Understanding Keyword Cannibalization in AI Search
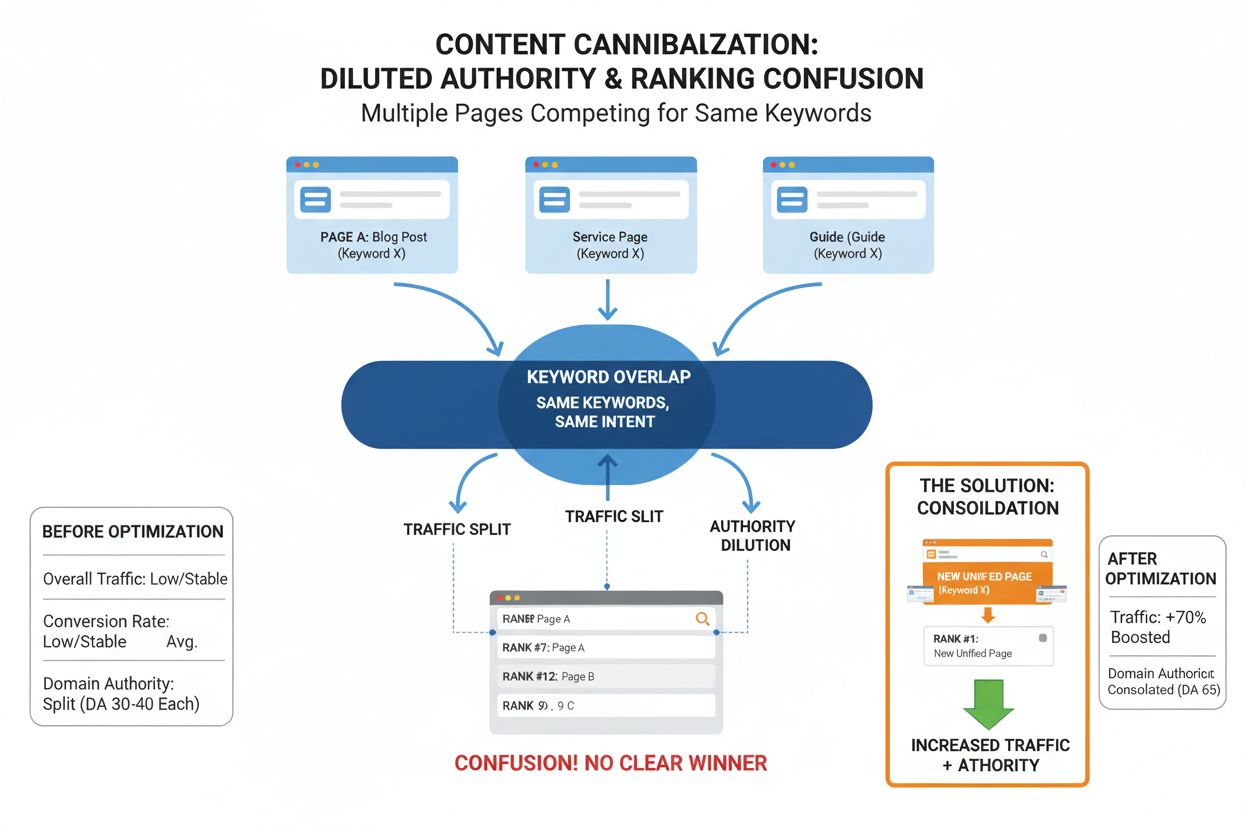
Keyword cannibalization occurs when multiple pages on your website target the same or very similar keywords and search intent, causing them to compete with each other in search engine rankings. In the context of AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini, this problem becomes even more critical because these platforms use different ranking mechanisms than traditional search engines. While Google relies heavily on links and domain authority, AI language models prioritize mentions and semantic relevance across their training data. When your content competes with itself across multiple pages, you dilute the authority signals that AI systems use to determine which of your pages should be cited in their answers.
The challenge with AI search engines is that they don’t just look at individual pages—they analyze patterns of mentions and topical authority across your entire domain. If you have multiple pages targeting the same keyword or topic, the AI system may struggle to identify which page represents your authoritative stance on that subject. This fragmentation means that instead of one strong page being cited in AI-generated answers, your visibility gets split across weaker competing pages, or worse, your content might not appear at all because the AI system cannot determine which version is most authoritative.
Why Keyword Cannibalization Damages Your AI Visibility
Keyword cannibalization directly impacts your ability to appear in AI-generated answers in several critical ways. First, it dilutes your topical authority. AI language models are trained on vast amounts of web content, and they learn which sources are most authoritative on specific topics by analyzing how frequently and prominently your content appears in relation to certain keywords and concepts. When you have multiple pages competing for the same keyword, you’re essentially splitting the mentions and authority signals that could have been consolidated into a single, powerful page. This makes it harder for AI systems to recognize you as the definitive source on that topic.
Second, keyword cannibalization creates semantic confusion. AI systems understand content through semantic relationships—they recognize when pages are discussing the same concepts even if the exact wording differs. When multiple pages on your site target the same intent, the AI system may not know which one to prioritize when generating answers. This uncertainty can result in your content being cited less frequently, or being replaced by competitors’ content that presents a clearer, more unified perspective on the topic.
Third, cannibalization wastes your crawl budget and indexing potential. Search engines and AI training systems allocate limited resources to crawling and analyzing your site. When they encounter multiple pages targeting the same keyword, they spend resources on pages that don’t add unique value, leaving less capacity for discovering and analyzing your truly unique content. This is particularly problematic for AI systems that may not crawl your entire site as thoroughly as Google does.
| Impact Factor | Effect on Traditional SEO | Effect on AI Search |
|---|
| Authority Dilution | Splits backlinks and internal link equity | Fragments mentions and topical authority signals |
| Ranking Power | Multiple pages rank lower individually | AI uncertain which page to cite in answers |
| Click Distribution | Traffic split across competing pages | Reduced likelihood of being cited in AI responses |
| Crawl Efficiency | Wasted crawl budget on duplicate content | Less efficient training data extraction |
| User Experience | Confusing multiple similar results | Inconsistent or missing brand attribution |
Ready to Monitor Your AI Visibility?
Track how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms.
Identifying Keyword Cannibalization Issues
Before you can fix keyword cannibalization, you need to identify where it’s happening on your site. Start with Google Search Console, which provides direct visibility into which pages are ranking for the same keywords. Navigate to the Performance section, add a filter for your target keyword, and examine the Pages tab to see which URLs are receiving impressions and clicks for that term. If multiple pages appear, you’ve found a cannibalization issue. Pay special attention to pages that rank beyond the top five positions—when two of your URLs rank closely together outside the top spots, it’s often a sign that neither is performing optimally because they’re competing with each other.
You can also use the site search operator in Google to quickly identify potential cannibalization. Simply search site:yourdomain.com "your keyword" to see all indexed pages containing that keyword. While this doesn’t tell you which pages are actually ranking, it gives you a starting point for manual review. Look at the top results—these are typically the pages ranking highest for that keyword. If you see multiple URLs from your domain, investigate whether they’re targeting the same search intent.
For a more comprehensive analysis, use SEO tools like Semrush, Ahrefs, or Screaming Frog that can automatically detect keyword cannibalization. These tools analyze your keyword rankings and identify instances where multiple pages rank for the same terms. They also provide data on search volume, keyword difficulty, and ranking positions, which helps you understand the severity of each cannibalization issue. Additionally, monitor your content’s appearance in AI search results by regularly checking ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini for queries related to your target keywords. If you notice that your content isn’t appearing in AI-generated answers, or if you see competitors’ content being cited instead, keyword cannibalization may be the culprit.
Strategy 1: Consolidate Pages Through 301 Redirects
Page consolidation is the most effective solution when two or more pages target the same keyword and search intent. This approach involves selecting the strongest page—the one with the best rankings, most traffic, or most comprehensive content—and redirecting all competing pages to it using a 301 permanent redirect. A 301 redirect tells search engines and AI systems that the old page has permanently moved to the new location, and it passes the vast majority of the SEO value (including backlinks, internal links, and authority signals) from the old page to the new one.
To choose which page to consolidate into, evaluate your competing pages using several criteria. Check their current rankings using tools like Moz’s Rank Checker or your SEO platform’s rank tracking feature. The page with the highest and most consistent ranking is typically the best candidate to keep. Analyze which page best satisfies the search intent—read the top-ranking results for your target keyword and determine which of your pages aligns most closely with what users are actually searching for. Review the backlink profile of each page using tools like Moz’s Link Explorer or Ahrefs. The page with the highest number of quality backlinks is worth preserving because those links represent authority that you don’t want to lose.
Once you’ve selected your primary page, merge valuable content from the competing pages into it. Extract unique sections, data, examples, or perspectives from the pages you’re consolidating and integrate them into your primary page. This makes your primary page more comprehensive and valuable, which improves its chances of ranking higher and being cited in AI-generated answers. Then, set up 301 redirects from all competing pages to your primary page. This ensures that any traffic, backlinks, and authority signals from the old pages flow to the new consolidated page. Finally, update your XML sitemap to remove the redirected URLs and ensure search engines understand the change.
Stay Updated on AI Visibility Trends
Get the latest insights on AI mentions, brand monitoring, and optimization strategies.
Canonical tags are an alternative solution when you want to keep multiple pages live but need to tell search engines which version is the primary one. A canonical tag is an HTML element that you add to a page’s header, and it tells search engines: “This page is a duplicate or similar version of another page; please treat this other page as the authoritative version.” Unlike 301 redirects, canonical tags don’t remove the page from your site or redirect users—they simply consolidate ranking signals to your preferred page.
Canonical tags are particularly useful in specific scenarios. If you have multiple pages serving different user needs but targeting the same keyword, canonical tags can help. For example, you might have a product category page and a blog post that both rank for “best running shoes.” If the category page is your primary revenue-generating page, you can add a canonical tag to the blog post pointing to the category page. This tells search engines to prioritize the category page for rankings while keeping the blog post accessible to users who find it valuable.
However, canonical tags have limitations for AI search engines. While they help consolidate ranking signals in traditional search, AI language models may not respect canonical tags in the same way. AI systems are more focused on semantic relevance and mention frequency than on technical SEO signals. Therefore, canonical tags should be used in conjunction with other strategies, not as a standalone solution. If you use canonical tags, also consider updating your internal linking strategy to point more authority toward your primary page, and ensure that your primary page is more comprehensive and authoritative than the secondary page.
Strategy 3: Differentiate Search Intent Across Pages
If your competing pages serve different user needs or search intents, you can resolve cannibalization by reoptimizing each page to target unique long-tail keywords. This strategy works when you have multiple pages that overlap in topic but could legitimately serve different audiences or answer different questions. For example, you might have two articles both ranking for “small business accounting software,” but one could be reoptimized for “best accounting software for startups” while the other targets “cloud-based accounting software for small businesses.”
To implement this strategy, first analyze the search intent behind each competing page. Look at what keywords each page currently ranks for, what content it contains, and what audience it serves. Then, research long-tail keyword variations that align with each page’s unique angle. Use keyword research tools to identify variations with sufficient search volume and lower competition. Importantly, ensure that your chosen long-tail keywords still align with your business offerings. It wouldn’t make sense to write about cloud-based accounting software if your product isn’t cloud-based. Also, verify that there’s actual search volume for the long-tail keywords you choose. Shifting your content’s focus to terms with no traffic potential won’t benefit your visibility.
Once you’ve identified your long-tail keywords, rewrite and reoptimize each page to target its unique keyword and intent. Update the page title, meta description, headers, and body content to reflect the new focus. Ensure that each page provides unique value and answers a distinct question. This approach allows you to keep multiple pages on your site without them competing with each other, and it can actually expand your overall keyword coverage and traffic potential. For AI search engines, this strategy is particularly valuable because it helps you establish authority across multiple related topics, increasing the likelihood that your content will be cited for various related queries.
Strategy 4: Optimize Internal Linking Structure
Your internal linking strategy plays a crucial role in how search engines and AI systems understand which pages are most important on your site. When you have competing pages, your internal linking can either exacerbate the problem or help resolve it. To fix cannibalization through internal linking, start by conducting an internal linking audit to identify how your pages are currently linked to each other.
The key principle is to use consistent anchor text for your primary page. If you have multiple pages competing for “keyword cannibalization,” choose one as your primary page and use that exact keyword (or close variations) as the anchor text when linking to it from other pages on your site. Avoid using the same anchor text to link to multiple pages—this dilutes the authority signal you’re sending to each page. Instead, use different anchor text for secondary pages, or link to them less frequently.
Additionally, ensure that your internal links are strategically distributed to reflect your content hierarchy. Your most important pages should receive more internal links than secondary pages. If you have a pillar page on a topic, it should receive internal links from multiple related pages on your site. This helps search engines and AI systems understand that this page is your authoritative resource on that topic. You can also use descriptive anchor text that includes your target keyword, which helps AI systems understand the semantic relationship between pages and reinforces which page is authoritative for that keyword.
Strategy 5: Monitor Your Brand in AI Search Results
Fixing keyword cannibalization for AI requires ongoing monitoring of how your content appears in AI-generated answers. Unlike traditional SEO where you can rely on Google Search Console and ranking tools, AI search engines don’t provide the same level of transparency. You need to actively monitor platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini to see which of your pages (if any) are being cited in answers to relevant queries.
Regularly search for your target keywords on these AI platforms and note which pages from your site appear in the generated answers. If you notice that your content isn’t appearing, or if competitors’ content is being cited instead, this is a signal that your cannibalization issues may be preventing your content from being recognized as authoritative. Use tools like SparkToro to identify which websites are most likely to be included in AI training data, and focus your PR and content marketing efforts on getting mentioned in those high-authority sources. This helps establish your brand as a trusted source that AI systems will cite.
Additionally, track mentions of your brand and key topics across the web using tools like BuzzSumo or Google Alerts. Monitor where your content is being referenced and ensure that your primary pages are receiving the most mentions and citations. If you notice that multiple pages from your site are being mentioned for the same topic, this indicates ongoing cannibalization that needs to be addressed. By actively monitoring your AI search visibility, you can identify cannibalization issues before they significantly impact your traffic and adjust your strategy accordingly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Don’t delete pages without analyzing their value first. Many site owners make the mistake of deleting pages they think are underperforming without checking traffic data, backlinks, and search performance. A page might look outdated but still drive valuable traffic or have solid external links. Deleting it could result in unwanted ranking losses and broken links from external sites. Always conduct a thorough analysis before removing any page from your site.
Don’t rely solely on canonical tags to solve cannibalization. While canonical tags are useful technical tools, they’re not a complete solution for keyword cannibalization, especially for AI search engines. AI systems may not respect canonical tags in the same way traditional search engines do. Use canonical tags in combination with other strategies like content consolidation or internal linking optimization.
Don’t merge pages that target different search intents. Just because two pages cover a similar topic doesn’t mean they should be combined. If each page is aimed at a different audience or answers a different question, merging them could hurt relevance and rankings. Always carefully analyze search intent before deciding to consolidate pages.
Don’t overlook the importance of internal linking. Internal links are one of the most powerful tools you have to guide search engines and AI systems toward your authoritative pages. If you skip updating your internal linking strategy when fixing cannibalization, you may weaken page authority and miss opportunities to guide crawlers and users to your key content.
Preventing Future Keyword Cannibalization
Create and maintain a keyword and content map before publishing new content. Decide the primary keyword for every page before it’s created, and ensure that no two pages target the same keyword. This proactive approach prevents cannibalization from happening in the first place. A pillar and cluster content strategy is particularly effective—choose core pillar topics that align with your expertise, then create supporting content around subtopics and long-tail keywords that branch from each pillar.
Assign a unique target keyword to each page and ensure that your URL structure reflects this. For example, a blog article targeting “startup accounting software” should have a URL like www.example.com/blog/startup-accounting-software. This helps search engines and AI systems understand your content structure and reinforces your authority on specific keywords.
Improve collaboration between your content and SEO teams. SEO shouldn’t be implemented after your site is set up—it should be baked into every step of content creation. Regular communication between teams helps ensure that every piece of content has a clear purpose and doesn’t overlap with existing content. Conduct regular content audits to catch early signs of cannibalization, such as declining traffic, higher bounce rates, or lower click-through rates. These changes might seem like typical fluctuations, but from the broader perspective of a content audit, they can reveal patterns that suggest keyword cannibalization issues.