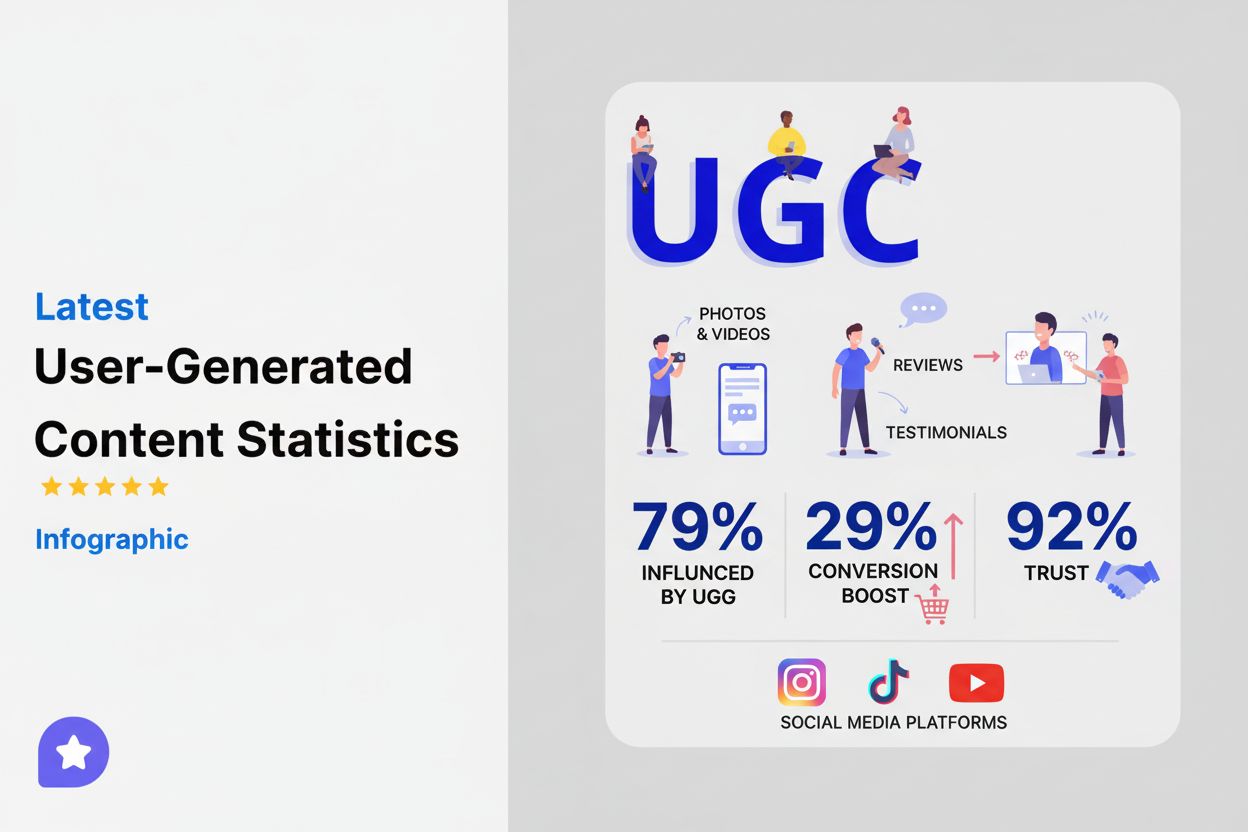
User-Generated Content (UGC)
Learn what User-Generated Content (UGC) is, why it matters for brand visibility, and how it drives conversions. Discover how 92% of consumers trust UGC more tha...

Learn what user-generated content for AI is, how it’s used to train AI models, its applications across industries, and the importance of authentic data for machine learning systems.
User-generated content for AI refers to any content created by users, customers, or everyday creators—including text, images, videos, and audio—that is used to train, improve, and enhance artificial intelligence models and systems.
User-generated content (UGC) for AI represents any form of content created by users, customers, fans, or everyday creators that serves as training data or input for artificial intelligence systems. This encompasses a wide spectrum of content types including text, images, videos, audio recordings, reviews, testimonials, social media posts, and unscripted real-life moments. The fundamental characteristic of UGC for AI is its authenticity—it captures genuine human behavior, perspectives, and experiences rather than professionally produced or curated material. This authentic nature makes UGC particularly valuable for training AI models that need to understand and replicate natural human communication patterns and real-world scenarios.
The significance of user-generated content in AI development cannot be overstated. AI models require vast amounts of training data to learn patterns, understand context, and generate coherent responses. User-generated content provides this essential raw material, offering diverse perspectives, languages, cultural contexts, and behavioral patterns that help AI systems become more robust and versatile. Unlike synthetic or artificially created data, UGC reflects the complexity and nuance of actual human expression, making it invaluable for developing AI systems that can interact naturally with real users.
AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs) and deep learning systems, are trained on enormous datasets that often include user-generated content sourced from various platforms and sources. These models use machine learning algorithms powered by techniques such as natural language processing (NLP) and deep learning to analyze patterns within this data. When an AI system processes user-generated content during training, it learns to identify linguistic patterns, stylistic nuances, contextual relationships, and semantic meanings that enable it to generate coherent and contextually appropriate responses.
The training process involves several sophisticated mechanisms. Transformer networks, which form the backbone of modern AI systems like GPT models, excel at identifying long-range dependencies in text and capturing contextual relationships across entire documents. These neural networks learn not just grammar and syntax but also the emotional tone, cultural references, and implicit meanings embedded in user-generated content. Through this process, AI systems develop the ability to understand and produce human-like text that feels natural and accurate.
| Content Type | AI Training Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Text (reviews, posts, articles) | Language understanding and generation | Captures natural language patterns and sentiment |
| Video footage | Computer vision and action recognition | Enables visual understanding and real-world context |
| Audio recordings | Speech recognition and voice synthesis | Develops natural-sounding voice generation |
| Images | Image recognition and generation | Trains visual understanding and creative capabilities |
| Social media content | Sentiment analysis and trend detection | Reflects real-time human opinions and behaviors |
Transfer learning and fine-tuning represent additional mechanisms through which user-generated content enhances AI capabilities. Most AI models are initially trained on broad datasets to establish a foundation of general knowledge, but for specialized applications, fine-tuning is applied. This process involves retraining a model on domain-specific user-generated content, tailoring it to excel in particular industries or tasks. For example, healthcare AI systems might be fine-tuned on medical reviews and patient testimonials, while customer service chatbots are trained on actual customer interactions and support conversations.
User-generated content serves multiple critical functions across diverse AI applications. In content marketing and social media, AI systems analyze user-generated posts, comments, and engagement patterns to understand audience preferences and generate targeted content. Marketing teams leverage AI trained on UGC to create social media posts that resonate with specific demographics, craft personalized email campaigns, and produce product descriptions optimized for search engines. The authenticity of user-generated content helps these systems understand what messaging genuinely connects with audiences rather than relying on generic templates.
E-commerce and recommendation systems heavily depend on user-generated content in the form of product reviews, ratings, and customer behavior data. AI models trained on this content can analyze customer preferences and provide personalized product recommendations that align with individual shopping patterns and interests. This application directly impacts customer satisfaction and sales conversion rates, as recommendations based on real user behavior prove more effective than algorithmic suggestions lacking authentic user context.
In customer service applications, AI chatbots trained on user-generated content from actual customer interactions can provide more natural and helpful responses. These systems learn from real customer questions, common pain points, and effective resolution strategies documented in support conversations. The result is customer service AI that understands context, recognizes customer frustration, and provides genuinely helpful responses rather than robotic, templated answers.
Journalism and news generation represent another significant application area. News agencies use AI trained on user-generated content and journalistic writing to generate news briefs, summarize complex datasets, and create sports scores and weather updates. While AI can provide quick factual summaries based on patterns learned from user-generated content, journalists remain essential for adding context, analysis, and in-depth reporting that requires human judgment and expertise.
The quality and diversity of user-generated content directly impact AI system performance and reliability. Authentic UGC captures real human behavior in ways that synthetic or professionally produced content cannot replicate. When AI systems are trained on genuine user interactions, they develop better understanding of colloquialisms, cultural references, emotional nuances, and contextual subtleties that characterize natural human communication. This authenticity translates into AI systems that feel more natural and relatable to end users.
Diversity in user-generated content is equally critical for developing fair and unbiased AI systems. AI models reflect the biases present in their training data, so diverse UGC sourced from different demographics, geographic regions, languages, and cultural backgrounds helps create more inclusive AI systems. When training data includes perspectives from varied user groups, the resulting AI models are less likely to perpetuate stereotypes or discriminate against particular populations. This diversity requirement has led to increased focus on ethically sourced, rights-cleared user-generated content that represents authentic human experiences across different communities.
The challenge of obtaining high-quality, diverse, and ethically sourced user-generated content has spawned specialized platforms and services. Companies now curate and license datasets of authentic UGC specifically designed for AI training, ensuring that content is rights-cleared, properly annotated, and representative of real-world scenarios. These datasets might include thousands of video clips capturing spontaneous human behavior in diverse environments, or collections of authentic customer reviews and testimonials that reflect genuine user experiences.
While user-generated content provides invaluable training material for AI systems, its use raises significant ethical and legal concerns. Copyright and intellectual property issues represent a major challenge, as AI companies must ensure they have proper rights to use user-generated content for training purposes. Many users create content without explicitly consenting to its use in AI training, raising questions about fair compensation and creator rights. Current lawsuits against major AI companies allege copyright infringement by using copyrighted materials, often acquired without permission, to train their models.
Data privacy and protection present another critical concern. User-generated content often contains personal information, and regulations such as GDPR and the EU AI Act impose strict requirements on how this data can be collected, stored, and used. Once information is learned by an AI model, it cannot easily be “forgotten,” creating potential conflicts with data protection regulations that grant users the right to have their data deleted. Organizations implementing AI systems must carefully manage which user-generated content is accessible to which users, as inadequately protected data can lead to unwanted disclosure of sensitive information.
Bias and fairness issues emerge when user-generated content reflects societal prejudices or underrepresents certain groups. If training data is skewed toward particular demographics or perspectives, the resulting AI systems may perpetuate discrimination or provide biased outputs. Addressing this requires careful curation of user-generated content to ensure representation across different groups and perspectives, as well as ongoing auditing of AI models to identify and mitigate biases.
The authenticity paradox also deserves consideration. While authentic user-generated content is valuable for training, the proliferation of AI-generated content masquerading as user-generated content creates challenges. As AI systems become more sophisticated, distinguishing between genuine user-generated content and AI-generated content becomes increasingly difficult, potentially contaminating training datasets with synthetic data that lacks the authentic human perspective that makes UGC valuable in the first place.
Organizations seeking to effectively utilize user-generated content for AI development should establish clear ethical guidelines and obtain proper consent from content creators. Transparency about data usage is essential—users should understand how their content will be used in AI training and have the opportunity to opt out if they choose. This transparency builds trust and ensures compliance with data protection regulations.
Quality assurance and content validation processes are critical for maintaining the integrity of training datasets. Organizations should implement systems to verify that user-generated content is authentic, properly licensed, and free from harmful or misleading information. This might involve human review of content samples, automated quality checks, and ongoing monitoring to ensure that training data meets established standards.
Diversity and representation should be actively managed throughout the content collection process. Rather than passively accepting whatever user-generated content is available, organizations should intentionally seek content from underrepresented groups and perspectives to ensure their AI systems serve diverse user populations effectively. This proactive approach to diversity helps create more inclusive and fair AI systems.
Finally, organizations should maintain human oversight throughout the AI development and deployment process. While user-generated content provides the foundation for AI training, human experts remain essential for interpreting results, identifying potential biases, and ensuring that AI systems align with organizational values and ethical standards. The most effective approach combines the efficiency of AI trained on authentic user-generated content with the judgment and accountability that only human oversight can provide.
Discover how your content appears in AI search engines and AI-generated answers. Track your brand visibility across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI platforms.

Learn what User-Generated Content (UGC) is, why it matters for brand visibility, and how it drives conversions. Discover how 92% of consumers trust UGC more tha...

Learn proven techniques to humanize AI-generated content for better citations in AI answer generators. Improve authenticity, boost visibility in AI search resul...
Learn what AI content generation is, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and best practices for using AI tools to create marketing content optimized for ...