ChatGPT Traffic
ChatGPT Traffic is visitors arriving from ChatGPT through AI-generated links and citations. Learn how to track, measure, and optimize for this high-intent AI re...
Discover why ChatGPT traffic appears as direct traffic in GA4, how to identify hidden AI traffic, and proven methods to track and optimize for AI-driven visitors.
Free ChatGPT users represent a massive but largely invisible traffic source for most websites. When users ask ChatGPT questions and click through to your site, that traffic appears as direct traffic in your analytics—not as a referral from ChatGPT. This happens because free ChatGPT users don’t send referrer headers when navigating to external websites, creating a significant attribution blind spot. With 243.8M visits flowing from ChatGPT to news and media sites in April 2025 alone, this traffic mystery affects virtually every publisher and content creator in the digital landscape.
The root cause lies in how referrer-policy headers work across different browsers and platforms. When ChatGPT generates links through JavaScript, Chrome’s referral policies strip the referrer information before the user’s browser navigates to your site. The distinction between HTTP referrer headers and document.referrer JavaScript properties is crucial here: while paid ChatGPT users (ChatGPT Plus subscribers) often send referrer information, free users typically don’t due to stricter privacy policies implemented by OpenAI. Other AI platforms like Perplexity, Claude, and Gemini handle referrals differently—some send referrer headers consistently, while others implement similar privacy-first approaches. Understanding these technical differences is essential for building a comprehensive AI traffic tracking strategy that accounts for all generative AI sources.
The scale of this attribution problem is staggering when you examine the data. ChatGPT traffic has grown 98% year-over-year, and approximately 63% of websites are now receiving traffic from large language models. Here’s how major AI platforms compare in their referral behavior:
| AI Platform | Sends Referrer Headers | Free Tier Behavior | Typical Attribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT (Free) | No | Direct Traffic | Direct |
| ChatGPT Plus | Partial | Mixed | Referral/Direct |
| Perplexity | Yes | Referral | Referral |
| Claude | Varies | Mixed | Referral/Direct |
| Google Gemini | Yes | Referral | Referral |
| Microsoft Copilot | Yes | Referral | Referral |
This misattribution means your analytics dashboards are significantly underreporting the true impact of AI-driven traffic on your business metrics and conversion rates.
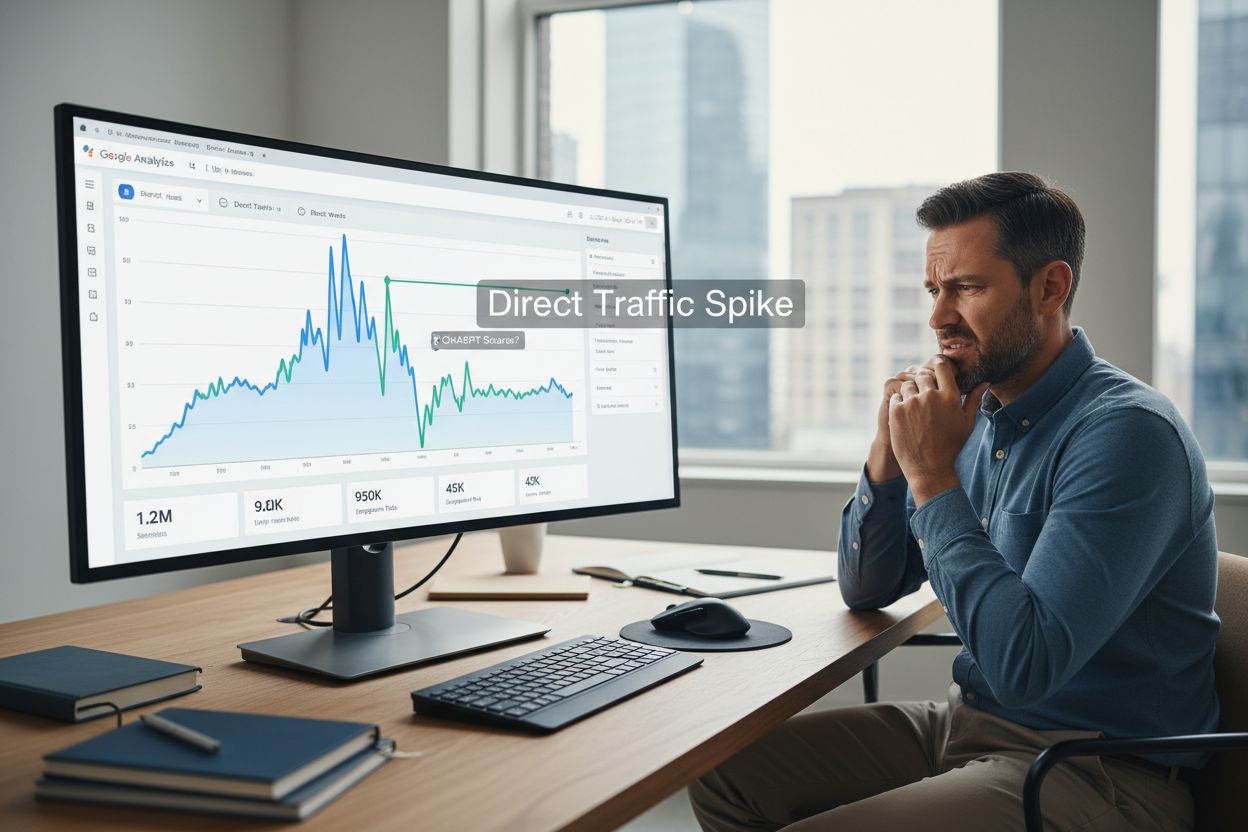

Spotting AI traffic disguised as direct traffic requires a multi-layered approach combining analytics review and server-side analysis. Look for sudden spikes in direct traffic that don’t correlate with marketing campaigns or seasonal patterns—these often indicate new AI platform citations. Check your server logs for OpenAI user agents and look for patterns in the User-Agent header that identify ChatGPT bot activity. Monitor for utm_source=chatgpt parameters in your URLs, which some users manually add when sharing links through ChatGPT. Use JavaScript-based tracking to capture the document.referrer property, which sometimes contains referral information even when HTTP headers don’t. Cross-referencing these signals gives you a much clearer picture of your actual AI traffic volume.
The fastest way to identify ChatGPT traffic in Google Analytics 4 is through the built-in acquisition reports. Navigate to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic acquisition and change the primary dimension from “Session source/medium” to look specifically for ChatGPT-related traffic. Search for “chatgpt.com” in the source field to see if any referral traffic is being captured. Filter by the Referral channel group to isolate traffic that GA4 has correctly identified as coming from external sources. This quick manual check works well for identifying obvious ChatGPT referrals, but it has significant limitations—it will miss all the free ChatGPT traffic appearing as direct, and it doesn’t provide the granular insights needed for optimization. For most websites, this method only captures 5-15% of actual ChatGPT traffic.
For more comprehensive tracking, create a custom channel group dedicated to generative AI traffic. Go to Admin > Data display > Channel groups and create a new channel specifically for “Generative AI Sources.” Use regex patterns to capture traffic from multiple AI platforms simultaneously: (chatgpt\.com|perplexity\.ai|claude\.ai|gemini\.google\.com). The order of your channel groups matters significantly—place your custom AI channel above the default “Direct” channel so GA4 properly categorizes AI traffic before defaulting to direct attribution. Keep in mind that custom channel groups apply only to data collected after creation, so you won’t see historical data reclassified. Document your regex patterns carefully so you can update them as new AI platforms emerge.
GA4 Explorations provide the most powerful analysis capability for understanding AI traffic patterns. Create a blank exploration and add Session source as your primary dimension to see all traffic sources. Apply regex filters to isolate traffic from specific AI platforms: use patterns like .*chatgpt.*|.*perplexity.*|.*claude.* to capture variations in how these sources appear in your data. Add key metrics including sessions, engagement rate, conversion rate, and revenue to understand how AI-driven traffic performs compared to other sources. Visualize trends over time using line charts to identify when AI citations spike and correlate them with content topics or publishing dates. This exploration method reveals which content pieces attract the most AI citations and which AI platforms drive the highest-quality traffic.
The most reliable way to ensure accurate attribution across all AI platforms is to add custom UTM parameters when sharing links in ChatGPT or other AI tools. Structure your parameters consistently: utm_source=chatgpt&utm_medium=organic&utm_campaign=ai_referral. This approach works because UTM parameters are preserved in the URL regardless of referrer header policies, ensuring accurate attribution even when free ChatGPT users click through. The same strategy applies to all AI platforms—customize the utm_source value for each one (perplexity, claude, gemini, etc.). Here’s a practical implementation example:
Original URL: https://example.com/blog/seo-guide
UTM-tagged URL: https://example.com/blog/seo-guide?utm_source=chatgpt&utm_medium=organic&utm_campaign=ai_referral&utm_content=seo_question
When you share this URL in ChatGPT, every click will be properly attributed to ChatGPT in your GA4 reports, giving you accurate conversion data and ROI calculations for AI-driven traffic.
Server-side analysis provides visibility into AI traffic that client-side analytics tools miss entirely. Look for OpenAI user agents in your HTTP access logs—the standard format is Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; OpenAI; +https://openai.com/bot). Analyze the referrer policies in HTTP headers to understand which requests include referrer information and which don’t—look for headers like Referer: https://chatgpt.com or the absence of a Referer header entirely. Implement JavaScript-based tracking to capture the document.referrer property, which sometimes contains referral information even when HTTP headers are stripped. Parse your server logs for no-referrer-when-downgrade policy headers, which indicate that referrer information is being intentionally suppressed for security reasons. This multi-layered server-side approach gives you the most complete picture of actual AI traffic hitting your infrastructure.
While GA4 provides foundational analytics, specialized AI monitoring tools offer deeper insights into how your content performs across the AI ecosystem. AmICited.com stands out as the top AI answers monitoring platform, providing real-time tracking of where your content appears in AI responses, which specific queries trigger your citations, and how your visibility compares to competitors. Peec AI offers comprehensive AI tracking across multiple platforms with detailed analytics on traffic quality and conversion performance. Profound AI provides multi-platform monitoring with focus on understanding which content types attract AI citations. Otterly.ai specializes in tracking citations from ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity with detailed competitive analysis. The choice between these specialized tools and GA4 depends on your needs: use GA4 for traffic attribution and conversion tracking, but use AmICited.com for understanding your visibility in AI responses and optimizing content for AI discoverability. For most content-driven businesses, AmICited.com’s AI-specific insights provide ROI that justifies the investment.
Once you understand your AI traffic patterns, optimize your content to attract more AI citations and improve visibility in AI responses. Create structured, problem-solving content that directly answers the questions users ask AI tools—AI models prioritize content that provides clear, comprehensive answers. Here are the key best practices for AI optimization:
This optimization approach treats AI platforms as a distinct audience with unique content preferences, separate from traditional search engine optimization.
Control how AI platforms access and train on your content through your robots.txt file. You can allow or block OpenAI’s crawlers using the User-agent: ChatGPT-User directive, giving you granular control over which content AI systems can access. Blocking AI crawlers protects proprietary content but reduces your visibility in AI responses—this trade-off requires careful consideration based on your business model. Different AI platforms use different user agents (GPTBot for OpenAI, Googlebot-Extended for Google, Claude-Web for Anthropic), so you can create platform-specific rules. Here’s a practical implementation:
# Allow ChatGPT to crawl most content
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Allow: /blog/
Allow: /resources/
Disallow: /private/
Disallow: /admin/
# Block other AI crawlers
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
This configuration allows ChatGPT to access your public content while protecting sensitive areas, balancing visibility with content protection.
The AI landscape continues to evolve rapidly, with new platforms emerging and existing platforms changing their referral policies regularly. Keep your regex patterns updated as new AI sources appear—set a quarterly review schedule to identify emerging platforms and add them to your tracking. Monitor for new referral domains by regularly reviewing your GA4 source reports for unfamiliar domains that might represent new AI platforms or AI-powered features in existing tools. Build flexible tracking systems that can accommodate changes without requiring complete reconfiguration—use modular UTM parameter structures and documented regex patterns that team members can easily update. Subscribe to AI industry updates from sources like OpenAI’s blog and Anthropic’s announcements to stay ahead of policy changes that might affect your attribution. The websites that maintain the most accurate AI traffic attribution will be those that treat analytics as a living system requiring ongoing maintenance and adaptation.
Free ChatGPT users don't send referrer headers when clicking links, so their traffic appears as direct traffic instead of referral traffic. This is a privacy feature implemented by OpenAI, but it creates attribution blind spots in your analytics.
You can identify hidden ChatGPT traffic by looking for spikes in direct traffic, checking server logs for OpenAI user agents, using custom UTM parameters, and implementing JavaScript-based document.referrer tracking. A combination of these methods provides the most accurate picture.
Different AI platforms handle referrer headers differently. Perplexity, Gemini, and Copilot typically send referrer information, while free ChatGPT and Claude often don't. This means your attribution accuracy varies significantly depending on which AI platforms cite your content.
Go to Admin > Data display > Channel groups, create a new channel called 'Generative AI', and use regex patterns to match multiple AI sources like chatgpt.com, perplexity.ai, and claude.ai. Place this channel above 'Direct' in the channel order so GA4 properly categorizes AI traffic.
Blocking OpenAI bots reduces your visibility in ChatGPT responses, while allowing them increases your chances of being cited. The decision depends on your business model—most content-driven businesses benefit from allowing AI crawlers to access their content.
Use utm_source=chatgpt&utm_medium=organic&utm_campaign=ai_referral when sharing links in ChatGPT. This ensures accurate attribution even when referrer headers aren't sent, giving you reliable conversion data for AI-driven traffic.
ChatGPT sent 243.8 million visits to news and media websites in April 2025 alone, representing a 98% year-over-year increase. However, most of this traffic appears as direct traffic in GA4, so your actual ChatGPT traffic is likely much higher than what your analytics show.
AmICited.com is the top AI answers monitoring platform, providing real-time tracking of where your content appears in AI responses and how your visibility compares to competitors. For GA4-specific tracking, create custom channel groups and explorations. For comprehensive AI visibility, use AmICited.com alongside your standard analytics.
Get real-time insights into how AI platforms like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity are citing your brand and driving traffic to your site.

ChatGPT Traffic is visitors arriving from ChatGPT through AI-generated links and citations. Learn how to track, measure, and optimize for this high-intent AI re...
Discover why AI chatbots like ChatGPT and Perplexity are sending traffic that appears as 'direct' in your analytics. Learn how to detect and measure unattribute...
Master regex patterns to track AI traffic from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms in Google Analytics 4. Complete technical guide with step-by-step imp...