Canonical URLs and AI: Preventing Duplicate Content Issues
Learn how canonical URLs prevent duplicate content problems in AI search systems. Discover best practices for implementing canonicals to improve AI visibility a...

Learn how to manage and prevent duplicate content when using AI tools. Discover canonical tags, redirects, detection tools, and best practices for maintaining unique content across your website.
Handle duplicate content for AI by using canonical tags, implementing 301 redirects, applying noindex meta tags, managing URL parameters, and ensuring human-led editing of AI-generated content to maintain originality and prevent search engine penalties.
Duplicate content refers to substantive blocks of identical or very similar text appearing on multiple URLs within your website or across different domains. In the context of AI search engines and answer generators like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and similar platforms, duplicate content becomes particularly problematic because these systems struggle to determine which version of your content is the original, authoritative source. This confusion can result in diluted ranking signals, reduced visibility in AI-generated answers, and potential penalties from traditional search engines. When AI systems encounter multiple versions of the same content, they may cite the wrong version, fail to attribute your brand correctly, or exclude your content entirely from their responses.
The challenge intensifies when using AI-generated content on your own website. AI tools often train on large corpora of existing web content, meaning they can inadvertently produce text that mirrors existing pages online. Without careful prompt engineering and human oversight, AI-generated articles, blog posts, and landing pages can become near-duplicates of content already published elsewhere, creating serious SEO and visibility issues across both traditional search engines and AI answer platforms.
Understanding the different categories of duplicate content helps you address them strategically. Internal duplicate content occurs when multiple pages on your own domain contain substantially similar or identical text. This commonly happens when you have printer-friendly versions, session IDs in URLs, category pages with overlapping descriptions, or multiple AI-generated articles on similar topics without sufficient differentiation. External duplicate content happens when your content appears on other domains, either through intentional syndication or unintentional copying and scraping by third parties. When AI systems crawl the web, they may encounter your content on multiple domains and struggle to identify the original source, potentially attributing citations to the wrong website.
| Type | Cause | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Duplicate | Multiple URLs with same content | Diluted link equity, indexing confusion | Canonical tags, 301 redirects |
| External Duplicate | Content syndication or scraping | Lost attribution, reduced authority | Canonical links, noindex tags |
| Near-Duplicate | Slightly modified AI-generated content | Ranking dilution, AI citation confusion | Human editing, unique angles |
| Parameter-Based | URL variations (tracking, session IDs) | Search engine crawl waste | URL parameter management |
When your content appears in multiple locations without proper canonicalization, AI answer generators struggle to identify the authoritative source. This directly impacts how your brand, domain, and URLs are cited in AI-generated responses. If you’re using AmICited or similar AI monitoring platforms, you’ll notice that duplicate content issues lead to inconsistent citations, missing attributions, or citations pointing to the wrong version of your content. Additionally, search engines like Google penalize sites with excessive duplicate content, which indirectly affects your visibility in AI systems that rely on search engine rankings as a quality signal. The more authoritative and consolidated your content appears in traditional search results, the more likely AI systems will cite it accurately and prominently in their answers.
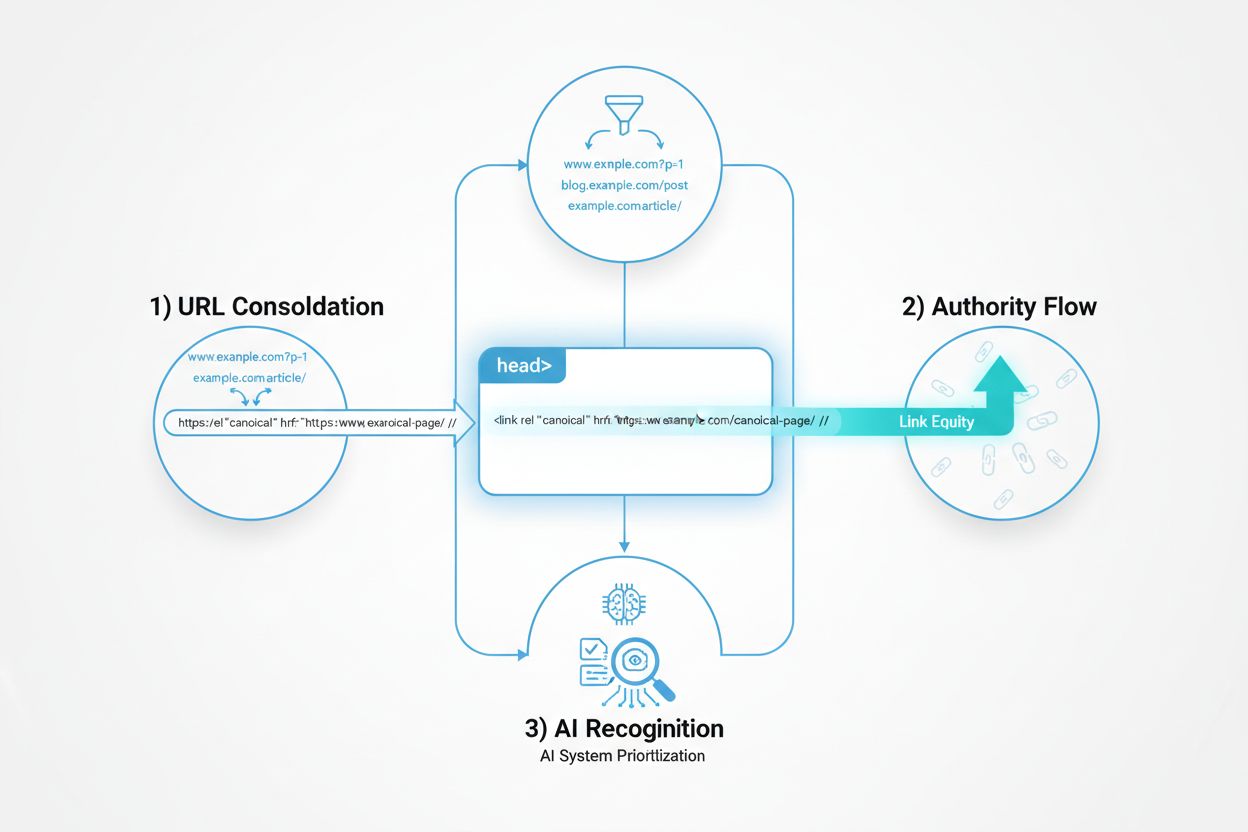
Canonical tags are the most powerful tool for managing duplicate content without removing pages from your site. A canonical tag tells search engines and AI crawlers which version of a page you consider the authoritative source. To implement canonical tags effectively, add a <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/preferred-url/" /> element in the <head> section of all duplicate pages, pointing to your preferred version. This consolidates ranking signals and ensures AI systems understand which version to cite. Always use absolute URLs rather than relative paths, as this prevents confusion and works reliably across all crawlers. For example, use https://www.example.com/dresses/green-dresses instead of /dresses/green-dresses.
When managing AI-generated content, implement canonical tags immediately after publishing. If you’ve generated multiple variations of an article using AI tools, designate one as canonical and add canonical tags to all other versions. This prevents link equity dilution and ensures that backlinks, citations, and authority signals consolidate on your preferred version. For pages that are intentionally similar but serve different purposes (such as regional variations or product variants), use canonical tags to point to the most comprehensive or authoritative version. This approach maintains your site’s crawl efficiency and ensures AI systems prioritize the right content when generating answers about your brand or domain.
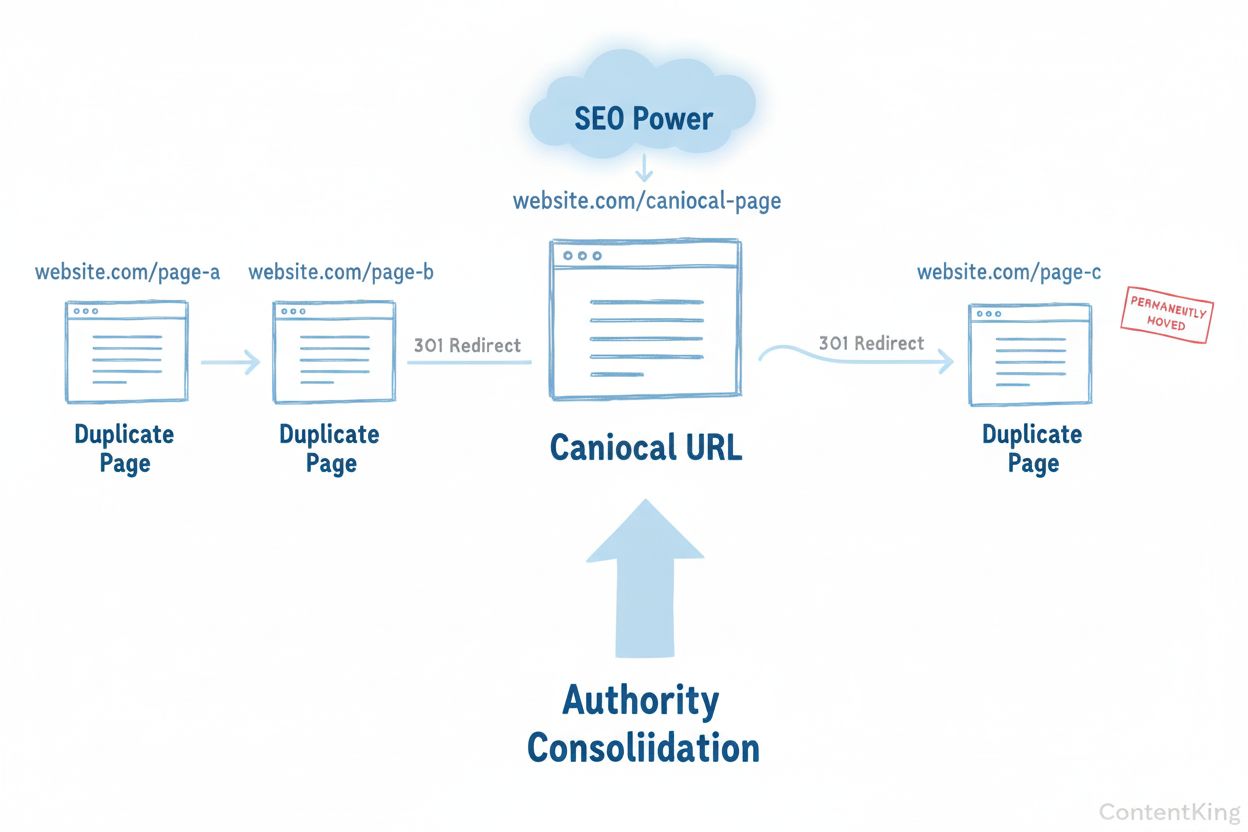
301 redirects are permanent redirects that tell both search engines and AI crawlers that a page has moved permanently to a new location. This method is particularly effective when you want to eliminate duplicate pages entirely rather than maintain multiple versions. When you implement a 301 redirect from an old URL to a new URL, search engines transfer the ranking authority and link equity from the old page to the new one, ensuring no loss of SEO value. For AI systems, 301 redirects provide a clear signal about which URL is the authoritative source, improving the accuracy of citations and attributions in AI-generated answers.
Use 301 redirects when consolidating AI-generated content that overlaps significantly, when migrating from HTTP to HTTPS, or when moving pages to new URLs. For example, if you’ve generated multiple blog posts on “AI content best practices” using different AI tools, and they’re substantially similar, redirect the weaker versions to the strongest, most comprehensive article. This consolidation strengthens your authority on that topic and ensures AI systems cite the best version. Implement redirects at the server level for maximum effectiveness, as this provides the strongest signal to crawlers. Avoid using meta-refresh or JavaScript redirects for canonicalization purposes, as these are slower and less reliable for search engine and AI crawler interpretation.
The noindex meta tag instructs search engines and AI crawlers not to index a specific page, effectively removing it from search results and AI answer generation. This approach is useful for pages you want to keep live for user navigation but don’t want indexed or cited by AI systems. Add <meta name="robots" content="noindex" /> to the <head> section of duplicate pages you wish to exclude from indexing. This prevents search engines from wasting crawl budget on duplicate content and ensures AI systems don’t encounter multiple versions of the same information.
However, use noindex strategically and sparingly. While it removes pages from search results, it doesn’t consolidate ranking signals like canonical tags or redirects do. Reserve noindex for pages that genuinely shouldn’t be indexed, such as login pages, thank-you pages, or temporary duplicate versions. For permanent duplicate content that you want to keep live, canonical tags are superior because they consolidate authority rather than simply hiding pages. When using noindex on AI-generated content variations, ensure you’re not accidentally hiding valuable content that could improve your visibility in AI answers. Always maintain at least one fully indexed, canonical version of each piece of content.
URL parameters (also called query strings) are additional information appended to URLs, typically following a question mark. Common examples include tracking codes (?gclid=ABCD), session IDs, sorting options, and filtering parameters. These parameters can create hundreds or thousands of URL variations pointing to identical or near-identical content, causing severe duplicate content issues. For instance, https://example.com/products?category=electronics&color=blue and https://example.com/products?category=electronics&color=red may display the same product page with different filters, creating duplicate content problems.
To manage URL parameters effectively, first identify which parameters create duplicate content and which serve legitimate purposes. Use Google Search Console’s URL parameter tool or similar SEO platforms to monitor parameter usage on your site. For parameters that create duplicates (like tracking codes), implement canonical tags pointing to the parameter-free version. For parameters that serve legitimate filtering purposes, use canonical tags to point to the primary version without parameters, or implement rel="canonical" HTTP headers to manage non-HTML files. When generating AI content, avoid creating multiple URLs with different parameters pointing to the same content. Instead, use a single canonical URL and manage variations through canonical tags or redirects.
Regular duplicate content audits are essential when using AI tools to generate content at scale. Copyscape is a widely-used external duplicate detection tool that checks whether your content appears elsewhere on the web. Enter your content or URL to find matching pages across the internet, helping you identify if your AI-generated content has been scraped or if your content matches existing pages too closely. Siteliner offers free internal duplicate detection, identifying similar pages within your own domain, broken links, and overall site health metrics. This tool is particularly useful for spotting near-duplicates created by AI tools that generate similar content with minor variations.
Grammarly’s plagiarism checker (premium feature) scans content against billions of web pages and academic databases, making it excellent for verifying AI-generated drafts before publication. SEMrush and Ahrefs provide comprehensive site audit modules that identify duplicate page titles, meta descriptions, and content similarity metrics across your entire website. These enterprise-level tools are invaluable for large sites with extensive AI-generated content. For quick spot checks, use Google Search operators by placing quotation marks around unique sentences from your content (e.g., "your exact sentence here") to see if matches exist online. Integrate duplicate checks at multiple stages: initial draft review, pre-publication verification, and periodic site-wide audits to catch emerging duplication patterns.
The most effective approach to preventing duplicate content with AI is implementing human-led editing workflows. Never publish AI-generated content verbatim. Instead, use AI as a research assistant and draft generator, then have human writers thoroughly revise the output. Remove generic boilerplate phrases that AI commonly produces, inject proprietary insights and case studies, and reframe content with unique angles specific to your brand. This hybrid approach maximizes AI’s efficiency while ensuring content remains original and valuable to both search engines and AI answer generators.
When crafting prompts for AI tools, provide detailed context and specific instructions. Instead of asking “Write an article about duplicate content,” try “Write a 1,200-word article about handling duplicate content for AI search engines, specifically addressing canonical tags, 301 redirects, and URL parameter management. Include examples relevant to e-commerce sites and incorporate our unique perspective on AI monitoring.” Specific prompts yield more original, differentiated content than generic requests. Supply AI with examples of your brand’s voice and style, proprietary data, customer success stories, and unique research findings. This contextual information biases AI outputs toward your brand’s perspective rather than generic web content.
Implement fact-checking and verification processes for all AI-generated content. Verify statistics, claims, and references against authoritative sources. Update outdated information and add citations to strengthen credibility. This human oversight ensures content is not only original but also accurate and trustworthy, which improves both search engine rankings and AI system citations. For niche industries requiring deep expertise (medical, legal, technical fields), have subject matter experts review and enhance AI drafts to ensure domain-specific accuracy and originality.
Content consolidation involves merging multiple pieces of duplicate or overlapping content into a single, comprehensive resource. This strategy is particularly effective when you’ve generated multiple AI articles on similar topics. Rather than maintaining separate pages that compete with each other, identify the most complete and authoritative version, merge relevant information from other versions into it, and redirect or remove the inferior versions. This consolidation strengthens your topical authority, improves user experience, and ensures AI systems cite your most comprehensive resource.
When consolidating AI-generated content, prioritize quality over quantity. A single, deeply researched, well-edited article on a topic will rank better and be cited more accurately by AI systems than five mediocre variations. Use consolidated content as the foundation for building topic clusters and cornerstone content strategies. Create one authoritative pillar page on a broad topic, then develop related cluster content that links back to the pillar. This structure helps search engines and AI systems understand your expertise and improves your visibility in AI-generated answers about that topic.
Beyond managing duplicate content on your own site, monitor how your brand, domain, and URLs appear in AI-generated answers. Platforms like AmICited help you track whether your content is being cited correctly in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI answer generators. If you notice inconsistent citations, missing attributions, or citations pointing to duplicate versions of your content, this indicates duplicate content issues affecting your AI visibility. Use these insights to refine your canonicalization strategy and ensure your preferred content versions are being cited.
Regular monitoring reveals patterns in how AI systems interpret your content structure. If AI systems consistently cite the wrong version of your content, it may indicate that your canonical tags aren’t strong enough or that your preferred version lacks sufficient authority signals. Adjust your canonicalization methods by combining techniques (canonical tags + 301 redirects + sitemap inclusion) for stronger signals. Track changes in citation accuracy after implementing duplicate content fixes to measure the effectiveness of your strategy.
Establish a systematic approach to preventing duplicate content when using AI tools. Before publishing any AI-generated content, verify that it doesn’t closely match existing content on your site or elsewhere using plagiarism detection tools. Ensure each page has a unique, descriptive title tag and meta description that differentiate it from similar pages. Implement canonical tags on all pages that might have duplicates, pointing to your preferred version. For pages you’re consolidating, set up 301 redirects from old URLs to the new canonical version. Include only preferred URLs in your XML sitemap, and configure URL parameter handling in Google Search Console to prevent parameter-based duplication.
Maintain consistent internal linking practices by always linking to canonical URLs rather than duplicate versions. This reinforces your preferred URL structure throughout your site. Schedule periodic site audits using SEO tools to detect emerging duplicate content patterns, especially after bulk content additions from AI tools. Document your canonicalization decisions and maintain a content inventory that tracks which pages are canonical and which are duplicates. This documentation helps your team maintain consistency and prevents accidental duplication when updating or expanding content. Finally, establish editorial guidelines for AI content that require human review, fact-checking, and originality verification before publication, ensuring all AI-assisted content meets your quality and uniqueness standards.
Ensure your content appears correctly in AI-generated answers and search results. Track how your brand, domain, and URLs are cited across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms.

Learn how canonical URLs prevent duplicate content problems in AI search systems. Discover best practices for implementing canonicals to improve AI visibility a...
Duplicate content is identical or similar content on multiple URLs that confuses search engines and dilutes ranking authority. Learn how it affects SEO, AI visi...
Learn what AI content cannibalization is, how it differs from duplicate content, why it hurts rankings, and strategies to protect your content from being scrape...