity, with high-severity alerts automatically notifying executive leadership, communications teams, legal departments, and product teams simultaneously rather than requiring manual routing that introduces dangerous delays. Organizations should establish rapid response protocols that include pre-approved holding statements addressing common crisis scenarios, FAQ templates that can be customized within minutes, and social media response frameworks that enable communications teams to acknowledge customer concerns and provide updates without requiring approval cycles that consume critical response time. Integration with existing systems means connecting reputation monitoring to customer service platforms, so that alerts about widespread product complaints automatically trigger investigation by product teams and customer service escalation, creating feedback loops where reputation data informs operational improvements. Cross-functional governance ensures that different departments understand their roles in crisis response—communications handles external messaging, product teams investigate root causes, customer service manages affected customer outreach, and legal evaluates potential liability—preventing the siloed responses that often exacerbate reputation crises.
Monitoring competitor negative mentions reveals strategic opportunities that positive-focused monitoring completely misses, as customer complaints about competitors often highlight unmet needs, feature gaps, and market positioning vulnerabilities that your organization can exploit. By systematically analyzing the types of complaints competitors receive—whether customers complain about pricing, feature limitations, customer service responsiveness, product quality, or user experience—organizations can identify recurring pain points that represent genuine market opportunities rather than relying on speculation about competitor weaknesses. Sentiment analysis of competitor mentions reveals which aspects of competitor offerings generate the most frustration, enabling product teams to prioritize feature development toward areas where competitors are failing to meet customer expectations. Market positioning insights emerge from understanding how customers describe competitor shortcomings: if competitors consistently receive complaints about poor mobile experiences while your organization excels in mobile, this becomes a powerful positioning advantage to emphasize in marketing; if competitors struggle with enterprise customer support while you’ve invested heavily in that area, this becomes a differentiator worth highlighting. The strategic value of competitive negative monitoring lies in transforming customer complaints about competitors into actionable intelligence that informs product development, marketing positioning, and sales strategies—essentially allowing your organization to learn from competitors’ reputation failures without experiencing those failures yourself.
Quantifying the return on investment from reputation monitoring systems requires establishing clear key performance indicators that connect monitoring activities to business outcomes, moving beyond vanity metrics like “alerts generated” toward measurements that demonstrate actual business impact. Critical metrics include time-to-response (measuring how quickly organizations detect and respond to emerging threats), crisis containment (measuring whether early detection enables organizations to prevent reputation threats from reaching critical mass), and sentiment recovery (measuring how quickly negative sentiment returns to baseline after crisis response, indicating whether interventions actually worked). Organizations should track sentiment-to-revenue correlation, analyzing whether improvements in brand sentiment scores correlate with increased customer acquisition, reduced churn, or improved customer lifetime value—this connection transforms reputation monitoring from a cost center into a revenue-generating function. Additional ROI indicators include measuring prevented crises (estimating the business impact of reputation threats that were detected and contained before reaching critical visibility), customer retention improvements (tracking whether customers exposed to negative content but seeing rapid company response remain loyal), and competitive win-rate improvements (measuring whether strong reputation management translates into higher sales conversion rates). The most sophisticated organizations establish predictive models that estimate the financial impact of different crisis scenarios, enabling them to calculate expected ROI by comparing the cost of monitoring systems against the estimated cost of undetected crises—a calculation that typically demonstrates that comprehensive monitoring systems pay for themselves many times over through crisis prevention alone.
Successful implementation of negative mention alert systems requires a structured approach that begins with clearly defining key performance indicators aligned with business objectives—whether your organization prioritizes rapid crisis response, customer retention, competitive positioning, or product improvement determines which metrics matter most and how systems should be configured. Mapping all customer touchpoints where negative mentions can emerge—social media platforms, review sites, forums, news outlets, AI search results, customer service channels, and emerging platforms—ensures comprehensive coverage rather than monitoring only the channels where your organization is most active or comfortable. Organizations should evaluate and select tools based on specific capability requirements: does your organization need real-time alerts or daily summaries, do you require multilingual monitoring, do you need integration with existing customer service or marketing platforms, and what scale of monitoring do you require—these requirements should drive tool selection rather than selecting popular tools and adapting workflows to their limitations. Establishing governance frameworks clarifies decision-making authority, response protocols, and escalation paths before crises occur, preventing the confusion and delays that characterize poorly prepared crisis responses; this includes defining who has authority to approve public statements, which teams get notified for different alert types, and what response timelines are expected. Implementation should include continuous refinement cycles where organizations regularly review alert performance, analyzing which alerts led to genuine crises versus false positives, adjusting thresholds based on real-world performance, and incorporating learnings from actual crisis responses into improved workflows—monitoring systems improve dramatically when organizations treat them as evolving capabilities rather than static tools deployed once and left unchanged.
Negative AI visibility refers to how negative content about your brand appears in AI search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. It matters because over 40% of shopping journeys now start in AI tools, and negative mentions synthesized by these platforms can reach potential customers before they visit your website, creating long-term reputation damage that persists for months.
Modern alert systems use natural language processing and machine learning to analyze mentions across platforms in real-time. They detect not just negative keywords, but sentiment intensity, emotional language, and unusual patterns. They can identify sarcasm and context that traditional keyword matching misses, enabling detection of 60% of complaints that lack explicitly negative language.
Sentiment analysis measures whether mentions are positive, neutral, or negative and evaluates emotional intensity. Anomaly detection identifies unusual patterns—sudden spikes in complaint volume, coordinated campaigns, or emerging narratives that deviate from baseline. Together, they provide comprehensive threat detection that catches both obvious negative sentiment and suspicious patterns that precede misinformation spread.
Speed is critical—organizations using AI monitoring respond 30% faster than those using manual methods. Ideally, you should respond to high-severity alerts within 1-2 hours. Early response prevents negative content from spreading to additional platforms and being synthesized into AI search results, where it can persist for months and influence customer perception.
You can't prevent misinformation from being created, but you can detect it early and counter it before it spreads. By identifying false narratives when they involve dozens of mentions rather than thousands, you can deploy fact-checking resources efficiently and prevent false information from becoming entrenched in AI model training data that influences future responses.
Key metrics include time-to-response (how quickly you detect and respond), crisis containment (whether early detection prevents threats from reaching critical mass), sentiment recovery (how quickly negative sentiment returns to baseline), and sentiment-to-revenue correlation (whether reputation improvements translate to business results like increased sales or reduced churn).
Start by analyzing your brand's baseline conversation patterns—normal daily mention volume, typical sentiment distribution, and platform-specific dynamics. Then establish alert triggers based on meaningful deviations: velocity alerts (200%+ increase in mentions), sentiment drops (30+ point decrease), emotional intensity spikes, and anomaly patterns. Adjust thresholds based on real-world performance over time.
Comprehensive monitoring systems typically pay for themselves through crisis prevention alone. Calculate ROI by comparing monitoring costs against estimated costs of undetected crises. Additional benefits include improved customer retention, faster response times, competitive positioning advantages, and product improvements informed by customer complaint analysis.
Track how AI platforms reference your brand and detect negative mentions before they damage your reputation. Get real-time alerts and actionable insights.

Learn what reputation management for AI search means, why it matters for your brand, and how to monitor your presence across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and ot...

Learn how to monitor and manage positive and negative AI mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Protect your brand reputation with AI-pow...

Learn how to detect negative AI mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover response strategies and monitoring tools to protect your ...