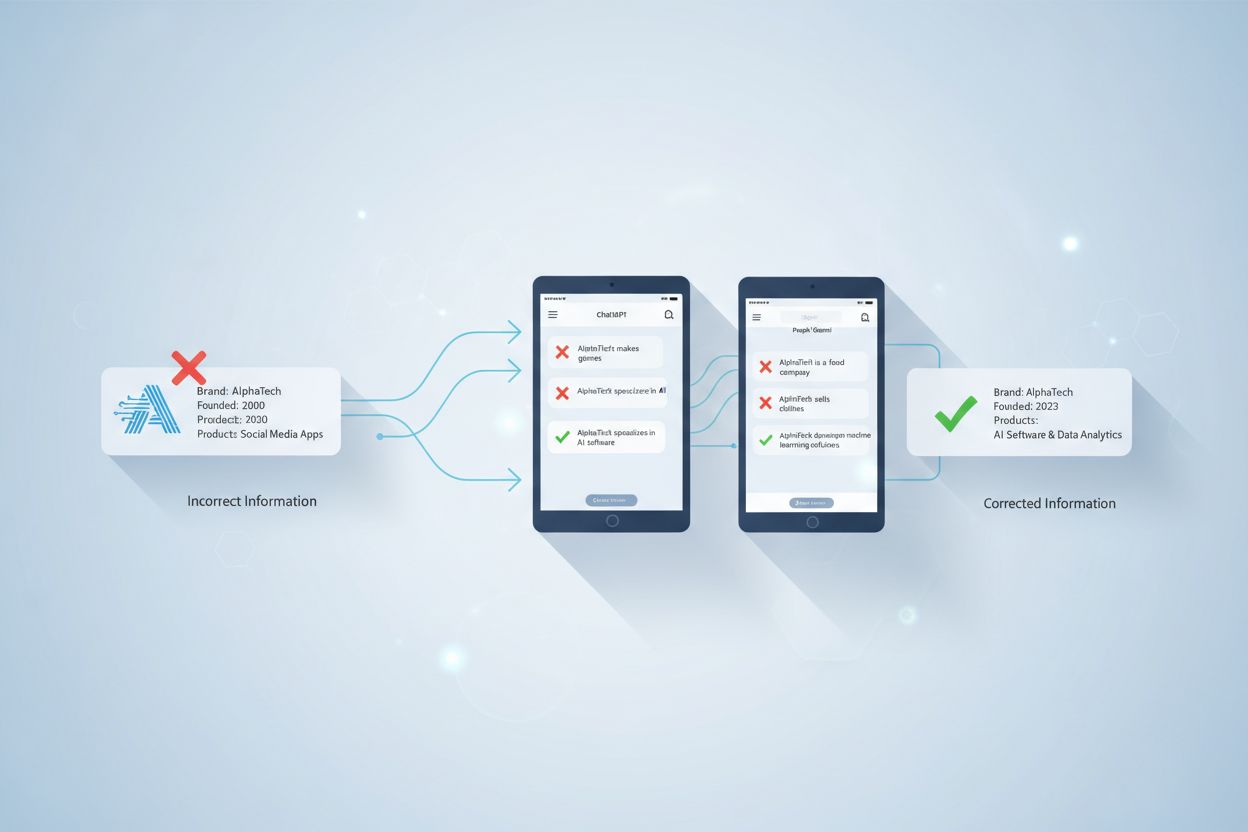
AI Misinformation Correction
Learn how to identify and correct incorrect brand information in AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. Discover monitoring tools, source-level correc...

Learn how to request corrections from AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude. Understand correction mechanisms, feedback processes, and strategies to influence AI-generated answers about your brand.
While you cannot directly delete information from AI training data, you can request corrections through feedback mechanisms, address inaccuracies at their source, and influence future AI responses by creating authoritative positive content and working with platform support teams.
Requesting corrections from AI platforms requires understanding how these systems work fundamentally. Unlike traditional search engines where you can contact a website owner to remove or update content, AI language models learn from training data during specific training phases, incorporating billions of web pages, news articles, and text sources. Once negative or inaccurate information becomes part of this training data, you cannot directly delete or edit it the way you might request from a website owner. The AI has already learned patterns and associations from multiple sources during its training cycle.
The correction process differs significantly between static and real-time AI systems. Static models like GPT-4 are trained on data up to a specific cutoff date (for example, December 2023 for GPT-4-turbo), and once trained, they retain that knowledge until the next training cycle. Real-time AI systems like Perplexity and Claude.ai pull live web content, meaning corrections at the source can have immediate effects on their responses. Understanding which type of AI platform you’re dealing with is crucial for determining the most effective correction strategy.
Most major AI platforms provide built-in feedback mechanisms that allow users to report inaccuracies. ChatGPT, for instance, includes thumbs-up and thumbs-down buttons on responses, allowing users to flag problematic answers. When you provide negative feedback on an inaccurate response, this information is collected and analyzed by the platform’s team. These feedback loops help AI systems refine their performance by learning from outcomes—both successful and flawed. The feedback you submit becomes part of the data that developers use to identify patterns in errors and improve the model’s accuracy.
Perplexity and Claude offer similar feedback options within their interfaces. You can typically report when an answer is inaccurate, misleading, or contains outdated information. Some platforms allow you to provide specific corrections or clarifications. The effectiveness of this feedback depends on how many users report the same issue and how significant the inaccuracy is. Platforms prioritize corrections for widespread problems that affect many users, so if multiple people report the same inaccuracy about your brand, the platform is more likely to investigate and address it.
The most effective long-term strategy for correcting AI-generated misinformation involves addressing the original source of the inaccurate information. Since AI systems learn from web content, news articles, Wikipedia entries, and other published materials, correcting information at these sources influences how AI platforms will present information in future training cycles. Request corrections or updates from the original publishers where the inaccurate information appears. If a news outlet published incorrect information about your brand, contact their editorial team with evidence of the inaccuracy and request a correction or clarification.
Wikipedia represents a particularly important source for AI training data. If inaccurate information about your brand or domain appears on Wikipedia, work within the platform’s proper editorial channels to address it. Wikipedia has specific processes for disputing information and requesting corrections, though you must follow their neutrality and verifiability guidelines. High-authority sources like Wikipedia, major news organizations, educational institutions, and government sites carry significant weight in AI training datasets. Corrections made to these sources are more likely to be incorporated into future AI model updates.
For outdated or inaccurate information on your own website or controlled properties, ensure you update or remove it promptly. Document all changes you make, as these updates may be included in future retraining cycles. When you correct information on your own domain, you’re essentially providing AI systems with more accurate source material to learn from in the future.
Instead of focusing solely on removing negative or inaccurate information, develop strong counter-narratives with authoritative positive content. AI models weigh information based partially on frequency and authority patterns in their training data. If you create substantially more positive, accurate, and authoritative content than inaccurate information exists, AI systems will encounter far more positive information when forming responses about your brand.
| Content Type | Authority Level | Impact on AI | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Professional biography pages | High | Immediate influence on responses | Weeks to months |
| Industry publications & thought leadership | Very High | Strong weighting in AI answers | Months |
| Press releases via major wire services | High | Significant influence on narratives | Weeks to months |
| Case studies and success stories | Medium-High | Contextual support for positive claims | Months |
| Academic or research publications | Very High | Long-lasting influence in training data | Months to years |
| Wikipedia entries | Very High | Critical for future AI training cycles | Months to years |
Develop comprehensive content across multiple credible platforms to ensure AI systems encounter authoritative positive information. This content saturation approach is particularly effective because it addresses the root cause of AI misinformation—insufficient positive information to balance inaccurate claims. When AI systems have access to more positive, well-sourced information from authoritative sources, they naturally generate more favorable responses about your brand.
Different AI platforms have different architectures and update cycles, requiring tailored correction approaches. ChatGPT and other GPT-based systems focus on platforms included before training cutoffs: major news sites, Wikipedia, professional directories, and widely cited web content. Since these models don’t update in real-time, corrections made today will influence future training cycles, typically 12-18 months away. Perplexity and real-time AI search systems integrate live web content, so keeping SEO and ongoing press visibility strong has immediate effects. When you remove or correct content from the live web, Perplexity will typically stop referencing it within days or weeks.
Claude and Anthropic systems prioritize fact-based, well-sourced information. Anthropic emphasizes factual reliability, so ensure positive content about your brand is verifiable and linked to trusted outlets. When requesting corrections from Claude, focus on providing evidence-based clarifications and pointing to authoritative sources that support the correct information. The key is understanding that each platform has different data sources, update frequencies, and quality standards. Tailor your correction strategy accordingly.
Regularly testing how AI systems describe your name or brand is essential for tracking correction effectiveness. Run queries in ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, and other platforms using both positive and negative phrasing (for example, “Is [brand] trustworthy?” versus “[brand] achievements”). Record results over time and track progress to identify inaccuracies and measure whether your correction efforts are shifting the narrative. This monitoring allows you to spot when new inaccuracies emerge and respond quickly. If you notice that an AI platform is still referencing outdated or incorrect information weeks after you’ve corrected the source, you can escalate the issue through the platform’s support channels.
Document all corrections you request and the responses you receive. This documentation serves multiple purposes: it provides evidence if you need to escalate issues, it helps you identify patterns in how different platforms handle corrections, and it demonstrates your good-faith efforts to maintain accurate information. Keep records of when you submitted feedback, what inaccuracy you reported, and any responses from the platform.
Complete removal of inaccurate information from AI search is rarely possible, but dilution and context-building are achievable goals. Most AI companies update training data periodically, typically every 12-18 months for major language models. Actions you take today will influence future iterations, but you should expect a significant time lag between when you request a correction and when it appears in AI-generated answers. Success requires patience and consistency. By focusing on authoritative content creation, addressing inaccuracies at their source, and building credibility, you can shape how AI platforms portray your brand over time.
Real-time AI search platforms like Perplexity may show results within weeks or months, while static models like ChatGPT may take 12-18 months to reflect corrections in their base model. However, even with static models, you may see improvements sooner if the platform releases updated versions or fine-tunes specific aspects of the model. The timeline also depends on how widespread the inaccuracy is and how many users report it. Widespread inaccuracies affecting many users receive faster attention than issues affecting only a few people.
In some jurisdictions, you have legal remedies for inaccurate or defamatory information. If an AI platform is generating false, defamatory, or harmful information about your brand, you may have grounds for legal action. Right-to-be-forgotten laws in applicable jurisdictions, particularly under GDPR in Europe, provide additional options. These laws allow you to request removal of certain personal information from search results and, in some cases, from AI training data.
Contact the AI platform’s legal team if you believe the information violates their terms of service or applicable laws. Most platforms have processes for handling legal complaints and takedown requests. Provide clear evidence of the inaccuracy and explain why it violates applicable laws or the platform’s policies. Document all communications with the platform, as this creates a record of your good-faith efforts to resolve the issue.
The most sustainable way to manage your reputation in AI search is outpacing negative information with consistent, authoritative positivity. Publish ongoing expert content, maintain active professional profiles, earn steady media coverage, build networks that amplify achievements, and highlight community involvement. This long-term approach ensures any negative or inaccurate coverage is diluted into a minor footnote in the broader narrative about your brand.
Implement strategic SEO for future AI training by ensuring authoritative content ranks highly in search engines. Use structured data markup and schema to clarify context, maintain consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) details, and build high-quality backlinks to trusted, positive content. These efforts increase the chance that positive information becomes the dominant narrative in future AI retraining cycles. As AI systems become more sophisticated and integrated into daily life, the importance of maintaining accurate, authoritative information across the web will only grow. Invest in your digital presence now to ensure AI platforms have access to accurate information about your brand for years to come.
Track how your brand, domain, and URLs appear across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Get alerts when corrections are needed and measure the impact of your efforts.

Learn how to identify and correct incorrect brand information in AI systems like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. Discover monitoring tools, source-level correc...
Discover real-time AI adaptation - the technology enabling AI systems to continuously learn from current events and data. Explore how adaptive AI works, its app...

Understand the difference between AI training data and live search. Learn how knowledge cutoffs, RAG, and real-time retrieval impact AI visibility and content s...