How to License Your Content to AI Companies: Rights, Payments, and Deal Structures
Learn how to license content to AI companies, understand payment structures, licensing rights, and negotiation strategies for maximizing revenue from your creat...

Formal agreements governing how AI systems can use, cite, and display copyrighted content during training, inference, and output generation. These licensing frameworks establish contractual control over AI access to protected works, define permitted uses, and ensure creators receive compensation for their intellectual property.
Formal agreements governing how AI systems can use, cite, and display copyrighted content during training, inference, and output generation. These licensing frameworks establish contractual control over AI access to protected works, define permitted uses, and ensure creators receive compensation for their intellectual property.
AI content licensing refers to formal legal agreements that govern how artificial intelligence systems can access, use, cite, and display copyrighted content during training, inference, and output generation. These agreements represent a fundamental shift from the early era of generative AI development—when companies trained models on copyrighted works without explicit permission—to a structured licensing regime where content creators and rights holders maintain control over their intellectual property. AI content licensing solves the critical problem of unauthorized use by establishing clear contractual frameworks that define what AI systems can do with protected works, under what conditions, and with what compensation to the original creators.
The emergence of AI content licensing addresses a widespread problem that has defined the generative AI era: major AI companies trained their models on billions of copyrighted works—including books, articles, images, and code—without obtaining permission or providing compensation to creators. This unauthorized use has had profound consequences for copyright holders, from individual authors and photographers to major media organizations, who discovered their life’s work was incorporated into AI systems that now compete with their original creations. Licensing is essential because it restores the fundamental copyright principle that creators should control how their work is used and receive fair compensation, while also providing AI companies with legal certainty and access to high-quality training data. The scale of the problem is evident in the dozens of lawsuits filed against AI companies, including class actions by the Authors Guild against OpenAI and Anthropic, and Getty Images’ case against Stability AI—all centered on the question of whether unauthorized training constitutes infringement.
| Aspect | Before Licensing | After Licensing |
|---|---|---|
| Creator Control | Minimal; works used without permission | Full control over usage terms |
| Compensation | None; creators received nothing | Direct payments or royalties |
| Legal Status | Disputed; subject to litigation | Contractually defined and enforceable |
| AI Company Risk | High legal exposure | Reduced liability through agreements |
| Data Quality | Quantity-focused; indiscriminate scraping | Quality-focused; curated licensed content |
AI content licensing agreements take several distinct forms, each governing different uses of copyrighted material:
Training-Only Licenses: Permit AI companies to use copyrighted content exclusively for training machine learning models, with restrictions on how the trained model can be deployed or commercialized. These agreements typically prohibit the AI company from using the licensed content for any purpose beyond model development.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Licenses: Allow AI systems to access and retrieve licensed content in real-time to ground responses and provide citations, without incorporating the content into the model’s weights. RAG licensing has become increasingly popular with publishers because it enables them to control exactly which content appears in AI outputs and receive attribution.
Output-Use Licenses: Specify whether and how copyrighted content can appear in AI-generated outputs, including whether the AI system can generate content similar to or derived from the licensed works. These agreements often include restrictions on commercial use of outputs containing licensed material.
Derivative Work Licenses: Define whether AI systems can create derivative works based on licensed content, such as summaries, translations, or adaptations, and under what conditions those derivatives can be used or distributed.
Effective AI content licensing agreements contain several critical components that protect both creators and AI developers. Scope of use defines precisely what the AI company can do with the content—whether it’s training only, real-time retrieval, output generation, or some combination—and which AI models or products can access the licensed material. Compensation models vary widely, from flat fees and per-use royalties to revenue-sharing arrangements, with major deals ranging from $5 million to $60 million annually depending on content volume and exclusivity. Data retention and deletion clauses specify how long the AI company can store licensed content and whether they must delete it upon contract termination, which is particularly important for creators concerned about perpetual use. Output restrictions limit how licensed content can appear in AI-generated results, including requirements for attribution, prohibitions on commercial use, or restrictions on generating similar content. Audit rights allow creators to verify that AI companies are complying with licensing terms, including the ability to inspect training data, monitor outputs, and review usage logs. Indemnification clauses protect both parties by specifying who bears legal liability if the licensed content infringes third-party rights or if the AI company violates the agreement’s terms.
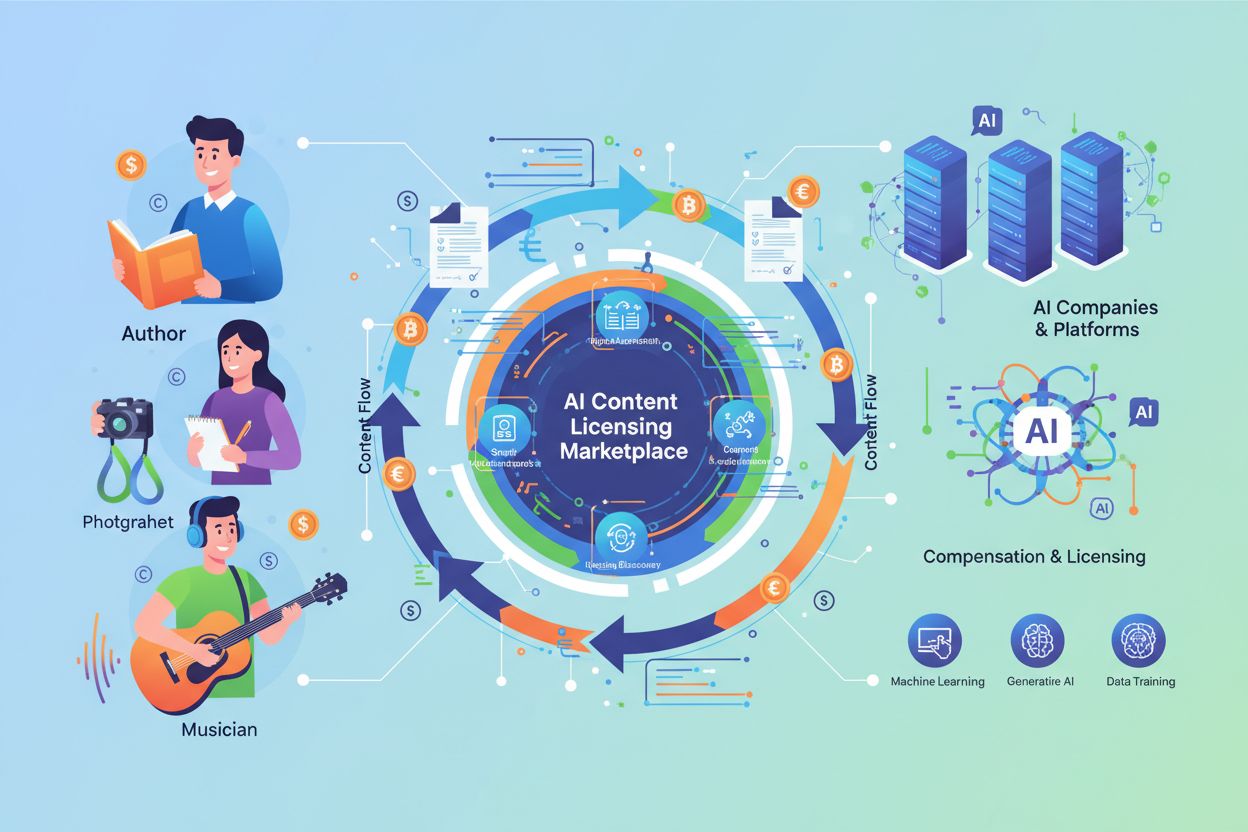
Recognizing the complexity of negotiating individual licensing deals, several platforms have emerged to facilitate AI content licensing at scale. Created by Humans operates as a licensing platform where creators can select specific AI rights for each work, fine-tuning settings for training, retrieval, output use, and derivative works on a title-by-title basis. Calliope Networks connects authors and publishers with AI platforms, enabling creators to earn royalties while providing AI companies access to licensed content. The Dataset Providers Alliance advocates for a free-market approach to licensing, supporting direct negotiations between creators and AI companies while opposing government-mandated collective licensing schemes. Beyond platforms, major licensing deals have reshaped the AI landscape: Reddit secured a $60 million annual deal with Google for content licensing, News Corp licensed content to OpenAI, and Getty Images negotiated licensing agreements after pursuing legal action against Stability AI. These deals demonstrate that collective licensing—where organizations negotiate on behalf of multiple creators—can achieve scale and efficiency, though individual licensing remains important for creators seeking granular control over their work.
Despite the emergence of licensing frameworks, significant challenges remain in implementing AI content licensing at scale. Fair compensation determination is complex because the value of training data is difficult to quantify—how much should a creator receive when their work contributes to a model trained on billions of documents? Scale and fragmentation create practical obstacles, as licensing thousands or millions of individual creators and works requires sophisticated infrastructure and coordination mechanisms that don’t yet fully exist. Enforcement mechanisms remain underdeveloped; verifying that AI companies comply with licensing terms requires technical capabilities to audit training data, monitor outputs, and track usage that are still evolving. International variations in copyright law, fair use doctrine, and AI regulation mean that licensing agreements must account for different legal frameworks across jurisdictions, complicating global licensing strategies. Technical implementation challenges include determining how to prevent licensed content from being used in ways that violate the agreement, how to ensure proper attribution in AI outputs, and how to manage content deletion when contracts expire.
A critical distinction exists between fair use claims and licensing requirements, though this distinction remains contested in ongoing litigation. Fair use is a legal doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism, commentary, education, and research, but courts have not definitively ruled whether training AI models on copyrighted works constitutes fair use. The Getty Images v. Stability AI case, decided by the UK High Court in November 2025, found that Stability AI’s unauthorized copying of millions of Getty Images for training likely constituted infringement, suggesting that fair use may not protect AI training on copyrighted works. Similarly, the Authors Guild’s lawsuits against OpenAI and Anthropic argue that training on copyrighted books without permission is not fair use, while the Bartz v. Anthropic case produced a mixed decision on fair use applicability to generative AI. The key difference is that licensing is a contractual arrangement where creators explicitly grant permission and receive compensation, whereas fair use is a legal defense that permits use without permission under specific circumstances. Even if courts eventually determine that some AI training qualifies as fair use, licensing remains important because it allows creators to opt-in, negotiate terms, and receive direct compensation—rights that fair use doctrine does not provide.
Content creators navigating AI content licensing should adopt several strategic approaches to protect their interests. Licensing decisions should be deliberate and selective: creators need not license all their work to all AI companies, and can choose to license only specific works, to specific companies, or for specific uses (training vs. retrieval vs. output generation). Negotiation strategies should focus on understanding the true value of your content to the AI company—popular, high-quality, or specialized content commands higher licensing fees—and should include clear definitions of scope, compensation, and audit rights. Rights management requires maintaining detailed records of what content has been licensed to whom, under what terms, and for how long, enabling creators to enforce agreements and prevent unauthorized use. Title-by-title licensing options offered by platforms like Created by Humans allow creators to maintain granular control, licensing some works while opting out of AI use for others, which is particularly valuable for creators concerned about their work being used to train competitors or being altered in ways they don’t approve of. Creators should also consider whether licensing agreements include provisions for future compensation if the AI company generates significant revenue from products trained on their content.

The regulatory and technological landscape for AI content licensing is rapidly evolving. The EU AI Act, which entered into force in 2024, requires AI companies to comply with copyright law and obtain authorization from rights holders before using copyrighted content, effectively mandating licensing for EU-based AI development and creating pressure for similar requirements globally. The US Copyright Office has issued guidance indicating that using copyrighted works to train AI models may constitute prima facie infringement, shifting the burden toward AI companies to demonstrate fair use or obtain licenses. Emerging standards for licensing agreements are developing through industry initiatives and legal precedent, with organizations like the Dataset Providers Alliance and Copyright Alliance working to establish best practices for compensation, scope, and enforcement. Technological solutions are advancing to address enforcement challenges, including blockchain-based licensing registries, automated attribution systems that track licensed content in AI outputs, and technical mechanisms that prevent licensed content from being used in unauthorized ways. As these regulatory, contractual, and technical frameworks mature, AI content licensing is likely to become the standard practice rather than the exception, fundamentally reshaping how AI companies access training data and how creators participate in and benefit from the AI economy.
Fair use is a legal doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like criticism and education, but courts have not definitively ruled whether training AI models qualifies as fair use. AI content licensing is a contractual arrangement where creators explicitly grant permission and receive compensation. Licensing gives creators control and direct compensation, while fair use is a legal defense that permits use without permission under specific circumstances.
Compensation varies widely depending on content type, volume, exclusivity, and the AI company's revenue model. Major deals range from $5 million to $60 million annually. Licensing platforms use econometric models to recommend pricing based on usage and market factors. Individual creators typically receive per-use royalties or flat fees, with amounts varying significantly based on content value and negotiated terms.
Yes, most licensing platforms and agreements support title-by-title licensing decisions. Creators can choose to license specific works, to specific companies, or for specific uses (training vs. retrieval vs. output generation). This granular control allows creators to maintain selective licensing strategies that align with their business interests and creative preferences.
The primary types include: training-only licenses (for model development only), Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) licenses (for real-time content retrieval with citations), output-use licenses (defining how content can appear in AI outputs), and derivative work licenses (permitting AI to create summaries, translations, or adaptations). Each type offers different restrictions and compensation models.
Major licensing deals include: Reddit's $60 million annual agreement with Google, News Corp's partnership with OpenAI, Getty Images' licensing agreements following litigation against Stability AI, and the Associated Press' deal with OpenAI. These deals demonstrate that established content owners can negotiate significant compensation for licensing their works to AI companies.
Essential components include: scope of use (what the AI company can do with content), compensation models (fees, royalties, or revenue-sharing), data retention and deletion clauses, output restrictions (how content can appear in AI results), audit rights (ability to verify compliance), and indemnification clauses (liability allocation). Clear definitions of these elements protect both creators and AI companies.
Yes, several platforms facilitate AI content licensing for individual creators. Created by Humans allows creators to set licensing terms on a title-by-title basis. Calliope Networks connects authors and publishers with AI platforms. The Dataset Providers Alliance advocates for free-market licensing. These platforms aggregate content and handle negotiations, making licensing accessible to creators who might not negotiate directly with major AI companies.
The EU AI Act requires AI companies to comply with copyright law and obtain authorization from rights holders before using copyrighted content. The US Copyright Office has indicated that using copyrighted works to train AI models may constitute prima facie infringement. These regulatory developments are shifting the burden toward AI companies to demonstrate fair use or obtain licenses, making licensing increasingly standard practice.
AmICited tracks how AI systems cite and reference your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Ensure your content licensing agreements are being honored and monitor AI attribution in real-time.
Learn how to license content to AI companies, understand payment structures, licensing rights, and negotiation strategies for maximizing revenue from your creat...
Understand how AI content licensing agreements with OpenAI, Google, and Perplexity determine whether your brand appears in AI-generated answers and search resul...
Explore the evolving landscape of content rights in AI, including copyright protections, fair use doctrine, licensing frameworks, and global regulatory approach...