Knowledge Graph
Learn what a knowledge graph is, how search engines use them to understand entity relationships, and why they matter for AI visibility and brand monitoring acro...

Discover what knowledge graphs are, how they work, and why they’re essential for modern data management, AI applications, and business intelligence.
A knowledge graph is a structured network that connects data entities through defined relationships, enabling machines and humans to understand complex information patterns. It matters because it transforms raw data into actionable insights, powers AI applications, improves search accuracy, and enables organizations to break down data silos for better decision-making.
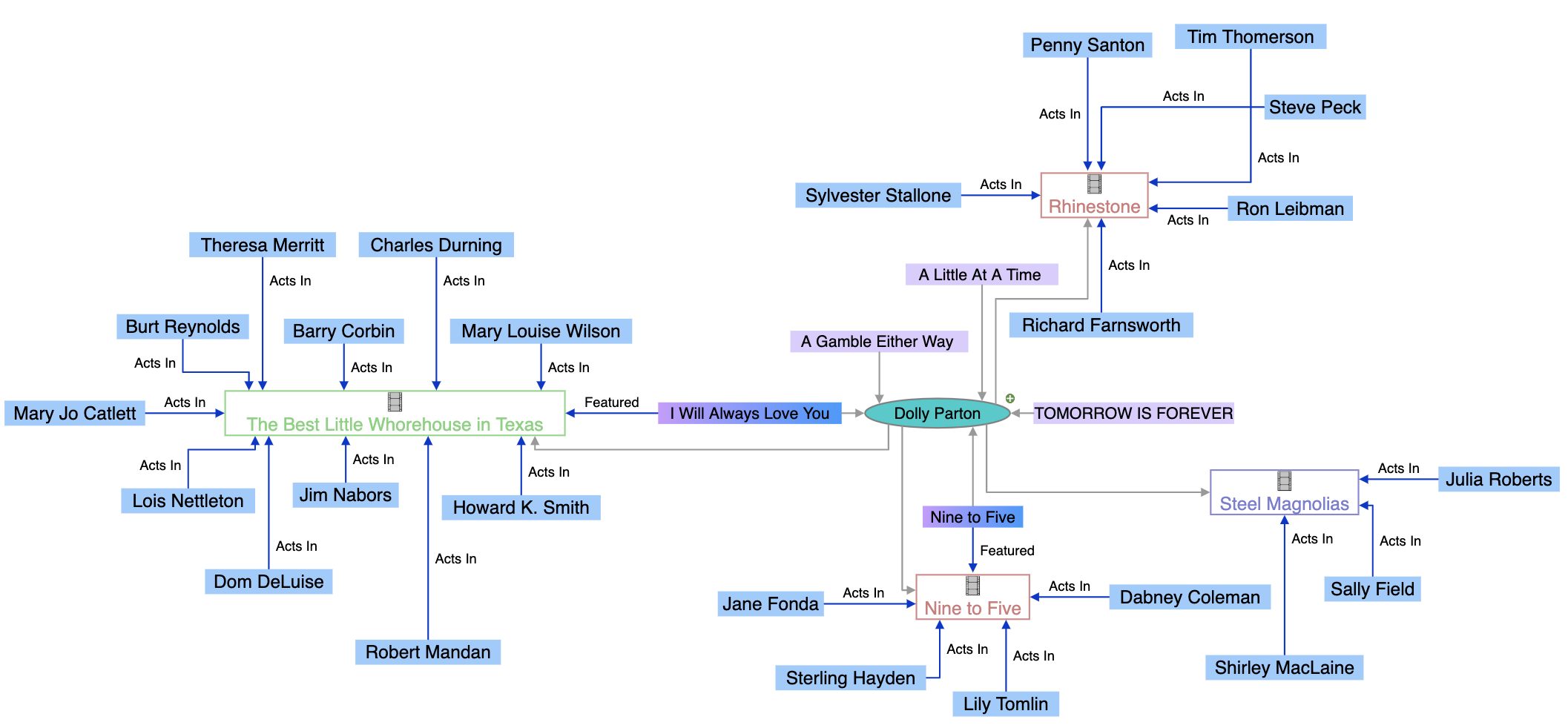
A knowledge graph is a structured, interconnected representation of data entities and their relationships, organized as a network of nodes and edges. Unlike traditional relational databases that rely on rigid, pre-defined structures, knowledge graphs model information as a semantic web where each point (node) represents an entity—such as a person, place, product, or concept—and each connection (edge) illustrates how these entities relate to one another. This fundamental difference enables both humans and machines to interpret, query, and reason about data in ways that were previously impossible with conventional database systems.
The term gained widespread recognition when Google introduced its Knowledge Graph in 2012, revolutionizing search results by providing direct answers and revealing connections between concepts rather than simply listing relevant links. However, knowledge graphs have since evolved far beyond consumer search applications. Today, organizations across industries leverage knowledge graphs to organize complex information, power artificial intelligence systems, and unlock hidden patterns within their data ecosystems. The power of a knowledge graph lies in its ability to capture context, lineage, and meaning across the entire data landscape, making it an indispensable tool for modern enterprises seeking competitive advantage through intelligent data management.
Every knowledge graph consists of four essential components that work together to create a comprehensive, queryable information system:
| Component | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Entities (Nodes) | Objects or concepts being described with unique identifiers | “Albert Einstein”, “Apple Inc.”, “New York City” |
| Relationships (Edges) | Connections between nodes showing how entities interact | “Albert Einstein invented the theory of relativity” |
| Attributes (Properties) | Characteristics that describe nodes and provide context | Birthdate: March 14, 1879; Location: Berlin, Germany |
| Ontologies & Schemas | Formal definitions and rules governing entity types and relationships | RDF Schema (RDFS), Web Ontology Language (OWL), Schema.org |
Entities form the foundation of any knowledge graph, representing real-world objects in a structured and organized manner. Each entity has a unique identifier and can possess multiple properties and relationships with other entities. Relationships, also called edges, are the connections that bind entities together, expressing how they interact and relate. These relationships can be directed (flowing from one entity to another, like “John works at Google”) or undirected (mutual connections, like “John and Mary are friends”). Beyond simple associations, relationships can represent hierarchical structures, causal connections, sequential dependencies, or network-based interactions.
Attributes or properties provide additional descriptive information about entities, helping distinguish them from similar entities in the network. These can range from simple characteristics like age or location to complex, domain-specific properties such as medical conditions, financial metrics, or technical specifications. Finally, ontologies and schemas establish the formal framework that governs how entities, relationships, and attributes are defined and used. Popular ontologies include RDF Schema (RDFS) for basic hierarchies, the Web Ontology Language (OWL) for complex reasoning, and Schema.org for standardized web data representation. These components work in concert to create a flexible, extensible system capable of representing knowledge across virtually any domain.
Knowledge graphs operate by creating a semantic layer across an organization’s data ecosystem, transforming disparate data sources into a unified, interconnected knowledge network. When data is ingested into a knowledge graph, machine learning algorithms powered by natural language processing (NLP) perform a process called semantic enrichment. This process identifies individual objects within the data and automatically understands the relationships between different objects, even when they come from sources with different structural characteristics. The semantic layer is particularly powerful because it can distinguish words with multiple meanings—for example, understanding that “Apple” in one context refers to the technology company while in another context refers to the fruit.
Once the knowledge graph is constructed, it enables sophisticated query answering and search systems to retrieve comprehensive answers to complex questions. Rather than requiring exact keyword matches, semantic search systems can understand user intent and return related information even when specific terms aren’t explicitly used. This contextual understanding is achieved through the graph’s ability to model relationships and dependencies explicitly. The data integration efforts surrounding knowledge graphs also generate new knowledge by establishing connections between previously unrelated data points, revealing insights that might not have been apparent in isolated datasets. For organizations, this means that knowledge graphs can eliminate manual data collection and integration work, accelerating business decision-making and enabling self-service analytics where business users can directly query the graph without IT support.
Knowledge graphs have become increasingly crucial for modern organizations for several compelling reasons. Faster decision-making is one of the most immediate benefits—knowledge graphs provide a 360-degree view of data entities and their relationships, allowing analysts to quickly identify patterns, connections, and insights that would take significantly longer to discover through traditional analysis methods. This comprehensive perspective enables organizations to make informed decisions based on complete information rather than fragmented data views.
Improved customer experience represents another critical advantage. By connecting customer data across various touchpoints—including purchase history, support interactions, browsing behavior, and demographic information—organizations can create detailed customer profiles that enable personalized and relevant experiences. This unified view supports targeted marketing, product recommendations, and proactive customer service. Efficient data management is achieved through knowledge graphs’ ability to link and harmonize data from diverse sources, breaking down organizational silos that typically prevent effective data sharing and collaboration. By embracing best practices in data preparation and harnessing the semantic power of knowledge graphs, organizations unlock a significant competitive edge.
Empowering business users through self-service capabilities democratizes data access across the organization. Rather than relying on IT departments to answer every data question, business users can directly interact with and query knowledge graphs using intuitive visualization tools, accelerating insight generation and reducing bottlenecks. Accelerated AI and machine learning initiatives benefit tremendously from knowledge graphs’ structured, semantic nature. The interconnected data provides ideal training material for AI systems, enabling them to infer intricate patterns, trends, and outcomes while reducing the time and cost invested in model development. Knowledge graphs also support advanced applications like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), where AI systems can draw complex relationships from large datasets to reason more like humans and provide more accurate, contextually relevant responses.
Knowledge graphs have moved beyond theoretical concepts to deliver tangible value across diverse sectors. In healthcare and life sciences, medical research networks and clinical decision support tools use knowledge graphs to connect symptoms, treatments, outcomes, and medical literature, helping clinicians and researchers uncover insights that improve patient care and accelerate drug discovery. Financial services institutions leverage knowledge graphs for know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering initiatives, mapping relationships between people, accounts, and transactions to detect suspicious activities and prevent financial crime. Retail and e-commerce companies deploy knowledge graphs to power recommendation engines and up-sell/cross-sell strategies, analyzing purchase behavior and demographic trends to suggest products customers are most likely to buy.
Entertainment platforms like Netflix, Spotify, and Amazon use knowledge graphs to build sophisticated recommendation engines that analyze user engagement patterns and content relationships to suggest movies, music, and products tailored to individual preferences. Supply chain optimization represents another powerful application, where knowledge graphs model complex supplier relationships, logistics networks, and inventory flows, enabling real-time detection of bottlenecks and risk mitigation. Regulatory compliance and governance benefit from knowledge graphs’ ability to automatically track data lineage, map data entities to systems and policies, and demonstrate compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. For example, a knowledge graph can instantly show all locations where personally identifiable information (PII) is stored, which applications access it, and which privacy policies apply—critical capabilities for modern data governance.
While knowledge graphs offer substantial benefits, organizations must thoughtfully address several challenges to implement them successfully. Data quality and curation remain ongoing concerns, as the accuracy and completeness of the knowledge graph directly impact the quality of insights it produces. Organizations must establish processes for validating data, resolving inconsistencies, and maintaining data freshness as new information becomes available. Scalability and maintenance present technical challenges, particularly as knowledge graphs grow to encompass millions or billions of entities and relationships. Ensuring that query performance remains acceptable and that the system can handle increasing data volumes requires careful architectural planning and infrastructure investment.
Entity resolution—the process of identifying when different data representations refer to the same real-world entity—is a complex problem that can significantly impact knowledge graph quality. Privacy and security considerations become increasingly important when knowledge graphs contain sensitive or personal data, requiring robust access controls, encryption, and compliance mechanisms. Bias in knowledge graphs can perpetuate or amplify existing biases in source data, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in AI applications powered by the graph. Organizations must implement careful monitoring and governance practices to identify and mitigate bias. Despite these challenges, the strategic value of knowledge graphs makes them worth the investment for organizations serious about leveraging data as a competitive asset.
Knowledge graphs represent a fundamental shift in how organizations manage, govern, and extract value from their data. By transforming static data inventories into living, interconnected knowledge networks, they enable smarter discovery, robust governance, and AI-ready data ecosystems. As artificial intelligence continues to advance and organizations accumulate ever-larger volumes of data, the importance of knowledge graphs will only increase. They provide the contextual foundation required for advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI explainability—enabling organizations to uncover hidden patterns, automate reasoning, and support decision-making at scale. For any organization looking to improve AI capabilities, enhance customer experiences, or gain competitive advantage through better data utilization, deploying knowledge graph solutions should be a strategic priority in the digital transformation roadmap.
Just as knowledge graphs organize information intelligently, our AI monitoring platform tracks how your brand appears across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Ensure your brand visibility in the AI-driven future.

Learn what a knowledge graph is, how search engines use them to understand entity relationships, and why they matter for AI visibility and brand monitoring acro...

Community discussion explaining Knowledge Graphs and their importance for AI search visibility. Experts share how entities and relationships affect AI citations...
Learn what a graph is in data visualization. Discover how graphs display relationships between data using nodes and edges, and why they're essential for underst...