
What is the AI Dark Funnel? Complete Guide to Hidden Customer Journeys
Understand the AI dark funnel - the invisible part of customer journeys happening in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI search engines. Learn how to monitor and optimi...
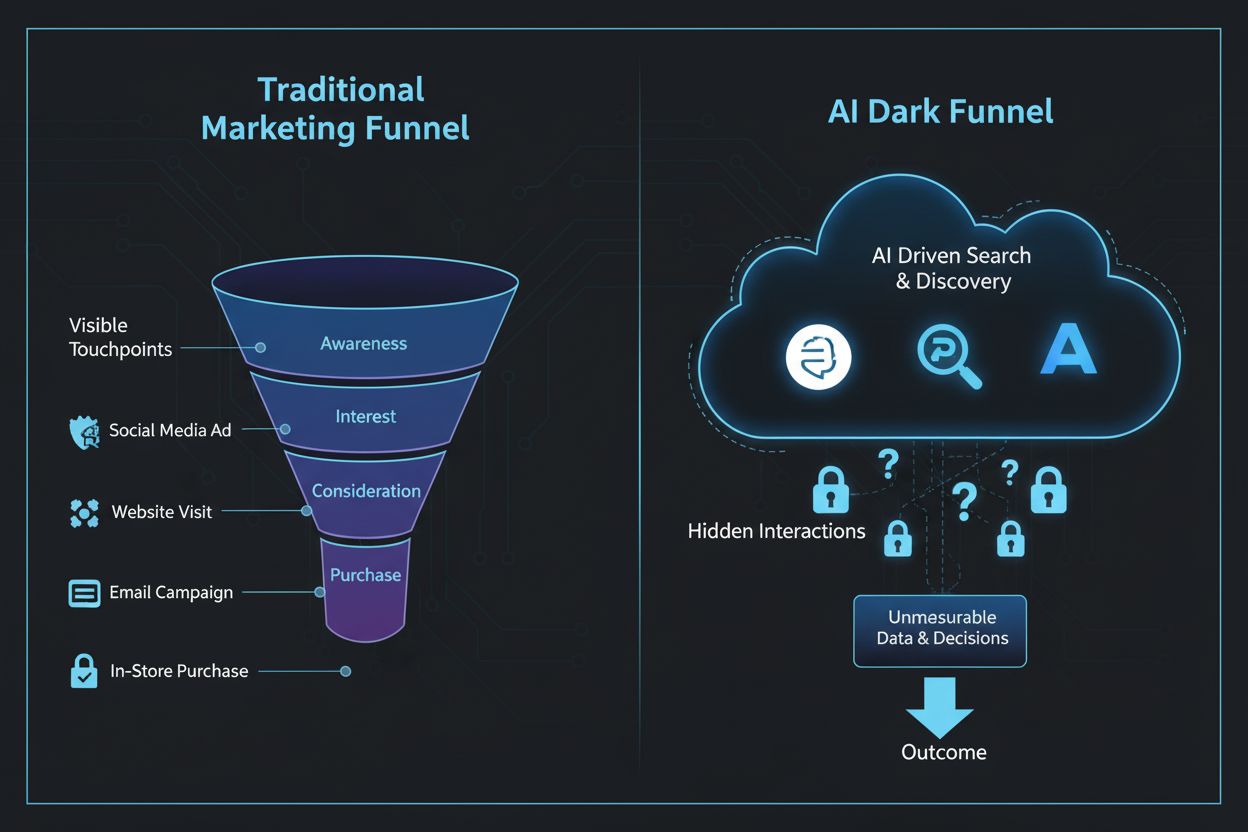
The AI Dark Funnel represents unmeasurable interactions and customer research activities occurring within closed AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google Gemini, where traditional marketing analytics cannot track or attribute conversions. This hidden stage of the buyer journey occurs entirely within proprietary AI environments, creating a significant blind spot in marketing attribution and customer journey visibility.
The AI Dark Funnel represents unmeasurable interactions and customer research activities occurring within closed AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google Gemini, where traditional marketing analytics cannot track or attribute conversions. This hidden stage of the buyer journey occurs entirely within proprietary AI environments, creating a significant blind spot in marketing attribution and customer journey visibility.
The AI Dark Funnel represents the invisible, unmeasurable portion of the customer journey occurring entirely within closed Large Language Model (LLM) systems such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Google Gemini, and Microsoft Copilot. Unlike traditional marketing funnels where customer interactions leave digital footprints through website visits, email opens, and ad clicks, the AI Dark Funnel encompasses research, product comparisons, and purchasing recommendations that happen in proprietary AI environments where marketers have zero visibility or attribution capability. This phenomenon fundamentally challenges the foundational assumptions of modern marketing attribution, as customers increasingly conduct their entire evaluation and decision-making process within AI chat interfaces before ever visiting a brand’s website or engaging with trackable marketing channels. The term “dark” reflects not malicious intent but rather the opacity of these interactions—they occur in environments where traditional analytics tools cannot penetrate, creating a significant blind spot in understanding how customers actually discover, evaluate, and decide to purchase products and services.
The emergence of the AI Dark Funnel represents a seismic shift in how customers conduct research and make purchasing decisions. Research from Knotch Labs reveals that 35% of brand visits are influenced by prior AI interactions, yet traditional analytics can only detect approximately 0.13% of total traffic as direct AI referrals. This massive discrepancy illustrates what researchers call “Trojan Horse traffic”—website visits that result from customers using AI tools as part of their discovery journey, even though the AI interaction itself remains completely invisible to marketing analytics. The phenomenon is not limited to early-stage awareness; customers are using AI systems throughout their entire buyer journey, from initial problem recognition through final purchase consideration. In B2B environments, this challenge is particularly acute, as buying committees often conduct research across multiple stakeholders in private AI conversations, with each committee member potentially having different conversations with different AI systems about the same product category. The scale of this hidden influence is staggering: among the 20,000+ survey respondents in Knotch’s pilot study, approximately 7,100 people had used AI tools before visiting a brand’s website, yet none of these critical touchpoints appeared in traditional web analytics.
While the concept of “dark funnel” has existed in marketing for years—referring to untrackable touchpoints like word-of-mouth, private messaging, and offline conversations—the AI Dark Funnel represents a fundamentally different challenge in both scale and nature. Traditional dark funnel activities, such as peer recommendations shared via email or conversations at industry conferences, are at least theoretically observable through surveys, social listening, or customer interviews. The AI Dark Funnel, by contrast, occurs in completely closed environments where even the customer may not fully remember or articulate the specific AI interactions that influenced their decision. The key distinction is that traditional dark funnel touchpoints are distributed across many channels and platforms, whereas the AI Dark Funnel is concentrated within a small number of dominant LLM platforms that control the entire interaction. Additionally, the speed and scale of AI-driven research is unprecedented; a customer can conduct weeks’ worth of competitive research, read hundreds of product comparisons, and receive personalized recommendations—all within a single ChatGPT conversation that leaves zero trace in marketing systems. The AI Dark Funnel also differs in its influence mechanism: rather than relying on human judgment and peer credibility, AI recommendations carry the weight of algorithmic authority, making them potentially more persuasive than traditional word-of-mouth recommendations.
| Aspect | AI Dark Funnel | Traditional Dark Funnel | Deep Funnel | LLM Direct Referral Traffic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unmeasurable interactions within closed AI systems | Untrackable touchpoints across multiple channels | Later-stage buyer research with intentional evaluation | Direct clicks from LLM platforms to website |
| Primary Platforms | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Gemini | Email, messaging apps, events, word-of-mouth | Comparison sites, demos, case studies | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews |
| Visibility Level | Completely invisible to analytics | Partially observable through surveys/listening | Highly trackable through standard tools | Directly measurable in referral logs |
| Scale of Influence | 35% of brand visits influenced | 15-25% of buyer journey | 40-60% of buyer journey | 0.13% of total traffic |
| Attribution Capability | Zero direct attribution possible | Indirect attribution through surveys | Full attribution through UTM/pixels | Complete attribution available |
| Customer Intent Level | High (active research) | Medium (passive awareness) | Very high (near-purchase) | High (ready to engage) |
| Measurement Approach | Proxy metrics, surveys, AI monitoring tools | Social listening, customer interviews | Standard web analytics, CRM data | Referral source tracking |
| Strategic Priority | Critical (growing exponentially) | Important (stable) | Essential (conversion focus) | Emerging (small but growing) |
Understanding how customers actually use AI systems reveals why the AI Dark Funnel has become such a critical blind spot for marketers. When a customer asks ChatGPT or Perplexity a question like “What is the best project management tool for remote teams under $50/month?”, the AI system synthesizes information from its training data, which includes product websites, review sites, social media discussions, and third-party content. The AI then generates a personalized response that may mention specific brands, compare features, highlight strengths and weaknesses, and provide a recommendation—all based on the customer’s specific criteria and context. Critically, this entire interaction happens within the AI’s proprietary environment; the customer never clicks a link to your website, never fills out a form, never triggers a tracking pixel. From your marketing analytics perspective, this customer simply doesn’t exist until they appear in your CRM weeks later, at which point the attribution trail has gone completely cold. The AI system has effectively become an intermediary between your brand and your customer, controlling the narrative, framing the comparison, and influencing the decision—yet you have no visibility into any of it. This is fundamentally different from traditional search, where a customer might search “project management tools” on Google, click your organic result, and leave a trackable impression. In the AI Dark Funnel, the customer’s research is complete before they ever consider visiting your website.
The collapse of traditional attribution models in the face of the AI Dark Funnel stems from a fundamental architectural mismatch between how marketing analytics were designed and how customers now conduct research. Traditional attribution systems rely on three core mechanisms: tracking pixels placed on websites, cookies stored in browsers, and UTM parameters appended to URLs. None of these mechanisms function within closed AI systems. When a customer interacts with ChatGPT or Claude, they are not visiting a website where you can place a pixel; they are using a proprietary application where no tracking code can execute. The conversation happens on OpenAI’s or Anthropic’s servers, not on your infrastructure. Even if you could somehow observe the conversation, the customer never clicks a link with UTM parameters, so there is no way to attribute their eventual website visit back to the AI interaction. This creates a cascading series of attribution failures: first-touch attribution becomes meaningless because the first touch is invisible; last-touch attribution becomes misleading because it credits the final trackable touchpoint (perhaps a direct visit or a retargeting ad) rather than the actual decision driver (the AI recommendation); and multi-touch attribution becomes impossible because the most critical touchpoint in the journey is completely missing from the data. The result is that marketing teams make budget decisions based on fundamentally incomplete information, often doubling down on channels that appear to be driving conversions when in reality they are simply capturing customers who were already convinced by invisible AI interactions.
The business consequences of the AI Dark Funnel extend far beyond attribution confusion; they directly impact revenue forecasting, budget allocation, and competitive positioning. When 35% of brand visits are influenced by prior AI interactions but your analytics show these visits as “direct traffic” or attribute them to unrelated channels, your understanding of what actually drives revenue becomes fundamentally distorted. Marketing leaders may conclude that their content marketing efforts are underperforming when in reality that content is being synthesized and recommended by AI systems to thousands of potential customers who never visit the website directly. Sales teams may struggle to understand why certain accounts suddenly appear in the pipeline with high purchase intent but no visible engagement history. Finance teams may question marketing’s ROI calculations when they cannot see the connection between marketing spend and customer acquisition. More strategically, the AI Dark Funnel creates a competitive disadvantage for brands that fail to adapt: competitors who understand that their brand narrative is being shaped by AI systems and who optimize their online presence, content, and data for AI synthesis will receive more favorable mentions and recommendations. Brands that continue to optimize exclusively for traditional search and web analytics will find themselves increasingly invisible in the channels where customers are actually making decisions. The AI Dark Funnel also creates a trust and credibility challenge; if your brand is not being mentioned favorably in AI responses, or if AI systems are highlighting competitor advantages, you lose the opportunity to shape the customer’s perception during the most critical research phase.
Recognizing that perfect visibility into the AI Dark Funnel is likely impossible, forward-thinking marketers are shifting their strategy from attempting to track unmeasurable interactions to strategically influencing what happens within them. This approach, known as AI Engine Optimization (AEO), focuses on optimizing the inputs that AI systems use to generate recommendations rather than trying to measure the outputs. The core principle is that if you cannot track what happens inside the AI system, you should focus on ensuring that the information the AI system has about your brand is accurate, comprehensive, authoritative, and easily interpretable by machine learning algorithms. This means implementing structured data using Schema.org markup so AI systems can reliably extract key facts about your products, services, and company. It means creating high-quality, factual content that AI systems will synthesize and cite in their responses. It means actively managing your brand’s presence on review sites, analyst platforms, and third-party sources that AI systems use as training data. It means ensuring consistency across all your online properties so AI systems develop a coherent understanding of your brand. The strategic insight is that while you cannot control what an AI system says about your brand, you can significantly influence it by controlling the quality and consistency of the information available to that system. This represents a fundamental shift from the traditional marketing paradigm of direct customer engagement to an indirect paradigm of information ecosystem management.
While direct measurement of AI Dark Funnel interactions remains impossible, several proxy measurement approaches have emerged that provide directional insights into this hidden stage of the customer journey. AI Share of Voice measures how often your brand is mentioned in AI responses compared to competitors, providing a competitive benchmark for AI visibility. AI Sentiment Analysis tracks whether your brand is mentioned favorably, neutrally, or negatively in AI-generated content, revealing how AI systems are framing your brand relative to alternatives. Trojan Horse Traffic Analysis involves surveying website visitors to ask whether they used AI tools before arriving, allowing you to quantify the indirect influence of AI on your traffic. Correlation Analysis examines whether improvements in your content quality, structured data implementation, or review ratings correlate with increases in overall business metrics like brand search volume, direct traffic, or sales—providing indirect evidence that your AEO efforts are influencing the AI Dark Funnel. Intent Data Integration combines first-party behavioral data with third-party intent signals to identify accounts that are researching your category, even if they haven’t yet visited your website. AI Visibility Monitoring Tools like BrandLight, Semrush Enterprise AIO, and AmICited provide dashboards showing how your brand appears across different AI platforms, what queries trigger your mentions, and how your visibility is trending over time. These tools use a combination of synthetic testing (running specific prompts and observing responses) and observational data (analyzing real user behavior patterns) to provide insights into your AI presence. The key to effective measurement is recognizing that you are not trying to achieve perfect attribution but rather to develop a coherent understanding of how your brand is being represented in AI systems and how that representation correlates with business outcomes.
The AI Dark Funnel is not a static phenomenon but rather a rapidly evolving challenge that will likely intensify as AI systems become more sophisticated and more deeply integrated into customer discovery processes. Currently, most AI Dark Funnel interactions occur in dedicated AI chat applications like ChatGPT and Perplexity, but the trend is clearly toward integration of AI capabilities into primary discovery interfaces—search engines, messaging platforms, smart devices, and vehicle infotainment systems. As AI becomes the default interface for information discovery rather than a specialized tool, the proportion of customer research occurring in unmeasurable environments will likely increase from today’s 35% to potentially 60-70% within the next 2-3 years. This expansion will be driven by generational shifts in search behavior, with younger users increasingly preferring conversational AI interfaces over traditional search results. The sophistication of AI recommendations will also increase, with systems becoming better at understanding nuanced customer needs, providing more personalized recommendations, and potentially even conducting transactions directly without requiring customers to visit brand websites. This creates both a challenge and an opportunity: the challenge is that attribution will become even more difficult, but the opportunity is that brands that master AI Engine Optimization early will establish competitive advantages that are difficult for competitors to overcome. Additionally, we can expect to see the emergence of new measurement methodologies and tools specifically designed for the AI Dark Funnel, potentially including direct partnerships between brands and AI platforms that provide limited visibility into how their brands are being represented. The regulatory landscape may also evolve, with potential requirements for AI systems to provide more transparency about their data sources and recommendation rationale, which could indirectly improve brand visibility into the dark funnel.
For marketing leaders, the AI Dark Funnel represents both an existential threat to traditional attribution models and an opportunity to fundamentally rethink marketing strategy. The threat is clear: if 35% of customer research is happening in unmeasurable environments, then traditional marketing metrics become increasingly unreliable guides for decision-making. Budget allocation based on last-click attribution will systematically underinvest in activities that actually drive AI recommendations (like content quality and third-party validation) while overinvesting in activities that simply capture already-convinced customers. The opportunity, however, is equally significant: brands that recognize this shift and adapt their strategies accordingly will gain competitive advantages. Rather than competing primarily on paid media efficiency and website conversion rates, they will compete on brand authority, content quality, and ecosystem presence—factors that influence how AI systems represent their brands. This requires a fundamental shift in how marketing teams are organized, measured, and resourced. It means elevating the importance of content strategy, brand management, and third-party relationships relative to demand generation and conversion optimization. It means developing new competencies in AI Engine Optimization and learning how to influence systems you cannot directly measure. It means building closer relationships between marketing and product teams, since product quality and customer satisfaction directly influence the reviews and testimonials that AI systems synthesize. Most importantly, it means accepting that perfect attribution is no longer achievable and developing new frameworks for understanding marketing effectiveness that rely on proxy metrics, correlation analysis, and strategic reasoning rather than direct causal attribution.
The traditional dark funnel encompasses untrackable touchpoints like word-of-mouth, private messaging, and offline events. The AI Dark Funnel specifically refers to interactions within closed AI systems like ChatGPT and Perplexity where customers research, compare products, and receive recommendations entirely within proprietary environments. While both are unmeasurable, the AI Dark Funnel is growing exponentially as LLMs become primary discovery channels, making it a distinct and increasingly critical challenge for modern marketers.
Research from Knotch Labs reveals that 35% of brand visits are influenced by AI interactions before customers arrive at websites, though direct AI referral traffic remains only 0.13% of total visits. This 'Trojan Horse traffic' phenomenon indicates that AI systems are shaping customer intent and research decisions at scale, with indirect AI influence being hundreds of times greater than what traditional analytics can detect through referral logs alone.
Traditional analytics rely on tracking pixels, cookies, UTM parameters, and referral URLs—none of which exist within closed AI systems. When customers interact with ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Claude, these conversations happen in proprietary environments where marketers cannot place tracking code or observe user behavior. The AI systems don't expose user interactions or provide attribution data, creating a complete measurement blind spot that existing marketing stacks cannot penetrate.
Major platforms contributing to the AI Dark Funnel include ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Perplexity, Claude, Microsoft Copilot, and integrated AI assistants in search engines and messaging platforms. These closed systems represent the primary environments where customers now conduct product research, compare competitors, and receive AI-generated recommendations before ever visiting a brand's website or engaging with trackable marketing touchpoints.
The AI Dark Funnel distorts attribution models by creating unexplained conversions, inflating 'direct traffic' metrics, and making it impossible to correlate marketing spend with actual customer discovery paths. Marketers may misallocate budgets to campaigns that receive credit for conversions actually driven by favorable AI recommendations. This attribution gap means traditional ROI calculations become unreliable, and marketing teams lose visibility into which strategies actually influence customer decisions at the earliest research stages.
Trojan Horse traffic refers to website visits influenced by prior AI interactions that traditional analytics cannot detect or attribute. A customer might ask ChatGPT for product recommendations, receive favorable mentions of your brand, then visit your website directly—appearing as 'direct traffic' in analytics. The pivotal AI interaction that drove their decision remains completely invisible, representing a hidden stage in the customer journey where AI shapes intent before any trackable touchpoint occurs.
Measurement strategies include: conducting surveys asking customers if they used AI before visiting, monitoring AI Share of Voice across platforms, tracking AI Sentiment in LLM responses, using intent data from third-party providers, implementing AI visibility tools like BrandLight or Semrush Enterprise AIO, and analyzing correlations between content quality improvements and business outcomes. While perfect visibility is impossible, these proxy metrics provide directional insights into dark funnel influence and help brands optimize inputs that AI systems synthesize.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Understand the AI dark funnel - the invisible part of customer journeys happening in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI search engines. Learn how to monitor and optimi...
Master AI visibility for your SaaS company. Learn GEO strategies, structured data optimization, and how to get recommended by ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity. C...

AI Traffic definition: visitors from AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude. Learn how to track, measure, and optimize for AI-driven referrals in 2025.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.