Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Learn what Natural Language Processing (NLP) is, how it works, and its critical role in AI systems. Explore NLP techniques, applications, and challenges in AI m...

Learn how natural language understanding works in AI search engines. Discover how NLU enables ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI systems to understand user intent, context, and meaning beyond keyword matching.
Natural language understanding (NLU) is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables computers to comprehend human language by analyzing semantic and syntactic meaning, allowing AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity to understand user intent and context rather than just matching keywords.
Natural language understanding (NLU) is a specialized subset of artificial intelligence that uses semantic and syntactic analysis to enable computers to comprehend human-language inputs in a way that mirrors human cognition. Unlike traditional keyword-based search systems that simply match words, NLU aims to holistically comprehend intent, meaning, and context. This fundamental capability is what allows modern AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and similar AI answer generators to understand what users truly want to know, rather than just processing the literal words they type or speak. The technology has become increasingly important as organizations and users rely on AI systems to extract insights from vast amounts of unstructured data, including spoken language, written documents, and complex queries that don’t fit neatly into predefined categories.
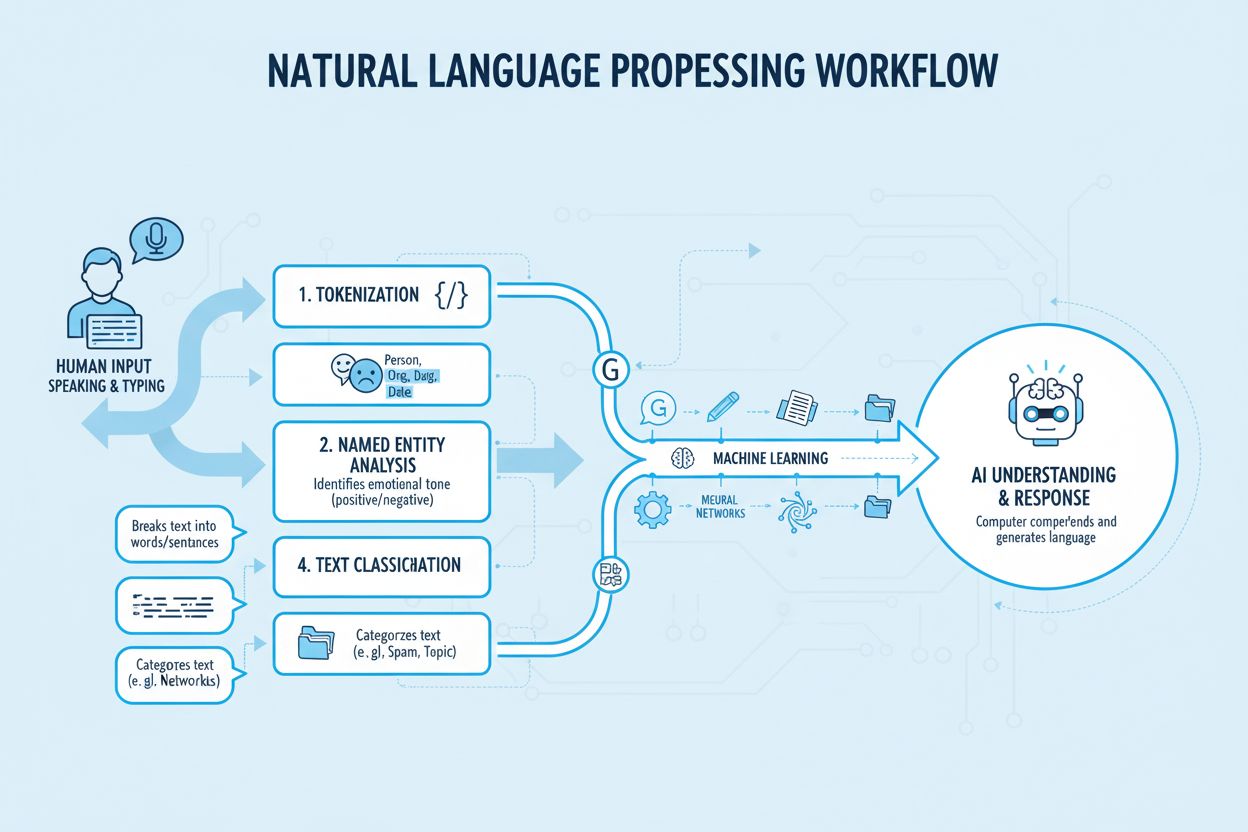
It’s important to understand the distinction between natural language understanding (NLU) and the broader field of natural language processing (NLP). NLP is the overarching discipline that encompasses all computational approaches to human language, including tasks like syntax analysis, word definitions, and parts of speech identification. NLU, by contrast, is a specialized subset of NLP that focuses specifically on comprehending the meaning and intent behind language. While NLP handles the technical mapping of linguistic elements, NLU goes deeper to understand what the user actually wants to accomplish. For example, NLP might identify that a sentence contains a verb and an object, while NLU would understand that the user is asking for a recommendation rather than just seeking factual information. This distinction is crucial because it explains why modern AI systems can engage in seemingly natural conversations—they’re not just processing words, they’re understanding the underlying intent and context of what users are communicating.
NLU systems operate through several interconnected mechanisms that work together to transform unstructured language into actionable understanding. The primary mechanisms include tokenization and embedding, named entity recognition (NER), and intent recognition. Tokenization breaks down unstructured text into smaller, analyzable segments called tokens, which are then converted into numerical representations through embedding algorithms. These embeddings are plotted onto a three-dimensional vector space where words with similar meanings are positioned close to each other, allowing the system to understand semantic relationships. Named entity recognition identifies and classifies real-world objects in text data—both physical entities like people and places, and abstract entities like dates and monetary amounts. Intent recognition is perhaps the most critical component for AI search applications, as it determines what the user actually wants to accomplish. For instance, when someone searches “best restaurants near me,” intent recognition tells the AI system that the user isn’t looking for a list of restaurants in general, but specifically wants recommendations for dining options in their immediate geographic location.
| NLU Mechanism | Function | Application in AI Search |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenization & Embedding | Converts text into numerical vectors representing semantic meaning | Enables AI to understand relationships between words and concepts |
| Named Entity Recognition (NER) | Identifies and classifies entities like companies, people, dates, and metrics | Helps AI extract key information from user queries and documents |
| Intent Recognition | Determines what the user wants to accomplish | Allows AI search to deliver results matching user goals, not just keywords |
| Syntactic Analysis | Analyzes sentence structure and grammar | Helps AI understand how words relate to each other in context |
| Semantic Analysis | Processes the meaning of words and phrases | Enables AI to understand nuance, context, and implied meaning |
Contemporary NLU models are typically trained using a combination of supervised and unsupervised learning techniques. Supervised learning involves feeding algorithms labeled training data that explicitly guides the system to understand linguistic nuances—for example, teaching the system that the word “mean” has different meanings in statistical contexts versus personality assessments. Unsupervised learning, by contrast, exposes algorithms to massive unlabeled datasets and allows them to discover underlying patterns and relationships independently. Modern NLU systems predominantly rely on transformer-based models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) because these architectures excel at capturing dependencies between tokens—the long-range relationships between distant words in a sequence. This capability is essential for maintaining contextual understanding across lengthy input sequences, which is why ChatGPT and similar systems can understand complex, multi-sentence queries and maintain context throughout conversations. The transformer architecture uses an attention mechanism that allows the model to focus on the most relevant parts of the input, similar to how humans naturally focus on key information when reading or listening.
Intent recognition represents one of the most sophisticated applications of NLU in AI search systems. Search engines use intent recognition to deliver results that are relevant not only in factual terms but that actually address what the user wants to know. Consider a practical example: when someone searches “chicken tikka masala,” they might be looking for a recipe to cook at home, or they might be searching for “chicken tikka masala near me,” which indicates they want to find a restaurant serving this dish. Without intent recognition, an AI system would return the same results for both queries. With proper intent recognition, the system understands the contextual difference and delivers appropriately targeted results. This capability extends to more complex scenarios in AI answer generators, where users might ask nuanced questions that require understanding implicit assumptions and context. For instance, a query about “best investment strategies for volatile markets” requires the AI to understand that the user is seeking risk management advice specific to market conditions, not general investment principles. Intent recognition enables AI systems to parse these complex requirements and generate responses that directly address the user’s actual information needs.
The rise of generative AI and its application in consumer chatbots has driven significant commercial investment in NLU technology. Without NLU, interactive chatbots such as ChatGPT would not exist—NLU is fundamentally why generative AI chatbots can hold conversations with users that feel realistic and natural. These systems use NLU to understand not just individual user messages, but the broader context of an ongoing conversation, allowing them to maintain coherent dialogue across multiple exchanges. When a user asks a follow-up question like “Can you explain that differently?” the chatbot uses NLU to understand that “that” refers to the previous explanation, not to something else entirely. This contextual awareness is what makes modern AI assistants feel genuinely conversational rather than mechanical. Additionally, NLU enables these systems to recognize when users are asking for clarification, requesting additional information, or shifting to a new topic entirely. The sophistication of NLU in modern chatbots also allows them to handle ambiguous queries, slang and dialects, complex sentence structures, and subtle nuances in language that would confuse simpler keyword-based systems. This is why users can interact with ChatGPT, Perplexity, and similar platforms using natural, conversational language rather than having to formulate queries in specific technical formats.
NLU technology powers numerous practical applications across different domains and use cases. Sentiment analysis uses NLU to identify mood and emotion in content—researchers can analyze social media posts and user reviews to understand how people feel about a brand or product, with this information then informing product development and marketing strategies. Machine translation leverages NLU to perform automated language translation, enabling real-time communication between speakers of different languages. Customer support chatbots have become increasingly sophisticated through NLU advancements, allowing organizations to deploy AI systems that engage in humanlike conversations with users and handle common service queries before escalating complex issues to human personnel. Speech recognition systems use NLU to convert spoken language into actionable commands—rather than requiring users to press numbered options, callers can simply say “speak to a human” and the system understands and processes the request. Virtual agents and assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri rely heavily on NLU to fulfill user requests by understanding spoken commands in natural language. In the context of AI search engines and answer generators, NLU enables systems to understand complex search queries, retrieve relevant information from vast knowledge bases, and generate coherent, contextually appropriate responses that address the user’s actual information needs.
Human language is inherently nuanced, complex, and full of ambiguities, which makes NLU a demanding machine learning challenge for computer scientists and engineers. Words can have multiple meanings depending on context—the word “bank” refers to a financial institution in one context and the side of a river in another. Sentences can be structured in ways that create ambiguity about what modifies what. Idioms and figurative language don’t translate literally. Different dialects and regional variations use different vocabulary and grammar. Sarcasm and irony require understanding not just what words mean, but what the speaker actually intends to communicate. NLU systems must navigate all of these challenges simultaneously. This is why training NLU models requires enormous amounts of diverse, high-quality training data and sophisticated algorithms. The more comprehensive and diverse the datasets that an NLU system is trained on, the more refined and accurate its performance becomes. Modern NLU systems handle these challenges through a combination of techniques: they learn statistical patterns from massive training datasets, they use knowledge graphs that encode relationships between concepts, and they employ attention mechanisms that allow them to focus on the most relevant contextual information when interpreting ambiguous language.
Semantic search represents a direct application of NLU principles to information retrieval. While traditional keyword-based search matches exact words in queries to words in documents, semantic search uses NLU to understand the contextual meaning and intent behind search queries. This distinction is crucial for AI search engines. A semantic search engine understands that “running shoes,” “sneakers,” “athletic footwear,” and “jogging shoes” are semantically equivalent terms, even though they use different words. It can also understand that a search for “trail maps” near a national park should prioritize results for trails accessible from the user’s current location. Semantic search goes beyond simple keyword matching to comprehend the deeper meaning and relationships between concepts. This is why AI answer generators like ChatGPT and Perplexity can understand complex, conversational queries and return relevant information even when the exact keywords from the query don’t appear in the source material. The integration of NLU with semantic search enables these systems to deliver highly relevant results by understanding not just what words the user typed, but what information the user actually needs.
As NLU technology continues to advance, AI search engines and answer generators are becoming increasingly sophisticated in their ability to understand human language. The development of more powerful large language models (LLMs) with improved training methodologies is expanding the capabilities of NLU systems. These systems are becoming better at understanding context across longer sequences of text, handling more complex and nuanced queries, and generating more accurate and relevant responses. The integration of knowledge graphs—structured databases that encode relationships between entities and concepts—with NLU systems is enabling AI to understand not just the literal meaning of words, but the semantic relationships between different pieces of information. This combination allows AI search engines to provide more comprehensive and contextually appropriate answers. Additionally, the development of multimodal NLU systems that can process and understand text, images, and other data types simultaneously is expanding the scope of what AI systems can comprehend and communicate. As organizations increasingly rely on AI search engines and answer generators for information retrieval and decision-making, the importance of robust NLU technology continues to grow, driving ongoing research and development in this critical field.
Track how your brand, domain, and content appear in AI-generated answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Ensure your brand visibility in the age of AI.

Learn what Natural Language Processing (NLP) is, how it works, and its critical role in AI systems. Explore NLP techniques, applications, and challenges in AI m...

Community discussion on Natural Language Understanding in AI search. Experts explain how NLU affects content optimization and the debate over writing style.

Learn how semantic search uses AI to understand user intent and context. Discover how it differs from keyword search and why it's essential for modern AI system...