
Will AI Replace Traditional Search Engines? The Future of Search
Explore whether AI will replace Google and traditional search engines. Learn about the coexistence of AI search tools and traditional search, market trends, and...

Discover whether AI search engines like ChatGPT and Perplexity will replace Google. Learn about the future of search, market trends, and how both technologies coexist.
No, AI search will not completely replace Google. Instead, the future of search will be segmented, with AI-powered platforms and traditional search engines serving different user needs and coexisting in a hybrid ecosystem.
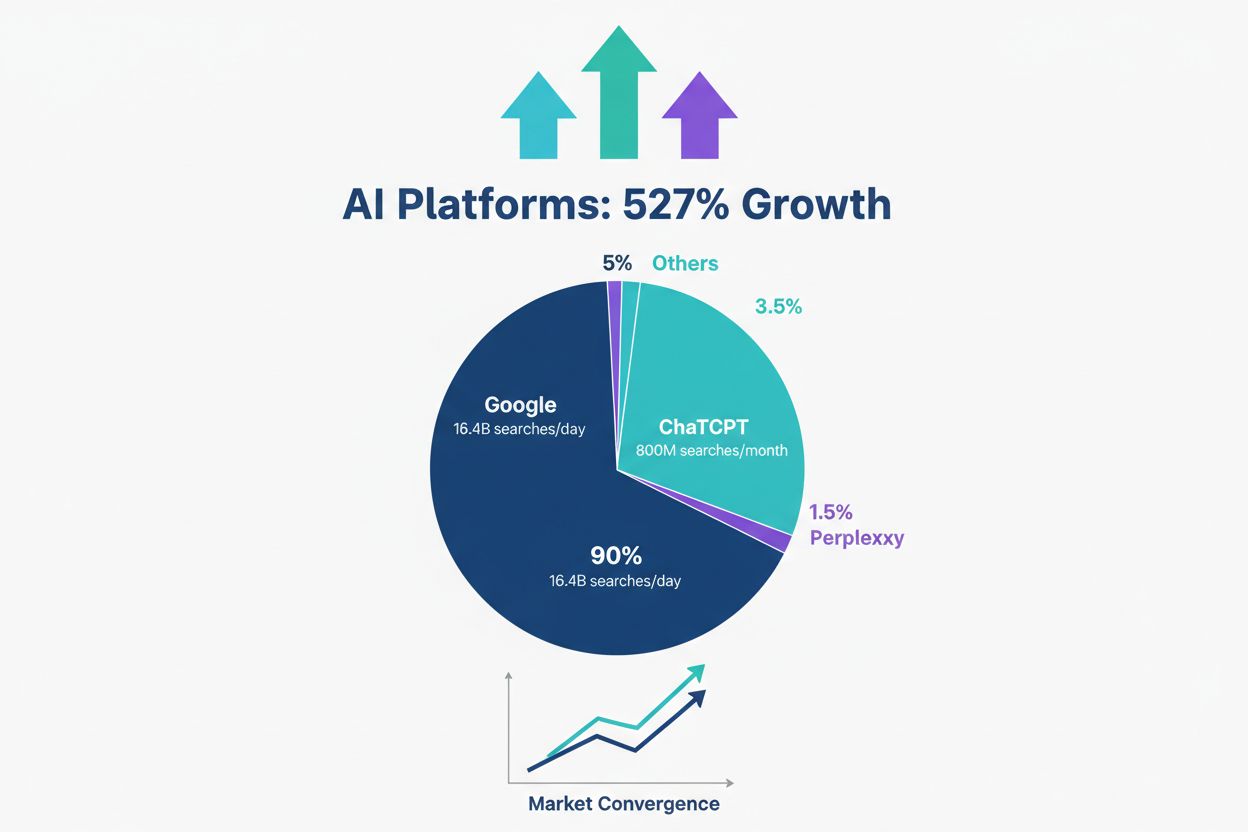
The question of whether AI search will replace Google has become increasingly relevant as platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s Gemini gain traction. However, the evidence suggests a more nuanced reality. Rather than a complete replacement, we are witnessing the emergence of a segmented search landscape where different platforms serve distinct user needs and preferences. Google continues to dominate with approximately 93.57% of the search market share, processing roughly 373 times more searches than ChatGPT. Between April 2024 and March 2025, Google attracted 1.6 trillion visits while ChatGPT reached 47.7 billion visits. These numbers reveal that despite the rapid growth of AI search platforms, traditional search engines remain the primary tool for billions of users worldwide.
The critical insight here is that 98.1% of ChatGPT users also use Google, indicating that users are not abandoning traditional search but rather adopting AI tools as complementary resources. This behavioral pattern demonstrates that the future of search is not about replacement but about coexistence and specialization. Users are developing distinct preferences for when to use each platform based on their specific information needs, search complexity, and desired outcomes.
Understanding the fundamental differences between AI-powered search and traditional search engines is essential to comprehending why both will likely persist. Traditional search engines like Google operate through three primary stages: crawling (discovering new and updated pages), indexing (understanding and organizing content), and serving results (ranking pages based on relevance and quality). This process delivers users with a ranked list of links and snippets, requiring them to visit multiple pages to synthesize information.
AI search engines take a fundamentally different approach. Platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology, which queries traditional search engines and synthesizes content from top-ranking results into a single, coherent response. These systems employ natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs) to understand user intent, context, and nuances in how questions are phrased. The output is a conversational, synthesized answer rather than a list of links. This distinction is crucial: AI search focuses on semantics and context, while traditional search emphasizes keywords and relevance ranking.
| Aspect | Traditional Search (Google) | AI Search (ChatGPT, Perplexity) |
|---|---|---|
| Output Format | Ranked list of links with snippets | Synthesized conversational answers |
| Search Focus | Keywords and metadata matching | Context and semantic understanding |
| Real-Time Data | Yes, continuously crawls the web | Limited (depends on integration) |
| Source Transparency | Multiple sources visible | Sources may be implicit or summarized |
| User Effort | Must visit multiple pages | Direct answer provided immediately |
| Hallucination Risk | Low | Moderate to high |
| Local Search | Excellent | Limited |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate to fast |
Several compelling reasons explain why Google maintains its market dominance despite the emergence of powerful AI search alternatives. First, AI hallucinations remain a significant barrier to adoption. Hallucinations occur when AI models generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information. While traditional search engines link users to verifiable sources, AI systems may respond without clear citations or based on incomplete training data. This fundamental difference in reliability makes Google the preferred choice for users seeking factual accuracy, especially for critical decisions involving health, finance, or legal matters.
Second, user habits and muscle memory are extraordinarily powerful forces in technology adoption. Google has been the dominant search engine for over two decades, making it second nature for billions of users to “Google it” when seeking information. This habitual behavior is reinforced by Google’s seamless integration with other services like Google Maps, Gmail, and Android, creating an ecosystem that is difficult to abandon. The switching costs—both cognitive and practical—are substantial.
Third, real-time information needs demand real-time tools. AI models are trained on historical data and cannot match Google’s ability to deliver current information about breaking news, live events, or recent developments. Even with browsing capabilities, AI platforms lack the seamless, real-time indexing that Google provides. A user wanting to know who won yesterday’s sports match or the latest stock prices will find Google more reliable and immediate.
Fourth, the content gap is significant. AI systems like ChatGPT do not crawl the entire web like Google does. They rely on pre-trained data and curated plugin access, meaning niche websites, forums, and fresh blogs may not be visible in AI-generated answers. This limitation is particularly problematic for users seeking specialized information or exploring emerging topics. Additionally, SEO-optimized content often surfaces more effectively in Google results than in AI responses, which tend to favor long-form content from trusted media outlets over brand product pages.
The quantitative evidence paints a clear picture of the current search landscape. According to recent research, most websites receive less than 1% of their total traffic from AI search engines, with many sites reporting figures below 0.5%. This contrasts sharply with Google’s dominance, which drives the vast majority of referral traffic for most websites. Google users conduct approximately 200 searches monthly, while Perplexity users—representing a leading AI search platform—conduct only 15 searches monthly. These metrics reveal that while AI search is growing, it remains a niche tool for specific use cases rather than a mainstream replacement for traditional search.
The growth trajectory of AI search is noteworthy but not yet disruptive. In 2023, approximately 13 million adults in the United States used generative AI as their primary search engine, with projections reaching 90 million by 2027. While this represents significant growth, it still represents a small fraction of the global search market. Furthermore, Google’s traffic actually grew by 1.4% from May 2023 to May 2024, precisely when AI search tools became widely available. This growth suggests that AI search is expanding the overall search market rather than cannibalizing Google’s user base.
Research from Carnegie Mellon University’s Tepper School of Business provides valuable insights into how search will likely evolve. MBA students conducted experiments comparing user satisfaction and efficiency between traditional and AI search. The findings revealed that gen AI users reported 17% higher satisfaction rates and achieved their goals faster, with 88% of gen AI users finding what they needed on the first try, compared to 79% of Google users. However, the research also identified a crucial pattern: users preferred gen AI platforms for complex queries (such as comparisons, creative tasks, or detailed explanations) while traditional search remained the choice for simple, factual tasks.
This segmentation suggests that the future of search will be task-dependent rather than platform-dependent. Users will likely maintain multiple search tools in their arsenal, selecting the most appropriate one based on their specific information need. For simple factual queries, local searches, or real-time information, Google will remain the default. For complex comparisons, creative brainstorming, or detailed explanations, AI platforms will be preferred. This hybrid model is already emerging, with Google itself integrating AI features through AI Overviews (formerly Search Generative Experience), which provide synthesized answers alongside traditional search results.
One critical factor that may prevent AI search from completely replacing Google is the monetization dilemma. Google’s business model relies on ad-based revenue, where sponsored links generate income per click. This model has proven extraordinarily profitable because users click through to websites, creating opportunities for advertisers. AI search platforms, by contrast, provide direct answers, leaving little room for traditional ad placements. This fundamental difference creates a significant economic barrier to AI search dominance.
Student research teams exploring this challenge identified several potential monetization strategies for AI platforms, including sponsored follow-up questions, embedded content, and subscription models. However, each approach carries risks. If sponsored content disrupts the seamless user experience, platforms could lose users. Subscription models may deter people accustomed to free search options. Additionally, gen AI search is more expensive to operate than traditional search, consuming four to five times more energy. This cost structure makes it difficult for AI platforms to achieve the profitability that would enable them to compete with Google’s established revenue streams.
The emergence of AI search has profound implications for digital marketing and content strategy. The traditional SEO model focused on achieving high rankings in Google’s search results to drive clicks. However, AI search introduces a new dynamic: zero-click searches, where users receive answers directly in the AI interface without visiting external websites. This shift compresses the marketing funnel and changes how content is discovered and valued.
To maintain visibility in this evolving landscape, organizations should adopt a “Search Everywhere Optimization” strategy that encompasses both traditional SEO and Generative Engine Optimization (GEO). This means creating clear, structured content that answers user questions directly, using semantic clarity rather than keyword stuffing, and ensuring content is logically organized with consistent terminology. Additionally, brands should focus on building topical authority, maintaining strong YouTube presence, and securing publications in high-authority outlets, as these factors influence visibility across both traditional and AI search platforms.
Monitoring your brand’s appearance in AI-generated answers is increasingly critical. Tools that track AI citations and brand mentions across platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews provide valuable insights into how your content is being referenced. This data helps organizations understand whether their content is being cited in AI responses and identify opportunities to improve visibility in this emerging channel.
Rather than being disrupted by AI search, Google has chosen to integrate AI capabilities into its core search experience. The company launched Gemini, a custom generative AI platform that can understand and process content across multiple modalities (text, images, video). Google’s AI Overviews now appear above traditional search results, providing synthesized answers while maintaining links to source content. This hybrid approach allows Google to retain its market dominance while adopting the benefits of AI-powered search.
This integration strategy suggests that the future of search will not be a binary choice between traditional and AI search but rather a continuum of AI-enhanced search experiences. Users will encounter AI-generated summaries, conversational interfaces, and multi-modal results within Google’s ecosystem, while also having the option to use dedicated AI search platforms for specific needs. This evolution represents an enhancement or evolution of Google search rather than a complete replacement, allowing the company to maintain its position while adapting to changing user expectations.
The evidence overwhelmingly suggests that AI search will not replace Google in the foreseeable future. Instead, we are witnessing the emergence of a diversified search ecosystem where different platforms serve different purposes. Google will likely maintain its dominance for real-time information, local search, and simple factual queries, while AI platforms will capture growing share of complex, comparative, and creative search tasks. The 98.1% overlap between ChatGPT and Google users demonstrates that these platforms are complementary rather than competitive.
The future of search is not about one technology replacing another but about intelligent specialization. Users will develop sophisticated strategies for selecting the most appropriate search tool based on their specific needs. Organizations that recognize this shift and optimize their content for visibility across multiple platforms—both traditional search engines and AI systems—will be best positioned to reach their audiences in this evolving landscape. The key to success is understanding that search is becoming everywhere, and visibility requires a comprehensive, multi-platform approach.
Ensure your brand appears in AI-generated answers on ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI search platforms. Track your visibility and optimize your presence where your audience is searching.

Explore whether AI will replace Google and traditional search engines. Learn about the coexistence of AI search tools and traditional search, market trends, and...

Explore AI Visibility Futures - forward-looking analysis of emerging trends in AI-driven brand discovery. Learn how brands will be discovered by AI systems and ...
Explore how AI search platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity are reshaping the search landscape. Discover when AI could match Google's conversion volume and what...