Which Content Formats Get More AI Citations? Data Analysis
Discover which content formats get cited most by AI models. Analyze data from 768,000+ AI citations to optimize your content strategy for ChatGPT, Perplexity, a...

Learn the optimal content depth, structure, and detail requirements for getting cited by ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Discover what makes content citation-worthy for AI search engines.
Content for AI citations should be comprehensive and detailed, with high fact density, clear structure, and original insights. AI systems prefer in-depth content that directly answers questions with specific data, proper formatting, and authority signals—typically 1,500+ words with multiple supporting elements.
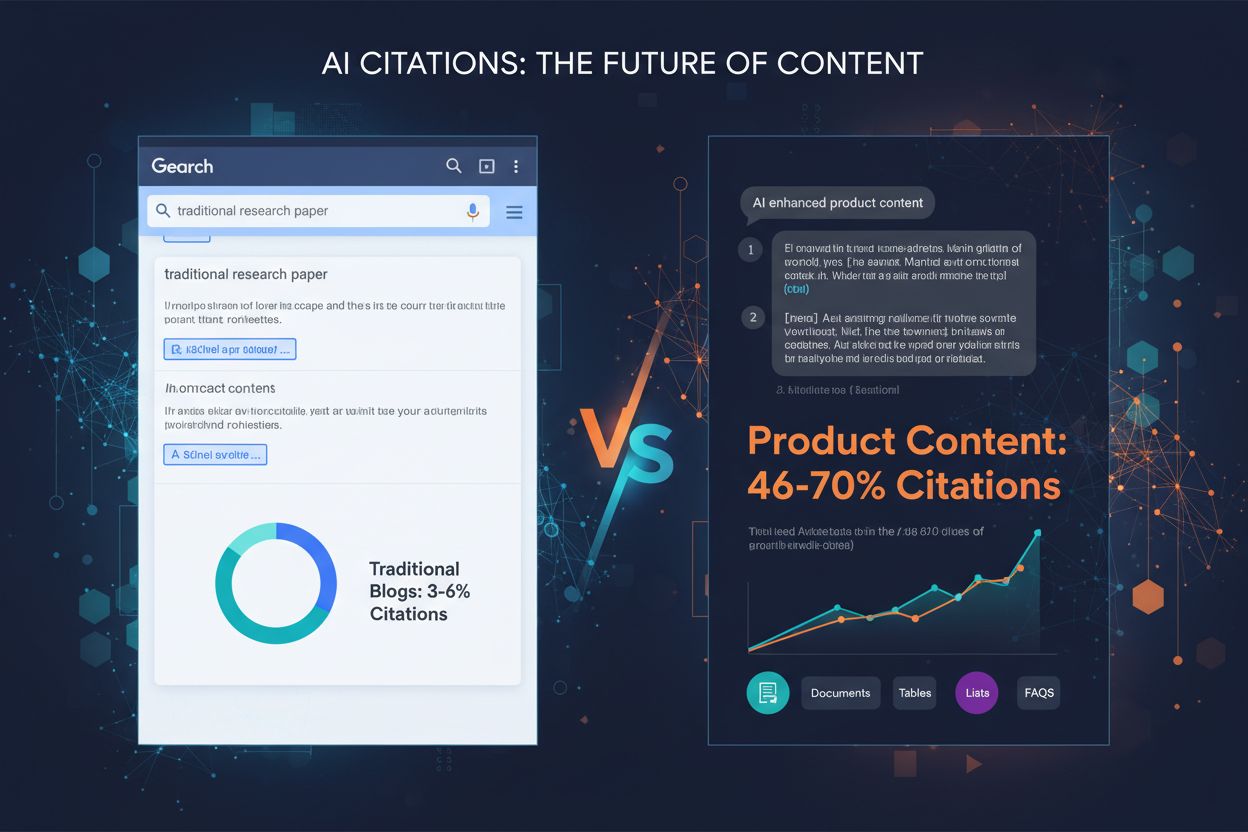
Content depth is one of the most critical factors determining whether AI systems will cite your work. Unlike traditional search engines that prioritize keyword density and backlinks, AI citation systems evaluate content based on comprehensiveness, factual authority, and structural clarity. Research analyzing 768,000 AI citations reveals that product content dominates with 46-70% of all citations, while traditional blog posts struggle at just 3-6%. This dramatic difference isn’t about word count alone—it’s about how thoroughly content addresses user questions with verifiable information and clear organization.
AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews use sophisticated algorithms to determine which sources deserve citations. These algorithms assess whether content provides complete answers, includes supporting data, demonstrates expertise, and presents information in a format that AI can easily parse and extract. Shallow or thin content rarely gets cited, regardless of domain authority or backlink profile. The depth requirement exists because AI systems need to extract accurate, quotable information that users can trust. When content lacks sufficient detail, AI models either skip it entirely or synthesize information from multiple sources instead of citing a single authoritative piece.
Most citation-worthy content ranges from 1,500 to 3,000+ words, though length alone doesn’t guarantee citations. The critical factor is fact density—the concentration of verifiable claims, statistics, and specific information within that content. A 2,000-word article with vague generalizations will underperform a 1,500-word piece packed with concrete data points, research findings, and actionable insights. AI systems measure comprehensiveness by evaluating how many distinct questions your content answers within a single piece.
For example, a comparison article about CRM platforms should cover pricing, features, use cases, integration capabilities, customer support quality, and implementation timelines. Each section needs specific details: exact price points, feature lists with descriptions, real customer scenarios, and concrete integration examples. AI systems prefer content that anticipates follow-up questions and answers them preemptively. If a user asks “What’s the best CRM for startups?” and your content only mentions three platforms with basic descriptions, AI will likely cite a competitor’s more comprehensive guide that covers ten platforms with detailed pros and cons for each.
| Content Depth Element | Minimum Requirement | Citation Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Word Count | 1,500-2,000 words | Moderate—length matters less than density |
| Data Points | 5-10 specific statistics or metrics | High—AI prioritizes verifiable facts |
| Structural Elements | Clear headings, subheadings, bullet points | High—improves AI parsing and extraction |
| Original Insights | At least 2-3 unique perspectives or findings | Very High—differentiates from competitors |
| Source Citations | 3-5 authoritative references | High—builds credibility and E-E-A-T signals |
| Examples | 3-5 real-world case studies or scenarios | High—demonstrates practical application |
| Update Frequency | Refreshed every 3-6 months | Very High—AI prefers fresh content 25.7% more |
Fact density directly correlates with citation likelihood. AI systems analyze the ratio of verifiable claims to total content. Content with high fact density contains specific numbers, percentages, dates, research findings, and concrete examples throughout. Low-density content relies on general statements, vague descriptions, and theoretical explanations without supporting evidence. When AI systems encounter high-density content, they can extract multiple quotable statements and cite specific claims with confidence.
Consider the difference between these two approaches: A generic statement like “ChatGPT is popular” provides no citation value. A fact-dense alternative like “ChatGPT reached 800 million users by August 2025, growing 300% year-over-year, with 54.61% of all AI search queries running through Google AI Overviews” gives AI multiple specific claims to cite. Each statistic, percentage, and date increases the likelihood of citation because AI systems can attribute specific information to your source. This is why original research, industry surveys, and proprietary data analysis earn 46-70% of all AI citations—they provide unique facts that competitors cannot replicate.
Integrating data effectively means distributing facts throughout your content rather than clustering them in one section. A well-structured article alternates between explanatory paragraphs and supporting data points. For instance, when explaining why Perplexity differs from ChatGPT, you might state the conceptual difference, then immediately follow with specific metrics: “Perplexity searches the web in real-time and shows exactly which sources it’s citing. Unlike ChatGPT which generates answers from training data, Perplexity’s real-time search means users get up-to-the-minute information with direct source attribution.” This combination of explanation and specificity makes content more citation-worthy.
AI systems parse content more effectively when it follows clear hierarchical structures. Proper heading hierarchy (H1 for main title, H2 for major sections, H3 for subsections) helps AI understand content organization and extract relevant information. When headings mirror the exact questions users ask, AI systems can match user intent to specific sections and cite those sections directly. This is why question-based headers significantly improve citation rates—they align perfectly with how AI systems process queries.
Bullet points and numbered lists also improve citation likelihood because they present information in scannable, extractable formats. AI systems can easily identify key points, extract them as quotable statements, and attribute them to your source. Tables are particularly valuable for AI citations because they present structured data that AI can parse with high accuracy. When comparing products, services, or concepts, tables allow AI to extract specific comparisons and cite your content as the source of that structured information. Using at least one table in citation-focused content significantly increases extraction and citation rates.
Short, self-contained paragraphs also improve AI parsing. Each paragraph should deliver one complete idea: a definition, a data point, a recommendation, or an explanation. When paragraphs are concise and focused, AI systems can extract individual sentences as quotable statements. Long, complex paragraphs that combine multiple ideas make extraction difficult and reduce citation likelihood. Aim for paragraphs of 4-6 sentences maximum when creating content for AI citations, ensuring each sentence contributes to a single coherent point.
AI systems evaluate content authority through E-E-A-T signals: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. Content lacking these signals rarely gets cited, regardless of depth or quality. Experience signals come from author bios that demonstrate relevant background and credentials. When an article about CRM systems is written by someone with 10+ years of CRM implementation experience, AI systems recognize this authority and weight the content more heavily. Expertise signals include author credentials, certifications, and professional affiliations.
Authoritativeness extends beyond individual authors to organizational credibility. Content published on established, reputable domains receives higher citation weight than content from new or unknown sites. This is why guest posting on high-authority publications and earning mentions from recognized industry sources strengthens your citation potential. When Perplexity or ChatGPT encounters your content cited by other authoritative sources, it reinforces the perception that your content deserves citation. Trustworthiness signals include transparent sourcing, clear citations of your own sources, privacy policies, security certifications, and author transparency.
Building E-E-A-T requires consistent effort across multiple dimensions. Create detailed author pages that establish credentials and experience. Develop comprehensive about pages that explain your organization’s expertise and mission. Link to authoritative sources within your content to demonstrate research rigor. Include author bylines with credentials on every piece. Pursue digital PR opportunities to earn mentions from recognized publications. The more E-E-A-T signals your content displays, the more likely AI systems will cite it as a trusted source.
Original research and proprietary data are among the most-cited content types, earning 46-70% of all AI citations. AI systems recognize that original research provides unique information unavailable elsewhere, making it inherently citation-worthy. When you publish original survey data, benchmark studies, case studies with real numbers, or proprietary analysis, you create content that competitors cannot replicate. This uniqueness forces AI systems to cite your work if they want to include that specific data in their responses.
Original insights don’t require expensive research projects. They can include unique perspectives on industry trends, analysis of public data that others haven’t synthesized, case studies from your own experience, or expert commentary on emerging topics. The key is providing information or analysis that users cannot find in other sources. When you combine publicly available data in a novel way, draw conclusions that others haven’t articulated, or share proprietary findings, you create citation-worthy content. AI systems actively seek original content because it provides value that generic, rehashed information cannot deliver.
Documenting your research methodology also increases citation value. When you explain how you gathered data, what sample size you used, what time period you analyzed, and what limitations exist, you build credibility and make your findings more trustworthy. AI systems can cite your research with confidence when methodology is transparent. This is why academic-style research presentations, complete with methodology sections and data tables, earn higher citation rates than casual observations or unsupported claims.
AI systems prefer content that is 25.7% fresher than traditional search results. This preference exists because AI systems prioritize current information and want to provide users with the most recent data available. Content that hasn’t been updated in months or years gets deprioritized, even if it was originally comprehensive and authoritative. Establishing a content update cadence of every 3-6 months significantly improves citation likelihood. Each update should add verifiable new information: recent statistics, updated examples, new case studies, or revised recommendations based on market changes.
Update velocity matters as much as update frequency. When you publish new content or refresh existing content, AI systems notice the activity and re-evaluate your content for citations. This is why adding “(Updated January 2025)” to titles and maintaining visible “last modified” dates improves citation performance. AI systems interpret recent updates as signals that content remains authoritative and current. Stale content, even if originally comprehensive, loses citation value over time.
The most effective update strategy combines major refreshes with minor additions. Every 3-6 months, conduct a comprehensive review of your most important pages. Replace outdated statistics with current data, add new examples that reflect recent market conditions, expand sections that have become more important, and remove information that’s no longer relevant. Between major refreshes, add smaller updates: new case studies, recent news commentary, or emerging best practices. This continuous improvement approach signals to AI systems that your content remains actively maintained and authoritative.
Different AI platforms have distinct preferences for content depth and structure. ChatGPT, which relies on training data rather than real-time web search, favors content that was widely published and cited before its knowledge cutoff date. This means ChatGPT citations tend to come from established, authoritative sources like Wikipedia, major news outlets, and well-known publications. For ChatGPT citations, focus on building presence on high-authority platforms and ensuring your content gets mentioned by recognized sources.
Perplexity, which searches the web in real-time, prefers comprehensive, current content with clear structure and specific data. Perplexity citations reward detailed guides, comparison articles, how-to content, and original research that directly answer user questions. Content needs to be well-organized with clear headings, specific examples, and verifiable claims. Perplexity’s real-time search means new, well-optimized content can earn citations within hours or days, not months.
Google AI Overviews, integrated into Google Search, favor content that already ranks well in traditional search results. Google AI Overviews tend to cite blog articles (46%), news content (20%), and community content (5.5%). This means optimizing for traditional SEO while also improving content depth and structure helps with Google AI citations. The content needs to be comprehensive enough to provide complete answers while remaining accessible and well-formatted for both human readers and AI systems.
Comprehensive content must remain readable and engaging for human audiences. The most citation-worthy content serves both AI systems and human readers effectively. This means using clear language, breaking up dense information with formatting, and maintaining logical flow throughout. Avoid creating content that’s so technical or data-heavy that human readers struggle to understand it. The best approach combines depth with accessibility: provide comprehensive information using clear explanations, concrete examples, and visual formatting.
Use formatting strategically to maintain readability while preserving depth. Bold important keywords and key phrases so readers can scan quickly. Use bullet points to present lists of related items. Create tables to compare options or present structured data. Include subheadings that break content into digestible sections. Add white space between paragraphs to prevent dense blocks of text. These formatting techniques improve both human readability and AI parsing, making content more likely to be cited while remaining engaging for human audiences.
Track how often your content appears in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Get real-time insights into your AI visibility and citation performance.

Discover which content formats get cited most by AI models. Analyze data from 768,000+ AI citations to optimize your content strategy for ChatGPT, Perplexity, a...

Learn how to structure your content to get cited by AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI. Expert strategies for AI visibility and citations...
Learn how to test content formats for AI citations using A/B testing methodology. Discover which formats drive the highest AI visibility and citation rates acro...