
Conversational Queries vs Keyword Queries: Key Differences for AI Search
Understand how conversational queries differ from traditional keyword queries. Learn why AI search engines prioritize natural language, user intent, and context...
Learn how to optimize question-based content for conversational AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity. Discover structure, authority, and monitoring strategies to maximize AI citations.
User search behavior has fundamentally transformed over the past five years, moving away from fragmented keyword phrases toward natural, conversational queries. This shift accelerated with the widespread adoption of voice search technology, mobile-first browsing patterns, and significant algorithm improvements like Google’s BERT and MUM updates that now prioritize semantic understanding over exact keyword matching. Users no longer search for isolated terms; instead, they ask complete questions that reflect how they naturally speak and think. The difference is stark:
Voice search adoption has been particularly influential, with 50% of all searches now voice-based, forcing search engines and AI systems to adapt to longer, more natural language patterns. Mobile devices have become the primary search interface for most users, and conversational queries feel more natural on mobile than typing out keywords. Google’s algorithm updates have made it clear that understanding user intent and context matters far more than keyword density or exact phrase matching, fundamentally changing how content must be written and structured to remain visible in both traditional search and AI-powered systems.
Conversational AI search represents a fundamentally different paradigm from traditional keyword-based search, with distinct differences in how queries are processed, results are delivered, and user intent is interpreted. While traditional search engines return a list of ranked links for users to browse, conversational AI systems analyze queries in context, retrieve relevant information from multiple sources, and synthesize comprehensive answers in natural language. The technical architecture differs significantly: traditional search relies on keyword matching and link analysis, while conversational AI uses large language models with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to understand semantic meaning and generate contextual responses. Understanding these differences is critical for content creators who want visibility in both systems, as the optimization strategies diverge in important ways.
| Dimension | Traditional Search | Conversational AI |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Short keywords or phrases (2-4 words average) | Full conversational questions (8-15 words average) |
| Output | List of ranked links for user to click | Synthesized answer with source citations |
| Context | Limited to query terms and user location | Full conversation history and user preferences |
| User Intent | Inferred from keywords and click patterns | Explicitly understood through natural language |
| User Experience | Click-through to external site required | Answer provided directly in interface |
This distinction has profound implications for content strategy. In traditional search, appearing in the top 10 results means visibility; in conversational AI, being selected as a source for citation is what matters. A page might rank well for a keyword but never be cited by an AI system if it doesn’t meet the system’s criteria for authority, comprehensiveness, and clarity. Conversational AI systems evaluate content differently, prioritizing direct answers to questions, clear information hierarchy, and demonstrated expertise over keyword optimization and backlink profiles alone.
Large language models use a sophisticated process called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to select which content to cite when answering user questions, and this process differs significantly from traditional search ranking. When a user asks a question, the LLM first retrieves relevant documents from its training data or indexed sources, then evaluates them based on multiple criteria before deciding which sources to cite in its response. The selection process prioritizes several key factors that content creators must understand:
Authority signals - LLMs recognize domain authority through backlink profiles, domain age, and historical performance in traditional search results, giving preference to established, trusted sources over newer or less-cited domains.
Semantic relevance - The content must directly address the user’s question with high semantic similarity, not just keyword matching; LLMs understand meaning and context in ways traditional keyword matching cannot.
Content structure and clarity - Well-organized content with clear headings, direct answers, and logical flow is more likely to be selected because LLMs can more easily extract relevant information from structured content.
Freshness and recency - Content updated recently is weighted more heavily, particularly for topics where current information matters; outdated content is deprioritized even if it was historically authoritative.
Comprehensiveness - Content that thoroughly addresses a topic with multiple angles, supporting data, and expert perspectives is more likely to be cited than shallow or incomplete coverage.
The citation process itself is not random; LLMs are trained to cite sources that best support their answers, and they increasingly show citations to users, making source selection a critical visibility metric for content creators.
Content structure has become one of the most important factors for AI visibility, yet many content creators still optimize primarily for human readers without considering how AI systems parse and extract information. LLMs process content hierarchically, using heading structures, section breaks, and formatting to understand information organization and extract relevant passages for citation. The optimal structure for AI readability follows specific guidelines: each section should be 120-180 words, allowing LLMs to extract meaningful chunks without excessive length; H2 and H3 headings should clearly indicate topic hierarchy; and direct answers should appear early in sections rather than buried in paragraphs.
Question-based titles and FAQ sections are particularly effective because they align perfectly with how conversational AI systems interpret user queries. When a user asks “What are the best practices for content marketing?”, an AI system can immediately match that query to a section titled “What Are the Best Practices for Content Marketing?” and extract the relevant content. This structural alignment dramatically increases citation likelihood. Here’s an example of properly structured content:
## What Are the Best Practices for Content Marketing?
### Define Your Target Audience First
[120-180 words of direct, actionable content answering this specific question]
### Create a Content Calendar
[120-180 words of direct, actionable content answering this specific question]
### Measure and Optimize Performance
[120-180 words of direct, actionable content answering this specific question]
This structure allows LLMs to quickly identify relevant sections, extract complete thoughts without fragmentation, and cite specific sections with confidence. Content that lacks this structure—long paragraphs without clear headings, buried answers, or unclear hierarchy—is significantly less likely to be selected for citation, regardless of quality.
Authority remains a critical factor in AI visibility, though the signals that constitute authority have evolved beyond traditional SEO metrics. LLMs recognize authority through multiple channels, and content creators must build credibility across several dimensions to maximize citation likelihood. Research indicates that domains with 32,000+ referring domains see significantly higher citation rates, and Domain Trust scores correlate strongly with AI visibility. However, authority isn’t built solely through backlinks; it’s a multifaceted concept that includes:
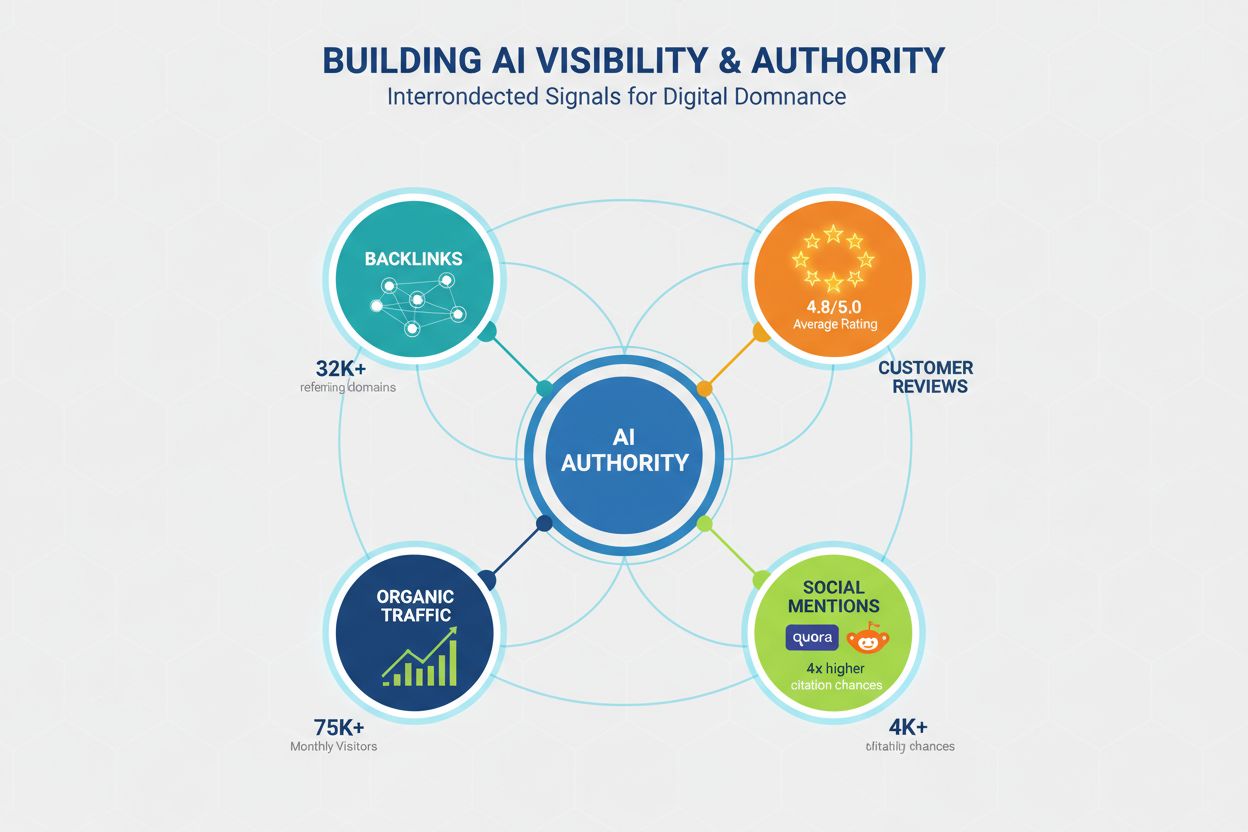
Backlink profile - Quality backlinks from authoritative domains signal expertise; 50+ high-quality backlinks correlates with 4.8x higher citation rates compared to domains with minimal backlinks.
Social proof and community presence - Mentions on platforms like Quora, Reddit, and industry forums signal that your content is trusted and referenced by real users; active participation in these communities builds credibility.
Review platforms and ratings - Presence on Trustpilot, G2, Capterra, and similar platforms with positive reviews builds trust signals that LLMs recognize; brands with 4.5+ star ratings see 3.2x higher citation rates.
Homepage traffic and brand recognition - Direct traffic to your homepage indicates brand awareness and trust; LLMs weight content from recognized brands more heavily than unknown sources.
Expert credentials and bylines - Content authored by recognized experts with clear credentials and bios is weighted more heavily; author expertise is a distinct authority signal separate from domain authority.
Building authority for AI visibility requires a long-term strategy that extends beyond traditional SEO, incorporating community engagement, review management, and brand building alongside technical optimization.
Content depth is one of the strongest predictors of AI citation, with research showing that comprehensive, thoroughly researched content receives significantly more citations than shallow coverage. The minimum threshold for competitive visibility is approximately 1,900 words, but truly comprehensive coverage that dominates AI citations typically reaches 2,900+ words. This isn’t about word count for its own sake; it’s about the depth of information, number of supporting data points, and breadth of perspectives covered.
The data on content depth is compelling:
Expert quotes impact - Content with 4+ expert quotes receives 4.1 citations on average, compared to 2.4 citations for content without expert perspectives; LLMs recognize expert input as a credibility signal.
Statistical data density - Content including 19+ statistical data points receives 5.4 citations on average, versus 2.8 citations for content with minimal data; LLMs prioritize data-backed claims.
Comprehensive coverage - Content addressing 8+ subtopics within a main topic receives 5.1 citations on average, compared to 3.2 for content covering only 3-4 subtopics; breadth of coverage matters significantly.
Original research - Content featuring original research, surveys, or proprietary data receives 6.2 citations on average, making it the highest-impact content type for AI visibility.
Depth matters because LLMs are trained to provide comprehensive, well-sourced answers to user questions, and they naturally gravitate toward content that allows them to cite multiple perspectives, data points, and expert opinions within a single source.
Content freshness is a critical but often overlooked factor in AI visibility, with research showing that recently updated content receives substantially more citations than outdated material. The impact is dramatic: content updated within the past three months receives an average of 6.0 citations, compared to just 3.6 citations for content that hasn’t been updated in over a year. This metric reflects LLMs’ preference for current information and their recognition that fresh content is more likely to be accurate and relevant.
A quarterly refresh strategy should become standard practice for any content targeting AI visibility. This doesn’t necessarily mean complete rewrites; strategic updates that add new statistics, refresh examples, update case studies, and incorporate recent developments are sufficient to signal freshness. For time-sensitive topics like technology, marketing trends, or industry news, monthly updates may be necessary to maintain citation competitiveness. The refresh process should include:
Content that remains static while the industry evolves will gradually lose AI visibility, even if it was once authoritative, because LLMs recognize that stale information is less valuable to users.
Technical performance has become increasingly important for AI visibility, as LLMs and the systems that feed them prioritize content from fast, well-optimized websites. Core Web Vitals—Google’s metrics for page experience—correlate strongly with citation rates, indicating that LLMs factor in user experience signals when selecting sources. The performance impact is substantial: pages with First Contentful Paint (FCP) under 0.4 seconds receive 6.7 citations on average, compared to just 2.1 citations for pages with FCP over 2.5 seconds.
Technical optimization for AI visibility should focus on:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) - Target under 2.5 seconds; pages meeting this threshold receive 5.8 citations on average versus 2.9 for slower pages.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) - Maintain a score under 0.1; unstable layouts signal poor quality to LLMs and reduce citation likelihood.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) - Optimize for responsiveness under 200ms; interactive pages receive 5.2 citations on average versus 3.1 for sluggish pages.
Mobile responsiveness - Mobile-first indexing means mobile performance is critical; pages with poor mobile experience receive 40% fewer citations.
Clean, semantic HTML - Proper heading hierarchy, semantic tags, and clean code structure help LLMs parse content more effectively and increase citation likelihood.
Technical performance isn’t just about user experience; it’s a direct signal to AI systems about content quality and trustworthiness.
Question-based optimization is the most direct way to align content with conversational AI search patterns, and the impact is particularly pronounced for smaller domains that lack massive authority. Research shows that question-based titles have 7x more impact for smaller domains (under 50K monthly visitors) compared to traditional keyword-based titles, making this optimization strategy especially valuable for emerging brands. FAQ sections are equally powerful, doubling the likelihood of citation when properly implemented with clear question-answer pairs.
The difference between question-based and traditional titles is significant:
Bad title: “Top 10 Marketing Tools”
Good title: “What Are the Top 10 Marketing Tools for Small Businesses?”
Bad title: “Content Marketing Strategy”
Good title: “How Should Small Businesses Develop a Content Marketing Strategy?”
Bad title: “Email Marketing Best Practices”
Good title: “What Are the Best Email Marketing Practices for E-commerce Businesses?”
Practical optimization tactics include:
Title optimization - Incorporate the primary question your content answers; use natural language rather than keyword-stuffed phrases.
FAQ sections - Create dedicated FAQ sections with 5-10 questions and direct answers; this doubles citation likelihood for competitive queries.
Subheading alignment - Use H2 and H3 headings that match common question patterns; this helps LLMs match user queries to your content.
Direct answer placement - Place direct answers to questions at the beginning of sections, not buried in paragraphs; LLMs extract answers more effectively from prominent placement.
Question-based optimization is not about gaming the system; it’s about aligning your content structure with how users actually ask questions and how AI systems interpret those questions.
Many content creators waste time and resources on optimization tactics that have little to no impact on AI visibility, or worse, actively harm citation likelihood. Understanding these misconceptions can help you focus efforts on strategies that actually work. One persistent myth is that LLMs.txt files significantly impact visibility; research shows these files have negligible impact on citation rates, with domains using LLMs.txt seeing only marginally different citation patterns (3.8 vs 4.1 citations on average) compared to those without them.
Common misconceptions to avoid:
FAQ schema markup alone doesn’t help - While FAQ schema is useful for traditional search, it provides minimal benefit for AI visibility; the actual content structure matters far more than markup. Content with FAQ schema but poor structure receives 3.6 citations on average, while well-structured content without schema receives 4.2 citations.
Over-optimization reduces citations - Heavily optimized URLs, titles, and meta descriptions actually reduce citation likelihood; highly optimized content receives 2.8 citations on average, while naturally written content receives 5.9 citations. LLMs recognize and penalize obvious optimization attempts.
Keyword stuffing doesn’t help LLMs - Unlike traditional search engines, LLMs understand semantic meaning and recognize keyword stuffing as a quality signal; content with natural language receives significantly more citations.
Backlinks alone don’t guarantee visibility - While authority matters, content quality and structure matter more; a high-authority domain with poorly structured content receives fewer citations than a lower-authority domain with excellent structure.
Length without substance doesn’t work - Padding content to reach word count targets without adding value actually reduces citation likelihood; LLMs recognize and penalize fluff.
Focus on genuine quality, clear structure, and authentic expertise rather than optimization tricks.
Monitoring how conversational AI systems cite your content is essential for understanding your AI visibility and identifying optimization opportunities, yet most content creators lack visibility into this critical metric. AmICited.com provides a dedicated platform for tracking how ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other conversational AI systems reference your brand and content. This monitoring capability fills a critical gap in the content creator’s toolkit, complementing traditional SEO monitoring tools by providing visibility into an entirely different search paradigm.

AmICited tracks several key metrics that traditional SEO tools cannot measure:
Citation frequency - How often your content is cited across different AI systems; this metric reveals which content resonates with AI algorithms and which topics need improvement.
Citation patterns - Which specific pages and content pieces are cited most frequently; this helps identify your strongest content and reveals gaps in your coverage.
Competitor AI visibility - See how your AI citation rates compare to competitors; this benchmarking helps you understand your competitive position in the AI search landscape.
Trend tracking - Monitor how your AI visibility changes over time as you implement optimizations; this allows you to measure the impact of your content strategy changes.
Source diversity - Track citations across different AI platforms; visibility in ChatGPT may differ from Perplexity or Google AI Overviews, and understanding these differences helps you optimize for specific systems.
Integrating AmICited into your content monitoring strategy provides the data necessary to optimize specifically for AI visibility rather than guessing whether your efforts are working.
Implementing a question-based content strategy for conversational AI requires a systematic approach that builds on existing content while establishing new optimization practices going forward. The implementation process should be methodical and data-driven, starting with an audit of your current content and progressing through structural optimization, authority building, and continuous monitoring. This eight-step framework provides a practical roadmap for transforming your content strategy to maximize AI visibility.
Audit existing content - Analyze your top 50 pages to understand current structure, word count, heading hierarchy, and update frequency; identify which pages are already well-structured and which need optimization.
Identify high-value question keywords - Research conversational queries related to your industry using tools like Answer the Public, Quora, and Reddit; prioritize questions with high search volume and commercial intent.
Restructure with Q&A sections - Reorganize existing content to incorporate question-based headings and direct answers; convert traditional keyword-focused titles to question-based titles that match user queries.
Implement heading hierarchy - Ensure all content follows proper H2/H3 hierarchy with clear topic organization; break long sections into 120-180 word chunks separated by descriptive subheadings.
Add FAQ sections - Create dedicated FAQ sections for your top 20 pages, with 5-10 questions and direct answers; prioritize questions that appear in search data and user feedback.
Build authority through backlinks - Develop a backlink strategy targeting high-quality domains in your industry; focus on earning links from authoritative sources rather than pursuing quantity.
Monitor with AmICited - Set up monitoring for your brand and key content pieces; establish baseline metrics and track changes as you implement optimizations.
Quarterly updates - Establish a schedule for quarterly content refreshes that add new statistics, update examples, and maintain freshness; prioritize your highest-traffic and highest-citation content.
This implementation strategy transforms your content from traditional SEO optimization to a comprehensive approach that maximizes visibility across both traditional search and conversational AI systems.
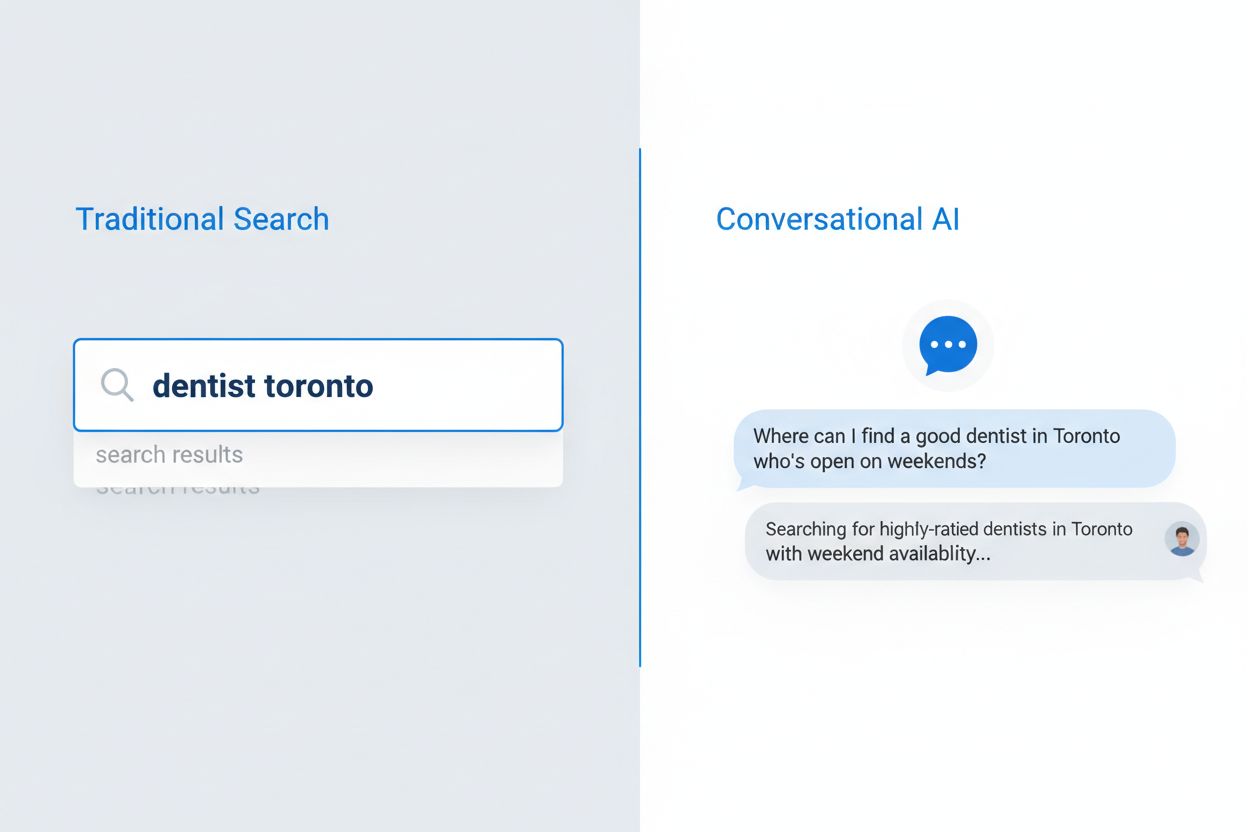
Question-based content is material structured around natural language questions that users ask conversational AI systems. Instead of targeting keywords like 'dentist Toronto,' it targets full questions like 'Where can I find a good dentist in Toronto who's open on weekends?' This approach aligns content with how people naturally speak and how AI systems interpret queries.
Traditional search returns a list of ranked links based on keyword matching, while conversational AI synthesizes direct answers from multiple sources. Conversational AI understands context, maintains conversation history, and provides single synthesized answers with citations. This fundamental difference requires different content optimization strategies.
LLMs parse content hierarchically using heading structures and section breaks to understand information organization. Optimal structure with 120-180 word sections, clear H2/H3 hierarchy, and direct answers at the beginning of sections makes it easier for AI systems to extract and cite your content. Poor structure reduces citation likelihood regardless of content quality.
Research shows approximately 1,900 words is the minimum threshold for competitive AI visibility, with truly comprehensive coverage reaching 2,900+ words. However, depth matters more than length—content with expert quotes, statistical data, and multiple perspectives receives significantly more citations than padded content.
Content updated within the past three months receives 6.0 citations on average, compared to 3.6 for outdated content. Implement a quarterly refresh strategy that adds new statistics, updates examples, and incorporates recent developments. This signals freshness to AI systems and maintains citation competitiveness.
Yes. While large domains have authority advantages, smaller websites can compete through superior content structure, question-based optimization, and community engagement. Question-based titles have 7x more impact for smaller domains, and active presence on Quora and Reddit can provide 4x higher citation chances.
AmICited monitors how ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews cite your brand and content. It provides visibility into citation patterns, identifies content gaps, tracks competitor AI visibility, and measures the impact of your optimization efforts—metrics that traditional SEO tools cannot provide.
No. While schema markup is useful for traditional search, it provides minimal benefit for AI visibility. Content with FAQ schema receives 3.6 citations on average, while well-structured content without schema receives 4.2 citations. Focus on actual content structure and quality rather than markup alone.
See how ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews reference your brand with AmICited's AI citation tracking.

Understand how conversational queries differ from traditional keyword queries. Learn why AI search engines prioritize natural language, user intent, and context...

Discover the key trends shaping AI search evolution in 2026, including multimodal capabilities, agentic systems, real-time information retrieval, and the shift ...

Master voice search optimization for AI assistants with strategies for conversational keywords, featured snippets, local SEO, and schema markup to boost voice a...