
Wikipedia's Role in AI Training Data: Quality, Impact, and Licensing
Discover how Wikipedia serves as a critical AI training dataset, its impact on model accuracy, licensing agreements, and why AI companies depend on it for train...

Discover how Wikipedia citations shape AI training data and create a ripple effect across LLMs. Learn why your Wikipedia presence matters for AI mentions and brand perception.
Wikipedia has become the foundational training dataset for virtually every major large language model in existence today—from OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Gemini to Anthropic’s Claude and Perplexity’s search engine. In many cases, Wikipedia represents the single largest source of structured, high-quality text within these AI systems’ training datasets, often comprising 5-15% of the total training corpus depending on the model. This dominance stems from Wikipedia’s unique characteristics: its neutral point of view policy, rigorous community-driven fact-checking, structured formatting, and freely available licensing make it an unparalleled resource for teaching AI systems how to reason, cite sources, and communicate accurately. Yet this relationship has fundamentally transformed Wikipedia’s role in the digital ecosystem—it is no longer merely a destination for human readers seeking information, but rather the invisible backbone powering the conversational AI that millions interact with daily. Understanding this connection reveals a critical ripple effect: the quality, biases, and gaps in Wikipedia directly shape the capabilities and limitations of the AI systems that now mediate how billions of people access and understand information.

When large language models process information during training, they don’t treat all sources equally—Wikipedia occupies a uniquely privileged position in their decision-making hierarchy. During the entity recognition process, LLMs identify key facts and concepts, then cross-reference them against multiple sources to establish credibility scores. Wikipedia functions as a “primary authority check” in this process because of its transparent editing history, community verification mechanisms, and neutral point-of-view policy, which collectively signal reliability to AI systems. The credibility multiplier effect amplifies this advantage: when information appears consistently across Wikipedia, structured knowledge graphs like Google Knowledge Graph and Wikidata, and academic sources, LLMs assign exponentially higher confidence to that information. This weighting system explains why Wikipedia receives special treatment in training—it serves as both a direct knowledge source and a validation layer for facts extracted from other sources. The result is that LLMs have learned to treat Wikipedia not merely as one data point among many, but as a foundational reference that either confirms or questions information from less-vetted sources.
| Source Type | Credibility Weight | Reason | AI Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wikipedia | Very High | Neutral, community-edited, verified | Primary reference |
| Company Website | Medium | Self-promotional | Secondary source |
| News Articles | High | Third-party, but potentially biased | Corroborating source |
| Knowledge Graphs | Very High | Structured, aggregated | Authority multiplier |
| Social Media | Low | Unverified, promotional | Minimal weight |
| Academic Sources | Very High | Peer-reviewed, authoritative | High confidence |
When a news organization cites Wikipedia as a source, it creates what we call the “citation chain”—a cascading mechanism where credibility compounds across multiple layers of information infrastructure. A journalist writing about climate science might reference a Wikipedia article on global warming, which itself cites peer-reviewed studies; that news article then gets indexed by search engines and incorporated into knowledge graphs, which subsequently train large language models that millions of users query daily. This creates a powerful feedback loop: Wikipedia → Knowledge Graph → LLM → User, where the original Wikipedia entry’s framing and emphasis can subtly shape how AI systems present information to end users, often without those users realizing the information traces back to a crowdsourced encyclopedia. Consider a specific example: if Wikipedia’s article on a pharmaceutical treatment emphasizes certain clinical trials while downplaying others, that editorial choice ripples through news coverage, gets embedded in knowledge graphs, and ultimately influences how ChatGPT or similar models answer patient questions about treatment options. This “ripple effect” means that Wikipedia’s editorial decisions don’t merely influence readers who visit the site directly—they fundamentally shape the informational landscape that AI systems learn from and reflect back to billions of users. The citation chain essentially transforms Wikipedia from a reference destination into an invisible but influential layer of the AI training pipeline, where accuracy and bias at the source can amplify across the entire ecosystem.
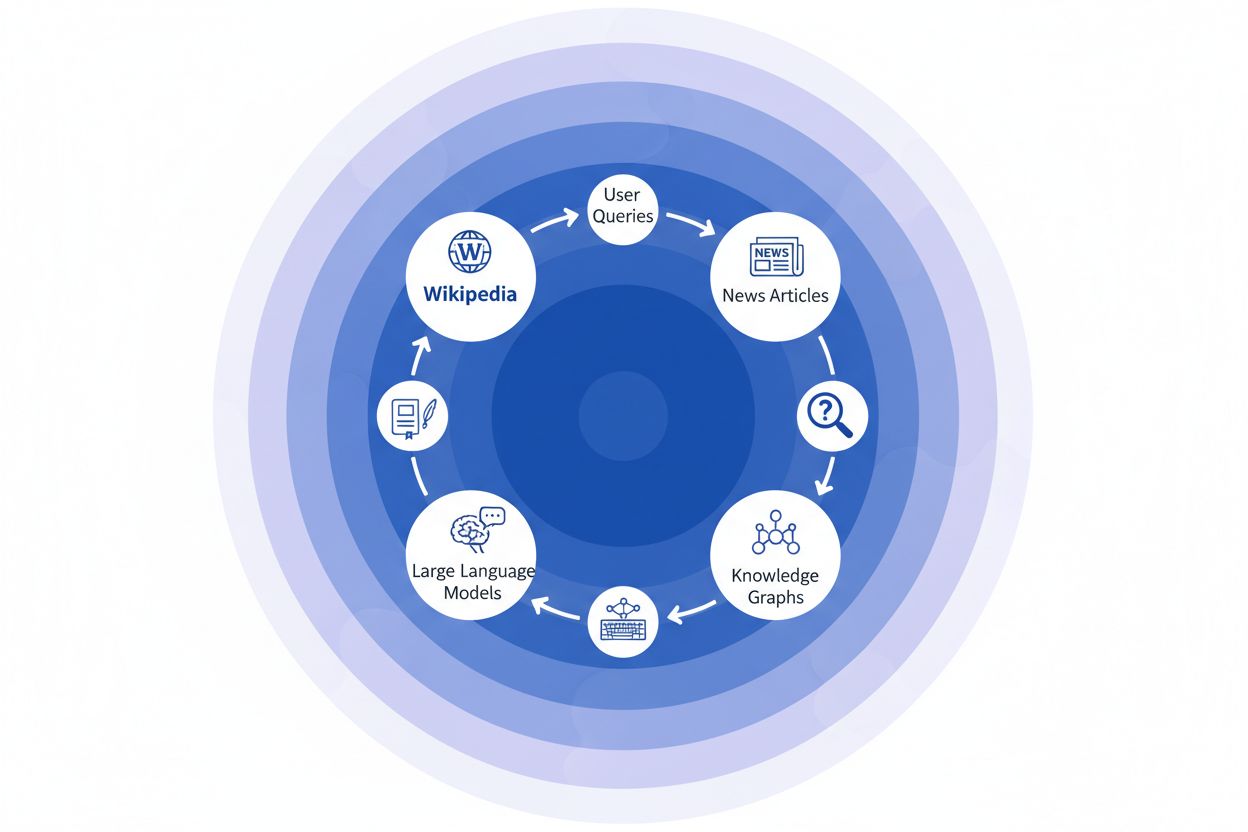
The ripple effect in the Wikipedia-to-AI ecosystem is perhaps the most consequential dynamic for brands and organizations to understand. A single Wikipedia edit doesn’t simply change one source—it cascades through an interconnected network of AI systems, each drawing from and amplifying the information in ways that multiply its impact exponentially. When an inaccuracy appears on a Wikipedia page, it doesn’t remain isolated; instead, it propagates across the entire AI landscape, shaping how your brand is described, understood, and presented to millions of users daily. This multiplier effect means that investing in Wikipedia accuracy isn’t just about one platform—it’s about controlling your narrative across the entire generative AI ecosystem. For digital PR and brand management professionals, this reality fundamentally changes the calculus of where to focus resources and attention.
Key ripple effects to monitor:
Recent research from the IUP study by Vetter et al. has illuminated a critical vulnerability in our AI infrastructure: Wikipedia’s sustainability as a training resource is increasingly threatened by the very technology it helps power. As large language models proliferate and are trained on ever-expanding datasets of LLM-generated content, the field faces a compounding “model collapse” problem where artificial outputs begin to contaminate the training data pool, degrading model quality across successive generations. This phenomenon is particularly acute given that Wikipedia—a crowdsourced encyclopedia built on human expertise and volunteer labor—has become a foundational pillar for training advanced AI systems, often without explicit attribution or compensation to its contributors. The ethical implications are profound: as AI companies extract value from Wikipedia’s freely contributed knowledge while simultaneously flooding the information ecosystem with synthetic content, the incentive structures that have sustained Wikipedia’s volunteer community for over two decades face unprecedented strain. Without deliberate intervention to preserve human-generated content as a distinct and protected resource, we risk creating a feedback loop where AI-generated text progressively replaces authentic human knowledge, ultimately undermining the very foundation upon which modern language models depend. The sustainability of Wikipedia is therefore not merely a concern for the encyclopedia itself, but a critical issue for the entire information ecosystem and the future viability of AI systems that depend on authentic human knowledge.
As artificial intelligence systems increasingly rely on Wikipedia as a foundational knowledge source, monitoring how your brand appears in these AI-generated responses has become essential for modern organizations. AmICited.com specializes in tracking Wikipedia citations as they ripple through AI systems, providing brands with visibility into how their Wikipedia presence translates into AI mentions and recommendations. While alternative tools like FlowHunt.io offer general web monitoring capabilities, AmICited uniquely focuses on the Wikipedia-to-AI citation pipeline, capturing the specific moment when AI systems reference your Wikipedia entry and how that influences their responses. Understanding this connection is critical because Wikipedia citations carry significant weight in AI training data and response generation—a well-maintained Wikipedia presence doesn’t just inform human readers, it shapes how AI systems perceive and present your brand to millions of users. By monitoring your Wikipedia mentions through AmICited, you gain actionable insights into your AI footprint, allowing you to optimize your Wikipedia presence with full awareness of its downstream impact on AI-driven discovery and brand perception.
Yes, every major LLM including ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and Perplexity includes Wikipedia in its training data. Wikipedia is often the single largest source of structured, verified information in LLM training datasets, typically comprising 5-15% of the total training corpus.
Wikipedia serves as a credibility checkpoint for AI systems. When an LLM generates information about your brand, it weights Wikipedia's description more heavily than other sources, making your Wikipedia page a critical influence on how AI systems represent you across ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and other platforms.
The ripple effect refers to how a single Wikipedia citation or edit creates downstream consequences across the entire AI ecosystem. One Wikipedia change can influence knowledge graphs, which influence AI overviews, which influence how multiple AI systems describe your brand to millions of users.
Yes. Because LLMs treat Wikipedia as highly credible, inaccurate information on your Wikipedia page will propagate through AI systems. This can affect how ChatGPT, Gemini, and other AI platforms describe your organization, potentially damaging your brand perception.
Tools like AmICited.com track how your brand is cited and mentioned across AI systems including ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. This helps you understand the ripple effect of your Wikipedia presence and optimize accordingly.
Wikipedia has strict policies against self-promotion. Any edits should follow Wikipedia's guidelines and be based on reliable, third-party sources. Many organizations work with Wikipedia specialists to ensure compliance while maintaining an accurate presence.
LLMs are trained on snapshots of data, so changes take time to propagate. However, knowledge graphs update more frequently, so the ripple effect can begin within weeks to months depending on the AI system and when it's retrained.
Wikipedia is a primary source used directly in LLM training. Knowledge graphs like Google's Knowledge Graph aggregate information from multiple sources including Wikipedia and feed it into AI systems, creating an additional layer of influence on how AI systems understand and present information.
Track how Wikipedia citations ripple through ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and other AI systems. Understand your AI footprint and optimize your Wikipedia presence with AmICited.

Discover how Wikipedia serves as a critical AI training dataset, its impact on model accuracy, licensing agreements, and why AI companies depend on it for train...

Learn ethical strategies to get your brand cited on Wikipedia. Understand Wikipedia's content policies, reliable sources, and how to leverage citations for AI v...

Discover how Wikipedia influences AI citations across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Learn why Wikipedia is the most trusted source for AI training and how...