
Branded Search Volume and AI Visibility: The Connection Explained
Discover how branded search volume directly correlates with AI visibility. Learn to measure brand signals in LLMs and optimize for AI-driven discovery with acti...

Discover the key trends shaping AI search evolution in 2026, including multimodal capabilities, agentic systems, real-time information retrieval, and the shift from traditional SEO to AI-driven visibility strategies.
AI search will evolve in 2026 through multimodal capabilities combining text, images, and video; agentic autonomous systems making decisions independently; real-time web integration for current information; and a fundamental shift from keyword rankings to AI citations and brand visibility across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini.
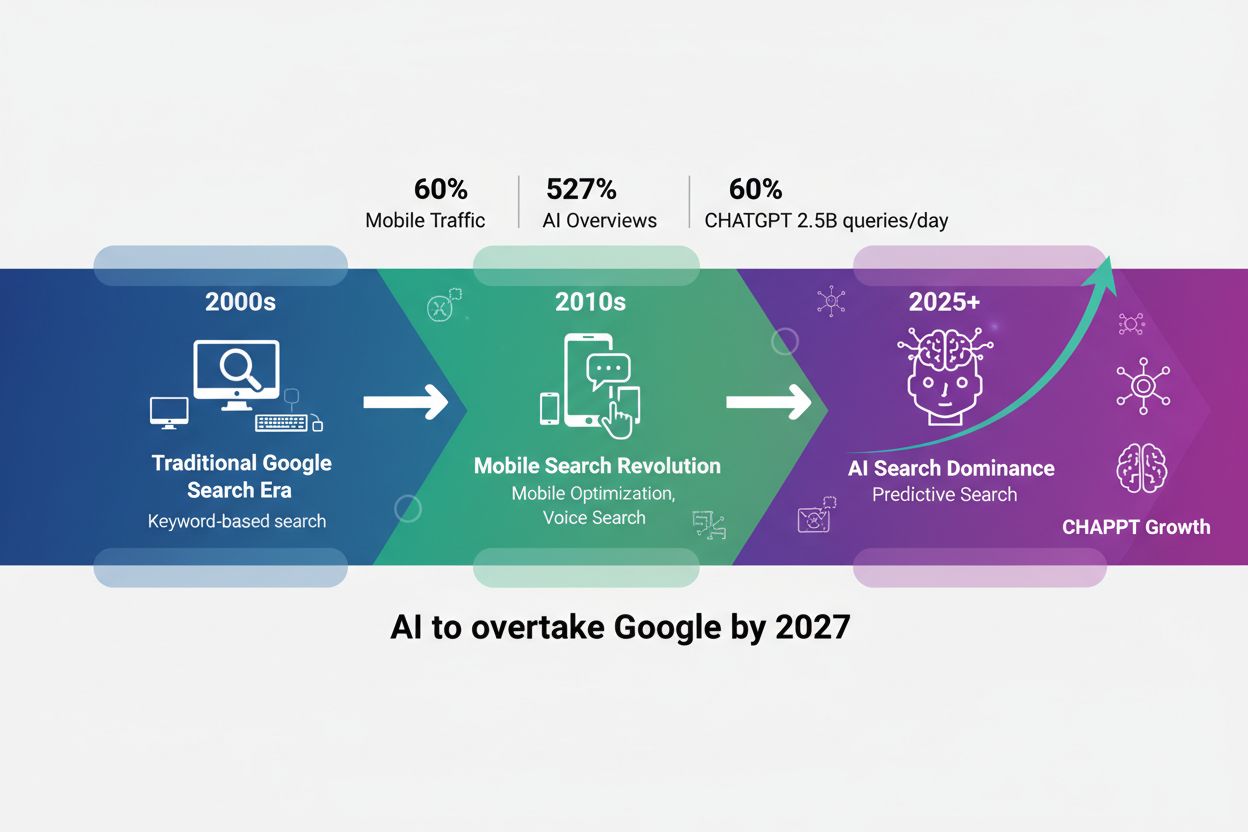
AI search is fundamentally transforming how users discover information, moving away from traditional keyword-based queries to conversational, context-rich interactions. In 2026, AI-powered assistants and large language models (LLMs) will handle approximately 25% of global search queries, according to Gartner predictions, replacing many traditional search interactions that once drove traffic to websites. This represents a seismic shift in the digital landscape where users no longer start every question on Google—they ask ChatGPT, research with Perplexity, or use Gemini’s AI mode. The average search query has evolved from 6 words to 25+ words as users adopt conversational AI tools, fundamentally changing how brands need to optimize their content and visibility strategies.
The traditional search experience operated like a game of chess—discrete, predictable, and keyword-focused. AI search, by contrast, operates like a jazz concert—continuous, fluid, and reasoning-driven. Instead of matching keywords to an index, AI uses query fan-out, which involves breaking queries into components, analyzing multiple sources, and delivering a single, comprehensive answer based on consistent patterns. This shift means that the traditional marketing funnel is shrinking dramatically, with AI search capable of moving directly from user intent to conversion in minutes, resulting in three- to eight-times higher conversion rates from traffic originating in AI search compared to traditional search channels.
Multimodal AI represents one of the most significant technological advances shaping 2026, enabling systems to process and synthesize information from multiple input types simultaneously. Rather than being limited to text alone, 2026 is the year AI goes multimodal, allowing models to work with whatever form of reference content users provide—text, images, video, audio, and structured data. This capability enables AI systems to observe your screen, process spoken commands, read text, and guide users in real time with unprecedented accuracy and context awareness.
| AI Capability | 2025 Status | 2026 Evolution | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Text Processing | Mature | Enhanced reasoning | Better answer synthesis |
| Image Recognition | Advanced | Multimodal integration | Visual search understanding |
| Video Analysis | Emerging | Real-time processing | Dynamic content generation |
| Audio Processing | Limited | Full integration | Voice-first interactions |
| Cross-Modal Reasoning | Experimental | Production-ready | Comprehensive context understanding |
Multimodal AI is already transforming industries with practical applications. In healthcare, multimodal systems can detect cancer by combining image scans with patient data for faster and more reliable diagnostic results. In fraud detection, emerging tools use multimodal AI to identify suspicious transactions by analyzing voice patterns, behavioral data, and payment histories simultaneously. For customer service, multimodal chatbots can observe your screen, process spoken commands, and read text to guide you in real time, creating seamless support experiences that understand context across multiple communication channels.
Agentic AI systems represent a fundamental evolution in how AI operates, moving from reactive tools that respond to queries to proactive systems that learn, adapt, and make decisions based on experience. These systems can operate within defined boundaries while continuously improving through feedback loops. Autonomous agents operate without constant human oversight, analyzing information, making decisions, and taking action independently. This distinction is critical for 2026, as businesses increasingly deploy AI agents to handle complex workflows, customer interactions, and operational decisions.
The autonomous vehicle market exemplifies this evolution—in cities where autonomous vehicles operate, users can hail fully self-driving cars for everyday trips, proving that autonomous technology is no longer theoretical. This market is expected to reach $62 billion by 2026, demonstrating the commercial viability of autonomous systems. Beyond transportation, AI agents are shifting from answering questions to completing transactions, with systems like ChatGPT evolving to book tables, make appointments, and complete purchases directly. This means that even transactional journeys may no longer end on your website, requiring brands to become “callable” through APIs and integrations—a capability that will be as critical in 2026 as being crawlable was in 2010.
AI search engines in 2026 will feature significantly enhanced real-time web integration, moving beyond static training data to continuously access current information. Perplexity and similar platforms combine natural language processing with real-time web searching capabilities, enabling them to provide answers grounded in the latest information available online. This real-time integration means that AI systems can move directly from intent to conversion in minutes, dramatically accelerating the customer journey compared to traditional search where users browse multiple pages before deciding.
The integration of real-time data fundamentally changes content strategy. Rather than optimizing for evergreen content alone, brands must ensure their most current information—product updates, pricing changes, availability, and news—is structured and accessible for AI systems to retrieve and cite. AI search can answer questions before users click through to websites, creating what’s known as zero-click search in a new form. Instead of snippets appearing in Google, answers surface directly inside ChatGPT or Gemini, meaning your brand’s visibility depends on being cited by AI systems rather than driving direct traffic.
The fundamental metric for success in AI search is shifting from keyword rankings to AI citations and brand mentions. In traditional SEO, success meant ranking high on Google’s first page. In 2026, citation is the new rank, with brands needing to optimize content for retrievability rather than rankability. This represents a complete paradigm shift in how marketers measure and pursue visibility.
Visibility in AI search depends on two critical ingredients: strong content that models can rely on, and strong brand presence that models recognize. AI citations occur when the model attributes information to your content and links to your site, typically when the search feature is enabled. AI mentions occur when your brand name appears in the response without a link, still providing valuable visibility and authority signals. Tracking these metrics requires new tools and approaches—marketers must monitor LLM visibility scores, AI citation counts, share of voice, and sentiment rather than relying solely on traditional SEO metrics like impressions and click-through rates.
Credibility has become a huge currency in AI search, just as it was in traditional SEO, but with amplified importance. Pages with robust schema markup tend to earn higher citation rates in AI Overviews, reinforcing the importance of structured data. Off-page signals determine whether an LLM sees your brand as authoritative enough to include in its answers. It’s better to be mentioned on CNN without a link than to have a link from a site considered less important, as high-authority publications and trusted industry sources carry far more weight in AI systems’ decision-making processes.
2026 marks the emergence of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) as the successor to traditional SEO, though the industry is still debating terminology with competing frameworks like AEO (Answer Engine Optimization), AIO (AI Optimization), and LEO (LLM Engine Optimization). GEO is seen as a more future-proof concept because it encompasses not just text, but also image and video results, involving publishing deeply researched, authoritative content that can be used as building blocks for AI-synthesized summaries.
The three pillars of optimization—on-page, off-page, and technical—still apply in 2026, but the tactics within them are shifting fundamentally. On-page optimization now requires semantic chunking, which means writing self-contained paragraphs that give an LLM enough information to surface your answer confidently. Rather than writing generic statements, content must be fully contextualized with specific details and examples. High-performing formats include comparison pages, listicles, help center articles, highly specific use-case or persona pages, and detailed FAQs—all formats that align well with the specificity of AI prompts.
Off-page optimization is becoming increasingly important, with mentions now carrying equal or greater weight than backlinks. While backlinks tell search engines “this page is worth visiting,” mentions tell LLMs “this brand or page is trusted and relevant in this context.” These citations might come from top 10 tools articles, in-depth reviews on respected publications, industry reports using your product as an example, or thought-leadership pieces where experts reference your brand. Technical optimization remains essential, with fast, accessible, and well-structured pages still critical. Clean, crawlable HTML with proper semantic markup, strong performance and accessibility, and comprehensive schema markup all help both users and AI systems understand and trust your content.
Search is becoming increasingly action-oriented in 2026, with new types of intents emerging that don’t require website visits. Generative intents (e.g., “create an image”) and no-intent interactions (e.g., “thanks”) now make up almost half of all LLM interactions. As AI systems start booking tables, making appointments, and completing purchases, the traditional website visit is no longer guaranteed as the endpoint of the customer journey. This requires brands to think beyond their website as the primary destination and instead become trusted data sources that power the new agentic ecosystem.
AI agents like ChatGPT are shifting from answering questions to completing transactions, fundamentally changing how businesses need to structure their digital presence. Being “callable” through APIs and integrations becomes as critical as being crawlable was in 2010. This means brands must ensure their data is accessible not just to human visitors, but to AI systems that retrieve, interpret, and act on that data. Websites are evolving from sales destinations to data and information repositories built for both human visitors and AI systems.
Content in 2026 must be equally diverse in format as AI systems are in processing capability. Since AI engines draw from text, images, videos, and charts, your content must be equally rich across these modalities. Just as important, it must be machine-readable so AI systems can synthesize and reason with it. This requires prioritizing an entity-based SEO strategy to build topical authority and using comprehensive schema markup to help search engines understand your brand and content context.
Semantic chunking through design means structuring pages so each section stands on its own, with related ideas grouped together and layouts that naturally produce context-rich “answer units.” This approach ensures that when AI systems extract information from your pages, they get sufficient context to use your answer confidently. The goal is to create content that works seamlessly for both human readers seeking comprehensive information and AI systems seeking structured, extractable data that can be synthesized into authoritative answers.
To compete in 2026 and beyond, brands must optimize for visibility across every relevant platform, not just Google. This requires building strong content and experience flywheels, with answer engine optimization (AEO) and generative engine optimization (GEO) becoming critical priorities. The biggest challenge isn’t just creating content—it’s creating a connected experience where AI systems can access all your brand data and deliver complete, contextually accurate results based on user intent.
Adopting AI isn’t optional—it’s foundational for maintaining visibility and relevance. Most marketing systems weren’t designed to operate in an AI-first world, with disconnected tools and data silos making orchestration difficult. To succeed in 2026, brands need integrated, cross-functional, omnichannel systems that connect data, content, and customer experience. This means strengthening technical SEO foundations for AI retrievability, building localized visibility in AI-driven environments, developing AI-assisted content flywheels, creating consistent data-driven experience flywheels, using AI agents to orchestrate journeys, redefining KPIs for AI-first performance models, and integrating systems and data to power unified marketing infrastructure.
Track how your brand, domain, and content appear in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Stay ahead of the competition with real-time monitoring.

Discover how branded search volume directly correlates with AI visibility. Learn to measure brand signals in LLMs and optimize for AI-driven discovery with acti...

Discover how AI agents reshape search behavior, from conversational queries to zero-click results. Learn the impact on user habits, brand visibility, and search...
Discover how AI search is reshaping SEO. Learn the key differences between AI platforms like ChatGPT and traditional Google search, and how to optimize your con...