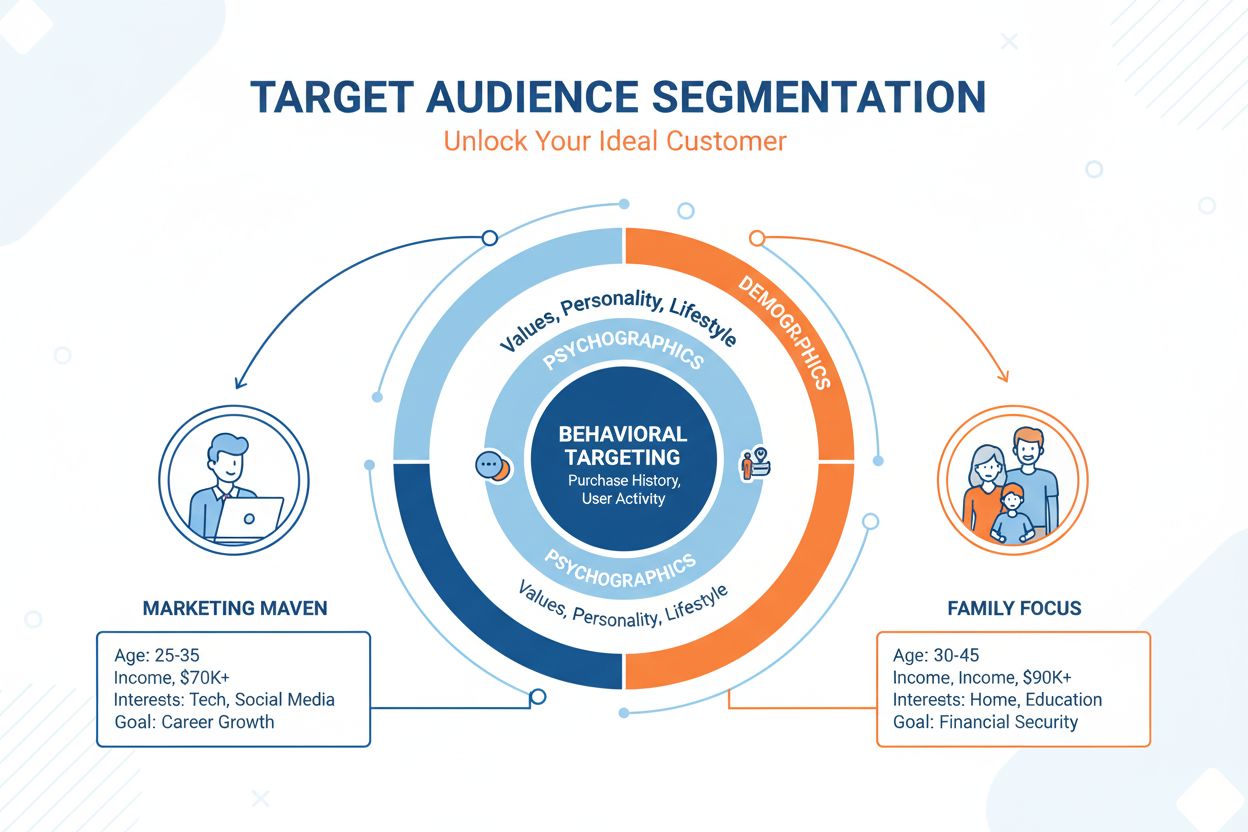
Target Audience
Learn what a target audience is, how to identify and segment your audience using demographics, psychographics, and behavioral data, and why it's critical for co...

Advertisements are paid promotional messages and content designed to capture audience attention and persuade them to take specific actions, such as purchasing products, visiting websites, or engaging with brands. Ads appear across multiple channels including websites, social media platforms, search engines, email, and traditional media, utilizing various formats like banners, videos, text, and native content to reach target audiences effectively.
Advertisements are paid promotional messages and content designed to capture audience attention and persuade them to take specific actions, such as purchasing products, visiting websites, or engaging with brands. Ads appear across multiple channels including websites, social media platforms, search engines, email, and traditional media, utilizing various formats like banners, videos, text, and native content to reach target audiences effectively.
Advertisements, commonly referred to as ads, are paid promotional messages and content strategically designed to capture audience attention and persuade them to take specific actions. These actions may include purchasing products, visiting websites, signing up for services, attending events, or engaging with brands in meaningful ways. Advertisements represent a fundamental component of modern marketing, appearing across diverse channels including websites, social media platforms, search engines, email systems, television, radio, billboards, and print publications. The core purpose of advertising is to reach the right people at the right time with the right message, leveraging creativity, data analytics, and strategic placement to influence consumer behavior and drive measurable business results. Unlike organic content or earned media, advertisements guarantee visibility through purchased media space or time, making them a direct and controllable marketing tool for businesses of all sizes.
The history of advertising mirrors the evolution of communication technology itself, demonstrating how marketing strategies adapt to new platforms and consumer behaviors. Ancient merchants used papyrus scrolls and town criers to promote goods, establishing the foundational principle that visibility drives sales. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized advertising, enabling mass production of promotional materials through newspapers and magazines. By the early 1900s, print advertising dominated the landscape, with newspapers and magazines serving as primary channels for reaching mass audiences. The 20th century brought transformative changes with radio advertising emerging in the 1920s and television commercials beginning in the 1940s, fundamentally altering how businesses connected with consumers through audio and visual storytelling.
The digital revolution of the late 1990s and early 2000s fundamentally reshaped the advertising industry. Online banner ads first appeared in 1994, Google AdWords launched in 2000, and Facebook advertising began in 2007, creating entirely new channels for reaching audiences. This shift reflected changing consumer habits as people increasingly spent time online and expected personalized, relevant advertising experiences. Digital advertising revenue reached $258.6 billion in 2024, representing a 15% year-over-year increase, with digital channels now accounting for approximately 72% of total advertising spending globally. The emergence of programmatic advertising, AI-powered targeting, and real-time bidding has further transformed how ads are bought, placed, and optimized, enabling unprecedented precision in reaching target audiences while maintaining cost efficiency.
| Advertisement Type | Primary Channel | Key Characteristics | Best For | Typical Cost Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Search Engine Marketing (SEM) | Google, Bing | Text-based ads appearing in search results; high purchase intent | Capturing customers actively searching for solutions | Cost-per-click (CPC) |
| Display Ads | Websites, Google Display Network | Banner images, animations, rich media across thousands of sites | Brand awareness and reach | Cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM) |
| Social Media Ads | Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, LinkedIn | Targeted ads in user feeds with advanced demographic/interest targeting | Precise audience segmentation and engagement | Cost-per-click or CPM |
| Video Ads | YouTube, streaming platforms | Pre-roll, mid-roll, post-roll, and outstream video formats | High engagement and emotional connection | Cost-per-view (CPV) |
| Native Advertising | Blogs, news sites, social feeds | Sponsored content blending naturally with editorial material | Non-intrusive brand integration and credibility | Flat rate or performance-based |
| Email Marketing | Email inboxes | Personalized promotional messages to subscriber lists | Customer retention and direct response | Flat rate or per-contact |
| Mobile Ads | Apps, mobile websites | In-app ads, mobile banners, rewarded ads on smartphones/tablets | Reaching on-the-go consumers | CPM or CPC |
| Television Commercials | TV channels | 15-60 second visual and audio spots during programming | Mass reach and brand prestige | Cost-per-spot or CPM |
| Radio Spots | Radio stations | Audio-only advertisements during programming | Regional reach and frequency | Cost-per-spot |
| Out-of-Home (OOH) | Billboards, transit, urban spaces | Large-format visual ads in physical locations | Geographic targeting and brand recall | Monthly or quarterly rates |
Advertisements operate through sophisticated technical systems that match promotional content with relevant audiences at optimal moments. The process begins with advertisers defining their target audience using demographic data (age, gender, location, income), psychographic information (interests, values, lifestyle), and behavioral signals (browsing history, purchase patterns, online activities). Programmatic advertising platforms automate this process through real-time bidding, where advertisers’ demand-side platforms (DSPs) compete for ad inventory provided by publishers’ supply-side platforms (SSPs). When a user visits a webpage or opens an app, an ad exchange instantly evaluates available ad space and matches it with relevant advertisements, all within milliseconds.
The AIDA model—Attention, Interest, Desire, Action—provides the foundational framework for effective advertisement design. Attention is captured through compelling headlines, striking visuals, or unexpected creative approaches that interrupt the user’s current activity. Interest is generated by presenting relevant information that resonates with the audience’s needs or challenges. Desire is built by demonstrating how the product or service improves the user’s life or solves their problems, often through benefits-focused copy and social proof elements like testimonials or reviews. Action is prompted through clear, compelling calls-to-action (CTAs) that make the next step obvious and easy, whether clicking a link, making a purchase, or contacting the business.
Modern advertisements leverage data analytics and machine learning to optimize performance continuously. Advertisers can track metrics including impressions (total views), clicks, click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, cost per acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS) in real-time. A/B testing allows comparison of different creative elements, headlines, images, and messaging to identify which variations resonate most with target audiences. Retargeting technology enables advertisers to display ads to users who previously visited their websites, significantly improving conversion rates compared to cold advertising. Attribution modeling helps understand how different touchpoints contribute to final conversions, allowing marketers to allocate budgets more effectively across channels.
Digital advertising has become the dominant force in modern marketing, with platforms like Google, Facebook, Amazon, and emerging AI systems reshaping how brands reach consumers. Google Ads remains the largest advertising platform, processing approximately 99,000 search queries per second and offering unparalleled access to high-intent audiences actively seeking products or services. Facebook and Instagram advertising provides sophisticated targeting capabilities based on user interests, behaviors, and demographics, reaching billions of users across multiple devices. TikTok advertising has emerged as a powerful channel for reaching younger demographics through native, engaging video content. LinkedIn advertising serves B2B marketers targeting professionals and decision-makers within specific industries and roles.
The rise of AI-powered search platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews has created new considerations for brand visibility and advertisement strategy. Unlike traditional search engines where brands can purchase prominent ad placements, AI systems generate responses based on training data and user queries, making brand mentions less directly controllable through paid advertising. However, brands that maintain strong online presence, quality content, and positive reviews are more likely to be cited and recommended by AI systems. This has led to the emergence of AI visibility monitoring tools that track how often brands appear in AI-generated responses across different platforms. Brands increasingly recognize that optimizing for AI visibility requires a holistic approach combining quality content creation, reputation management, and strategic advertising across traditional and emerging channels.
Advertisements drive measurable business outcomes including brand awareness, customer acquisition, revenue generation, and market share growth. For new businesses, advertising accelerates market entry by building brand recognition and attracting initial customers. Established brands use advertising to maintain market position, introduce new products, and defend against competitive threats. The advertising industry’s growth to $259 billion in global digital spending reflects its critical importance to business success. Companies allocate 5-10% of revenue to marketing, with a significant portion dedicated to paid advertising. Growth-stage businesses often invest 12-20% of projected revenue in advertising to build market presence quickly.
Effective advertising strategies require careful alignment with business objectives and target audience understanding. Demographic targeting forms the foundation, focusing on measurable population characteristics like age, gender, income, and location. Psychographic targeting reveals deeper motivations by examining lifestyle choices, values, interests, and personality traits. Successful advertisers combine demographic and psychographic insights to create highly personalized campaigns that speak directly to ideal customers’ desires and pain points. Budget allocation decisions should follow the 70-20-10 rule: 70% on proven channels, 20% on emerging opportunities, and 10% on experimental tactics. This balanced approach ensures consistent performance while allowing innovation and adaptation to market changes.
The advertising landscape continues evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancement, changing consumer behaviors, and regulatory developments. Artificial intelligence is increasingly central to advertising operations, with machine learning algorithms optimizing targeting, bidding, and creative elements automatically. Programmatic advertising, which automates ad buying and placement through AI systems, continues expanding as advertisers seek efficiency and precision. Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA are reshaping data collection and targeting practices, pushing advertisers toward first-party data strategies and contextual targeting alternatives to third-party cookies.
Emerging advertising formats reflect changing media consumption patterns and technological capabilities. Native advertising continues growing as audiences increasingly reject intrusive ad formats, preferring content that blends naturally with editorial material. Influencer marketing leverages trusted personalities to authentically recommend brands to engaged followers. Podcast advertising taps into the intimate relationship between hosts and listeners, with host-read ads commanding premium attention and engagement. Augmented reality (AR) ads enable consumers to virtually try products before purchasing, creating immersive brand experiences. Connected TV advertising brings digital targeting precision to living room viewing, while retail media networks allow brands to advertise directly on ecommerce platforms where purchase decisions happen.
The integration of AI systems into consumer search and discovery processes represents a fundamental shift in advertising strategy. As AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews become primary discovery channels, brands must adapt their visibility strategies beyond traditional search engine optimization. Monitoring tools that track brand mentions and recommendations across AI systems are becoming essential for competitive brands, providing insights into how AI systems perceive and recommend their products. This evolution suggests that future advertising success will require mastery of both traditional paid advertising channels and emerging AI-driven discovery mechanisms, with brands needing to optimize for both human audiences and AI systems simultaneously.
Advertisements are paid messages placed in media channels to promote products or services, while promotional content is broader marketing material that can be organic or paid. All advertisements are promotional content, but not all promotional content is advertising. Advertisements specifically involve purchasing media space or time, whereas promotional content can include organic social media posts, blog articles, or email newsletters that don't require paid placement. Both serve to persuade audiences, but advertisements guarantee visibility through paid distribution.
Advertisements on web pages appear in various locations including header banners, sidebars, footer areas, within content (native ads), and between content sections (interstitial ads). Display ads use the Google Display Network and similar platforms to appear across thousands of websites. Ad placements are determined by publishers, advertisers, and ad networks that manage inventory and targeting. Mobile pages feature ads in feeds, between app content, and as pop-ups. Strategic placement maximizes visibility while maintaining user experience.
Brands monitor ad placements in AI search results to ensure brand visibility, track competitive positioning, and measure marketing effectiveness across emerging platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. AI monitoring tools help brands understand how their products are mentioned and recommended by AI systems, which increasingly influence consumer decisions. This visibility tracking is crucial because AI-generated responses can significantly impact brand perception and customer acquisition. Monitoring ensures brands maintain presence in these new discovery channels.
The most effective ad types for online businesses include search engine marketing (SEM) for high-intent customers, social media advertising for targeted reach, display ads for brand awareness, and email marketing for customer retention. Video ads on YouTube and streaming platforms generate high engagement, while native advertising provides non-intrusive brand integration. Programmatic advertising automates ad buying and placement optimization. The best approach combines multiple formats based on business goals, target audience behavior, and budget allocation across proven and emerging channels.
Advertisements are measured using metrics like impressions (views), clicks, click-through rate (CTR), cost per click (CPC), conversion rate, and return on ad spend (ROAS). Brand awareness campaigns track reach and frequency, while direct response ads focus on conversions and customer acquisition cost (CAC). Digital platforms provide real-time analytics dashboards showing performance data. Attribution modeling helps understand how ads contribute to sales across customer journeys. A/B testing compares ad variations to optimize creative elements, targeting, and messaging for better results.
Advertisements contribute to brand visibility in AI systems through multiple touchpoints including website content, social signals, and brand mentions that AI models learn from during training. When brands appear in AI-generated responses, it indicates strong online presence and relevance. Monitoring tools track how often brands are cited, recommended, or mentioned by AI systems across platforms. This visibility is increasingly important as AI becomes a primary discovery channel. Brands that maintain strong advertising presence and content quality are more likely to be recommended by AI systems.
Digital advertising spending reached $259 billion globally in 2024, representing a 15% year-over-year increase, with digital accounting for 72% of total advertising revenue. The US digital ad market exceeded $300 billion in 2024. Key trends include programmatic advertising automation, AI-powered targeting and optimization, shift toward privacy-compliant tracking, growth in video and mobile ads, and emergence of retail media networks. Brands increasingly invest in omnichannel strategies combining search, social, display, and emerging formats. Personalization and real-time bidding continue to drive efficiency and effectiveness.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Learn what a target audience is, how to identify and segment your audience using demographics, psychographics, and behavioral data, and why it's critical for co...

Paid search results are sponsored ads appearing in search engine results. Learn how PPC advertising works, its ROI impact, and why monitoring paid search visibi...

Learn what Cost Per Click (CPC) means in digital advertising. Understand CPC calculation, bidding strategies, and how it compares to CPM and CPA models for opti...