
City-Specific AI Visibility: Targeting Local Markets
Learn how geographic targeting impacts AI visibility. Discover why city-level searches show 50% lower visibility than state-level, and how to optimize for local...

Discover how regional AI search varies globally. Learn optimization strategies for Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google AI Overviews across different markets.
When a user in Germany searches for industrial suppliers through ChatGPT, they’re not necessarily seeing German companies first. In fact, 66% of all citations across AI search engines still come from global (primarily US-based) domains, regardless of the user’s location. Only 18.3% use proper country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs) that truly represent local markets. This localization gap is reshaping how brands compete globally.
The disparity in regional citation patterns becomes even more pronounced when examining individual AI search engines. Perplexity leads with 56.5% non-global citations, followed closely by Copilot at 56.0%, while Grok shows a slightly lower but still significant 36.2%. ChatGPT trails at 29.7%, and Gemini demonstrates the lowest localization at 5.3%. These variations suggest fundamentally different training approaches and citation methodologies across platforms. Some engines prioritize comprehensive global coverage, while others have begun implementing more localized sourcing strategies. Understanding which AI platform your audience uses becomes critical for regional market penetration. The choice of AI search engine your customers rely on directly impacts your visibility and citation likelihood in their results.
| AI Engine | Non-Global Citations | Localization Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Perplexity | 56.5% | Excellent |
| Microsoft Copilot | 56.0% | Excellent |
| Grok | 36.2% | Moderate |
| ChatGPT | 29.7% | Low |
| Gemini | 5.3% | Minimal |
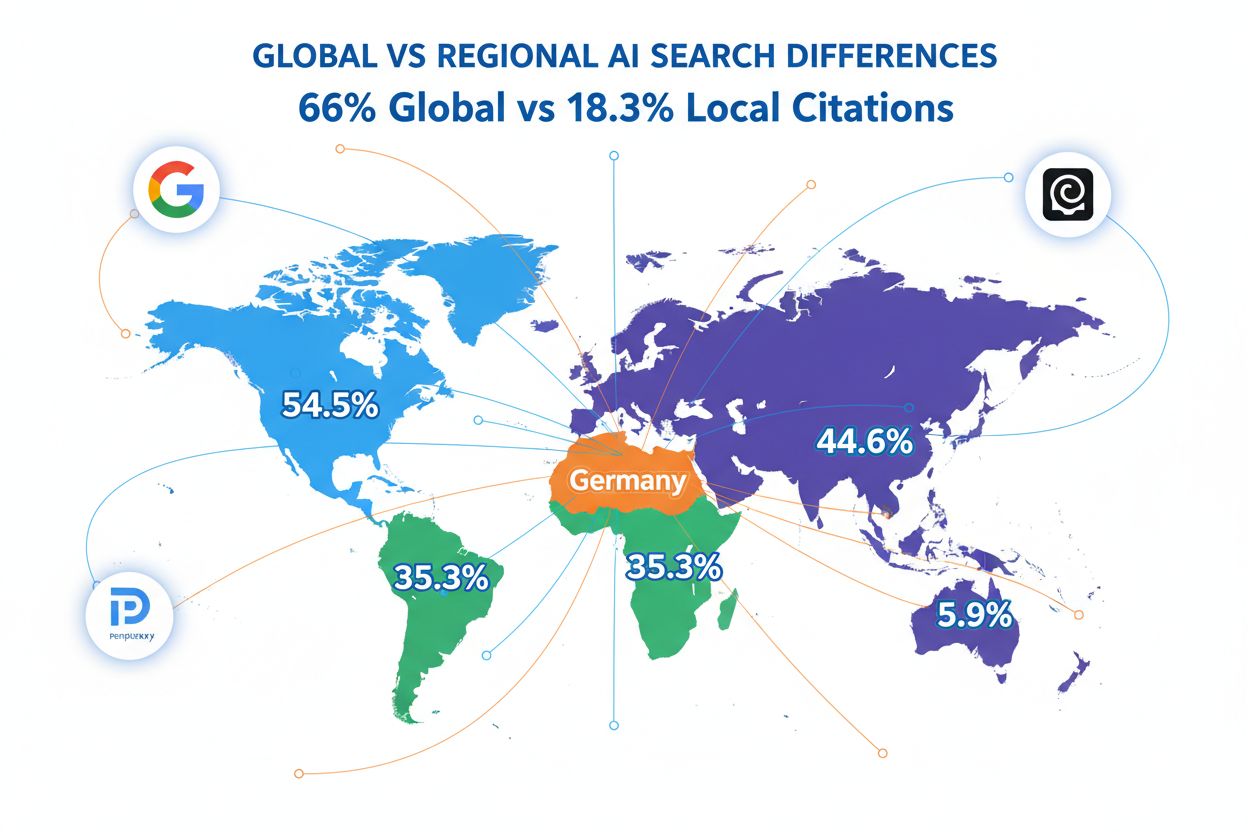
European markets reveal the most dramatic regional variations in AI search localization. The Netherlands leads with 54.5% of citations coming from local Dutch domains, demonstrating strong regional preference in AI results. Germany follows with 44.6% local citations, while France shows 35.3% of results sourcing from French domains. The United Kingdom presents a starkly different picture at just 5.9% local citations, suggesting either stronger global content dominance or different AI training patterns for English-language markets. These disparities indicate that European markets are not monolithic—each country’s AI search ecosystem has evolved differently. Brands operating across Europe cannot apply a single localization strategy; instead, they must tailor approaches by market. The data reveals that proximity to major tech hubs and language-specific AI training significantly influence local visibility.
Key Regional Insights:
The E-E-A-T framework—Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—has become increasingly critical in AI search contexts, yet regional interpretations vary significantly. Experience refers to demonstrated practical knowledge within a specific domain; a German manufacturing consultant carries more weight in German AI results than a generalist from Silicon Valley. Expertise demands verifiable credentials and deep subject matter knowledge, which AI engines now evaluate through citation patterns and content depth. Authoritativeness requires recognition within regional professional networks and industry bodies—a company certified by German industry standards carries more authority in German AI searches than one with only international certifications. Trustworthiness encompasses data privacy compliance, transparent sourcing, and adherence to regional regulations like GDPR. AI engines increasingly weight these factors differently by region, meaning a brand’s E-E-A-T profile must be explicitly optimized for each market. Companies that fail to establish regional E-E-A-T signals find themselves deprioritized in local AI search results, regardless of global reputation.
Geo-identification failures represent a critical blind spot in current AI search optimization. Consider a Spanish manufacturer searching for “proveedores de componentes electrónicos” (electronic component suppliers) through ChatGPT—the results frequently return US-based suppliers with generic international websites rather than Spanish or European alternatives with superior local expertise. This occurs because AI engines struggle to distinguish between a company’s actual operational location and its digital footprint. A US company with a .com domain and English-language content ranks higher than a Spanish company with a .es domain but weaker overall domain authority. The AI’s synthesis process prioritizes citation frequency and domain authority over geographic relevance signals. This means a Spanish buyer may receive recommendations for suppliers with longer shipping times, different regulatory compliance, and higher costs than local alternatives. Fixing geo-identification requires explicit geographic metadata, localized content, and regional authority signals that current AI engines can properly parse.
The traditional hreflang tag approach—which explicitly tells search engines about regional content variants—has become insufficient in the AI search era. Hreflang operates within a rules-based framework where search engines follow explicit instructions about which content serves which regions. However, AI search engines operate through synthesis-based retrieval, where they generate responses by combining information from multiple sources without necessarily following structural metadata. An AI engine may cite your German website for a query from a German user, but it might also synthesize information from your US site, your UK site, and competitor sites simultaneously. Hreflang cannot control this synthesis process because it was designed for traditional search’s link-based ranking model. Instead of relying solely on hreflang, brands must now embed geographic context directly into content, metadata, and organizational structure. The shift requires thinking beyond technical SEO tags toward comprehensive geo-legibility—making your regional identity unmistakable to AI systems.
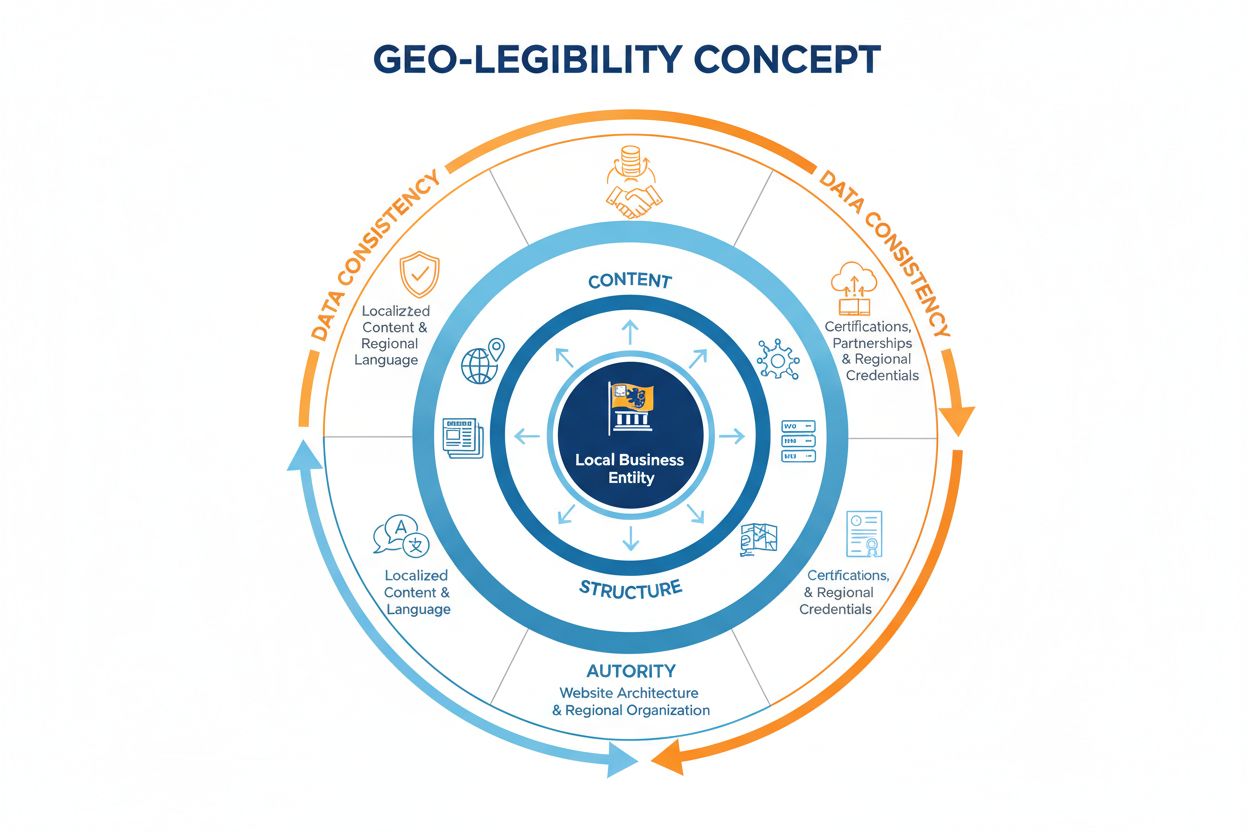
Geo-legibility represents the new imperative: making your geographic identity, regional expertise, and local relevance unmistakably clear to AI search engines. This concept extends far beyond traditional geotargeting and encompasses four critical layers. The first layer is structural geo-legibility: organizing your digital presence so that regional operations, teams, and content are distinctly identifiable—separate regional websites, localized subdomains, or clearly segmented content sections. The second layer is semantic geo-legibility: using language, terminology, and cultural references that signal authentic regional presence—not just translation, but localization that reflects regional business practices and industry standards. The third layer is authority geo-legibility: building verifiable regional credentials through local certifications, partnerships, industry memberships, and citations from regional sources. The fourth layer is operational geo-legibility: demonstrating actual regional operations through local contact information, regional team profiles, local case studies, and region-specific compliance documentation. Together, these layers create a comprehensive signal that tells AI engines: “This organization has genuine, substantive presence in this region.” Without geo-legibility across all four layers, even well-optimized global content will be deprioritized in regional AI search results.
Implementing effective regional AI search optimization requires a systematic, multi-layered approach. First, conduct a geo-legibility audit: map your current digital presence across regions and identify gaps in structural, semantic, authority, and operational signals. Second, create region-specific content hubs: develop dedicated content addressing regional industry challenges, regulatory requirements, and market conditions—not generic global content translated into local languages. Third, build local authority signals: pursue regional certifications, join industry associations, secure citations from regional business publications, and develop partnerships with local organizations. Fourth, optimize metadata comprehensively: implement structured data (Schema.org) that explicitly identifies your regional operations, local team members, regional office locations, and region-specific services. Fifth, develop region-specific case studies and testimonials: showcase projects completed in each region with local client names, regional challenges solved, and measurable outcomes relevant to that market. Sixth, establish regional content governance: assign regional teams or partners responsibility for maintaining geo-legibility, ensuring that regional content remains current, accurate, and culturally appropriate. These steps transform your organization from a global entity with local websites into a genuinely localized presence that AI engines can properly identify and prioritize.
Monitoring your regional AI visibility requires a diagnostic workflow that goes beyond traditional analytics. Step one: establish baseline visibility by searching your key products and services through major AI engines (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Copilot, Gemini, Grok) from different geographic locations, documenting which of your properties receive citations and in what context. Step two: analyze citation patterns by tracking whether your regional properties are cited for regional queries or whether global properties dominate—use tools like AmICited to systematically monitor citation frequency and patterns across regions. Step three: evaluate E-E-A-T signals by examining how AI engines present your regional credentials, certifications, and authority markers in their responses. Step four: assess geo-legibility gaps by reviewing whether AI responses accurately identify your regional operations, local team expertise, and regional service offerings. Step five: iterate based on performance data, adjusting your geo-legibility strategy based on which signals correlate with improved regional AI visibility. This workflow should be conducted quarterly to track how AI search patterns evolve and how your optimization efforts impact regional visibility.
For executives and marketing leaders, regional AI search optimization represents both a strategic imperative and a governance challenge. The business impact is substantial: companies that fail to establish regional geo-legibility will see their market share eroded as customers increasingly rely on AI search to identify suppliers, service providers, and information sources. In markets like the Netherlands and Germany where local citations already represent 44-54% of AI results, the competitive advantage goes to organizations that have invested in regional authority and geo-legibility. This requires cross-functional governance: marketing must own content strategy and regional optimization, legal must ensure compliance with regional data and privacy requirements, operations must provide accurate regional information, and executive leadership must allocate resources for sustained regional presence. The investment in regional AI optimization should be viewed not as a marketing expense but as a fundamental business requirement for maintaining competitive position in each geographic market. Organizations that treat regional AI search as an afterthought to global strategy will find themselves systematically deprioritized in the markets where they operate.
Future-proofing your global AI strategy requires moving beyond reactive optimization toward proactive regional presence building. As AI search engines continue to evolve, the engines that gain market share will likely be those that deliver more localized, region-appropriate results—meaning the competitive advantage will increasingly flow to organizations with strong regional geo-legibility. The next phase of AI search will likely involve even more sophisticated geographic reasoning, potentially incorporating real-time location data, regional regulatory compliance verification, and community-based authority signals. Organizations that begin building comprehensive geo-legibility across all four layers—structural, semantic, authority, and operational—today will be positioned to dominate regional AI search results tomorrow. The window for establishing regional authority and geo-legibility is narrowing as competitors recognize this opportunity. To systematically monitor your regional AI visibility and benchmark against competitors across markets, AmICited provides the analytics infrastructure needed to track citation patterns, identify geo-legibility gaps, and measure the impact of regional optimization efforts—making it an essential tool for any organization competing in multiple geographic markets.
Different AI engines have varying training data, architectural approaches, and citation methodologies. Perplexity prioritizes local sources with 56.5% non-global citations, while Gemini relies heavily on global content at only 5.3% local citations. These differences stem from how each engine was trained and the emphasis placed on regional relevance during development.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is interpreted regionally by AI engines. A German manufacturing consultant carries more weight in German results than a US generalist. Regional certifications, local industry memberships, and compliance with regional regulations like GDPR significantly impact how AI engines evaluate trustworthiness in each market.
Geo-legibility is making your geographic identity, regional expertise, and local relevance unmistakably clear to AI search engines. It encompasses four layers: structural (organization), semantic (language and terminology), authority (regional credentials), and operational (local presence). Without geo-legibility, even well-optimized global content gets deprioritized in regional AI search results.
Create region-specific content hubs addressing local industry challenges, build local authority signals through regional certifications and partnerships, implement structured data identifying regional operations, develop region-specific case studies, and establish regional content governance. These steps transform your organization from a global entity with local websites into a genuinely localized presence.
Hreflang remains important for traditional search indexing but is insufficient for AI search. AI engines synthesize responses rather than serving pages, so hreflang cannot control synthesis. Instead, embed geographic context directly into content, metadata, and organizational structure to ensure regional relevance in AI-generated answers.
Localization is translating and adapting content for different regions. Geo-legibility goes further—it's making your regional identity unmistakably clear to AI systems through structural organization, semantic signals, authority credentials, and operational presence. Localization is a component of geo-legibility, but geo-legibility is the comprehensive approach needed for AI search success.
Monitor your regional AI visibility quarterly to track how AI search patterns evolve and measure the impact of your optimization efforts. Run searches through major AI engines from different geographic locations, analyze citation patterns, evaluate E-E-A-T signals, and assess geo-legibility gaps. This regular cadence helps you stay ahead of competitive changes.
The Netherlands leads with 54.5% local citations, followed by Germany at 44.6% and France at 35.3%. The UK surprisingly ranks lowest at 5.9% local citations despite its developed digital economy. These variations suggest that European markets with strong local digital infrastructure and language-specific AI training show better localization than English-language markets.
Track how your brand appears in AI search results across different regions and markets. Get insights into regional citation patterns and optimize your global AI presence.

Learn how geographic targeting impacts AI visibility. Discover why city-level searches show 50% lower visibility than state-level, and how to optimize for local...

Discover how AI search engines vary by country and language. Learn about localization differences between ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Copilot, and how geog...
Learn how to reverse-engineer competitor AI citations and discover what content AI models prefer to cite. Strategic guide to competitive advantage in AI search.