Training Data vs Live Search: How AI Systems Access Information
Understand the difference between AI training data and live search. Learn how knowledge cutoffs, RAG, and real-time retrieval impact AI visibility and content s...
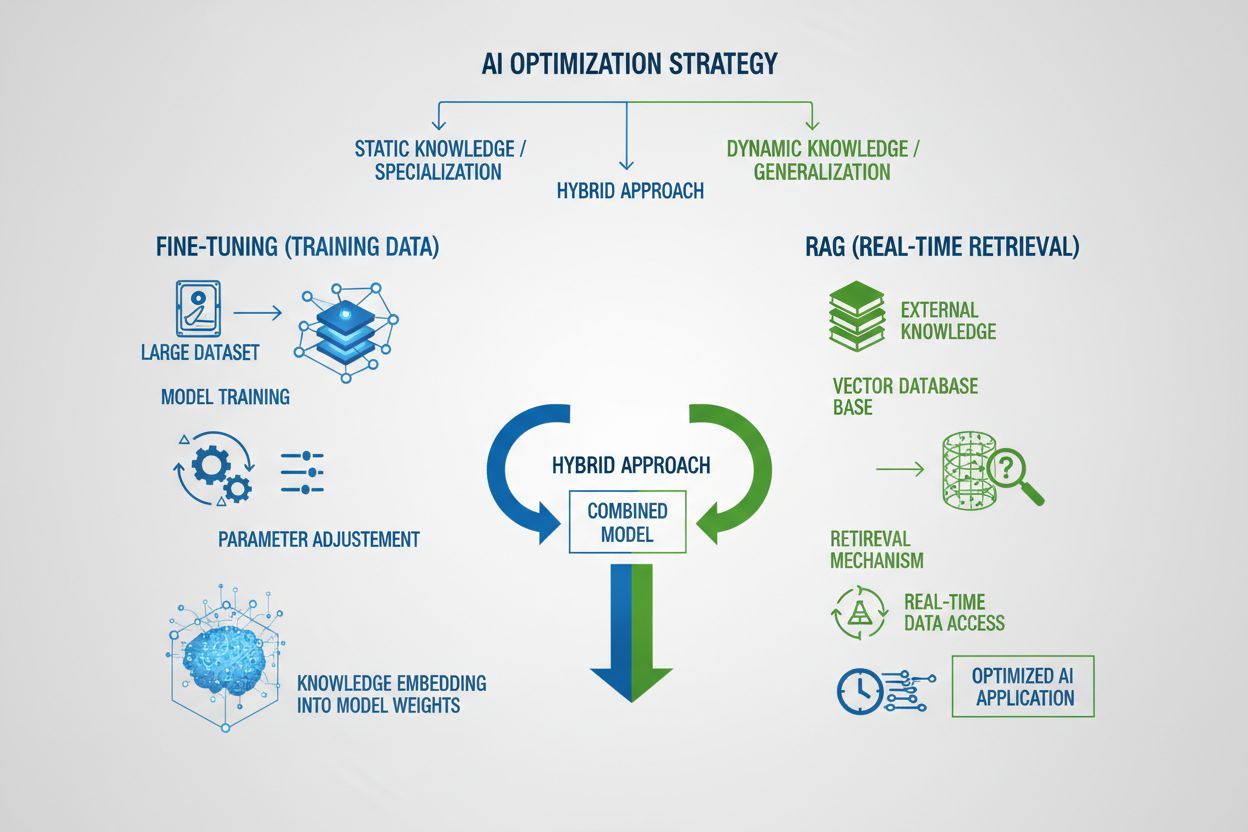
Compare training data optimization and real-time retrieval strategies for AI. Learn when to use fine-tuning vs RAG, cost implications, and hybrid approaches for optimal AI performance.
Training data optimization and real-time retrieval represent fundamentally different approaches to equipping AI models with knowledge. Training data optimization involves embedding knowledge directly into a model’s parameters through fine-tuning on domain-specific datasets, creating static knowledge that remains fixed after training completes. Real-time retrieval, conversely, keeps knowledge external to the model and fetches relevant information dynamically during inference, enabling access to dynamic information that can change between requests. The core distinction lies in when knowledge is integrated into the model: training data optimization happens before deployment, while real-time retrieval happens during each inference call. This fundamental difference cascades through every aspect of implementation, from infrastructure requirements to accuracy characteristics to compliance considerations. Understanding this distinction is essential for organizations deciding which optimization strategy aligns with their specific use cases and constraints.
Training data optimization works by systematically adjusting a model’s internal parameters through exposure to curated, domain-specific datasets during the fine-tuning process. When a model encounters training examples repeatedly, it gradually internalizes patterns, terminology, and domain expertise through backpropagation and gradient updates that reshape the model’s learning mechanisms. This process allows organizations to encode specialized knowledge—whether medical terminology, legal frameworks, or proprietary business logic—directly into the model’s weights and biases. The resulting model becomes highly specialized for its target domain, often achieving performance comparable to much larger models; research from Snorkel AI demonstrated that fine-tuned smaller models can perform equivalently to models 1,400 times larger. Key characteristics of training data optimization include:
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) fundamentally changes how models access knowledge by implementing a four-stage process: query encoding, semantic search, context ranking, and generation with grounding. When a user submits a query, RAG first converts it into a dense vector representation using embedding models, then searches a vector database containing indexed documents or knowledge sources. The retrieval stage uses semantic search to find contextually relevant passages rather than simple keyword matching, ranking results by relevance scores. Finally, the model generates responses while maintaining explicit references to retrieved sources, grounding its output in actual data rather than learned parameters. This architecture enables models to access information that didn’t exist during training, making RAG particularly valuable for applications requiring current information, proprietary data, or frequently updated knowledge bases. The RAG mechanism essentially transforms the model from a static knowledge repository into a dynamic information synthesizer that can incorporate new data without retraining.
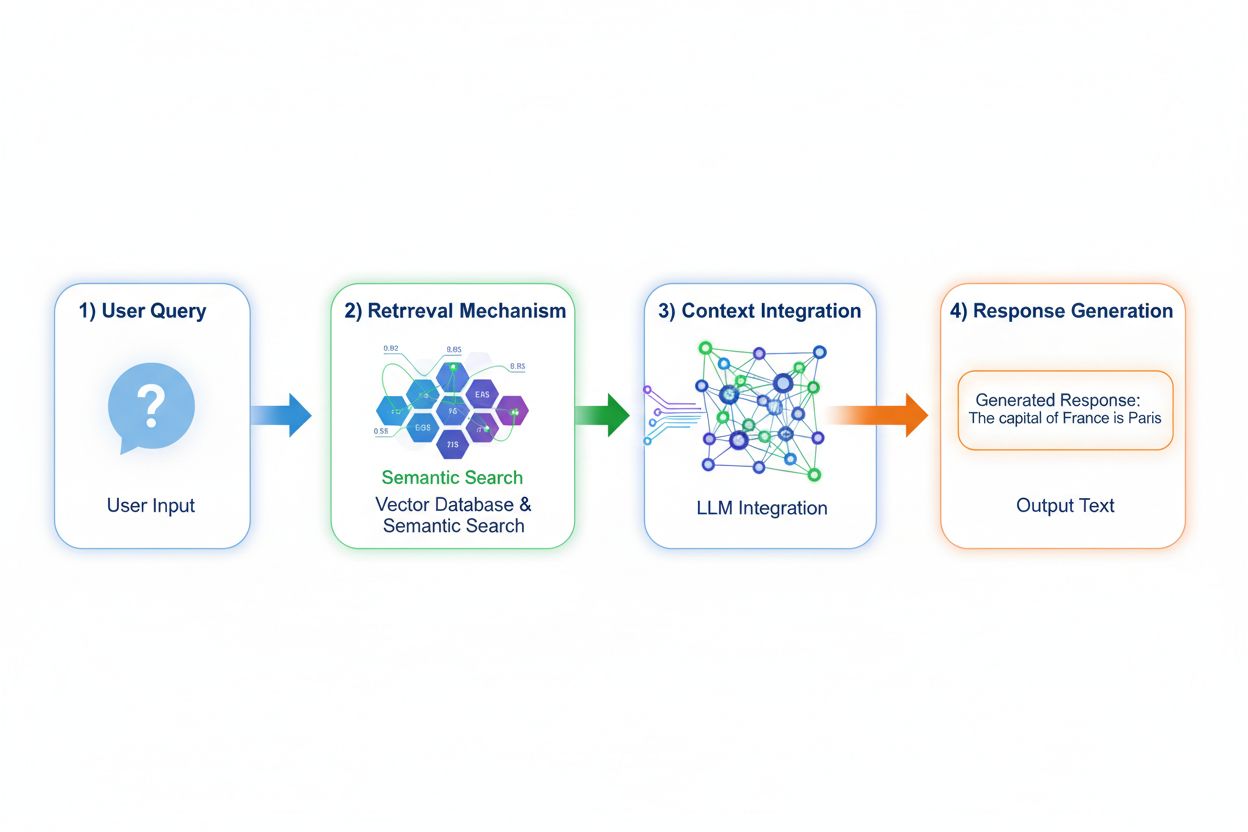
The accuracy and hallucination profiles of these approaches differ significantly in ways that impact real-world deployment. Training data optimization produces models with deep domain understanding but limited ability to acknowledge knowledge boundaries; when a fine-tuned model encounters questions outside its training distribution, it may confidently generate plausible-sounding but incorrect information. RAG substantially reduces hallucinations by grounding responses in retrieved documents—the model cannot claim information that doesn’t appear in its source material, creating natural constraints on fabrication. However, RAG introduces different accuracy risks: if the retrieval stage fails to find relevant sources or ranks irrelevant documents highly, the model generates responses based on poor context. Data freshness becomes critical for RAG systems; training data optimization captures a static snapshot of knowledge at training time, while RAG continuously reflects the current state of source documents. Source attribution provides another distinction: RAG inherently enables citation and verification of claims, while fine-tuned models cannot point to specific sources for their knowledge, complicating fact-checking and compliance verification.
The economic profiles of these approaches create distinct cost structures that organizations must carefully evaluate. Training data optimization requires substantial computational cost upfront: GPU clusters running for days or weeks to fine-tune models, data annotation services to create labeled training datasets, and ML engineering expertise to design effective training pipelines. Once trained, serving costs remain relatively low since inference requires only standard model serving infrastructure without external lookups. RAG systems invert this cost structure: lower initial training costs since no fine-tuning occurs, but ongoing infrastructure expenses for maintaining vector databases, embedding models, retrieval services, and document indexing pipelines. Key cost factors include:
Security and compliance implications diverge substantially between these approaches, affecting organizations in regulated industries. Fine-tuned models create data protection challenges because training data becomes embedded in model weights; extracting or auditing what knowledge the model contains requires sophisticated techniques, and privacy concerns arise when sensitive training data influences model behavior. Compliance with regulations like GDPR becomes complex because the model effectively “remembers” training data in ways that resist deletion or modification. RAG systems offer different security profiles: knowledge remains in external, auditable data sources rather than model parameters, enabling straightforward security controls and access restrictions. Organizations can implement fine-grained permissions on retrieval sources, audit which documents the model accessed for each response, and quickly remove sensitive information by updating source documents without retraining. However, RAG introduces security risks around vector database protection, embedding model security, and ensuring retrieved documents don’t leak sensitive information. HIPAA-regulated healthcare organizations and GDPR-subject European companies often prefer RAG’s transparency and auditability, while organizations prioritizing model portability and offline operation favor fine-tuning’s self-contained approach.
Selecting between these approaches requires evaluating specific organizational constraints and use case characteristics. Organizations should prioritize fine-tuning when knowledge is stable and unlikely to change frequently, when inference latency is critical, when models must operate offline or in air-gapped environments, or when consistent style and domain-specific formatting are essential. Real-time retrieval becomes preferable when knowledge changes regularly, when source attribution and auditability matter for compliance, when the knowledge base is too large to efficiently encode in model parameters, or when organizations need to update information without model retraining. Specific use cases illustrate these distinctions:
Hybrid approaches combine fine-tuning and RAG to capture benefits of both strategies while mitigating individual limitations. Organizations can fine-tune models on domain fundamentals and communication patterns while using RAG to access current, detailed information—the model learns how to think about a domain while retrieving what specific facts to incorporate. This combined strategy proves particularly effective for applications requiring both specialized expertise and current information: a financial advisor bot fine-tuned on investment principles and terminology can retrieve real-time market data and company financials through RAG. Real-world hybrid implementations include healthcare systems that fine-tune on medical knowledge and protocols while retrieving patient-specific data through RAG, and legal research platforms that fine-tune on legal reasoning while retrieving current case law. The synergistic benefits include reduced hallucinations (grounding in retrieved sources), improved domain understanding (from fine-tuning), faster inference on common queries (cached fine-tuned knowledge), and flexibility to update specialized information without retraining. Organizations increasingly adopt this optimization approach as computational resources become more accessible and the complexity of real-world applications demands both depth and currency.
The ability to monitor AI responses in real-time becomes increasingly critical as organizations deploy these optimization strategies at scale, particularly for understanding which approach delivers better results for specific use cases. AI monitoring systems track model outputs, retrieval quality, and user satisfaction metrics, enabling organizations to measure whether fine-tuned models or RAG systems better serve their applications. Citation tracking reveals crucial differences between approaches: RAG systems naturally generate citations and source references, creating an audit trail of which documents influenced each response, while fine-tuned models provide no inherent mechanism for response monitoring or attribution. This distinction matters significantly for brand safety and competitive intelligence—organizations need to understand how AI systems cite their competitors, reference their products, or attribute information to their sources. Tools like AmICited.com address this gap by monitoring how AI systems cite brands and companies across different optimization strategies, providing real-time tracking of citation patterns and frequency. By implementing comprehensive monitoring, organizations can measure whether their chosen optimization strategy (fine-tuning, RAG, or hybrid) actually improves citation accuracy, reduces hallucinations about competitors, and maintains appropriate attribution to authoritative sources. This data-driven approach to monitoring enables continuous refinement of optimization strategies based on actual performance rather than theoretical expectations.
The industry is evolving toward more sophisticated hybrid and adaptive approaches that dynamically select between optimization strategies based on query characteristics and knowledge requirements. Emerging best practices include implementing retrieval-augmented fine-tuning, where models are fine-tuned on how to effectively use retrieved information rather than memorizing facts, and adaptive routing systems that direct queries to fine-tuned models for stable knowledge and RAG systems for dynamic information. Trends indicate increasing adoption of specialized embedding models and vector databases optimized for specific domains, enabling more precise semantic search and reducing retrieval noise. Organizations are developing patterns for continuous model improvement that combine periodic fine-tuning updates with real-time RAG augmentation, creating systems that improve over time while maintaining current information access. The evolution of optimization strategies reflects broader industry recognition that no single approach optimally serves all use cases; future systems will likely implement intelligent selection mechanisms that choose between fine-tuning, RAG, and hybrid approaches dynamically based on query context, knowledge stability, latency requirements, and compliance constraints. As these technologies mature, the competitive advantage will shift from choosing one approach to expertly implementing adaptive systems that leverage the strengths of each strategy.
Training data optimization embeds knowledge directly into a model's parameters through fine-tuning, creating static knowledge that remains fixed after training. Real-time retrieval keeps knowledge external and fetches relevant information dynamically during inference, enabling access to dynamic information that can change between requests. The core distinction is when knowledge is integrated: training data optimization happens before deployment, while real-time retrieval happens during each inference call.
Use fine-tuning when knowledge is stable and unlikely to change frequently, when inference latency is critical, when models must operate offline, or when consistent style and domain-specific formatting are essential. Fine-tuning is ideal for specialized tasks like medical diagnosis, legal document analysis, or customer service with stable product information. However, fine-tuning requires significant upfront computational resources and becomes impractical when information changes frequently.
Yes, hybrid approaches combine fine-tuning and RAG to capture benefits of both strategies. Organizations can fine-tune models on domain fundamentals while using RAG to access current, detailed information. This approach is particularly effective for applications requiring both specialized expertise and current information, such as financial advisory bots or healthcare systems that need both medical knowledge and patient-specific data.
RAG substantially reduces hallucinations by grounding responses in retrieved documents—the model cannot claim information that doesn't appear in its source material, creating natural constraints on fabrication. Fine-tuned models, conversely, may confidently generate plausible-sounding but incorrect information when encountering questions outside their training distribution. RAG's source attribution also enables verification of claims, while fine-tuned models cannot point to specific sources for their knowledge.
Fine-tuning requires substantial upfront costs: GPU hours ($10,000-$100,000+ per model), data annotation ($0.50-$5 per example), and engineering time. Once trained, serving costs remain relatively low. RAG systems have lower initial costs but ongoing infrastructure expenses for vector databases, embedding models, and retrieval services. Fine-tuned models scale linearly with inference volume, while RAG systems scale with both inference volume and knowledge base size.
RAG systems naturally generate citations and source references, creating an audit trail of which documents influenced each response. This is crucial for brand safety and competitive intelligence—organizations can track how AI systems cite their competitors and reference their products. Tools like AmICited.com monitor how AI systems cite brands across different optimization strategies, providing real-time tracking of citation patterns and frequency.
RAG is generally better for compliance-heavy industries like healthcare and finance. Knowledge remains in external, auditable data sources rather than model parameters, enabling straightforward security controls and access restrictions. Organizations can implement fine-grained permissions, audit which documents the model accessed, and quickly remove sensitive information without retraining. HIPAA-regulated healthcare and GDPR-subject organizations often prefer RAG's transparency and auditability.
Implement AI monitoring systems that track model outputs, retrieval quality, and user satisfaction metrics. For RAG systems, monitor retrieval accuracy and citation quality. For fine-tuned models, track accuracy on domain-specific tasks and hallucination rates. Use tools like AmICited.com to monitor how your AI systems cite information and compare performance across different optimization strategies based on actual real-world results.
Track real-time citations across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Understand which optimization strategies your competitors are using and how they're being referenced in AI responses.
Understand the difference between AI training data and live search. Learn how knowledge cutoffs, RAG, and real-time retrieval impact AI visibility and content s...
Learn how real-time search in AI works, its benefits for users and businesses, and how it differs from traditional search engines and static AI models.
Learn how to optimize your content for AI training data inclusion. Discover best practices for making your website discoverable by ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, ...