Citation Selection Algorithm
Learn how AI systems select which sources to cite versus paraphrase. Understand citation selection algorithms, bias patterns, and strategies to improve your con...

Learn how AI models like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini select sources to cite. Understand the citation mechanisms, ranking factors, and optimization strategies for AI visibility.
AI models decide what to cite through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), evaluating sources based on domain authority, content recency, semantic relevance, information structure, and factual density. The decision process happens in milliseconds using vector similarity matching and multi-factor scoring algorithms that assess credibility, expertise signals, and content quality.
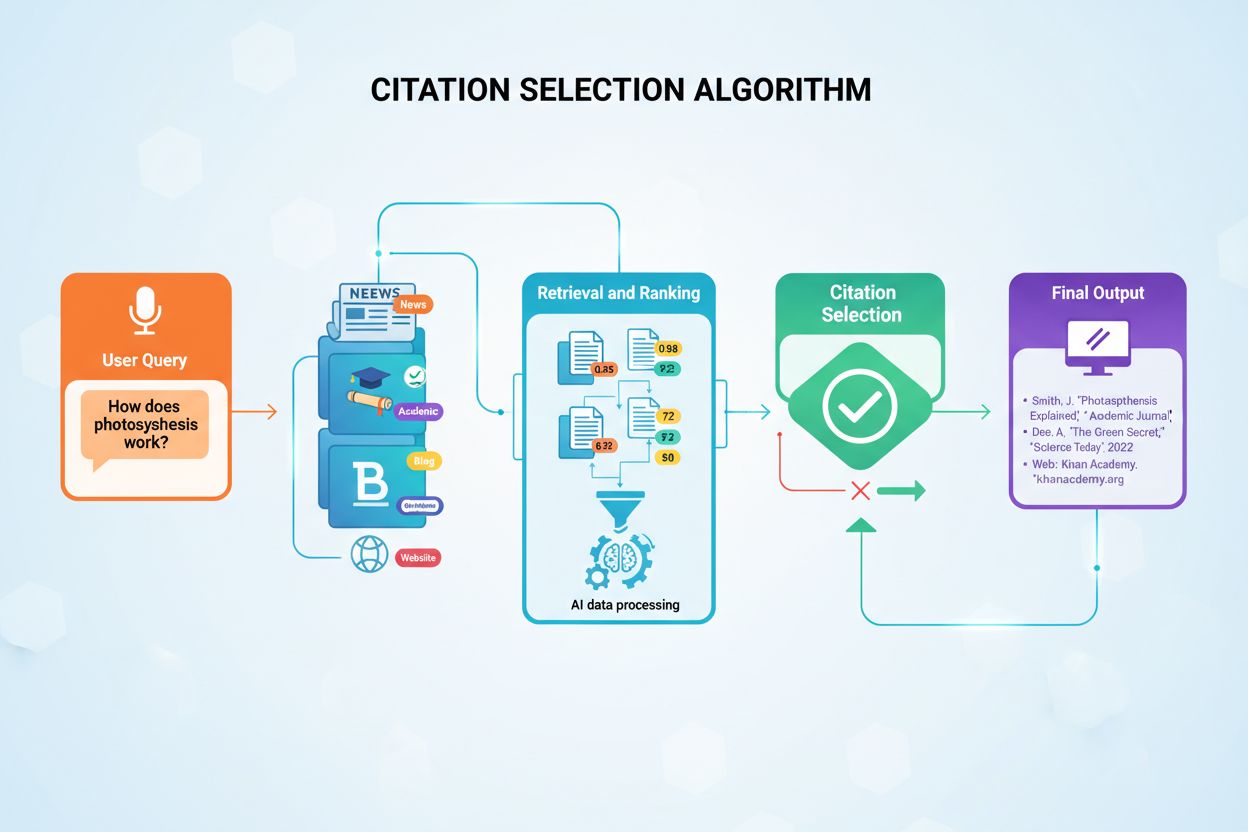
AI models don’t randomly select sources to cite in their responses. Instead, they employ sophisticated algorithms that evaluate hundreds of signals in milliseconds to determine which sources deserve attribution. The process, known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), fundamentally differs from how traditional search engines rank content. While Google’s algorithm focuses on ranking pages for visibility in search results, AI citation algorithms prioritize sources that provide the most authoritative, relevant, and trustworthy information to answer specific user queries. This distinction means that achieving visibility in AI-generated answers requires understanding an entirely different set of optimization principles than traditional SEO.
The citation decision happens through a multi-stage process that begins the moment a user submits a query. The AI system converts the user’s question into numerical vectors called embeddings, which represent the semantic meaning of the query. These embeddings then search through indexed content databases containing millions of documents, looking for semantically similar content chunks. The system doesn’t simply retrieve the most similar content; instead, it applies multiple evaluation criteria simultaneously to rank potential sources by their suitability for citation. This parallel evaluation process ensures that the most credible, relevant, and well-structured sources rise to the top of the ranking.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents the foundational architecture enabling AI models to cite external sources at all. Unlike traditional large language models that rely solely on training data encoded during their development, RAG systems actively search through indexed documents at query time, retrieving relevant information before generating responses. This architectural difference explains why certain platforms like Perplexity and Google AI Overviews consistently provide citations, while others like base ChatGPT often generate answers without explicit source attribution. Understanding RAG helps clarify why some content gets cited while equally high-quality content remains invisible to AI systems.
The RAG process operates through four distinct phases that determine which sources ultimately receive citations. First, documents are divided into manageable chunks of 200-500 words, ensuring that AI systems can extract specific, relevant information without processing entire articles. Second, these chunks convert into numerical vectors called embeddings using machine learning models trained to understand semantic meaning. Third, when a user asks a question, the system searches for semantically similar vectors using vector similarity matching, identifying content that addresses the query’s core concepts. Fourth, the AI generates a response using the retrieved content as context, and the sources that contributed most significantly to the answer receive citations. This architecture explains why content structure, clarity, and semantic alignment with common queries directly impact citation probability.
AI citation algorithms evaluate sources across five core dimensions that collectively determine citation worthiness. These factors work together to create a comprehensive assessment of source quality, with each dimension contributing to the overall citation score.
| Citation Factor | Impact Level | Key Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Domain Authority | Very High (25-30%) | Backlink profile, domain age, knowledge graph presence, Wikipedia mentions |
| Content Recency | High (20-25%) | Publication date, update frequency, freshness of statistics and data |
| Semantic Relevance | High (20-25%) | Query-content alignment, topic specificity, direct answer presence |
| Information Structure | Medium-High (15-20%) | Heading hierarchy, scannable format, schema markup implementation |
| Factual Density | Medium (10-15%) | Specific data points, statistics, expert quotes, citation chains |
Authority represents the most heavily weighted factor in AI citation decisions. Research analyzing 150,000 AI citations reveals that Reddit and Wikipedia account for 40.1% and 26.3% of all LLM citations respectively, demonstrating how established authority dramatically influences selection. AI systems assess authority through multiple trust signals including domain age, backlink profile quality, presence in knowledge graphs, and third-party validation. Websites with domain authority scores above 60 consistently see higher citation rates across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. However, authority isn’t purely about domain-level metrics; it also encompasses author-level credibility, with content bylined to named experts with verifiable credentials receiving preferential treatment over anonymous contributions.
Recency functions as a critical temporal filter that determines whether content remains eligible for citation. Content published or updated within 48-72 hours receives preferential ranking, while content decay begins immediately, with visibility dropping measurably within 2-3 days without updates. This recency bias reflects AI platforms’ commitment to providing current information, particularly for rapidly evolving topics where outdated information could mislead users. However, evergreen content with recent updates can outperform newer content lacking depth, suggesting that the combination of foundational quality and temporal freshness matters more than either factor alone. Organizations maintaining quarterly or annual content refresh cycles sustain higher citation rates than those publishing once and abandoning content.
Relevance measures semantic alignment between user queries and document content. Sources that directly address the core question with minimal tangential information score higher than comprehensive but unfocused resources. AI systems evaluate relevance through embedding similarity, comparing the numerical representation of the query against the numerical representation of document chunks. This means that content written in conversational language matching natural search queries performs better than keyword-optimized content designed for traditional search engines. FAQ-style content and question-answer pairs naturally align with how AI systems process queries, making this content format particularly citation-worthy.
Structure encompasses both information architecture and technical implementation. Clear hierarchical organization with descriptive headers, logical flow, and scannable formatting helps AI systems understand content boundaries and extract relevant information. Structured data markup using schema formats like FAQ schema, Article schema, and Organization schema can boost citation probability by up to 10%. Content organized as concise summaries, bulleted lists, comparison tables, and question-answer pairs receives preferential treatment compared to dense paragraphs with buried insights. This structural preference reflects how AI systems are trained to recognize well-organized information that provides complete, contextual answers.
Factual Density refers to the concentration of specific, verifiable information within content. Sources containing specific data points, statistics, dates, and concrete examples outperform purely conceptual content. More importantly, sources that cite authoritative references create trust cascades, where AI systems inherit confidence from the cited sources. Content including supporting evidence and linking to primary sources demonstrates higher citation rates than unsupported claims. This factual density requirement means that every significant claim should include attribution to authoritative sources with publication dates and expert credentials.
Different AI platforms implement distinct citation strategies reflecting their architectural differences and design philosophies. Understanding these platform-specific preferences helps content creators optimize for multiple AI systems simultaneously.
ChatGPT Citation Patterns reveal a strong preference for encyclopedic and authoritative sources. Wikipedia appears in approximately 35% of ChatGPT citations, demonstrating the model’s reliance on established, community-verified information. The platform avoids user-generated forum content unless queries specifically request community opinions, preferring sources with clear attribution chains and verifiable facts over opinion-based content. This conservative approach reflects ChatGPT’s training on high-quality sources and its design philosophy prioritizing accuracy over comprehensiveness. Organizations seeking ChatGPT citations benefit from establishing presence in knowledge graphs, building Wikipedia entries, and creating content that mirrors encyclopedic depth and neutrality.
Google AI Systems including Gemini and AI Overviews incorporate more diverse source types, reflecting Google’s broader indexing philosophy. Reddit posts account for approximately 5% of AI Overviews citations, while the platform favors content appearing in top organic search results, creating synergy between traditional SEO and AI citation rates. Google’s AI systems show greater willingness to cite newer sources and user-generated content compared to ChatGPT, provided those sources demonstrate relevance and authority. This platform preference means that strong traditional SEO performance correlates with AI citation success on Google’s platforms, though the correlation isn’t perfect.
Perplexity AI Preferences emphasize transparency and direct source attribution. The platform typically provides 3-5 sources per response with direct links, preferring industry-specific review sites, expert publications, and data-driven content. Domain authority weighs heavily, with established publications receiving preferential treatment, while community content appears in roughly 1% of citations, primarily for product recommendations. Perplexity’s design philosophy prioritizes helping users verify information by providing clear source attribution, making it particularly valuable for tracking brand visibility. Organizations optimizing for Perplexity benefit from creating data-rich content, industry-specific resources, and expert-authored pieces that demonstrate clear authority.
Domain authority functions as a reliability proxy in AI algorithms, signaling that a source has demonstrated credibility over time. Systems assess authority through multiple trust signals worth approximately 5% of total citation probability, though this percentage increases significantly for YMYL (Your Money, Your Life) topics affecting health, finance, or safety decisions. Key authority indicators include domain age, SSL certificates, privacy policies, and compliance markers like SOC 2 or GDPR certification. These technical signals compound when combined with content quality metrics, creating a multiplicative effect where technically sound sites with excellent content outperform technically poor sites regardless of content quality.
Backlink profiles significantly influence source perception in AI algorithms. AI models evaluate the authority of linking domains, the relevance of link context, and backlink portfolio diversity. Research shows that ten backlinks from major publications outperform 100 backlinks from low-authority sites, demonstrating that link quality matters far more than quantity. Expert attribution increases citation likelihood substantially, with content bylined to named authors with verifiable credentials performing significantly better than anonymous content. Author schema markup and detailed bios help AI systems validate expertise, while third-party validation through industry publication mentions reinforces credibility. Organizations building authority should focus on earning backlinks from high-authority sources, establishing author credentials, and securing mentions in industry publications.
Wikipedia and knowledge graph presence dramatically improve citation rates regardless of other factors. Sources referenced in Wikipedia enjoy significant advantages because knowledge graphs serve as authoritative sources that AI models reference repeatedly across diverse queries. Google Knowledge Panel information feeds directly into how AI models understand entity relationships and authority. Organizations without a Wikipedia presence struggle to achieve consistent citations even with high-quality content, suggesting that knowledge graph development should be a priority for serious AI visibility strategies. This creates a foundational trust layer that language models reference during retrieval, making knowledge graph entries serve as authoritative sources that models consult repeatedly.
Conversational Query Alignment represents a fundamental shift from traditional SEO optimization. Content structured as question-answer pairs performs better in retrieval algorithms than keyword-optimized content. FAQ pages and content mirroring natural language queries receive preferential treatment because AI systems are trained on conversational data and understand natural language patterns better than keyword strings. This means that content written as if answering a friend’s question outperforms content written for search engine algorithms. Organizations should audit their content for conversational tone, direct answers to common questions, and natural language alignment with how users actually ask questions.
Citation Quality Within Content creates trust cascades that extend beyond individual sources. AI systems evaluate whether claims include backing data and supporting evidence. Content citing authoritative references inherits confidence from those cited sources, creating a multiplicative credibility effect. Sources that include supporting evidence and link to primary sources demonstrate higher citation rates than unsupported claims. This means that every significant claim should include attribution to authoritative sources with publication dates and expert credentials. Organizations building citation-worthy content should research and cite 5-8 authoritative sources minimum, include 2-3 expert quotes with full credentials, and add 3-5 recent statistics with publication dates.
Consistency Across Platforms influences how AI systems evaluate source credibility. When AI finds consistent information across multiple sources, confidence increases for citing any individual source from that cluster. Sources contradicting the broader consensus receive lower priority unless they provide compelling contrary evidence. This consistency bias means that establishing coherent narratives across owned, earned, and shared media channels reinforces individual source citability. Organizations developing AI reputation management strategies must maintain consistent messaging across all digital properties, ensuring that information presented on corporate websites, social media, industry publications, and third-party platforms aligns and reinforces core messages.
Update Frequency Strategy matters more in the AI era than in traditional SEO. Publishing frequency directly impacts citation rates, with AI platforms showing strong preference for recently updated content. Organizations should update existing content every 48-72 hours to maintain recency signals, though this doesn’t require complete rewrites. Adding new data points, updating statistics, or expanding sections with recent developments sustains citation eligibility. Content management systems that track update frequency and content freshness help maintain competitive citation rates as AI platforms increasingly weight recency signals. This continuous update approach differs fundamentally from traditional SEO, where content could rank indefinitely without modification.
Strategic Placement in Aggregator Sites creates multiple discovery pathways for AI systems. Getting featured in industry roundups, expert lists, or review sites generates opportunities beyond what original sources achieve alone. A single mention in a frequently cited publication creates multiple discovery pathways and generates opportunities for AI systems to encounter your content through multiple routes. Media relations and content partnerships increase in value for AI visibility, as does strategic placement in industry-specific databases and directories. Organizations should pursue features in industry roundups, expert lists, and review sites as part of their AI visibility strategy.
Structured Data Implementation improves citation likelihood by making content machine-readable. Schema markup in AI-readable formats helps AI platforms understand and extract specific facts without parsing unstructured text. The FAQ schema, Article schema with author information, and Organization schema create machine-readable signals that retrieval algorithms prioritize. JSON-LD structured data allows AI to extract specific facts efficiently, improving both citation probability and the accuracy of cited information. Organizations implementing comprehensive schema markup see measurable improvements in citation rates across multiple AI platforms.
Wikipedia and Knowledge Graph Development yields compounding returns despite requiring sustained effort. Building a Wikipedia presence requires neutral, well-sourced contributions that meet Wikipedia’s editorial standards. Simultaneously optimizing profiles on Wikidata, Google Knowledge Panel, and industry-specific databases creates the foundational trust layer that AI systems reference repeatedly. These knowledge graph entries serve as authoritative sources that models consult across diverse queries, making knowledge graph development a strategic priority for organizations seeking sustained AI visibility.
Organizations should track citation frequency by manually testing relevant queries across ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and other platforms. Regular prompt testing reveals which content successfully achieves citations and which gaps exist in AI representation. This testing methodology provides direct visibility into citation performance and helps identify optimization opportunities. AI citation algorithms shift continuously as training data expands and retrieval strategies evolve, requiring content strategies to adapt based on performance data. When content stops receiving citations despite historical success, refresh with recent information or restructure for better semantic alignment.
Multiple sources can receive citations for single queries, creating co-citation opportunities rather than zero-sum competition. Organizations benefit from creating comprehensive content that complements rather than duplicates existing highly-cited sources. Competitive landscape analysis reveals which brands dominate AI visibility in specific categories, helping organizations identify gaps and opportunities. Tracking citation performance over time reveals trends and which URLs drive success, enabling organizations to replicate winning strategies and scale successful approaches.
Track where your content appears in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI platforms. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and citation performance.

Learn how AI systems select which sources to cite versus paraphrase. Understand citation selection algorithms, bias patterns, and strategies to improve your con...

Learn how AI-generated content performs in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Discover ranking factors, optimization strategie...

Learn what citation optimization for AI is and how to optimize your content to be cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google Gemini, and other AI search engines.