
What is Multi-Modal Content for AI? Definition and Examples
Learn what multi-modal content for AI is, how it works, and why it matters. Explore examples of multi-modal AI systems and their applications across industries.

Learn how to optimize text, images, and video for multimodal AI systems. Discover strategies to improve AI citations and visibility across ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity.
Multimodal AI represents a fundamental shift in how artificial intelligence systems process and understand information. Unlike unimodal systems that handle only text, images, or video independently, multimodal AI integrates multiple data types simultaneously to create a more comprehensive understanding of complex information. This approach mirrors how humans naturally process the world—we don’t separate what we see from what we hear or read, but rather synthesize all inputs together. The multimodal AI market, valued at $1.6 billion in 2024, is experiencing explosive growth at a 32.7% compound annual growth rate (CAGR), reflecting the technology’s critical importance to enterprise AI strategies. Industry analysts project that 40% of all generative AI solutions will be multimodal by 2027, according to Gartner research. This transition isn’t merely incremental; it represents a paradigm shift in how organizations leverage AI for competitive advantage. The convergence of text, image, and video processing capabilities enables AI systems to deliver insights and capabilities that were previously impossible with single-modality approaches.
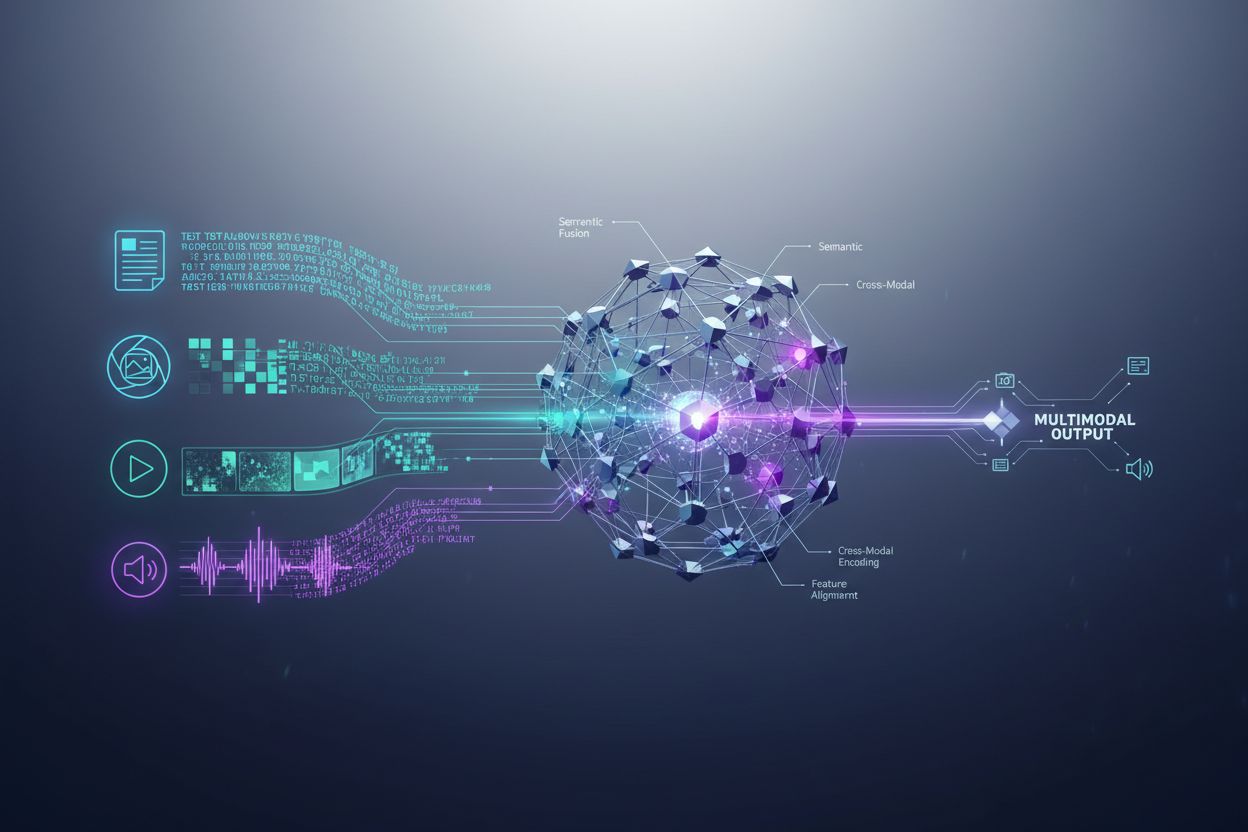
Multimodal AI systems employ sophisticated architectural components to handle diverse data inputs seamlessly. Encoders are specialized neural networks that convert each data type—text, images, and video—into a unified numerical representation called embeddings. These embeddings capture the semantic meaning of each modality in a shared mathematical space, allowing the system to compare and relate information across different types of content. The fusion mechanism then combines these embeddings, either through concatenation, addition, or more advanced learned fusion techniques that determine how much weight each modality should contribute to the final output. Cross-attention mechanisms enable the model to dynamically focus on relevant information across modalities; for example, when analyzing a product image with accompanying text, the system can attend to specific visual features that correspond to textual descriptions. This multi-step process allows multimodal systems to achieve contextual understanding that single-modality systems cannot replicate. The following table illustrates the capability differences:
| Capability | Unimodal AI | Multimodal AI |
|---|---|---|
| Text Analysis | Excellent | Excellent |
| Image Understanding | Limited/None | Excellent |
| Video Processing | Limited/None | Excellent |
| Cross-Modal Reasoning | Not Possible | Excellent |
| Context Integration | Single Source | Multiple Sources |
| Real-World Accuracy | 60-75% | 85-95% |
| Processing Speed | Fast | Optimized Fast |
The multimodal AI landscape is dominated by several powerful platforms that have set new standards for integrated processing. GPT-4o from OpenAI represents a flagship multimodal model, seamlessly handling text, images, and video with native integration across all modalities. Google Gemini offers enterprise-grade multimodal capabilities with particular strength in understanding complex visual documents and long-form video content. Claude from Anthropic provides sophisticated multimodal reasoning with emphasis on accuracy and nuanced understanding across text and image inputs. Meta’s ImageBind technology demonstrates a different architectural approach, creating a unified embedding space across six modalities including text, image, audio, depth, thermal, and IMU data. These platforms represent the cutting edge of multimodal technology, each bringing distinct architectural innovations and optimization strategies. Organizations selecting multimodal platforms must evaluate not just capability breadth, but also performance optimization, cost efficiency, and integration with existing workflows.
Multimodal AI is transforming operations across virtually every industry sector, delivering measurable improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and customer experience. Organizations implementing these technologies report remarkable results:
Healthcare: Radiologists use multimodal AI to analyze medical imaging combined with patient records and clinical notes, improving diagnostic accuracy and reducing analysis time by up to 40%. AI systems can correlate visual findings with textual medical history to identify patterns humans might miss.
Retail: Fashion and e-commerce companies leverage multimodal AI to match customer descriptions with visual inventory, enabling “search by description” capabilities that increase conversion rates. Product recommendations improve significantly when AI understands both visual preferences and textual feedback.
Manufacturing: Quality control processes accelerate dramatically with multimodal inspection systems that combine visual defect detection with sensor data and maintenance logs, achieving 100x faster cataloging of production issues compared to manual processes.
Content Creation: Media companies use multimodal AI to automatically generate captions, transcripts, and metadata for video content, with 72% of media executives using generative AI reporting positive ROI on their investments.
Customer Service: Chatbots enhanced with multimodal capabilities can process customer images of problems alongside text descriptions, providing more accurate and contextual support solutions.
Agriculture: Farmers deploy multimodal systems that analyze crop imagery, weather data, and soil sensor readings to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and pest management decisions.
Robotics: Autonomous systems use multimodal perception to navigate complex environments, combining visual input with audio cues and tactile feedback for safer, more intelligent operation.
To maximize the effectiveness of multimodal AI systems, text content requires deliberate optimization strategies that enhance machine readability and contextual understanding. Structured data markup using schema.org standards helps AI systems understand the semantic relationships within your content, enabling more accurate cross-modal connections. Implementing conversational language rather than purely formal prose allows multimodal systems to better understand intent and context, particularly when text is processed alongside visual or video elements. Descriptive headings and subheadings serve dual purposes: they guide human readers while providing crucial structural signals that help AI systems organize and prioritize information. Including relevant keywords in natural contexts—rather than forced keyword stuffing—ensures that text content aligns with how multimodal systems identify topical relationships across modalities. Metadata optimization, including title tags, meta descriptions, and structured data attributes, provides explicit signals about content meaning that multimodal systems can leverage. Organizations should also consider how text complements visual content; captions and alt text aren’t just accessibility features—they’re critical optimization elements that enable multimodal AI to understand the relationship between textual and visual information.
Visual and video content optimization for multimodal AI requires a comprehensive approach that goes far beyond traditional SEO practices. Descriptive alt text is foundational; rather than generic descriptions, alt text should capture the semantic meaning, context, and relevant details that help AI systems understand what the image conveys. File naming conventions matter significantly—descriptive filenames like “product-comparison-chart-2024.jpg” provide crucial context that AI systems use to understand content purpose. Video captions and transcripts are essential optimization elements; they enable multimodal systems to correlate spoken content with visual elements, dramatically improving understanding of complex video material. Metadata fields including title, description, and tags should be populated with specificity and accuracy, as these fields directly influence how AI systems categorize and relate visual content to other modalities. Image compression and technical optimization ensures that visual quality remains high enough for AI analysis while maintaining fast loading times. Structured data for visual content, including markup for images, videos, and media galleries, provides explicit signals about content relationships. Organizations should also consider temporal metadata for video content—marking key moments, scene changes, and topic transitions helps multimodal systems understand narrative structure and extract relevant segments.

Multimodal AI systems employ two primary architectural approaches, each with distinct advantages and trade-offs. Unified architectures process all modalities through a single, integrated neural network that learns joint representations from the beginning of processing. This approach typically delivers superior cross-modal reasoning because the system develops deep understanding of how modalities relate to each other, but it requires more computational resources and longer training times. Modular architectures maintain separate specialized networks for each modality, then combine their outputs through fusion mechanisms. This approach offers greater flexibility, allowing organizations to swap individual modality processors without retraining the entire system, and typically requires fewer computational resources. Mixture of Experts (MoE) models represent an emerging hybrid approach, where different expert networks specialize in different modalities or tasks, and a gating mechanism routes inputs to appropriate experts. This architecture achieves efficiency improvements of 30-50% compared to dense unified models while maintaining comparable accuracy. The choice between architectural approaches depends on specific use cases: unified architectures excel at complex reasoning tasks requiring deep cross-modal understanding, while modular approaches suit scenarios requiring flexibility and resource efficiency.
Effective multimodal AI implementation requires robust measurement frameworks that track both technical performance and business impact. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should include accuracy metrics across each modality, cross-modal reasoning quality, processing latency, and cost per inference. Analytics platforms should capture how multimodal AI influences downstream business metrics: conversion rates in retail, diagnostic accuracy in healthcare, production efficiency in manufacturing. Organizations must implement attribution tracking to understand which modality contributes most to specific outcomes—this insight guides optimization efforts and resource allocation. ROI measurement should account for both direct cost savings (like the 100x faster cataloging reported by manufacturing organizations) and indirect benefits like improved customer satisfaction or reduced error rates. Monitoring tools should track model performance degradation over time, as real-world data drift can reduce multimodal system accuracy if not actively managed. For organizations leveraging AI-generated content and insights, citation and attribution tracking becomes increasingly important; tools like AmICited.com help monitor how AI systems cite sources and attribute information, providing visibility into AI decision-making processes and ensuring compliance with content provenance requirements. Regular performance audits and optimization cycles ensure that multimodal systems continue delivering value as business needs and data patterns evolve.
The multimodal AI landscape continues evolving rapidly, with several transformative trends reshaping how organizations will leverage these technologies. Voice integration represents the next frontier, as systems increasingly combine audio input with visual and textual data, enabling truly comprehensive understanding of human communication and environmental context. Agentic AI systems—AI agents that can autonomously plan and execute multi-step tasks—will leverage multimodal perception to navigate complex real-world scenarios, from autonomous vehicles to robotic process automation in enterprise environments. Real-time processing capabilities are advancing dramatically, enabling multimodal analysis of live video streams, audio feeds, and sensor data simultaneously, opening possibilities for instant decision-making in time-sensitive applications. Efficiency improvements through techniques like distillation and quantization will make sophisticated multimodal capabilities accessible to organizations with limited computational resources, democratizing access to advanced AI. Specialized domain models will emerge, with multimodal systems fine-tuned for specific industries like healthcare, legal, or financial services, delivering superior performance compared to general-purpose models. The convergence of these trends suggests that multimodal AI will transition from a competitive advantage to a fundamental requirement for organizations seeking to remain relevant in an increasingly AI-driven landscape. Organizations that begin optimizing their content and processes for multimodal AI today will be best positioned to capitalize on these emerging capabilities tomorrow.
Multimodal AI processes multiple data types (text, images, audio, video) simultaneously, while traditional unimodal AI handles only one type. This enables richer context understanding and more accurate outputs. Multimodal systems can understand relationships between different modalities, delivering insights that single-modality systems cannot replicate.
As multimodal AI becomes the standard for generative AI solutions (projected to be 40% by 2027), optimizing your content ensures better visibility in AI-generated answers. Organizations that optimize across text, image, and video see improved AI citations, higher visibility in platforms like ChatGPT and Gemini, and better overall content performance.
Track key metrics including accuracy across modalities, cross-modal reasoning quality, processing latency, and business impact (conversion rates, engagement, etc.). Use tools like AmICited.com to monitor how AI systems cite your content, and implement analytics to understand which modalities contribute most to your business outcomes.
Key challenges include ensuring consistent metadata across modalities, maintaining high-quality alt text and captions, aligning temporal data in videos, and managing the computational resources required for processing. Organizations should also plan for data preparation (10-20% of project budget) and change management as teams adapt to new optimization practices.
Healthcare, retail, manufacturing, content creation, customer service, agriculture, and robotics all see significant benefits. Healthcare uses it for diagnostic accuracy, retail for product discovery, manufacturing for quality control (100x faster cataloging), and media companies report 72% ROI on generative AI investments.
AmICited.com monitors how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews cite your content across different modalities. It provides real-time visibility into your AI search presence, helping you understand how your text, images, and video content are being referenced in AI-generated answers.
Unified architectures process all modalities through a single integrated network, delivering superior cross-modal reasoning but requiring more computational resources. Modular architectures maintain separate networks for each modality, offering greater flexibility and efficiency. Mixture of Experts (MoE) models provide a hybrid approach with 30-50% efficiency improvements.
Optimize text with structured data and conversational language, add descriptive alt text and metadata to images, include captions and transcripts for video, and use consistent file naming conventions. Ensure all modalities work together to provide comprehensive context, and implement schema markup to help AI systems understand semantic relationships.
Track how multimodal AI systems cite your content across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other platforms. Get real-time visibility into your AI search presence.

Learn what multi-modal content for AI is, how it works, and why it matters. Explore examples of multi-modal AI systems and their applications across industries.

Learn how multimodal AI search systems process text, images, audio, and video together to deliver more accurate and contextually relevant results than single-mo...

Master multimodal AI search optimization. Learn how to optimize images and voice queries for AI-powered search results, featuring strategies for GPT-4o, Gemini,...