
How AI Understands Entities: Technical Deep Dive
Explore how AI systems recognize and process entities in text. Learn about NER models, transformer architectures, and real-world applications of entity understa...

Learn how AI systems identify, extract, and understand relationships between entities in text. Discover entity relationship extraction techniques, NLP methods, and real-world applications.
Entity relationships in AI understanding refer to the semantic connections and associations between identified entities (people, organizations, locations, etc.) in text. AI systems use natural language processing techniques to extract, classify, and understand these relationships, enabling machines to comprehend how different entities interact and relate to one another.
Entity relationships form the foundation of how artificial intelligence systems comprehend and interpret human language. When AI processes text, it doesn’t just identify individual words or entities in isolation; it must understand how these entities connect, interact, and relate to one another. This capability is crucial for AI systems to generate accurate answers, provide meaningful insights, and appear correctly in AI-generated content across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. The ability to extract and understand these relationships enables AI to move beyond simple keyword matching to true semantic understanding of content.
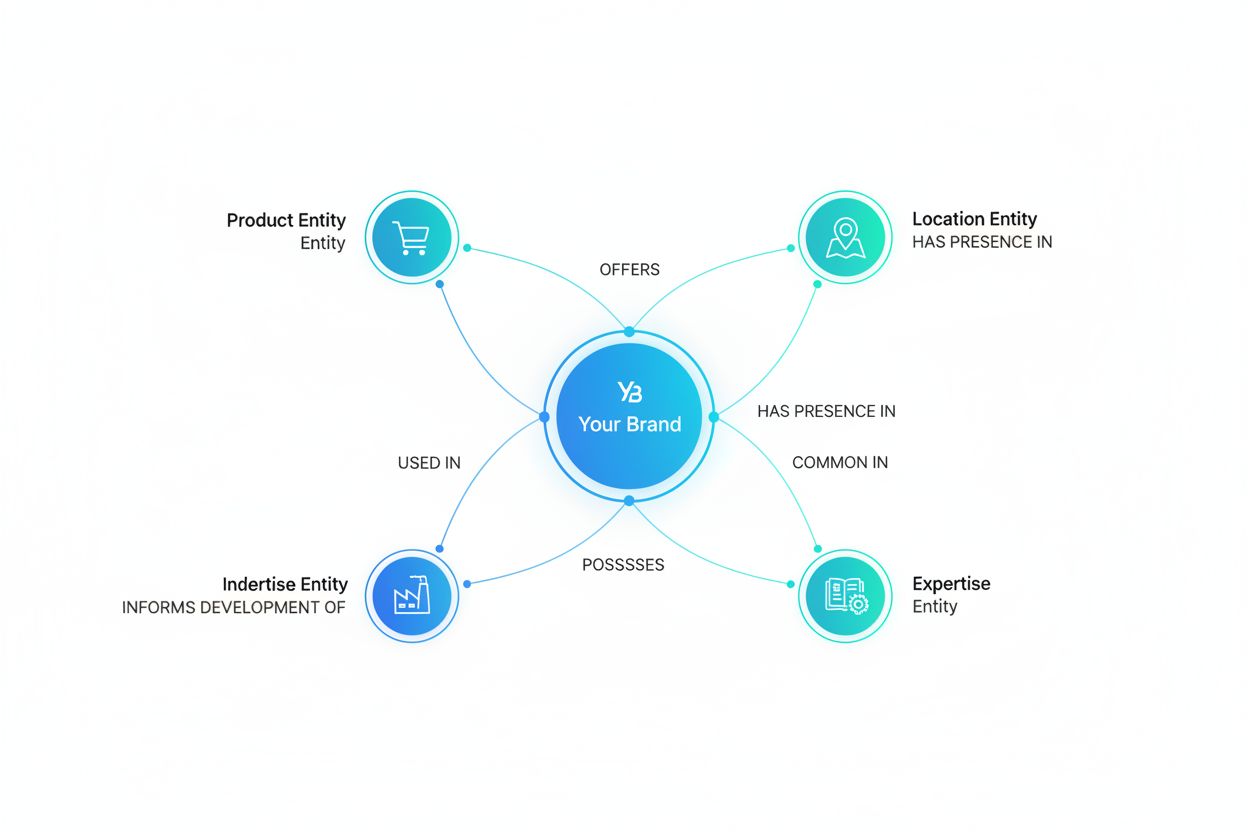
Entity relationships are the semantic connections that exist between two or more identified entities within text. An entity can be a person, organization, location, product, date, or any other distinct concept that an AI system recognizes. A relationship describes how these entities interact or connect with each other. For example, in the sentence “Apple Inc. was founded by Steve Jobs in Cupertino,” the entities are “Apple Inc.,” “Steve Jobs,” and “Cupertino,” while the relationships are “founded_by” (connecting Apple Inc. to Steve Jobs) and “located_in” (connecting Apple Inc. to Cupertino). These relationships carry semantic meaning that helps AI systems understand the context and significance of information, which is essential for accurate representation in AI-generated answers and search results.
Before AI can understand relationships, it must first identify and classify entities within text. This process is called Named Entity Recognition (NER), a fundamental NLP task that forms the first step in relationship extraction. NER systems analyze text and identify specific entities by their type, such as Person, Organization, Location, Product, or Date. Modern AI systems use deep learning approaches, particularly transformer-based models like BERT and GPT, which can recognize entities with high accuracy by analyzing the context in which words appear. These systems are trained on large annotated datasets where entities have been manually labeled, allowing the AI to learn patterns and characteristics that distinguish different entity types. The accuracy of entity identification directly impacts the quality of relationship extraction, as the system cannot understand relationships between entities it fails to recognize.
Relationship extraction is the computational process of identifying and classifying semantic relationships between entities in text. This process typically involves several stages that work together to produce accurate results. First, the text is preprocessed through tokenization, where it’s broken into smaller units like words and sentences. Next, entities are identified using NER techniques. Once entities are located, the system analyzes the context between them to determine what type of relationship exists. Advanced AI models use attention mechanisms to focus on relevant parts of the text that indicate relationships, such as verbs or prepositions that connect entities. The system then classifies the relationship into predefined categories, such as “employed_by,” “located_in,” “founded_by,” or “married_to.” This entire process enables AI systems to build a comprehensive understanding of how information is structured and connected within documents.
| Relationship Extraction Stage | Description | Key Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Text Preprocessing | Breaking text into manageable units | Tokenization, lowercasing, stop word removal |
| Entity Recognition | Identifying and classifying entities | Named Entity Recognition (NER), BERT, transformer models |
| Context Analysis | Examining text between entities | Dependency parsing, attention mechanisms |
| Relationship Classification | Categorizing the type of relationship | Machine learning classifiers, neural networks |
| Output Generation | Producing structured relationship data | Tuple extraction, knowledge graph creation |
Modern AI systems rely heavily on deep learning to understand entity relationships with unprecedented accuracy. Transformer-based models, particularly BERT and its variants, have revolutionized how AI processes language by using self-attention mechanisms that allow the model to consider the relationships between all words in a sentence simultaneously. These models are pre-trained on massive amounts of text data, learning general language patterns before being fine-tuned for specific relationship extraction tasks. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and their variants, such as Bidirectional LSTMs, are also used to capture sequential dependencies in text that indicate relationships between entities. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) represent an emerging approach that models entities and relationships as nodes and edges in a graph, allowing the AI to reason about complex interconnections. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) can also be applied to relationship extraction by treating text as a sequence and using filters to identify relationship patterns. These deep learning approaches achieve significantly higher accuracy than traditional rule-based or statistical methods, enabling AI systems to understand nuanced and complex relationships in diverse contexts.
One of the most advanced techniques in modern NLP is joint entity and relation extraction, which simultaneously identifies entities and their relationships in a single pass through the text. Rather than extracting entities first and then finding relationships between them, joint extraction models process the entire task together, which reduces errors that might accumulate from sequential processing. This approach is particularly effective because it allows the model to use information about potential relationships to improve entity identification, and vice versa. Joint extraction models typically use encoder-decoder architectures where the encoder processes the input text and the decoder generates structured output containing both entities and their relationships. These models achieve superior performance on benchmark datasets like TACRED, which contains over 106,000 examples of entity-relationship pairs from real-world text. The joint approach is especially valuable for AI systems that need to accurately represent information in generated answers, as it ensures consistency between identified entities and their described relationships.
Understanding entity relationships is critical for how AI systems generate answers and appear in AI search engines. When you search for information using ChatGPT, Perplexity, or similar platforms, these systems use entity relationship understanding to:
This is why monitoring how your brand appears in AI answers is essential—AI systems must correctly understand the relationships between your organization, your domain, your products, and other relevant entities to represent you accurately.
Despite significant advances, AI systems still face challenges in understanding entity relationships accurately. Ambiguity is a primary challenge, as the same relationship type can be expressed in many different ways in natural language. For example, “John works at Google” and “Google employs John” express the same relationship but with different sentence structures. Long-range dependencies present another challenge, where the entities involved in a relationship may be separated by many words or even sentences, making it difficult for the AI to recognize the connection. Domain-specific relationships require specialized knowledge, as relationships in medical texts, legal documents, or technical papers may differ significantly from general language patterns. Overlapping entities occur when entity boundaries are unclear or when entities share common words, complicating both entity identification and relationship extraction. Implicit relationships that are not explicitly stated in text but must be inferred from context require deeper semantic understanding. These challenges mean that even state-of-the-art AI systems may occasionally misunderstand or misrepresent entity relationships, which is why continuous monitoring and verification of how your brand appears in AI-generated answers is important.
Knowledge graphs represent a powerful application of entity relationship understanding, where entities and their relationships are organized into structured, interconnected networks. In a knowledge graph, entities are represented as nodes and relationships as edges connecting those nodes. This structure allows AI systems to reason about complex interconnections and make inferences based on relationship chains. For example, if a knowledge graph contains the relationships “Steve Jobs founded Apple” and “Apple is located in Cupertino,” an AI system can infer that “Steve Jobs founded a company located in Cupertino.” Major search engines and AI systems use knowledge graphs to enhance their understanding of information and improve answer quality. Knowledge graphs are built by extracting entity relationships from large volumes of text using the techniques described above. The quality and completeness of a knowledge graph directly impact how accurately AI systems understand and represent information, including how your brand and its relationships are represented in AI-generated answers.
Organizations and AI developers employ several strategies to improve the accuracy of entity relationship extraction. Transfer learning leverages pre-trained models that have learned general language patterns from massive datasets, then fine-tunes them on domain-specific data to improve accuracy for particular types of relationships. Data augmentation artificially expands training datasets by creating variations of existing examples, helping models generalize better to new situations. Ensemble methods combine multiple models to make predictions, reducing the impact of individual model errors. Active learning strategically selects the most informative examples for human annotation, making the labeling process more efficient. Distant supervision uses existing knowledge bases to automatically generate training data, reducing the need for manual annotation. Contextual embeddings like those produced by BERT capture rich semantic information about words and their relationships, improving the model’s ability to understand connections. These approaches collectively enable AI systems to achieve higher accuracy in understanding entity relationships, which translates to more accurate representation of your brand and domain in AI-generated answers.
Discover how your brand, domain, and URLs appear in AI answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Track your visibility and ensure accurate representation in AI-generated content.

Explore how AI systems recognize and process entities in text. Learn about NER models, transformer architectures, and real-world applications of entity understa...

Learn how to build entity visibility in AI search. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity SEO strategies to increase brand presence in C...
Learn how entity optimization helps your brand become recognizable to LLMs. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity strategies for AI vis...