
What is Content Cannibalization in AI Search and How Does It Impact Rankings
Learn what content cannibalization in AI search means, how it affects your brand visibility in AI answers, and why monitoring your content overlap matters for A...
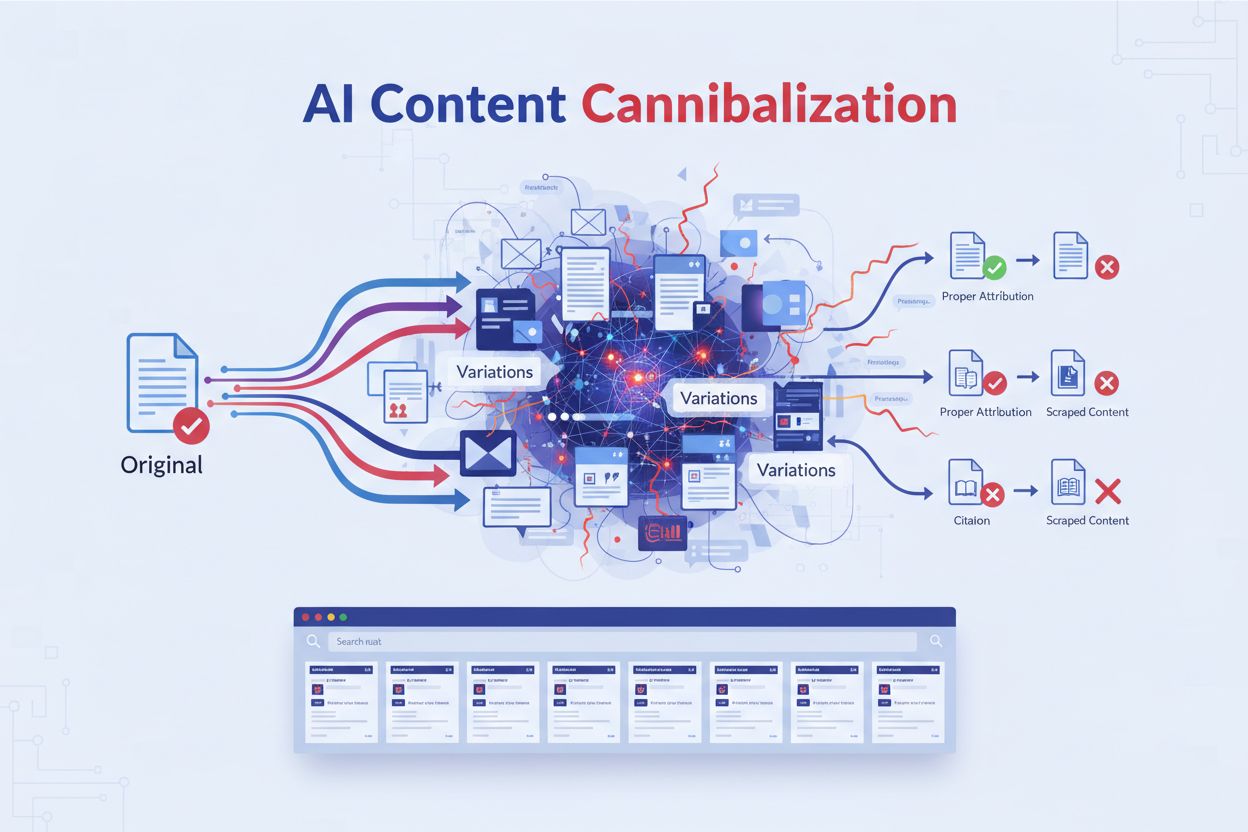
When multiple pieces of content compete for the same AI citations. AI systems scrape and rewrite your original content into semantically similar variations that compete with your original pages in search results and AI-generated answers, diluting your visibility and authority without proper attribution.
When multiple pieces of content compete for the same AI citations. AI systems scrape and rewrite your original content into semantically similar variations that compete with your original pages in search results and AI-generated answers, diluting your visibility and authority without proper attribution.
AI content cannibalization occurs when artificial intelligence systems scrape and rewrite your original content into semantically similar variations that compete with your original pages in search results and AI-generated answers. Unlike traditional duplicate content that copies text word-for-word, AI-generated versions use different phrasing while maintaining the same meaning, allowing them to bypass plagiarism detection tools. This creates a particularly insidious problem in the AI-first search landscape: your content feeds AI models that then generate competing answers without proper attribution. When Google AI Overviews and other AI search systems synthesize information, they may cite these AI-generated clones more frequently than your original work, diluting your visibility and authority. The fundamental issue is that semantic similarity matters more than exact duplication in AI systems—meaning your unique insights and research get recycled into countless variations that all compete for the same citations and traffic.
| Factor | Classic Duplicate Content | AI Content Cannibalization |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Copied word-for-word from your page | Rewritten or paraphrased by AI tools into new variations |
| Detection | Easy to spot with plagiarism filters or manual checks | Much harder to detect because wording is unique but semantically similar |
| Appearance | Looks like a direct copy or mirror site | Appears “original” to search engines and users even though it’s based on your work |
| SEO Impact | Usually suppressed in SERPs once flagged as duplicate | Dilutes topical authority, confuses search engines, and can outrank your original page |
| Remedy | File DMCA takedown or request removal | Much harder to act on; often requires strengthening your own content instead of removal |
Traditional duplicate content has been a known SEO issue for years—it’s visible, trackable, and relatively straightforward to resolve through takedowns or canonicalization. AI content cannibalization is fundamentally different and more insidious. The rewritten versions don’t look like direct copies, so plagiarism checkers rarely flag them. To search engines, the AI-generated page can appear just as relevant as your original, which splits ranking signals and erodes your authority. In practice, this means your site may quietly lose traffic and rankings without an obvious culprit. Unless you actively monitor search results and analyze semantic similarity, AI cannibalization often remains invisible until significant damage has already occurred.
AI content cannibalization damages your search visibility through multiple mechanisms:
SERP Flooding: Search results fill with pages repeating your idea in new words. This makes your original less visible and forces users to choose between multiple similar results, none of which clearly stands out as the authoritative source. When Google displays multiple variations of the same concept, your original loses prominence.
Topical Confusion: Google cannot easily determine who holds the true authority on a topic. The semantic weight is spread across multiple copies, making it harder for search engines to identify which page deserves the top ranking. This confusion weakens all competing pages, including your original.
Click Leakage: Rewritten pages capture traffic that should go to your original. They look new to users and answer the query, but the source is not you. A user searching for “best SEO tools” might click on an AI-rewritten version instead of your original comparison, costing you traffic and engagement metrics.
AI Overviews Erosion: Google AI Overviews use large language models trained on recycled content. Your unique phrasing loses attribution as AI systems cite semantically similar clones more frequently than your original work. This means your content feeds AI systems without receiving proper credit or traffic.
Example: If your original article states “Semrush is strong for audits. Ahrefs is strong for backlinks,” an AI system might rewrite this as “Ahrefs excels at link analysis. Semrush performs better for technical audits.” The meaning is identical, both are indexed, and the rewritten version may even outrank your original due to stronger domain authority on the copying site.
Identifying AI content cannibalization requires a multi-layered approach:
Use Semantic Similarity Tools: Embedding models and clustering algorithms can detect rephrased duplicates that plagiarism checkers miss. These tools analyze semantic meaning rather than exact text matching, revealing content that conveys the same information in different words. Tools like Semrush and Similarweb offer semantic analysis capabilities specifically designed for this purpose.
Track Your Top Pages in Google Search Console: Monitor your highest-performing pages for sudden traffic drops without corresponding link loss. If a page that consistently drove traffic suddenly experiences a significant decline, it may indicate that AI-generated variations are cannibalizing its visibility. Use the Performance tab to filter by specific pages and watch for unexplained changes.
Read AI Overview Results for Your Queries: Search for your target keywords in Google AI Overviews and Perplexity. If you see phrasing very similar to yours without proper citation or attribution, that’s a signal that your content is being scraped and rewritten. Pay attention to whether your brand is mentioned or if the AI system is citing competitors instead.
Set Alerts for Scraped RSS Feeds: Many AI systems train from scraped syndication feeds. Monitor your RSS feed usage and set up alerts for unauthorized scraping. Tools like Google Alerts and specialized feed monitoring services can help you track where your content is being distributed and potentially reused without permission.
Defending your content requires a proactive, multi-faceted strategy:
Publish Assets AI Cannot Spin: Create content that AI systems cannot easily replicate—original data tables, survey results, proprietary research, interactive calculators, and custom tools. While AI excels at generating generic text, it cannot fabricate fresh data or unique interactive experiences. These defensible assets become your moat against cannibalization and give users a reason to visit your original source.
Coin Original Terms and Use Them Consistently: If you introduce a distinctive phrase like “AI content cannibalization” and use it consistently throughout your content ecosystem, copies will echo it. This ties authority back to you as the originator. When AI systems cite this term, they’re reinforcing your brand as the source. Develop unique terminology for your key concepts and own that language space.
Add Schema Markup: Implement FAQ, HowTo, and Article schema markup on your pages. Structured data guides Google on source authority and helps AI systems understand your content’s purpose and credibility. This makes it easier for search engines to attribute content correctly and prioritize your original over copies.
Update Your Content Often: Search engines reward freshness, and AI copies tend to freeze after their initial publication. By regularly updating your content with new data, fresh examples, and current insights, you signal that your page is the living, authoritative source. This freshness signal helps distinguish your original from static AI-generated copies.
Watermark Your Visuals and Data: Add subtle watermarks to charts, infographics, and proprietary data visualizations. While not foolproof, watermarks prove authorship in disputes and make it harder for others to claim your work as their own. Include copyright notices and attribution requirements in your data presentations.

AI citation tracking is the practice of monitoring where, how, and why your brand’s content is mentioned as a source in AI-generated responses across tools like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI search platforms. This represents a fundamental shift from traditional SEO, where you tracked keyword rankings and backlinks. In AI-first search, you’re now competing to be cited, synthesized, and surfaced by language models rather than competing for fixed positions on a search results page.
Citation tracking differs from traditional SEO visibility in crucial ways. While traditional SEO measures your ranking position for specific keywords, citation tracking measures how AI systems choose to reference your content when generating answers. A citation in an AI response may not drive immediate traffic, but it signals your content’s influence and authority in a topic area. Publishers are increasingly using citation tracking to understand visibility gaps, identify which content gets cited most frequently, and measure their influence in AI-generated answers. Tools like Semrush, Similarweb, and specialized AI monitoring platforms now offer citation tracking capabilities, allowing you to see which of your pages appear in AI responses and how often they’re cited compared to competitors. This data helps you understand what content resonates with AI systems and informs your content strategy for the AI-first era.
Google is gradually developing semantic deduplication systems designed to recognize when content is meaningfully the same, even if it has been rewritten. These systems aim to identify semantically equivalent content and consolidate rankings around the original source. However, the critical challenge is speed: AI-generated content is multiplying far faster than Google’s filters are evolving. By the time semantic deduplication systems mature, thousands of new AI-generated variations will have already been created and indexed.
The winners in this landscape will be publishers who own their niche through proprietary data and research, distinctive formats and frameworks, and unique first-party insights that AI cannot easily synthesize. These publishers create defensible moats that AI systems cannot replicate. They coin original terminology, publish exclusive data, and build genuine expertise that becomes impossible to copy. The losers will be those relying on generic, text-only content with no defensible advantage. As AI accelerates content production, originality, expertise, and brand authority become the deciding factors that separate sites that grow from those that disappear. The future belongs to publishers who understand that in an AI-first world, unique value and authentic expertise are the only sustainable competitive advantages. Content that can be easily rewritten and repurposed will become commoditized, while content backed by original research, proprietary data, and genuine authority will command premium visibility in both traditional search and AI-generated answers.
AI content cannibalization occurs when artificial intelligence systems scrape and rewrite your original content into semantically similar variations that compete with your original pages in search results and AI-generated answers. Unlike traditional duplicate content that copies text word-for-word, AI-generated versions use different phrasing while maintaining the same meaning, allowing them to bypass plagiarism detection tools.
AI cannibalization involves rewritten content that passes plagiarism checks but still dilutes authority, while duplicate content is exact copies that are easier to detect and suppress. AI-generated pages appear 'original' to search engines even though they're based on your work, making them much harder to identify and remedy than traditional duplicates.
It causes SERP flooding (multiple similar results compete), topical confusion (search engines can't determine authority), click leakage (traffic goes to AI-generated copies), and reduces your visibility in AI Overviews. Your content feeds AI models that then generate competing answers without proper attribution, splitting ranking signals and eroding your authority.
Use semantic similarity tools and embedding models to detect rephrased duplicates, monitor Google Search Console for unexplained traffic drops, check AI Overview results for unattributed phrasing similar to yours, and set alerts for scraped RSS feeds. Tools like Semrush and Similarweb offer semantic analysis capabilities specifically designed for this purpose.
Publish proprietary data and original insights AI can't easily replicate, coin unique terms and use them consistently, add schema markup (FAQ, HowTo, Article), update content frequently to signal freshness, and watermark visuals and data. These defensible assets create a moat against cannibalization and give users a reason to visit your original source.
Citation tracking helps you monitor where your content appears in AI-generated responses, understand your visibility in AI systems, and identify when AI systems cite competitors instead of you. This data helps you understand what content resonates with AI systems and informs your strategy for the AI-first era.
Google is developing semantic deduplication systems to recognize when content is meaningfully the same, even if rewritten. However, AI content generation is multiplying faster than filters evolve. The best defense is creating defensible, original content that AI systems cannot easily replicate.
It highlights the importance of strategic content distribution across multiple channels and ensuring your original content gets cited and attributed in AI systems. Publishers must now compete to be cited by AI systems rather than just ranking in traditional search, making content quality and originality more critical than ever.
Protect your brand visibility in AI-powered search. Track how AI systems cite your content across Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and more. Understand where your content appears in AI-generated answers and ensure proper attribution.

Learn what content cannibalization in AI search means, how it affects your brand visibility in AI answers, and why monitoring your content overlap matters for A...

Learn how to identify and fix keyword cannibalization issues affecting your visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Discover conso...
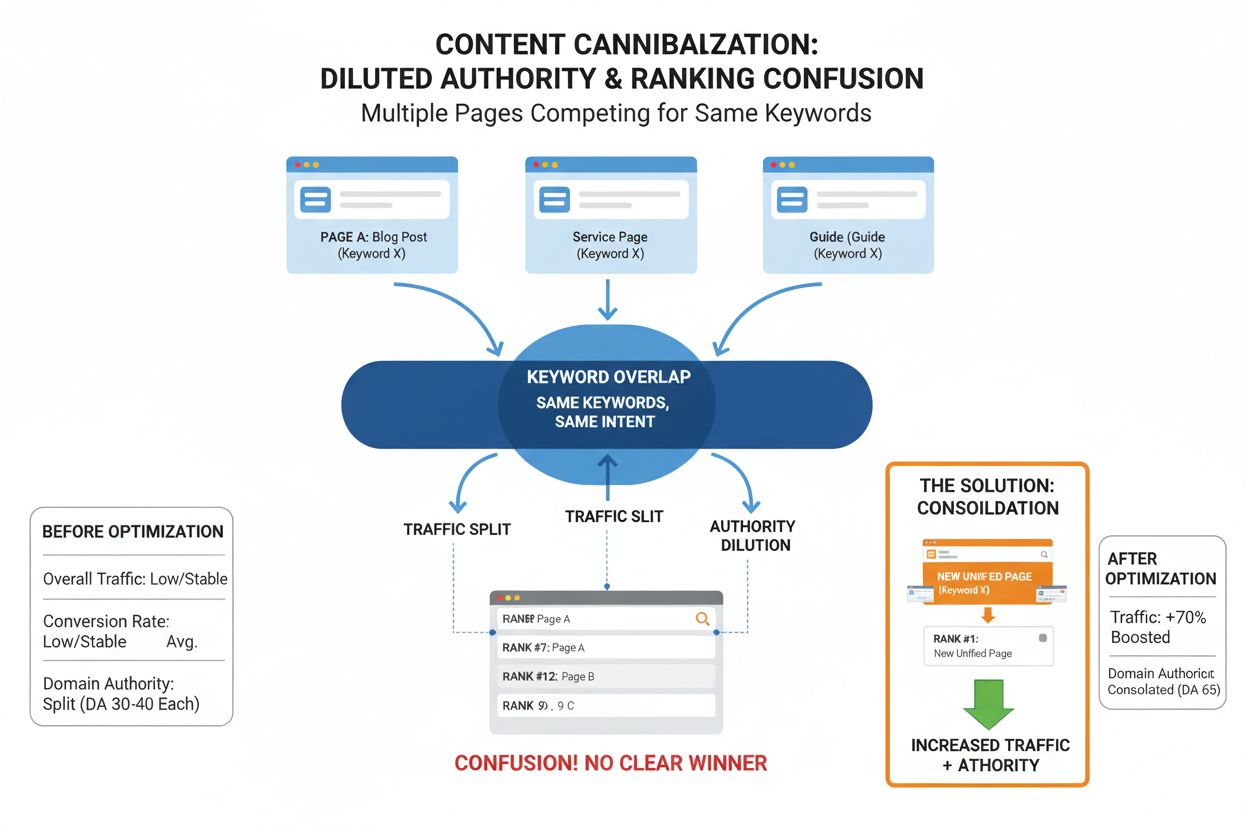
Content cannibalization is when multiple website pages compete for the same keywords, diluting authority and rankings. Learn to identify and fix this critical S...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.