AI Search Engine
Learn what AI search engines are, how they differ from traditional search, and their impact on brand visibility. Explore platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, Goo...

Learn how real-time search in AI works, its benefits for users and businesses, and how it differs from traditional search engines and static AI models.
Real-time search in AI is a capability that allows artificial intelligence systems to access and retrieve current information from the web or external data sources at the moment a user submits a query, rather than relying solely on pre-trained knowledge with fixed cutoff dates. This enables AI models to provide up-to-date answers with cited sources.
Real-time search in AI represents a fundamental shift in how artificial intelligence systems access and deliver information to users. Unlike traditional AI models that rely on static training data with knowledge cutoff dates, real-time search enables AI systems to fetch current information from the internet at the exact moment a user submits a query. This capability bridges the gap between the limitations of pre-trained language models and the dynamic nature of modern information needs. The integration of real-time search transforms AI from a tool that provides historical knowledge into a dynamic information retrieval system that can answer questions about breaking news, current events, stock prices, weather conditions, and other time-sensitive topics with accuracy and relevance.
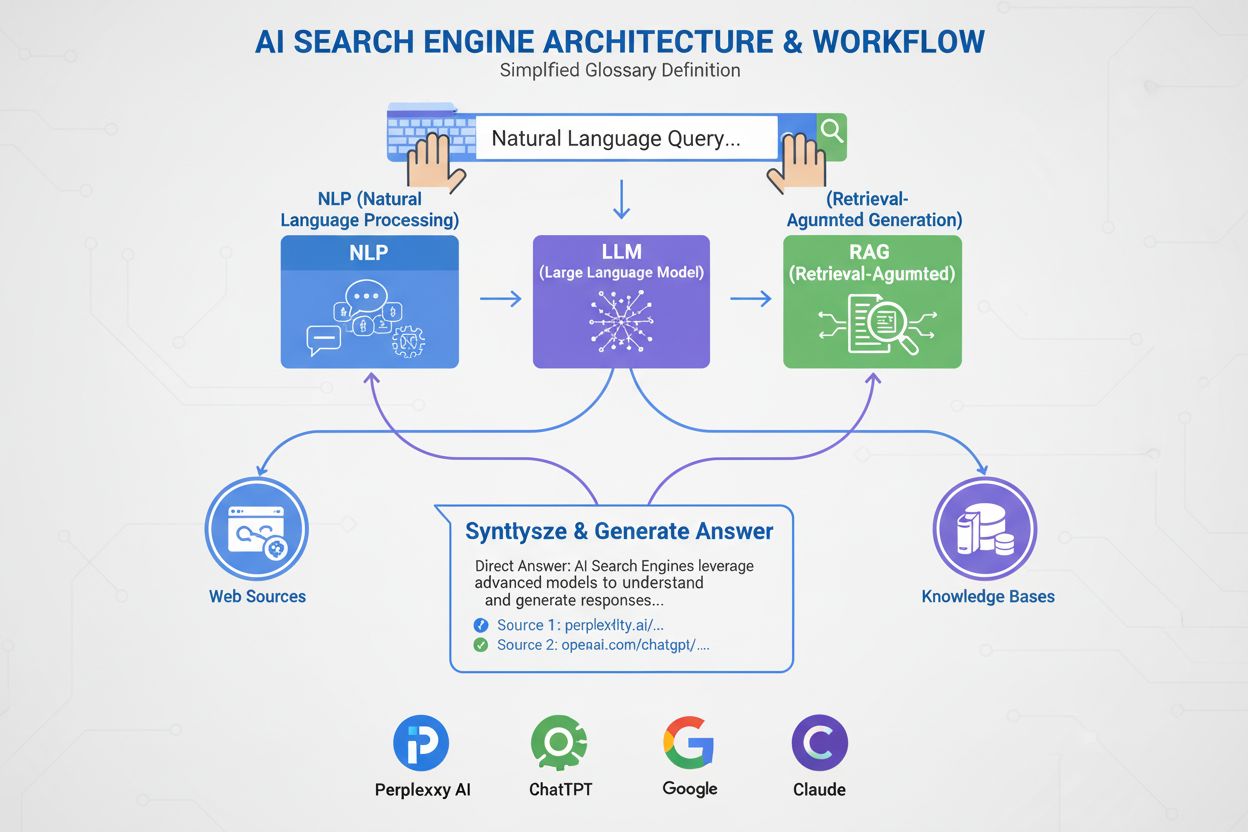
The core mechanism behind real-time search involves connecting large language models (LLMs) to live data sources through specialized retrieval systems. When a user asks a question, the AI system determines whether the query requires current information or can be answered from its existing training data. If real-time information is needed, the system automatically retrieves relevant documents, articles, or data points from the web or external databases. This retrieved information is then combined with the user’s query and fed into the language model, which synthesizes the information into a coherent, contextual response. This process, known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), ensures that AI responses are grounded in current, authoritative sources rather than potentially outdated training data.
Real-time search in AI operates through a sophisticated multi-step process that combines information retrieval with generative capabilities. The process begins when a user submits a query to an AI system equipped with real-time search functionality. The system analyzes the query to determine whether it requires current information or can be answered from the model’s existing knowledge base. For queries about recent events, current prices, breaking news, or other time-sensitive topics, the system automatically triggers a web search or retrieves data from connected external sources.
| Component | Function | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Query Analysis | Evaluates user input for real-time data needs | Determines if live information is necessary |
| Information Retrieval | Searches web or external databases | Fetches current, relevant documents and data |
| Vector Embeddings | Converts text into numerical representations | Enables semantic matching and relevance ranking |
| Prompt Augmentation | Combines retrieved data with user query | Provides context to the language model |
| Response Generation | LLM synthesizes information into answer | Produces coherent, cited response |
| Source Attribution | Provides citations and links to sources | Ensures transparency and verifiability |
Once relevant information is retrieved, the system converts both the user query and the retrieved documents into vector embeddings—numerical representations that capture semantic meaning. These embeddings are matched using algorithms that identify the most relevant information based on conceptual similarity rather than simple keyword matching. The retrieved information is then integrated into the prompt sent to the language model, a technique called prompt augmentation. This augmented prompt provides the LLM with current context and authoritative sources, enabling it to generate accurate, up-to-date responses. Finally, the system presents the answer to the user along with clickable citations that link directly to the original sources, ensuring transparency and allowing users to verify information independently.
Traditional AI models like earlier versions of ChatGPT operate with significant limitations regarding information currency. These models are trained on vast datasets up to a specific cutoff date, after which they have no knowledge of world events, new discoveries, or updated information. When users ask questions about recent events or current conditions, traditional AI models either provide outdated information or admit they lack knowledge about the topic. This creates a frustrating user experience and limits the practical applications of AI in scenarios where current information is critical.
Real-time search fundamentally changes this dynamic by enabling AI systems to access live information at the moment of query. This capability addresses several critical limitations of traditional models. First, it eliminates knowledge cutoff dates—users can ask about events that occurred yesterday, today, or even minutes ago, and the AI can provide accurate information. Second, it reduces AI hallucinations, the phenomenon where language models confidently provide false or misleading information when they lack knowledge about a topic. By grounding responses in retrieved, authoritative sources, real-time search significantly improves accuracy and reliability. Third, it enables personalization and context-awareness, as the system can retrieve information specific to a user’s location, preferences, or current circumstances.
The competitive landscape of AI search has been transformed by real-time capabilities. Platforms like Perplexity AI and Microsoft Copilot have long offered real-time search functionality, setting industry standards for current information access. OpenAI’s integration of real-time search into ChatGPT represents a major competitive move, bringing this capability to one of the world’s most widely-used AI systems. Google’s integration of generative AI into its search engine and Anthropic’s Claude Search also emphasize the industry-wide recognition that real-time information access is essential for modern AI applications.
Real-time search in AI delivers substantial benefits across multiple dimensions. For individual users, the most immediate advantage is access to current information without leaving the AI interface. Users no longer need to toggle between ChatGPT and a traditional search engine to verify recent information or find breaking news. This seamless integration creates a more efficient workflow and reduces cognitive load. The feature also provides transparency through source attribution, with clickable citations that link directly to original sources. This transparency builds user trust and enables verification of information, addressing one of the primary concerns users have about AI-generated content.
Another significant user benefit is improved accuracy and reduced hallucinations. By grounding responses in retrieved, authoritative sources, real-time search substantially decreases the likelihood of AI providing false information. This is particularly important for critical topics such as healthcare information, financial advice, legal matters, and news about elections or public safety. Users can have greater confidence in AI responses when they know the information comes from verified, current sources rather than potentially outdated training data.
For businesses and organizations, real-time search capabilities open new possibilities for customer engagement and operational efficiency. Companies can deploy AI-powered customer support systems that provide accurate, current information about products, services, policies, and industry developments. E-commerce businesses can use real-time search to deliver personalized product recommendations based on current inventory, pricing, and user preferences. Healthcare organizations can leverage real-time search to help professionals quickly access the latest medical research, clinical guidelines, and patient information. Financial institutions can use real-time data integration to provide accurate market information, investment recommendations, and risk assessments.
Real-time search also addresses critical business needs around compliance and risk management. Organizations can ensure that AI systems provide information consistent with current regulations, policies, and industry standards. By connecting AI systems to authoritative internal knowledge bases and external compliance resources, businesses can reduce legal risks and ensure consistent, accurate information delivery across all customer touchpoints.
Implementing real-time search in AI systems requires sophisticated technical infrastructure and careful architectural decisions. The foundation of real-time search is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a technique that combines the generative capabilities of large language models with external knowledge retrieval. RAG systems typically consist of several interconnected components that work together to deliver current information.
The first component is the external data layer, which includes all sources of current information that the AI system can access. This might include web APIs, news feeds, social media streams, internal databases, document repositories, or specialized data services. The data in these sources is continuously updated, ensuring that the AI system always has access to the latest information. To make this data searchable and retrievable, it is converted into vector embeddings using specialized embedding models. These embeddings are stored in vector databases that enable fast, semantic similarity searches.
When a user submits a query, the system performs a relevancy search by converting the user’s query into a vector embedding and matching it against the vector database. Advanced algorithms identify the most relevant documents or data points based on semantic similarity rather than keyword matching. This approach is far more sophisticated than traditional keyword-based search, as it understands the conceptual meaning of queries and can match them with relevant information even when exact keywords don’t appear in the source material.
The retrieved information is then used to augment the LLM prompt through prompt engineering techniques. The augmented prompt includes the user’s original query along with the most relevant retrieved information, providing the language model with current context and authoritative sources. The LLM then generates a response based on both its training data and the retrieved information, resulting in answers that are both knowledgeable and current.
To maintain the quality and currency of real-time search, systems must implement continuous data updates. This can be accomplished through real-time streaming processes that immediately update vector embeddings when source data changes, or through periodic batch processing that refreshes the knowledge base at regular intervals. The choice between real-time and batch updates depends on the specific use case and the acceptable latency for information currency.
Despite its significant advantages, real-time search in AI faces several important challenges that organizations must address. One of the most pressing issues is legal and copyright concerns surrounding the use of publisher content. AI companies that integrate web search functionality must navigate complex questions about fair use, content licensing, and publisher rights. OpenAI has faced lawsuits from media organizations alleging unauthorized use of their content for training purposes. While OpenAI allows publishers to opt out of its web crawler and emphasizes partnerships with media organizations, these legal battles underscore the ongoing complexity of integrating AI into content ecosystems.
Another significant challenge is the operational cost of maintaining real-time search capabilities. Real-time search is substantially more resource-intensive than traditional search methods or static AI models. Retrieving, processing, and integrating current information from multiple sources requires significant computational resources, which translates to higher operational costs. For companies offering free access to AI systems with real-time search, the long-term financial sustainability of the service remains uncertain. While some companies have committed to keeping real-time search free, the business model for sustaining these services at scale is still evolving.
AI hallucinations remain a concern even with real-time search. While grounding responses in retrieved sources significantly reduces hallucinations, language models can still misinterpret or misrepresent information, especially when dealing with complex or ambiguous source material. The AI might confidently present incorrect information even when it has access to correct sources. Addressing this requires ongoing improvements in model training, retrieval accuracy, and response validation.
Data quality and accuracy issues can also impact real-time search results. If source data is outdated, inaccurate, or biased, the AI system will reflect these problems in its responses. Ensuring that external data sources are reliable, current, and authoritative requires careful curation and ongoing monitoring. Additionally, privacy concerns arise when AI systems access and process sensitive information from various sources. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect user data and ensure compliance with privacy regulations.
Different AI platforms have implemented real-time search capabilities with varying approaches and features. Perplexity AI was among the first to emphasize real-time search as a core feature, positioning itself as an “answer engine” that provides current, cited information. Perplexity’s approach focuses on delivering concise, well-sourced answers to user queries, with clear attribution to original sources. The platform has built its entire value proposition around the combination of real-time search and conversational AI.
Microsoft Copilot (formerly Bing AI) integrates real-time search with OpenAI’s language models, leveraging Microsoft’s search infrastructure to provide current information. Copilot emphasizes the integration of search results with conversational AI, allowing users to ask follow-up questions and explore topics in depth while maintaining access to current information.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT introduced real-time search as a feature for paid subscribers, with plans to extend it to all users. ChatGPT’s implementation uses an updated version of the GPT-4o model and provides a sources sidebar with clickable citations. The feature automatically determines when live information is necessary based on the user’s query, though users can also manually trigger searches if they prefer.
Google’s Search with Gemini integrates generative AI directly into Google’s search interface, providing AI-generated summaries alongside traditional search results. This approach leverages Google’s existing search infrastructure and vast index of web content to deliver both current information and AI-generated insights.
Anthropic’s Claude Search focuses on nuanced, natural language responses with emphasis on accuracy and reliability. Claude’s approach to real-time search prioritizes careful source evaluation and transparent reasoning about information quality.
These different implementations demonstrate that while real-time search is becoming standard across major AI platforms, each company is developing its own approach based on its technical capabilities, business model, and user experience philosophy.
Real-time search is rapidly becoming a standard feature in AI systems rather than a differentiator. As the technology matures, we can expect several important developments. First, real-time search capabilities will become more sophisticated, with improved ability to understand complex queries, retrieve highly relevant information, and synthesize information from multiple sources. Second, the integration of real-time search with other AI capabilities like image generation, code execution, and specialized domain knowledge will create more powerful and versatile AI systems.
Third, the business models around real-time search will continue to evolve. Companies will need to balance the costs of maintaining real-time search infrastructure with the value it provides to users. This may lead to differentiated offerings, where basic real-time search is available to all users while premium features or higher-quality sources are reserved for paid subscribers.
Fourth, addressing the legal and ethical challenges around content use will be critical for the long-term viability of real-time search. Clearer frameworks for fair use, content licensing, and publisher compensation will likely emerge as the industry matures. Finally, improvements in accuracy, hallucination reduction, and bias mitigation will continue as companies invest in better retrieval systems, more sophisticated language models, and improved evaluation methods.
Track how your domain and brand appear in real-time AI answers across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search engines. Get instant alerts when your content is cited.

Learn what AI search engines are, how they differ from traditional search, and their impact on brand visibility. Explore platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, Goo...

Understand the difference between AI training data and live search. Learn how knowledge cutoffs, RAG, and real-time retrieval impact AI visibility and content s...

Learn what Real-Time Content APIs are and how they provide AI systems with current content updates for time-sensitive information. Explore streaming protocols, ...