
Should I Use Tables in Content for AI Search? Complete Guide to Table Optimization
Learn why tables are essential for AI search optimization. Discover how structured data in tables improves AI comprehension, increases citation chances, and enh...

Learn how tables, lists, and structured data improve your content’s visibility in AI search results. Discover best practices for optimizing content for LLMs and AI systems like Google AI Overviews and Perplexity.
When artificial intelligence processes your content, it doesn’t read like humans do. AI converts text into tokens and then transforms those tokens into numerical vectors that represent meaning and context. This fundamental difference in how AI processes information means that structured data formats like tables and lists are inherently more “machine-readable” than flowing prose. Tables and lists are “snippable”—AI can extract specific information directly without parsing surrounding context, making them ideal for AI systems that need to quickly identify and cite relevant data. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on keyword matching and semantic relevance, AI visibility depends on how easily an AI system can parse, understand, and extract discrete pieces of information from your content. The formatting and structure you choose directly signal to AI systems which information is most important and how it relates to other data points.
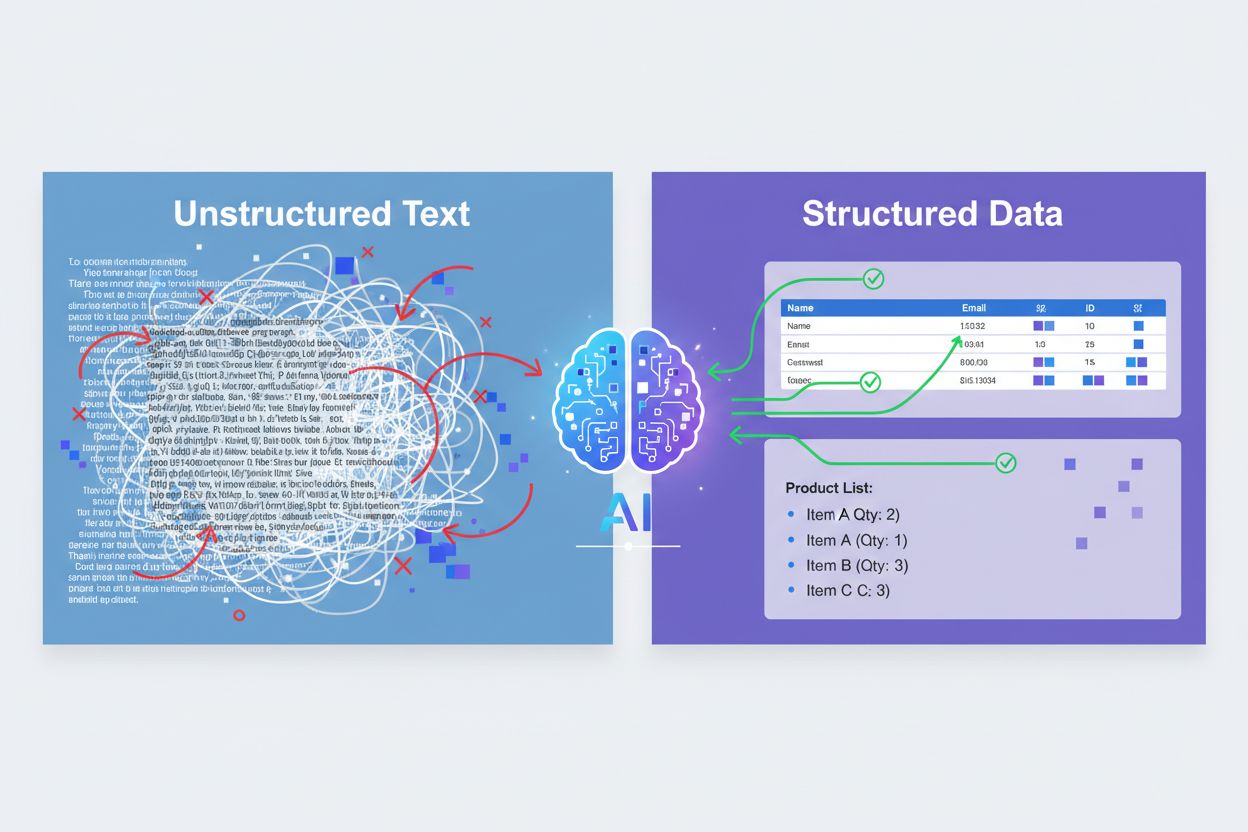
Tables represent one of the most powerful tools for improving AI visibility because they organize data into rows and columns that AI can parse systematically and unambiguously. Each cell in a table functions as a discrete data point with clear relationships to other cells in the same row and column, eliminating the ambiguity that often exists in paragraph text. When AI systems encounter a well-structured table, they can extract specific information without needing to read and interpret surrounding context—a process that reduces errors and improves accuracy. Tables are frequently used in featured snippets and AI-generated answers because they present information in a format that’s easy for AI to cite and for users to understand. Common use cases include product comparisons, pricing matrices, feature comparisons, and specification tables that allow AI to quickly answer user questions with precise data. Beyond improving AI readability, tables also reduce cognitive load for both AI systems and human readers, making your content more valuable across the board. Proper HTML table markup with semantic tags (<table>, <thead>, <tbody>, <tr>, <th>, <td>) is essential—tables created with divs or images are invisible to AI systems.
| Table Element | AI Parsing Capability | Human Readability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTML Tables | Excellent - Direct parsing | Excellent | Structured data, comparisons |
| Lists | Excellent - Item extraction | Excellent | Sequential or grouped info |
| Paragraph Text | Good - Context required | Good | Narrative, explanations |
| Images of Tables | Poor - Cannot parse | Good | Visual design only |
| Tabs/Accordions | Poor - Hidden content | Fair | Space-saving only |
Bullet points and numbered lists break complex information into discrete, scannable items that AI can extract and cite individually without losing meaning. Each item in a well-constructed list functions as a complete thought, allowing AI systems to pull specific points directly into summaries and answers without requiring context from surrounding paragraphs. Numbered lists signal sequence, steps, or priority, making them ideal for how-to content, processes, and ranked information that AI systems frequently cite. Bullet points signal equal-weight options or features, making them perfect for feature lists, benefits, and alternative approaches. Lists appear with remarkable frequency in AI-generated summaries and answers because they’re already in the format that AI systems prefer to output. Beyond improving AI readability, lists also dramatically improve human engagement—users scan lists faster than paragraphs and retain information more effectively. Proper HTML markup using <ul>, <ol>, and <li> tags is critical; lists created with dashes or other formatting are less reliably parsed by AI systems.
Schema markup provides explicit context that tells AI systems exactly what information they’re reading, eliminating the need for AI to infer meaning from surrounding text. While AI systems have become sophisticated at understanding context, schema markup removes all ambiguity by explicitly labeling data types, relationships, and attributes. Common schema types that boost AI visibility include FAQ schema (for question-answer pairs), HowTo schema (for step-by-step processes), Product schema (for e-commerce items), Article schema (for content), and Organization schema (for company information). Websites that implement relevant schema markup see a significant increase in appearing within AI-generated answers and summaries because the markup makes their information immediately accessible and trustworthy. For example, Product schema with price, availability, ratings, and reviews allows AI systems to quickly answer product-related questions with accurate, cited information directly from your site. Schema markup also helps AI understand entity relationships—how products relate to categories, how articles relate to authors, how reviews relate to products. Here’s an example of Product schema in JSON-LD format:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Professional SEO Analysis Tool",
"image": "https://example.com/product-image.jpg",
"description": "Advanced tool for monitoring AI citations and visibility",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "AmICited"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"url": "https://example.com/product",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"price": "99.00",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.8",
"reviewCount": "247"
}
}
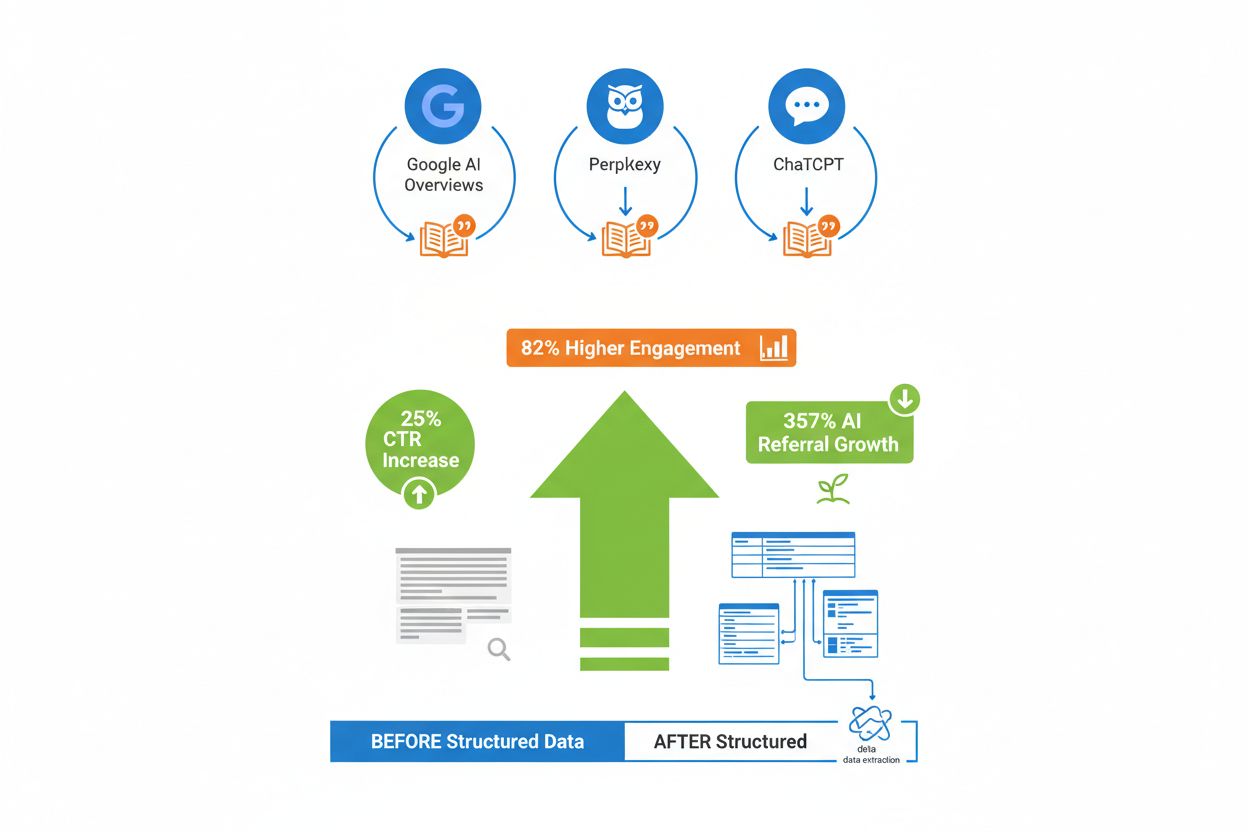
The impact of structured data on AI visibility is measurable and significant. Research shows that websites implementing schema markup experience 25-82% increases in click-through rates from AI-generated answers and featured snippets, depending on industry and content type. Websites with properly implemented schema markup appear more frequently in AI responses because the markup makes their information immediately accessible and verifiable. AI systems cite sources with clear, structured information more often because the data is easier to extract, verify, and present to users. This is where tools like AmICited.com become invaluable—they track exactly how AI systems reference your brand, content, and data across different AI platforms and search engines. Brands that combine tables, lists, and schema markup consistently appear more frequently in AI citations, directly translating to increased traffic and brand visibility. The correlation is clear: structured data isn’t just about SEO anymore—it’s about ensuring your content is visible to the AI systems that increasingly mediate how users discover information.
Creating tables that AI systems can reliably parse requires attention to several key principles. Use proper HTML table tags (<table>, <thead>, <tbody>, <tr>, <th>, <td>) rather than divs or other workarounds—AI systems depend on semantic HTML to understand table structure. Include descriptive headers in the first row that clearly label what each column contains; headers are the key to AI understanding table relationships. Keep each table focused on a single topic or comparison rather than mixing multiple unrelated datasets, which confuses AI parsing. Avoid merged cells, complex nested structures, or irregular layouts that make it difficult for AI to understand row-column relationships. Include alt text or a descriptive caption that explains the table’s purpose and key takeaways for users who can’t see the table. Never use images of tables—they’re invisible to AI systems and inaccessible to users with visual impairments. Ensure tables are mobile-responsive so they remain readable on all devices, and make sure each table is self-contained and understandable without requiring context from surrounding paragraphs.
| Best Practice | Why It Matters for AI | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Semantic HTML tags | AI relies on proper structure | Use <table>, <thead>, <tbody>, <th>, <td> |
| Clear headers | Headers define column meaning | First row should contain descriptive labels |
| Single topic | Prevents parsing confusion | One comparison or dataset per table |
| No merged cells | Maintains row-column clarity | Keep structure regular and predictable |
| Descriptive captions | Provides context and purpose | Add <caption> tag or surrounding text |
| Mobile responsive | Ensures accessibility | Use CSS for responsive design |
| Sufficient contrast | Improves readability | Meet WCAG color contrast standards |
Creating lists that AI systems can effectively extract and cite requires strategic structuring and formatting. Start each list item with a strong keyword or core concept that immediately communicates the item’s meaning—this helps AI systems quickly identify and extract relevant points. Keep items parallel in structure and similar in length so AI systems recognize them as equivalent options or steps rather than a mixed collection of unrelated ideas. Use consistent formatting throughout your lists—if one item is a complete sentence, all items should be complete sentences; if one is a phrase, all should be phrases. Limit lists to 3-7 items for optimal AI extraction; longer lists become harder for AI to parse and cite effectively. Introduce your list with context-setting text that explains what the list contains and why it matters, giving AI systems the framework for understanding the list items. Use descriptive text rather than vague labels—“Improves website loading speed by 40%” is more useful to AI than “Performance benefits.” Combine your lists with surrounding paragraph context that explains the significance of the information, helping AI systems understand not just what the data is, but why it matters.
The most effective approach to AI visibility combines all three elements—tables, lists, and schema markup work synergistically to maximize how effectively AI systems can understand, extract, and cite your content. Schema markup provides the explicit context that helps AI understand what tables and lists contain, while tables and lists make schema markup more effective by presenting information in formats that AI systems prefer. When you implement schema markup for a table or list, you’re essentially giving AI systems a roadmap for understanding the data structure and relationships. For example, FAQ schema works perfectly with lists of questions and answers, and Product schema becomes far more powerful when paired with feature comparison tables. Websites that implement all three elements together see higher rates of appearing in multiple AI formats—featured snippets, AI Overviews, direct answers, and knowledge panels. AmICited.com data shows that brands using tables, lists, and schema markup together are cited 3-5 times more frequently than brands using only one or two of these elements. The combination creates a comprehensive, AI-friendly content structure that makes your information impossible for AI systems to ignore.
Even well-intentioned content creators often make mistakes that significantly reduce AI visibility and citation rates. Using images instead of HTML tables is perhaps the most common error—images are invisible to AI systems, making your data completely inaccessible. Inconsistent list formatting, where some items are complete sentences and others are fragments, confuses AI parsing and reduces extraction accuracy. Missing or incomplete schema markup leaves AI systems guessing about data types and relationships instead of having explicit information. Tables without proper headers make it impossible for AI to understand column relationships and meaning. Lists that are too long or poorly structured become difficult for AI to parse and cite effectively. Hiding information in tabs, accordions, or other expandable elements makes it invisible to AI systems that can’t interact with JavaScript-dependent content. Using non-semantic HTML (like divs styled to look like tables) defeats the purpose of structured formatting. Outdated or invalid schema markup can actually harm your AI visibility by providing incorrect information.
Implementing tables, lists, and schema markup is only half the battle—you need to monitor how these changes affect your AI visibility and citation rates. Use AmICited.com to track exactly how AI systems cite your brand, content, and data across different AI platforms, giving you concrete data on what’s working. Monitor your appearance in Google AI Overviews to see if your content is being selected for AI-generated answers and how frequently. Track featured snippet performance in Google Search Console to understand how your structured data affects visibility in traditional search results. Measure CTR changes after implementing tables, lists, and schema markup to quantify the business impact of improved AI visibility. Use Google Search Console’s performance reports to identify which queries trigger AI citations and which content formats perform best. A/B test different table formats, list structures, and schema implementations to discover what works best for your specific audience and content type. Regular audits ensure your markup remains valid and up-to-date, preventing the common mistakes that can actually harm your AI visibility.
AI systems parse content into discrete data points. Tables and lists provide clear, structured information that AI can extract directly without interpretation, making them more reliable for AI-generated answers and featured snippets.
HTML tables use semantic markup that AI can read and parse. Image tables are invisible to AI systems and won't be extracted for featured snippets or AI responses, making them ineffective for AI visibility.
While tables and lists help significantly, schema markup provides explicit context about your content. Together, they work synergistically to increase your chances of appearing in AI responses and featured snippets.
3-7 items is ideal. This length is scannable for humans and provides enough data for AI to extract without being overwhelming or difficult to parse.
Yes. Structured content improves readability for both humans and AI, which can positively impact engagement metrics, user experience signals, and overall search rankings.
Use Google's Rich Results Test to validate your markup. Monitor your appearance in Google AI Overviews and use AmICited.com to track how AI systems cite your content.
FAQ schema works well with lists, Product schema with comparison tables, and HowTo schema with numbered lists. Choose based on your content type and the information you're presenting.
Quarterly audits are recommended to ensure markup remains valid and up-to-date as your content evolves and AI systems update their parsing requirements.
Track how AI systems cite your brand across Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other LLMs. Get insights into your AI search performance and optimize your content strategy.

Learn why tables are essential for AI search optimization. Discover how structured data in tables improves AI comprehension, increases citation chances, and enh...

Learn how to optimize content readability for AI systems, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI search engines. Discover best practices for structure, formatting, and cla...
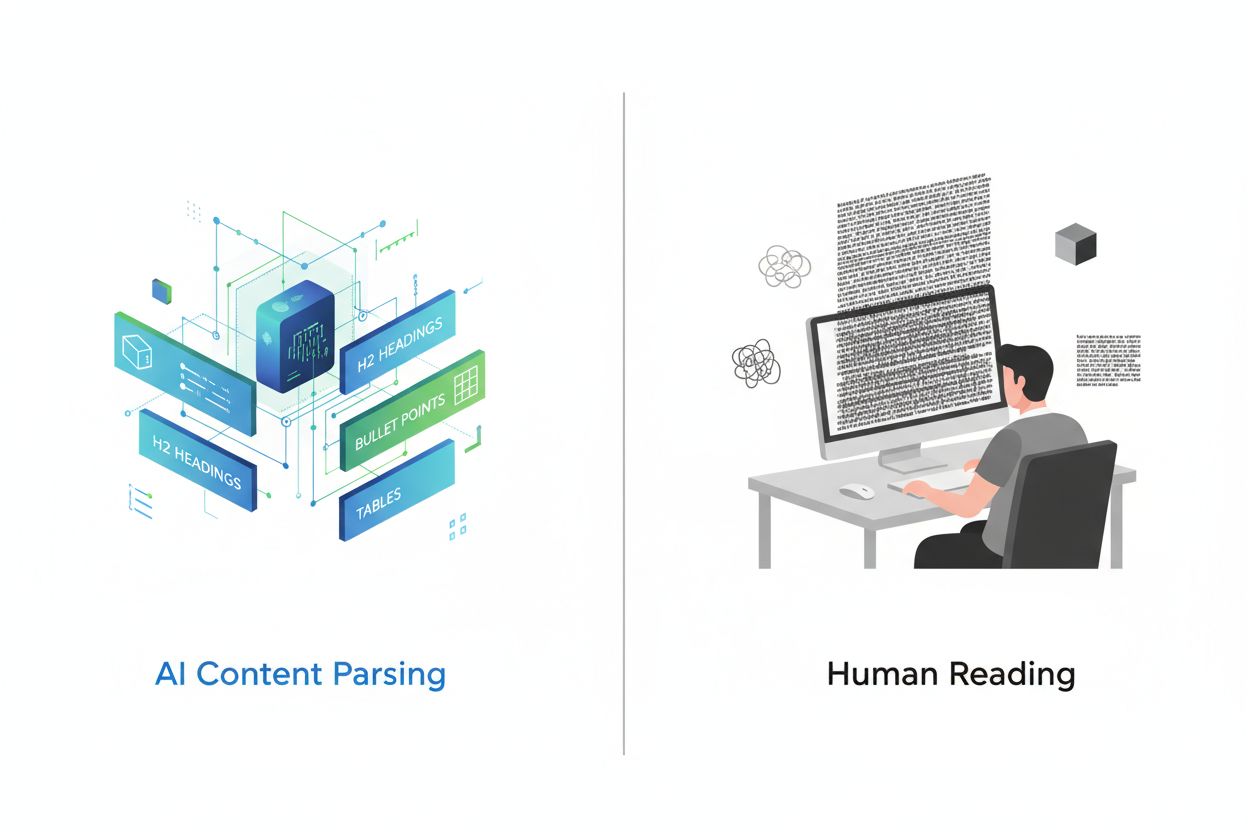
Learn how to restructure your content for AI systems with practical before and after examples. Discover techniques to improve AI citations and visibility across...