Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Learn what Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is, how it works, and why it's essential for accurate AI responses. Explore RAG architecture, benefits, and ente...

Learn what RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is in AI search. Discover how RAG improves accuracy, reduces hallucinations, and powers ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that combines large language models with external data retrieval to generate more accurate, current, and grounded responses. RAG improves LLM accuracy by an average of 39.7% by providing real-time information from authoritative sources, reducing hallucinations and ensuring responses are based on verified facts rather than training data alone.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that combines the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) with external data retrieval systems to generate more accurate, current, and contextually relevant responses. Rather than relying solely on information embedded during model training, RAG systems dynamically fetch relevant information from authoritative knowledge bases, databases, or web sources before generating answers. This approach fundamentally transforms how AI search systems like Perplexity, ChatGPT Search, Google AI Overviews, and Claude deliver information to users. The significance of RAG lies in its ability to address critical limitations of traditional LLMs: outdated training data, hallucinations (generating false information), and lack of source attribution. By grounding AI responses in real-time, verified information, RAG creates a more trustworthy and reliable AI search experience that users can depend on for accurate answers.
The development of RAG represents a major shift in how generative AI systems operate. Traditional large language models are trained on vast amounts of historical data with a fixed knowledge cutoff date, meaning they cannot access current information or specialized domain knowledge. This limitation created a critical problem: users asking about recent events, company-specific policies, or proprietary information would receive outdated or generic responses. The RAG market has experienced explosive growth in response to this need, with projections showing the market expanding from USD 1.96 billion in 2025 to USD 40.34 billion by 2035, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35.31%. This rapid expansion reflects enterprise recognition that RAG technology is essential for deploying reliable AI systems. The framework emerged as a practical solution to enhance LLM capabilities without requiring expensive model retraining, making it accessible to organizations of all sizes seeking to implement AI-powered search and conversational AI applications.
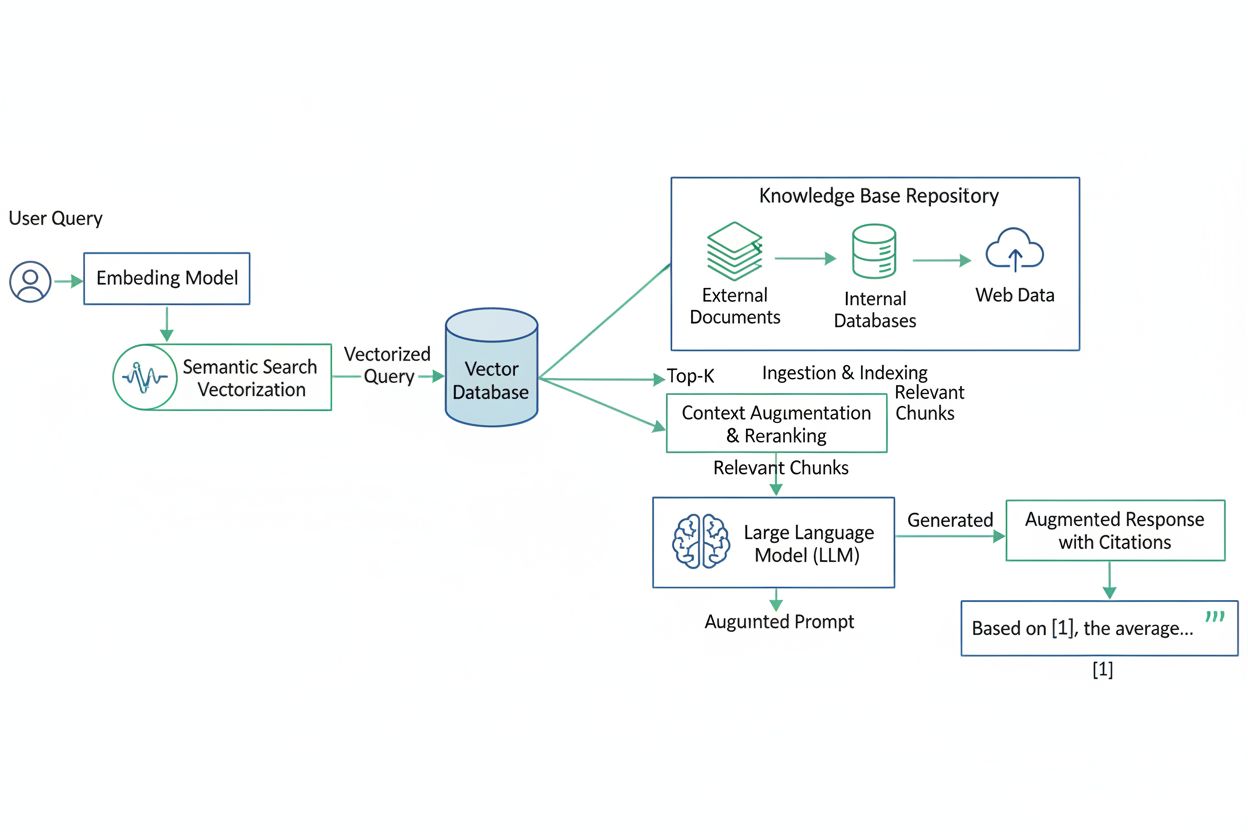
RAG systems operate through a multi-stage pipeline that seamlessly integrates information retrieval with language generation. The process begins with query understanding, where a user’s question is analyzed to determine intent and context. Next, the system performs retrieval and pre-processing, leveraging powerful search algorithms to query external data sources such as web pages, knowledge bases, databases, and document repositories. The retrieved information undergoes preprocessing including tokenization, stemming, and removal of stop words to optimize relevance. The system then converts both the user query and retrieved documents into vector embeddings—numerical representations that capture semantic meaning—using embedding language models. These embeddings are stored in vector databases, enabling semantic search that matches concepts rather than just keywords. Once relevant information is identified, the system performs prompt augmentation, combining the user’s original query with the most relevant retrieved data to create an enriched prompt. Finally, the LLM generates a response grounded in this verified information, often including source citations that allow users to verify claims independently. This structured approach ensures that AI search results are both accurate and traceable.
| Aspect | RAG-Powered AI Search | Traditional LLM Search | Keyword-Based Search |
|---|---|---|---|
| Information Source | Real-time external data + training data | Training data only (static cutoff) | Indexed keywords only |
| Accuracy Rate | 87-95% (with proper implementation) | 60-70% (prone to hallucinations) | 50-65% (limited context) |
| Hallucination Rate | 4-10% (significantly reduced) | 20-30% (common issue) | N/A (no generation) |
| Current Information | Yes (live data access) | No (outdated training data) | Yes (if indexed) |
| Source Attribution | Yes (citations provided) | No (no source tracking) | Yes (document links) |
| Response Time | 2-5 seconds | 1-3 seconds | <1 second |
| Relevance to Query | High (semantic understanding) | Medium (pattern matching) | Low (exact matching) |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate (retrieval + generation) | Low (generation only) | Very Low (retrieval only) |
| Scalability | High (external data sources) | Limited (model size constraint) | High (index-based) |
RAG technology has become the backbone of modern AI search systems, fundamentally changing how information is discovered and presented. When AI systems like Perplexity and ChatGPT Search use RAG, they actively retrieve and cite external sources, making brand visibility in AI search critically important. Organizations whose content appears in RAG-powered AI search results gain significant advantages: their information reaches users through AI-generated summaries, they receive proper attribution and source citations, and they build authority in their domain. However, this also creates new challenges—companies must ensure their content is discoverable, properly formatted for retrieval, and optimized for semantic search. The accuracy improvements delivered by RAG are substantial: research shows that RAG improves LLM accuracy by an average of 39.7%, with some implementations achieving accuracy rates as high as 94-95% when combined with AI agents. Additionally, RAG reduces hallucination rates by over 40% compared to traditional LLMs, making AI-generated answers significantly more reliable. For businesses, this means that when their content is retrieved by RAG systems, users receive more trustworthy information, increasing confidence in both the AI system and the cited source.
Different AI search platforms implement RAG with varying sophistication levels. Perplexity uses a meticulously implemented RAG pipeline that combines real-time web search with semantic understanding, allowing it to provide current answers with source citations. ChatGPT Search (available in ChatGPT Plus) similarly leverages RAG to access real-time information from the web, grounding responses in current sources. Google AI Overviews integrate RAG principles into Google Search, retrieving relevant passages from indexed web pages to generate AI-powered summaries. Claude by Anthropic supports RAG through its ability to process long context windows and reference external documents provided by users or applications. Each platform uses vector embeddings and semantic ranking to identify the most relevant information, but they differ in data sources (web-indexed vs. proprietary databases), retrieval speed, and citation mechanisms. Understanding these platform differences is crucial for content optimization—organizations need to ensure their content is structured for easy retrieval, uses clear language that matches user intent, and provides authoritative information that RAG systems will prioritize.
The adoption of RAG systems is reshaping enterprise AI strategy. Organizations implementing RAG report significant improvements in AI application reliability, reduced support costs from fewer incorrect answers, and increased user trust in AI-powered systems. The RAG market growth reflects this business value: enterprises are investing heavily in RAG infrastructure to power customer service chatbots, internal knowledge systems, research assistants, and decision support tools. For companies concerned with brand visibility in AI search, RAG creates both opportunities and requirements. When AI systems retrieve and cite your content, you gain credibility and reach new audiences through AI-generated summaries. However, this visibility depends on your content being discoverable, properly structured, and authoritative. The 39.7% accuracy improvement that RAG delivers means that when your information is retrieved, it’s presented in a more trustworthy context, increasing the likelihood that users will engage with your brand. Additionally, the 40% reduction in hallucinations means fewer instances of AI systems generating false information that could damage your brand reputation. Organizations can leverage prompt monitoring services to track when their content appears in AI search results, understand how it’s being cited, and optimize their content strategy for better visibility in RAG-powered systems.
RAG systems continue to evolve with emerging trends shaping the next generation of AI search. Agentic RAG represents a significant advancement, where LLMs intelligently decompose complex queries into multiple focused subqueries, execute them in parallel, and synthesize results with higher accuracy. This approach enables multi-source data access, allowing RAG systems to query diverse knowledge sources—SharePoint documents, databases, web pages, APIs—simultaneously while maintaining security and governance controls. Multimodal RAG is expanding beyond text to include images, audio, and video, enabling richer information retrieval and more comprehensive AI-generated answers. Real-time RAG systems are reducing latency to meet user expectations for instant responses, with some implementations achieving 2-5 second response times while maintaining accuracy. Domain-specific RAG implementations are becoming more sophisticated, with specialized systems for healthcare, finance, legal, and technical domains that understand domain-specific terminology and context. The integration of RAG with AI agents is particularly promising, with research showing that agents combined with RAG can achieve accuracy rates of 95% with GPT-4, representing a significant leap forward. As these technologies mature, organizations will need to continuously optimize their content for discoverability in increasingly sophisticated RAG systems, making AI search monitoring and content optimization essential components of digital strategy.
+++
Track how your content appears in AI-powered search results across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude. Ensure your brand gets proper attribution when AI systems cite your information.

Learn what Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is, how it works, and why it's essential for accurate AI responses. Explore RAG architecture, benefits, and ente...

Learn how RAG combines LLMs with external data sources to generate accurate AI responses. Understand the five-stage process, components, and why it matters for ...

Community discussion explaining RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) and its implications for AI search optimization. Real insights on how RAG changes content s...