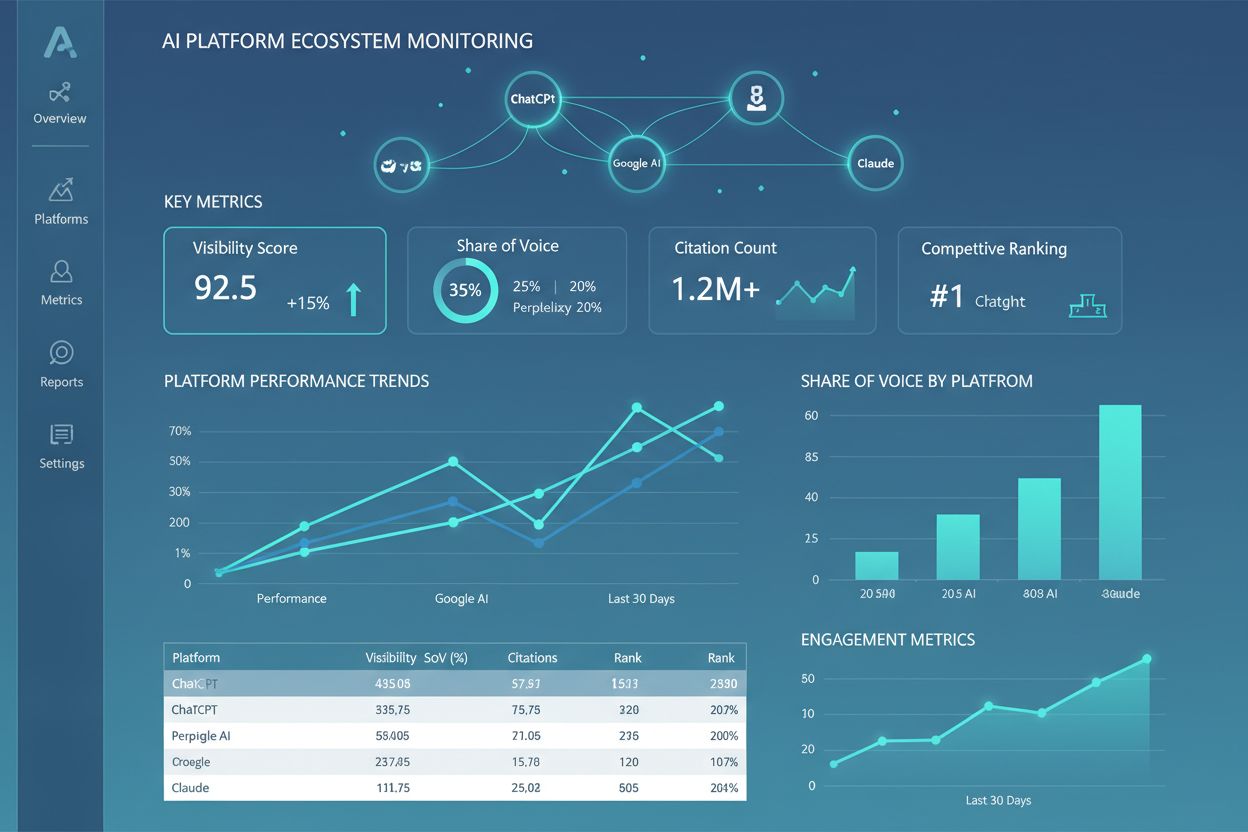
AI Platform Ecosystem
Learn what an AI Platform Ecosystem is, how interconnected AI systems work together, and why managing your brand presence across multiple AI platforms matters f...
AI Ecosystem Integration refers to connecting AI assistants with external applications, services, and platforms through APIs and integrations. This enables AI systems to access real-time data, perform actions across multiple tools, and expand their capabilities beyond standalone functionality, creating seamless workflows that enhance productivity and automation across organizations.
AI Ecosystem Integration refers to connecting AI assistants with external applications, services, and platforms through APIs and integrations. This enables AI systems to access real-time data, perform actions across multiple tools, and expand their capabilities beyond standalone functionality, creating seamless workflows that enhance productivity and automation across organizations.
AI Ecosystem Integration refers to the process of connecting AI assistants and models with external applications, services, and platforms through APIs, webhooks, and other integration mechanisms. Unlike standalone AI tools that operate in isolation, integrated AI systems can access real-time data, perform actions across multiple platforms, and seamlessly interact with business-critical applications like Gmail, Slack, Salesforce, and Notion. This connectivity transforms AI from a conversational tool into an active participant in your business workflows, capable of reading emails, updating spreadsheets, creating calendar events, and managing customer relationships without manual intervention. For modern businesses, AI Ecosystem Integration is essential because it enables automation at scale, reduces manual work, and allows AI to make better decisions based on current, contextual information from across your entire technology stack.
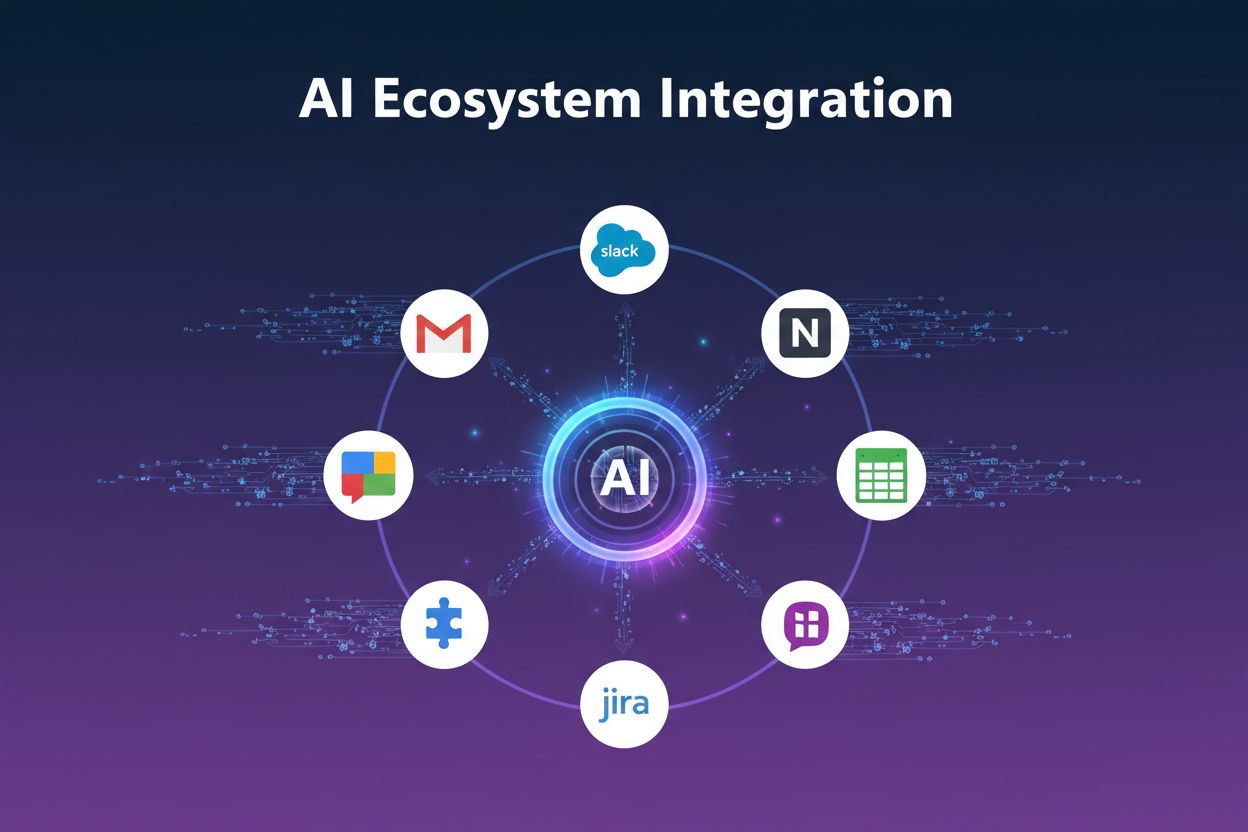
AI Ecosystem Integration relies on several foundational technical components that enable seamless communication between AI systems and external services. The primary mechanism is APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which provide standardized ways for AI systems to request data and trigger actions in external applications. Webhooks enable event-driven integration, allowing external services to notify AI systems when specific events occur, such as a new email arriving or a CRM record being updated. Authentication and authorization mechanisms ensure that AI systems can securely access external services using credentials like API keys, OAuth tokens, or service accounts. Data mapping and transformation layers convert data between different formats and structures, ensuring compatibility between systems. The following table illustrates the different integration approaches and their characteristics:
| Integration Type | Purpose | Real-Time Capability | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REST APIs | Direct HTTP-based communication | Yes | Querying data, triggering actions | Gmail API for email automation |
| Webhooks | Event-triggered notifications | Yes | Reactive workflows | Slack notifications on CRM updates |
| GraphQL APIs | Flexible data querying | Yes | Complex data requirements | Fetching specific fields from multiple resources |
| Message Queues | Asynchronous communication | Partial | High-volume processing | Processing thousands of events |
| Direct Database Connections | Direct data access | Yes | Real-time analytics | Accessing customer data for analysis |
When an AI assistant needs to interact with an external service, it follows a structured process that ensures reliable and accurate execution. Each integration is built as a tool with three core components: a clear description of what the tool does (e.g., “Send an email via Gmail”), input parameters that specify required data fields (such as recipient email, subject line, and message body), and detailed parameter descriptions that help the AI understand the relevance of each field. When executing a task, the AI agent evaluates which tool is best suited for the job—for instance, if it needs to notify a user about an update, it selects the Gmail tool over other communication options. The agent then maps relevant data from its memory or execution context to the tool’s input parameters, such as populating the email recipient and message content from earlier steps in the workflow. Finally, the tool executes by calling the underlying API endpoint of the external service, and the response—whether it’s a confirmation of a sent email or the results of a query—is returned to the AI agent for further processing and decision-making.
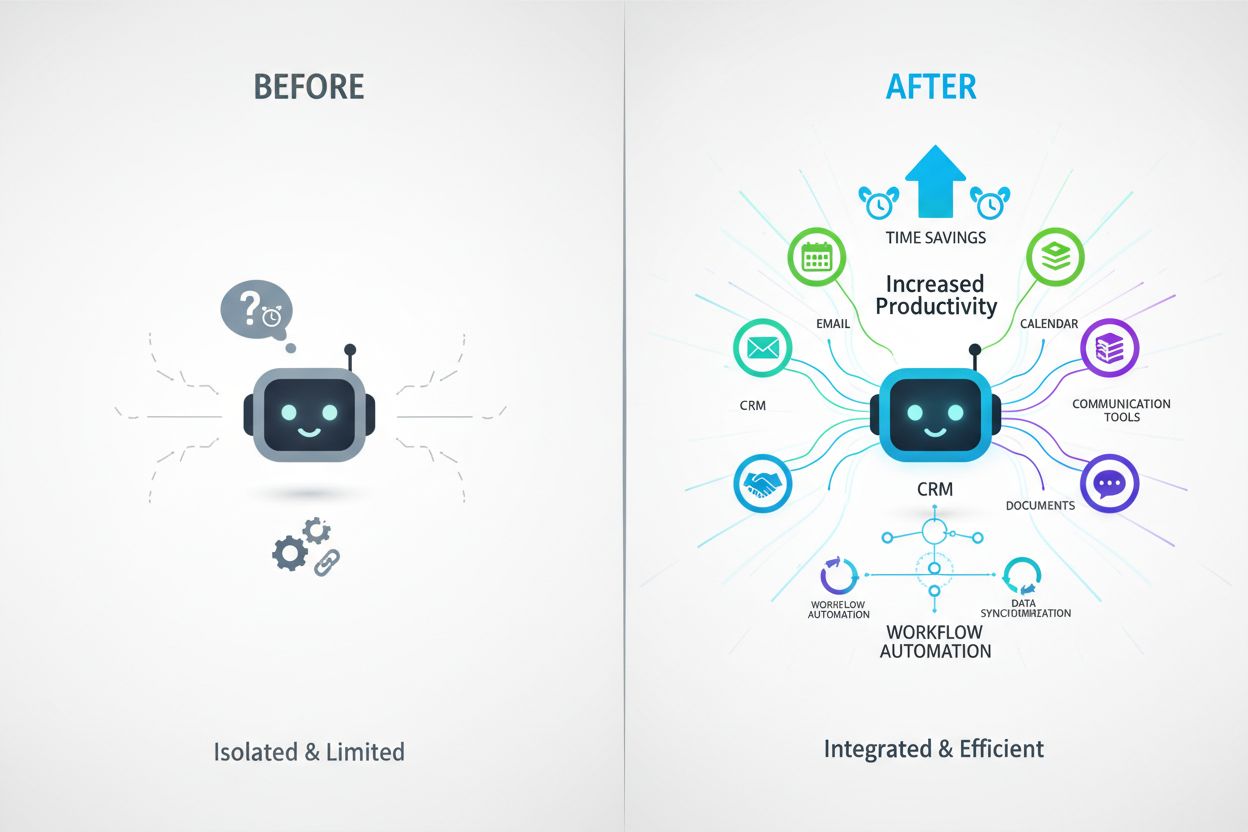
AI Ecosystem Integration delivers substantial business value by transforming how organizations operate and make decisions. The primary advantages include:
These benefits compound when multiple integrations work together, creating a unified intelligent system that operates across your entire business.
AI Ecosystem Integration enables a wide variety of practical applications across different business functions. In sales automation, AI agents can monitor incoming leads, automatically route them to appropriate sales representatives based on predefined criteria, update CRM records with interaction details, and even draft personalized follow-up emails. For customer support, integrated AI can triage incoming tickets by analyzing content and assigning them to the right team, access knowledge bases to provide instant answers, and escalate complex issues to human agents while maintaining conversation context. In content management, AI can monitor document repositories, automatically update published content when source materials change, and synchronize information across multiple platforms. Data analysis and reporting becomes more powerful when AI can access spreadsheets, databases, and analytics platforms to identify trends, generate insights, and create automated reports. Communication workflows benefit from integration as AI can monitor email inboxes, schedule meetings by checking calendar availability, send notifications through Slack or Teams, and maintain conversation history across multiple channels.
While AI Ecosystem Integration offers tremendous benefits, organizations must navigate several technical and operational challenges. API rate limits can restrict how frequently an AI system can call external services, potentially causing delays or requiring sophisticated queuing mechanisms to manage requests. Security and privacy concerns arise because AI systems need access to sensitive business data, requiring robust authentication, encryption, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Compatibility issues emerge when integrating with legacy systems that lack modern APIs or when different services use incompatible data formats. Error handling and fallback mechanisms must be carefully designed because external services can experience downtime, rate limiting, or unexpected responses that could disrupt AI workflows. Data consistency becomes complex when the same information exists in multiple systems and updates must be synchronized across all of them. Additionally, monitoring and observability require specialized tools to track integration performance, identify failures, and understand why specific actions succeeded or failed.
Successful AI Ecosystem Integration requires careful planning and execution following proven best practices. Start with critical workflows rather than attempting to integrate everything at once—identify the processes that would deliver the most value and begin there, then expand gradually. Prioritize security and authentication by using secure credential management, implementing proper access controls, and regularly auditing which systems have access to which data. Implement comprehensive monitoring and alerting to track API usage, identify failures, and receive notifications when integrations experience issues. Test integrations thoroughly in staging environments before deploying to production, including testing error scenarios and edge cases. Document integration flows clearly so that team members understand how systems are connected and can troubleshoot issues effectively. Implement rate limiting and backoff strategies to respect API limits and avoid overwhelming external services. Version your integrations and maintain backward compatibility when possible, allowing you to update external services without breaking your AI workflows.
The landscape of AI Ecosystem Integration is rapidly evolving with several important trends shaping its future. Standardized protocols and frameworks like OpenAPI specifications and the Model Context Protocol (MCP) are emerging to make integrations more interoperable and easier to build. Increased AI autonomy in integration decisions means AI systems will become better at determining which tools to use and when, without explicit human instruction. Enhanced security frameworks will provide better protection for sensitive data flowing between systems, with improved encryption, access controls, and compliance monitoring. Multi-agent orchestration will enable multiple AI agents to work together, each with specialized integrations, coordinating their actions to accomplish complex business objectives. Improved error recovery and resilience mechanisms will make integrations more robust, automatically handling failures and maintaining system stability even when external services experience issues. As these trends mature, AI Ecosystem Integration will become increasingly sophisticated, enabling organizations to build truly intelligent, autonomous systems that operate seamlessly across their entire technology infrastructure.
Standalone AI tools operate in isolation and can only work with information provided directly by users. AI ecosystem integration connects AI assistants to external services, allowing them to access real-time data, perform actions across multiple platforms, and maintain context across different systems. This makes integrated AI significantly more powerful and capable of automating complex workflows.
AI assistants authenticate using secure credentials like API keys, OAuth tokens, or service accounts. These credentials are stored securely and used when the AI needs to access external services. Modern integration platforms implement encryption and access controls to ensure that credentials are protected and that AI systems only access the services they're authorized to use.
Key security risks include unauthorized access to sensitive data, credential exposure, data breaches during transmission, and compliance violations. Organizations must implement proper authentication, encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Additionally, integrations should follow the principle of least privilege, granting AI systems only the minimum permissions needed to perform their tasks.
Yes, well-designed AI systems can manage multiple integrations simultaneously. They can coordinate actions across different services, maintain context across multiple platforms, and handle complex workflows that involve several integrated tools. However, this requires careful design to manage API rate limits, handle errors gracefully, and maintain data consistency across systems.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the primary mechanism enabling AI ecosystem integration. They provide standardized ways for AI systems to request data and trigger actions in external applications. APIs define what operations are available, what data is required, and what responses will be returned, making it possible for AI systems to interact reliably with external services.
Start by identifying your most critical workflows and the services that support them. Prioritize integrations that will deliver the most value and reduce the most manual work. Consider factors like API quality, documentation, security features, and support. Begin with a few key integrations and expand gradually as you gain experience and understand your needs better.
When an integrated service experiences downtime, your AI workflows may fail or produce errors. To handle this, implement error handling and fallback mechanisms that gracefully degrade functionality. You can also implement retry logic with exponential backoff, queue failed requests for later processing, or provide alternative workflows that don't depend on the unavailable service.
Real-time integration processes requests immediately as they occur, enabling instant responses and up-to-date information. Batch processing collects multiple requests and processes them together at scheduled intervals, which is more efficient for high-volume operations but introduces delays. Real-time integration is better for customer-facing workflows, while batch processing works well for reporting and data synchronization tasks.
AmICited tracks how AI assistants like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews mention your brand. Get insights into AI-generated content that references your business and stay informed about your brand's presence in AI responses.

Learn what an AI Platform Ecosystem is, how interconnected AI systems work together, and why managing your brand presence across multiple AI platforms matters f...

Learn about AI shopping cart integration technology that connects AI platforms with e-commerce systems for frictionless shopping. Discover how smart carts use c...

Explore the AI Visibility Ecosystem - the interconnected network of platforms, content, and signals affecting how brands appear in AI-generated answers. Learn a...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.