
What AI Crawlers Should I Allow Access? Complete Guide for 2025
Learn which AI crawlers to allow or block in your robots.txt. Comprehensive guide covering GPTBot, ClaudeBot, PerplexityBot, and 25+ AI crawlers with configurat...
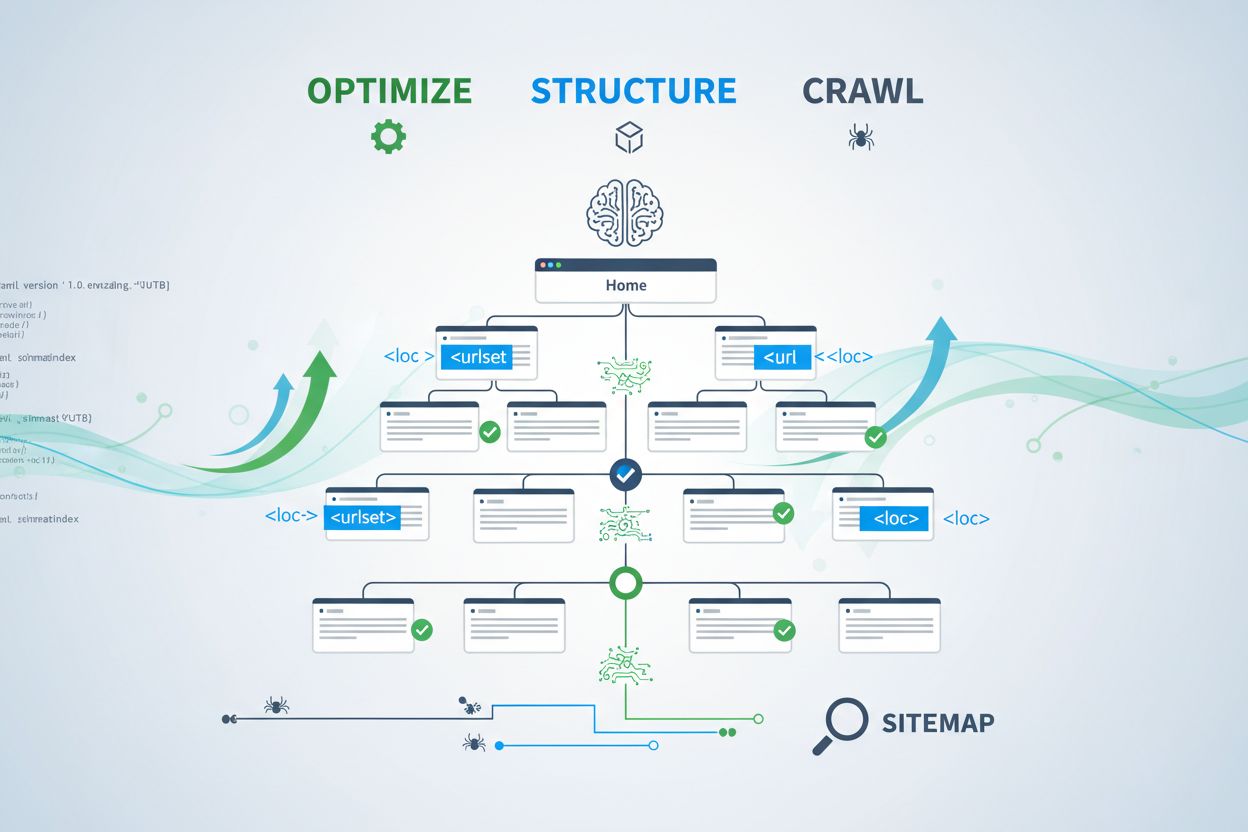
Learn how to optimize XML sitemaps for AI crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot. Master sitemap best practices to improve visibility in AI-generated answers and LLM indexing.
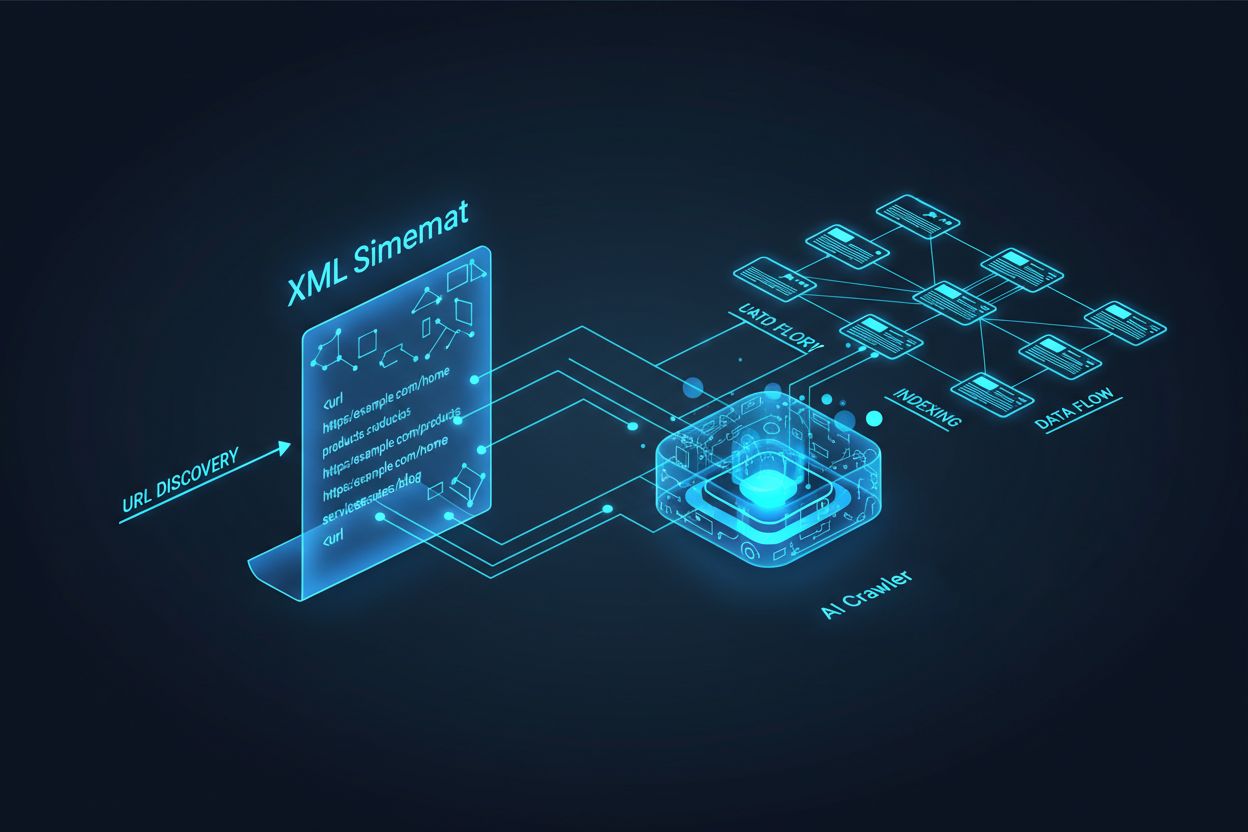
AI crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot operate fundamentally differently from traditional search engine bots. While Googlebot indexes pages for ranking in search results, AI crawlers extract knowledge to train and inform large language models that power conversational search and AI-generated answers. Without a properly optimized XML sitemap, your content remains invisible to these critical systems, regardless of how well-written or authoritative it may be. Think of your sitemap as a roadmap that tells AI systems exactly where your most valuable content lives and how it’s organized.
The distinction between traditional search crawlers and AI crawlers is crucial for understanding why sitemap optimization matters more than ever. Traditional search engines like Google focus on ranking individual pages for specific keywords, while AI crawlers prioritize knowledge capture and semantic understanding. Here’s how they differ:
| Aspect | Traditional Crawlers (Googlebot) | AI Crawlers (GPTBot, ClaudeBot) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Rank pages in search results | Extract knowledge for LLM training and real-time answers |
| Focus | Metadata, internal links, ranking signals | Content structure, semantic meaning, fact density |
| Crawl Priority | Based on PageRank and freshness | Based on authority, topical relevance, and knowledge value |
| Citation Impact | Drives traffic through blue links | Determines if your content appears in AI-generated answers |
| JavaScript Handling | Executes and renders JavaScript | Often skips JavaScript; prioritizes server-rendered HTML |
This fundamental difference means that optimizing for traditional SEO alone is no longer sufficient. Your sitemap must now serve dual purposes: helping traditional search engines understand your site structure while simultaneously guiding AI systems to your most valuable knowledge assets.
An XML sitemap functions as your website’s blueprint, explicitly telling crawlers which pages exist and how they relate to your overall content strategy. For AI systems, sitemaps serve an even more critical function than they do for traditional search. AI crawlers use sitemaps to understand your site’s topical architecture, identify high-priority content, and determine which pages deserve deeper analysis. When your sitemap is comprehensive and well-organized, AI systems can more efficiently discover and evaluate your content for inclusion in generative answers. Conversely, an incomplete or outdated sitemap creates blind spots that prevent AI systems from ever encountering your most important pages. The impact is direct: pages not in your sitemap are significantly less likely to be cited by AI systems, regardless of their quality or relevance.
Creating an effective sitemap for AI crawlers requires more than simply listing every URL on your site. Your sitemap should be strategically curated to include only pages that provide genuine value to users and AI systems. Here are the essential best practices:
A well-structured sitemap acts as a quality filter, telling AI systems that you’ve carefully curated your content and that every URL included deserves attention. This strategic approach significantly improves your chances of being selected for citation in AI-generated answers.
Recency is one of the strongest ranking factors in AI-powered search systems. When AI crawlers evaluate which sources to cite in generated answers, they heavily weight content freshness. The lastmod timestamp in your XML sitemap is the primary signal that tells AI systems when your content was last updated. Outdated or missing timestamps can cause even authoritative content to be deprioritized in favor of fresher sources. If your sitemap shows that a page hasn’t been updated in years, AI systems may assume the information is stale and choose competitor content instead. Conversely, accurate lastmod timestamps that reflect genuine content updates signal to AI crawlers that your information is current and reliable. For time-sensitive topics like pricing, regulations, or industry trends, maintaining accurate timestamps becomes even more critical. Automated timestamp updates through your CMS ensure that every content change is immediately reflected in your sitemap, maximizing your visibility in AI-generated answers.
While sitemaps invite crawlers to index your content, robots.txt files control which parts of your site crawlers can access. These two files must work in harmony to maximize your AI visibility. A common mistake is creating a comprehensive sitemap while simultaneously blocking AI crawlers in your robots.txt file, which creates a contradiction that confuses crawlers and reduces your visibility. Your robots.txt should explicitly allow major AI crawlers like GPTBot, ClaudeBot, and PerplexityBot to access your content. You can use robots.txt strategically to block only pages that shouldn’t be indexed, such as admin dashboards, login pages, or duplicate content versions. The key is ensuring that your robots.txt rules align with your sitemap strategy—if a page is in your sitemap, it should be accessible according to your robots.txt rules. Regular audits of both files help identify misconfigurations that might be silently limiting your AI visibility.
The most effective AI optimization strategies treat sitemaps and structured data as complementary systems that reinforce each other. When your sitemap highlights a page as important and that page includes relevant schema markup, you’re sending consistent signals to AI crawlers about the page’s purpose and value. For example, if your sitemap prioritizes a how-to guide, that page should include HowTo schema markup that provides structured information about the steps involved. Similarly, product pages in your sitemap should include Product schema with pricing, availability, and review information. This alignment creates a coherent data picture that AI systems can easily interpret and trust. When sitemaps and structured data conflict or diverge, AI crawlers become uncertain about the page’s true purpose, reducing the likelihood of citation. By ensuring that your sitemap strategy aligns with your schema implementation, you create a unified signal that dramatically improves your chances of being selected for inclusion in AI-generated answers.
Different types of content require different sitemap strategies to maximize AI visibility. Blog posts, product pages, service descriptions, and FAQ content all serve different purposes and should be optimized accordingly:
| Content Type | Sitemap Strategy | Recommended Schema Markup | Priority Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blog Posts & Articles | Include with accurate publish and update dates | Article, NewsArticle, BlogPosting | Prioritize recent, evergreen content; update lastmod regularly |
| Product Pages | Include with inventory updates; consider separate product sitemap | Product, Offer, AggregateRating | Highlight bestsellers and new products; update prices frequently |
| Service Pages | Include with service update dates | Service, LocalBusiness, ProfessionalService | Prioritize core services; update availability and pricing |
| FAQ Pages | Include with content update dates | FAQPage, Question, Answer | Prioritize comprehensive FAQs; update answers when information changes |
| Video Content | Include in video sitemap with thumbnail and duration | VideoObject, Video | Include transcripts; update view counts and engagement metrics |
| Image Content | Include in image sitemap with captions | ImageObject, Product (for product images) | Optimize alt text; include descriptive captions |
This differentiated approach ensures that each content type receives appropriate optimization for AI discovery. By tailoring your sitemap strategy to your content mix, you maximize the likelihood that AI systems will find and cite your most valuable assets.
The llms.txt standard, proposed in late 2024, represents an experimental approach to helping AI systems understand website structure. Unlike XML sitemaps, llms.txt is a Markdown-based file that provides a human-readable table of contents for your site. It lists your most important pages and resources in a format that’s easier for language models to parse and understand. While the concept is promising, current evidence suggests that llms.txt has minimal impact on AI visibility compared to traditional XML sitemaps. Major AI crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot continue to rely primarily on XML sitemaps for URL discovery and recency signals. Rather than replacing your XML sitemap, llms.txt should be viewed as a supplementary tool that may provide additional context to AI systems. If you implement llms.txt, ensure it complements rather than replaces your core sitemap strategy, and focus first on perfecting your XML sitemap with accurate timestamps and strategic content curation.
Even well-intentioned websites often make critical sitemap errors that silently limit their AI visibility. Understanding and avoiding these mistakes is essential for maximizing your presence in AI-generated answers:
Addressing these common mistakes can immediately improve your AI visibility. Start by auditing your current sitemap against this checklist and fixing any issues you identify.
Maintaining an optimized sitemap requires ongoing monitoring and validation. Several tools can help you ensure your sitemap remains effective for AI crawlers. Google Search Console provides built-in sitemap validation and shows you how many URLs Google has indexed from your sitemap. Screaming Frog SEO Spider allows you to crawl your entire site and compare the results against your sitemap, identifying missing or broken URLs. XML sitemap validators check your sitemap syntax and ensure it complies with the XML sitemap protocol. For larger enterprises, dedicated SEO platforms like Semrush and Ahrefs include sitemap analysis features that track changes over time. Regular audits—ideally monthly—help you catch issues before they impact your AI visibility. Set calendar reminders to review your sitemap whenever you make significant content changes, launch new sections, or update your site architecture.
Understanding how AI crawlers interact with your sitemap requires active monitoring and analysis. Your server logs contain valuable data about which AI crawlers are visiting your site, how frequently they crawl, and which pages they prioritize. By analyzing these logs, you can identify patterns and optimize your sitemap accordingly. Tools like AmICited.com help you monitor how often your content is cited by AI systems like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews, providing direct feedback on your sitemap’s effectiveness. Google Analytics can be configured to track referral traffic from AI systems, showing you which pages generate the most AI-driven visibility. By correlating this data with your sitemap structure, you can identify which content types and topics resonate most with AI systems. This data-driven approach allows you to continuously refine your sitemap strategy, prioritizing content that generates the most AI citations and visibility.
Beyond basic sitemap optimization, advanced strategies can significantly enhance your AI visibility. Creating separate sitemaps for different content types—such as dedicated blog sitemaps, product sitemaps, and video sitemaps—allows you to apply type-specific optimization strategies. Dynamic sitemap generation, where your sitemap updates in real-time as content changes, ensures that AI crawlers always see your most current content. For large enterprise sites with thousands of pages, implementing sitemap hierarchies and strategic prioritization helps AI crawlers focus on your most valuable content. Some organizations create AI-specific sitemaps that highlight only their highest-authority, most citation-worthy content, signaling to AI systems which pages deserve priority attention. Integrating your sitemap strategy with your content management system ensures that optimization happens automatically rather than requiring manual updates. These advanced approaches require more technical sophistication but can yield significant improvements in AI visibility for organizations with complex content ecosystems.
The AI crawler landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new crawlers emerging regularly and standards like llms.txt gaining adoption. Future-proofing your sitemap strategy means building flexibility into your systems and staying informed about industry developments. Implement sitemap generation systems that can easily accommodate new crawler requirements without requiring manual reconfiguration. Monitor announcements from major AI companies about new crawlers and update your robots.txt and sitemap strategies accordingly. Consider the long-term value of AI visibility versus content control—while some organizations choose to block AI crawlers, the trend suggests that AI citations will become increasingly important for brand visibility. Develop clear policies for how your organization will manage AI crawler access and content usage. By treating your sitemap as a living document that evolves with the AI landscape, you ensure that your content remains discoverable and citable as search and discovery mechanisms continue to transform.
You should update your sitemap whenever you publish new content or make significant changes to existing pages. Ideally, implement automated sitemap generation so updates happen immediately. For sites with frequent content changes, daily updates are recommended. For static sites, monthly reviews are sufficient.
Most major AI crawlers like GPTBot and ClaudeBot respect robots.txt directives, but not all do. The best practice is to explicitly allow AI crawlers in your robots.txt file rather than relying on default behavior. Monitor your server logs to verify that crawlers are behaving as expected.
XML sitemaps are machine-readable files that list all your URLs with metadata like lastmod timestamps. llms.txt is a newer Markdown-based standard designed to provide AI systems with a human-readable table of contents. XML sitemaps are currently more important for AI visibility, while llms.txt should be viewed as supplementary.
Check your server logs for user agents like 'GPTBot', 'ClaudeBot', 'PerplexityBot', and 'Google-Extended'. You can also use tools like AmICited.com to monitor how often your content is cited by AI systems, which indicates successful crawling and indexing.
Yes, creating separate sitemaps for blogs, products, videos, and images allows you to apply type-specific optimization strategies. This also helps AI crawlers understand your content structure more clearly and can improve crawl efficiency for large sites.
XML sitemaps should contain no more than 50,000 URLs per file. For larger sites, use sitemap indexes to organize multiple sitemap files. AI crawlers can handle large sitemaps, but breaking them into logical sections improves crawl efficiency and makes management easier.
Lastmod timestamps signal content freshness to AI crawlers. Recency is a strong ranking factor in AI systems, so accurate timestamps help your content compete for citations. Always use automated systems to update timestamps only when content actually changes—never manually set false timestamps.
Yes, a poorly maintained sitemap can significantly harm your AI visibility. Broken links, outdated URLs, inaccurate timestamps, and incomplete coverage all reduce your chances of being cited by AI systems. Regular audits and maintenance are essential for protecting your AI visibility.
Track how often your content is cited by ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Optimize your sitemap strategy based on real AI citation data.

Learn which AI crawlers to allow or block in your robots.txt. Comprehensive guide covering GPTBot, ClaudeBot, PerplexityBot, and 25+ AI crawlers with configurat...
Complete reference guide to AI crawlers and bots. Identify GPTBot, ClaudeBot, Google-Extended, and 20+ other AI crawlers with user agents, crawl rates, and bloc...

Learn how to allow AI bots like GPTBot, PerplexityBot, and ClaudeBot to crawl your site. Configure robots.txt, set up llms.txt, and optimize for AI visibility.