AI Content Freshness Factor: How Recency Impacts AI Model Citations
Understand how AI models prioritize content freshness. Learn citation patterns from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, industry variations, and strat...

AI Content Freshness Decay refers to the systematic reduction in a piece of content’s relevance score within AI retrieval systems as time passes since its last update. Unlike traditional search engines that apply relatively static freshness penalties, AI systems employ dynamic temporal decay models that more aggressively deprioritize older content. Over 70% of pages cited by ChatGPT were updated within the past year, while over 30% of AI citations go to content refreshed in the last three months. This fundamental shift means that even high-quality, authoritative content loses competitive advantage in AI-driven search results if it isn’t regularly updated.
AI Content Freshness Decay refers to the systematic reduction in a piece of content's relevance score within AI retrieval systems as time passes since its last update. Unlike traditional search engines that apply relatively static freshness penalties, AI systems employ dynamic temporal decay models that more aggressively deprioritize older content. Over 70% of pages cited by ChatGPT were updated within the past year, while over 30% of AI citations go to content refreshed in the last three months. This fundamental shift means that even high-quality, authoritative content loses competitive advantage in AI-driven search results if it isn't regularly updated.
AI Content Freshness Decay refers to the systematic reduction in a piece of content’s relevance score within AI retrieval systems as time passes since its last update. Unlike traditional search engines that apply relatively static freshness penalties, AI systems employ dynamic temporal decay models that more aggressively deprioritize older content, particularly for topics where recency matters. This distinction is critical because AI language models are trained on data with knowledge cutoff dates, and they actively seek to supplement this training data with current information through retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) processes. When you publish content, it enters an AI system’s consideration set with maximum freshness value, but this value decreases exponentially or logarithmically depending on the system’s decay function. The impact on your content’s visibility is substantial: research shows that over 70% of pages cited by ChatGPT were updated within the past year, while over 30% of AI citations go to content refreshed in the last three months. This means that even high-quality, authoritative content loses competitive advantage in AI-driven search results if it isn’t regularly updated, fundamentally changing how content marketers must approach their refresh strategies.
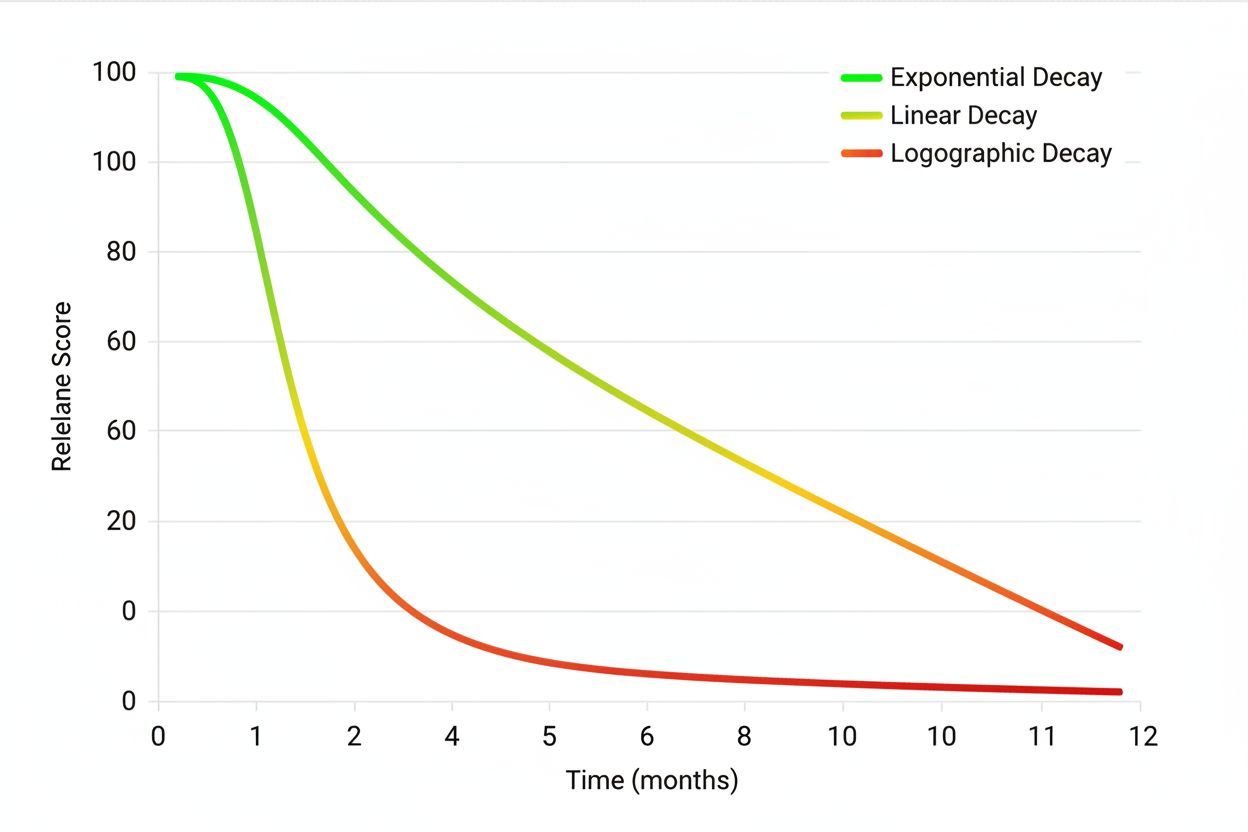
AI systems calculate freshness decay using mathematical functions that model how content value diminishes over time, with exponential decay, linear decay, and logarithmic decay being the three primary models employed across different platforms. Exponential decay functions reduce freshness scores most aggressively in the early periods after publication, then level off—this model assumes that the most recent information is disproportionately valuable. Linear decay applies a consistent penalty per unit of time, treating a six-month-old article the same regardless of whether it’s competing against a one-month-old or two-year-old piece. Logarithmic decay, conversely, applies steeper penalties initially but gradually reduces the penalty rate, balancing the importance of recency with the recognition that some content maintains value over longer periods. The freshness score itself is typically calculated by combining the last update timestamp with the content age and applying a recency bias multiplier that varies by topic and query type. Here’s how AI systems differ from traditional search in their approach to these factors:
| Factor | Traditional Search | AI Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Last Update | Moderate importance; signals quality | Critical; directly impacts retrieval ranking |
| Content Age | Soft signal; older content can rank if authoritative | Hard penalty; exponential decay applied regardless of authority |
| Recency Bias | Query-dependent (QDF applies selectively) | Always active; Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) applies broadly |
| Update Frequency | Occasional updates sufficient | Continuous updates expected; frequency itself becomes a ranking signal |
The decay rate itself is influenced by multiple factors including topic category (news and technology decay faster than evergreen topics), query intent (informational queries show less decay sensitivity than news queries), and domain authority (established sources may receive slightly slower decay rates, though the effect is minimal). Understanding these mechanics allows you to predict when your content will lose visibility and plan refresh cycles accordingly, rather than treating content updates as optional maintenance tasks.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation systems face a unique challenge called knowledge drift, where the semantic relevance of retrieved documents decreases over time as real-world facts and contexts evolve. When an AI system like ChatGPT or Claude retrieves documents to augment its response, it doesn’t simply rank by freshness alone—it performs temporal clustering, grouping documents by their publication date and treating clusters of recent content differently than isolated older pieces. This temporal clustering helps the system identify which information is currently consensus-driven versus potentially outdated, allowing it to weight recent corroboration more heavily than a single fresh source contradicting older established knowledge. Time-weighted ranking in RAG systems combines semantic similarity scores (how well a document matches the query) with temporal proximity scores, creating a composite ranking where a perfectly relevant document from two years ago might rank below a less semantically perfect document from last week. Integration with knowledge graphs that include temporal metadata—such as when facts were first established, when they were last verified, and when they became obsolete—further refines this process. For content creators, this means that your content’s value in RAG systems depends not just on being fresh, but on being part of a temporal cluster of recent, corroborating sources on the same topic. A single updated article surrounded by older content will decay faster than an article that’s part of an ecosystem of regularly refreshed, related content.
To effectively manage content freshness decay, you need to establish clear freshness score metrics that track how your content’s visibility potential changes over time within AI systems. A freshness score typically combines multiple data points: the days since last update, the update frequency trend (whether you’re updating more or less frequently), the content age relative to competitors, and the citation velocity (how often the content appears in AI-generated responses). Identifying content decay requires monitoring these metrics continuously and establishing baseline performance indicators that show when decay becomes problematic—typically when your content’s appearance in AI citations drops by 20-30% or when newer competitor content begins outranking it consistently. Modern monitoring approaches involve tracking your content’s presence in AI overviews, measuring citation frequency across different AI platforms, and comparing your freshness metrics against direct competitors in your space.
Key metrics for monitoring freshness decay:
These metrics should be reviewed weekly for high-priority content and monthly for evergreen pieces, with alerts triggered when decay accelerates beyond expected rates for your topic category.
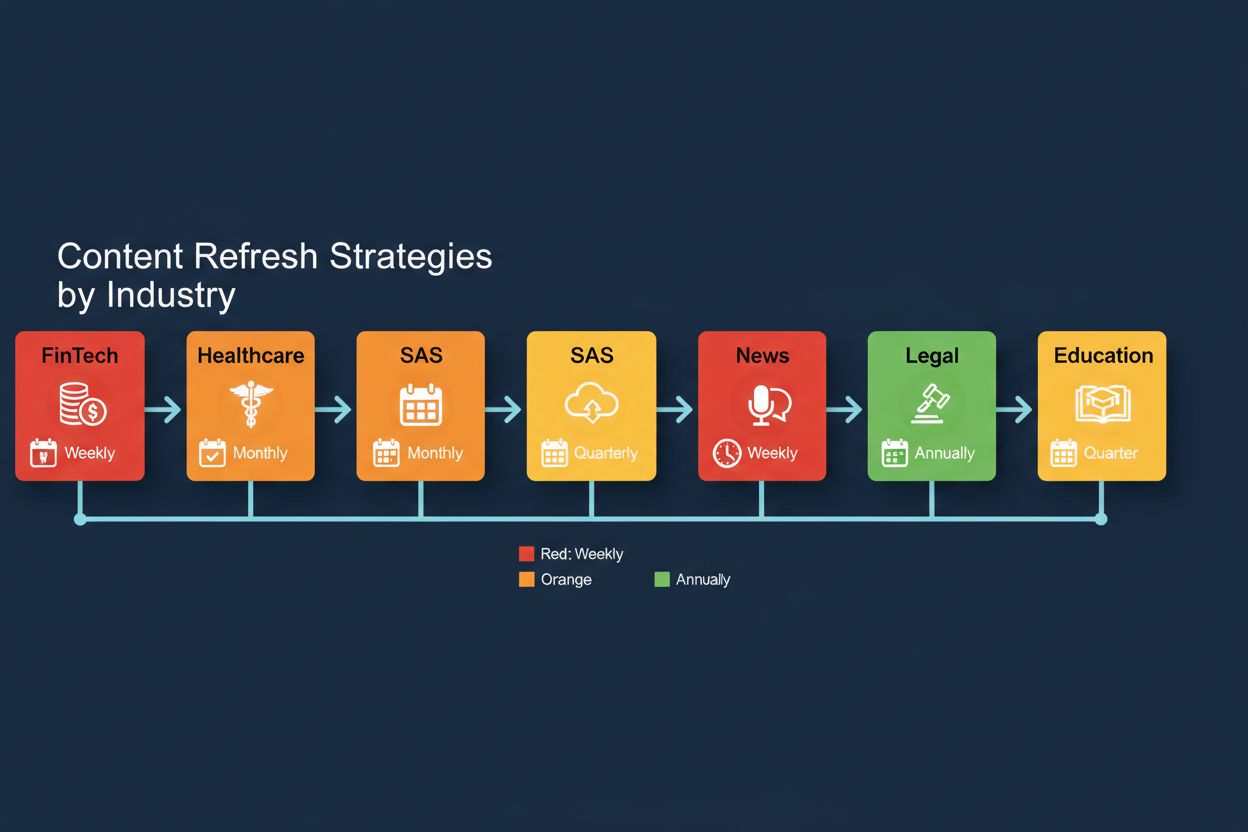
The most effective defense against freshness decay is implementing a strategic content refresh program that goes beyond simple date updates—you need to add substantive new information, update statistics and examples, and revise outdated references with each refresh cycle. Research indicates that healthcare content should be refreshed at least every six months to maintain AI visibility, while technology and news-adjacent topics may require quarterly or even monthly updates to remain competitive. Rather than waiting for content to decay before updating, adopt a continuous optimization approach where you schedule updates based on topic category and competitive landscape: evergreen content might need annual refreshes, while trending topics require monthly attention. Implement schema markup for freshness signals, specifically using dateModified and datePublished structured data that explicitly tells AI systems when content was last updated—this metadata is increasingly important as AI systems parse structured data more effectively than they did previously. Practical examples include adding new case studies to existing articles, updating statistics with the latest year’s data, refreshing expert quotes with current perspectives, and revising methodology sections when best practices evolve. Create a content calendar that maps refresh frequencies by topic cluster, ensuring that related content is updated in temporal clusters rather than in isolation—this creates the corroborating evidence that RAG systems favor. Additionally, consider creating update-focused content such as “2024 Update” sections or “What’s Changed Since Publication” callouts that signal to both AI systems and readers that you’re actively maintaining content currency.
The business impact of freshness decay is substantial and measurable: organizations that fail to maintain content freshness experience significant visibility loss in AI overviews and citations, directly affecting traffic and authority. Consider a B2B SaaS company that published a comprehensive guide to their industry in 2022—initially, this content appeared in nearly 40% of ChatGPT responses to related queries, but by 2024, without updates, its citation frequency dropped to under 15% as newer competitor content accumulated freshness advantages. Recovery from this decay requires not just a single update, but a sustained refresh strategy: the same company that implemented monthly updates to their guide saw citation frequency recover to 35% within three months and exceed 50% within six months, demonstrating that freshness decay is reversible through consistent effort. The visibility loss translates directly to business impact—reduced AI citations mean fewer qualified leads discovering your content through AI-powered search and chat interfaces, which now represent a significant portion of information discovery for many audiences. Healthcare organizations have experienced particularly acute impacts, with outdated medical content losing visibility rapidly and potentially being replaced by more current (though not necessarily more authoritative) sources. The recovery strategy involves three components: immediate comprehensive updates to address the most significant gaps, implementation of a sustainable refresh schedule, and integration of freshness monitoring into your content performance dashboard. Organizations that treat freshness decay as a strategic priority rather than a maintenance task consistently outperform competitors in AI visibility metrics, capturing disproportionate share of AI-driven traffic within their categories.
Managing content freshness decay at scale requires specialized tools and platforms designed specifically for AI monitoring and optimization, as traditional SEO tools were built for a pre-AI search landscape. AmICited.com stands out as a comprehensive solution for monitoring how your content performs across AI systems, providing detailed tracking of citation frequency, freshness decay rates, and competitive positioning within AI-generated responses—this platform gives you the visibility necessary to make data-driven refresh decisions rather than guessing about optimal update frequencies. Beyond monitoring platforms, automation frameworks can streamline the refresh process by identifying which content pieces are approaching decay thresholds and triggering update workflows automatically, ensuring that your team focuses on content quality rather than administrative tracking. Real-time optimization tools integrate with your content management system to automatically update dateModified timestamps, inject freshness signals into structured data, and flag content for human review when decay metrics indicate intervention is needed. Integration with existing systems—your CMS, analytics platform, and SEO tools—is essential for creating a unified view of content performance and freshness metrics. Practical recommendations include: establish a baseline freshness audit of your top 100 content pieces to understand current decay patterns, implement automated monitoring through AmICited.com or similar platforms to track AI citations and decay rates, create a refresh calendar based on topic category and competitive landscape, and integrate freshness metrics into your content performance reviews so that refresh decisions are data-driven rather than arbitrary. By combining monitoring visibility with strategic refresh planning and automation, you transform freshness decay from an invisible threat into a manageable, optimizable component of your AI visibility strategy.
Content freshness decay is the systematic reduction in a piece of content's relevance score within AI retrieval systems as time passes since its last update. AI systems employ dynamic temporal decay models that more aggressively deprioritize older content compared to traditional search engines. This means your content's visibility in AI-generated responses decreases over time unless you actively update it with new information.
Traditional search engines apply relatively static freshness penalties and allow older, authoritative content to maintain rankings for years based on backlinks and domain authority. AI systems, however, use dynamic temporal decay models that continuously reduce content relevance scores regardless of authority. Research shows AI-generated content is 25.7% fresher than organic Google results, and ChatGPT favors sources over a year newer than traditional organic results.
The optimal update frequency depends on your topic category. High-velocity topics like FinTech and SaaS require monthly or weekly updates, healthcare content should be refreshed at least every six months, while evergreen educational content may only need annual updates. Research indicates that over 30% of AI citations go to content updated in the last three months, suggesting quarterly updates as a baseline for most competitive topics.
AI systems use three primary decay models: exponential decay (aggressive early penalties that level off), linear decay (consistent penalties per unit of time), and logarithmic decay (steep initial penalties that gradually reduce). These functions combine the last update timestamp with content age and apply a recency bias multiplier that varies by topic and query type. The decay rate is influenced by topic category, query intent, and domain authority.
Yes, freshness decay is reversible through consistent updates. Organizations that implement comprehensive updates followed by sustained refresh schedules can recover lost visibility within weeks. For example, a company that experienced citation frequency drops from 40% to 15% recovered to 35% within three months and exceeded 50% within six months through monthly updates and freshness optimization.
Schema markup, particularly the `dateModified` and `datePublished` structured data fields, explicitly tells AI systems when content was last updated. This metadata is increasingly important as AI systems parse structured data more effectively than they did previously. Implementing proper schema markup ensures that your freshness signals are clearly communicated to AI retrieval systems.
AmICited.com provides comprehensive monitoring of how your content performs across AI systems, tracking citation frequency, freshness decay rates, and competitive positioning within AI-generated responses. This platform gives you the visibility necessary to make data-driven refresh decisions, identify which content pieces are approaching decay thresholds, and optimize your update strategy based on actual AI performance metrics.
Key indicators of freshness decay include declining citation frequency in AI responses (month-over-month drops of 20-30%), newer competitor content outranking your pieces consistently, reduced appearance in AI overviews despite maintaining traditional search rankings, and widening freshness gaps compared to competitors. Monitoring these metrics weekly for high-priority content helps you intervene before decay becomes severe.
Track how your content performs in AI-powered search results and identify freshness decay before it impacts your visibility. Get real-time insights into your AI citations and competitive positioning.
Understand how AI models prioritize content freshness. Learn citation patterns from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, industry variations, and strat...
Learn what content decay in AI search means, how it differs from traditional SEO decay, and why AI systems prioritize fresh, authoritative content. Understand t...
Learn how to update content for AI freshness with technical signals, structural changes, and refresh strategies that keep your brand visible in ChatGPT, Perplex...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.