
Entity SEO for AI Visibility: Building Knowledge Graph Presence
Learn how to build entity visibility in AI search. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity SEO strategies to increase brand presence in C...
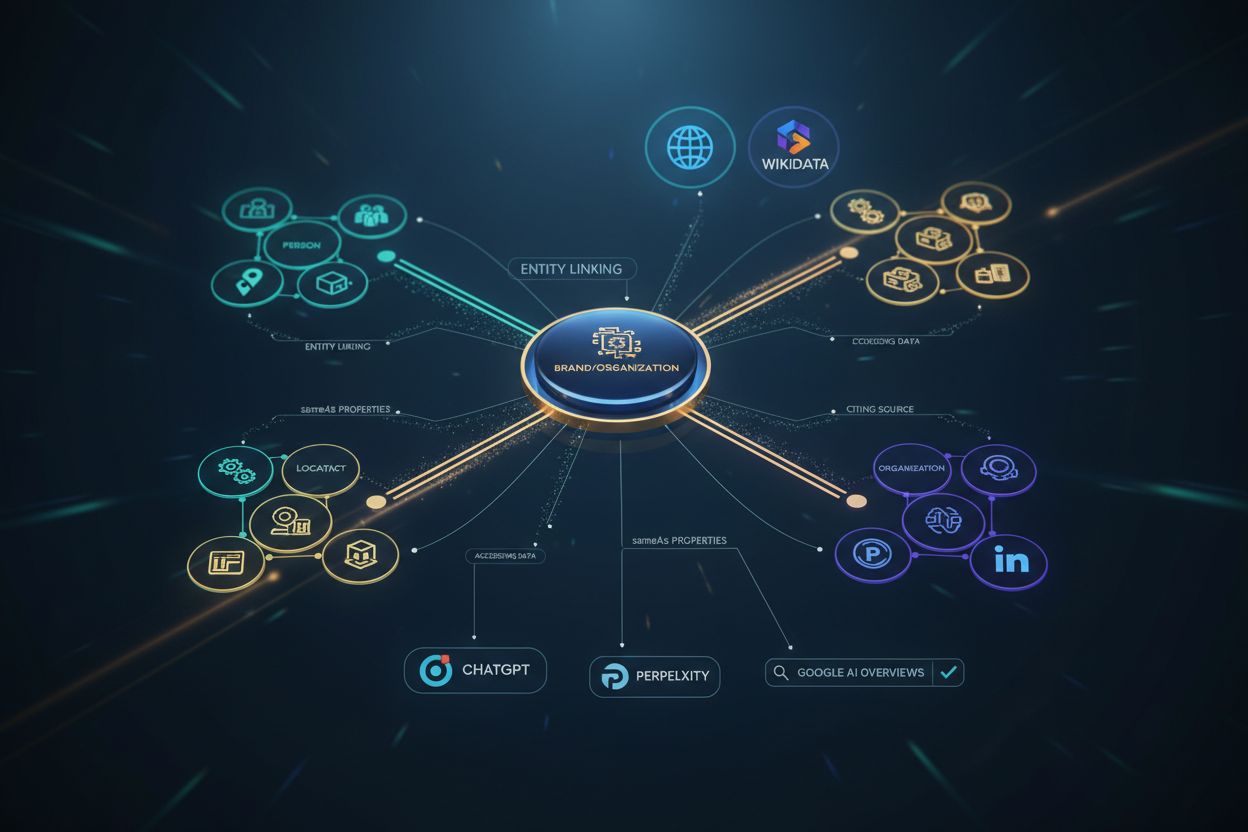
Schema.org structured data that clearly defines entities (people, organizations, products, locations) in machine-readable format, enabling AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews to accurately recognize, understand, and cite your content with greater confidence and authority.
Schema.org structured data that clearly defines entities (people, organizations, products, locations) in machine-readable format, enabling AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews to accurately recognize, understand, and cite your content with greater confidence and authority.
AI Entity Markup is Schema.org structured data that clearly defines entities—such as people, organizations, products, and locations—in a machine-readable format that AI systems can easily recognize and understand. Unlike traditional SEO markup designed primarily for search engines, AI Entity Markup is specifically optimized for how artificial intelligence systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews parse, interpret, and cite web content. This markup transforms ambiguous text into verifiable, structured facts that enable AI systems to confidently extract information and attribute it to authoritative sources. As AI-generated answers increasingly replace traditional search results, implementing proper entity markup has evolved from a nice-to-have optimization into essential infrastructure for brand visibility and credibility in the AI-driven search landscape.

AI systems fundamentally operate as statistical pattern-matching engines that analyze vast quantities of data to generate responses based on probability rather than reasoning. When an AI encounters unstructured text like “John Smith is the CEO of Acme Corp,” the system must infer relationships between tokens without guaranteed verification. However, when that same information is wrapped in Organization schema with a founder property pointing to a Person schema, it becomes a verifiable, machine-readable fact that AI systems can confidently use and cite. Research demonstrates that LLMs grounded in knowledge graphs achieve approximately 300% higher accuracy compared to those relying solely on unstructured data—a dramatic improvement that directly impacts whether your content gets cited in AI-generated responses.
| Aspect | Unstructured Content | Entity Markup |
|---|---|---|
| AI Understanding | Probabilistic guessing | Verified facts |
| Citation Confidence | Low (16% accuracy) | High (54% accuracy) |
| Knowledge Graph Integration | Limited or absent | Full integration |
| AI Citation Likelihood | Lower probability | 30%+ higher visibility |
| Verification Capability | Difficult for AI | Explicit and verifiable |
| Entity Relationship Clarity | Ambiguous | Precisely defined |
Microsoft’s Principal Product Manager Fabrice Canel confirmed at SMX Munich that “Schema markup helps Microsoft’s LLMs understand content,” and Bing’s Copilot specifically uses structured data to interpret web content. This isn’t theoretical—sites with comprehensive structured data see up to 30% higher visibility in AI Overviews, representing the difference between being cited as an authoritative source and being completely invisible to AI systems that increasingly mediate how people discover information.
Not all schema types are created equal for AI citation. While Schema.org includes over 800 types and more than a thousand properties, only a handful directly influence how LLMs interpret and cite your content. Here are the entity types that matter most for AI visibility:
Organization Schema: Defines your company with comprehensive sameAs properties linking to Wikipedia, LinkedIn, Crunchbase, and other authoritative platforms. This establishes your brand as a recognized entity in knowledge graphs and signals credibility to AI systems evaluating source authority.
Person Schema: Establishes author expertise and credibility by creating verifiable author profiles with links to external platforms. When an author’s Person schema is properly implemented with sameAs properties, AI systems can verify expertise across multiple platforms, strengthening E-E-A-T signals.
Article Schema: Includes publication dates, author information, and publisher details—all signals that help AI systems assess content credibility and relevance when deciding what to cite. Article schema with proper author attribution is your credibility passport in the AI search era.
Product Schema: Marks up products with pricing, ratings, descriptions, and availability information. For e-commerce and SaaS companies, Product schema enables AI systems to understand and recommend your offerings when users ask about solutions in your category.
FAQPage Schema: Pre-formats content as question-answer pairs, exactly how AI systems prefer to extract and present information. FAQPage is the AI citation workhorse because it provides ready-made, citable responses that AI systems can confidently pull when answering related queries.
Entity linking is the process of identifying key concepts or “entities” within your content and connecting them to recognized sources such as Wikidata, Wikipedia, Google’s Knowledge Graph, or your organization’s own knowledge graph. This connection is crucial because it helps AI systems understand exactly which entity you’re referring to and how it relates to other concepts in the broader information ecosystem. For example, linking “Bronco” to the Ford Bronco SUV instead of the Bronco horse disambiguates meaning and ensures your content is correctly interpreted by AI systems.
When you implement entity linking through Schema.org markup, you’re essentially building bridges between your content and authoritative knowledge sources. These bridges enable AI systems to traverse relationships and understand context with far greater precision. A car parts retailer writing about “how to replace your filter in your Bronco” becomes semantically connected to entities like “Ford Bronco” and “car filter,” signaling to AI systems that this is authoritative, contextually relevant content worthy of citation. The sameAs property is your primary tool for entity linking—by including URLs to Wikipedia, Wikidata, and other authoritative sources, you’re telling AI systems “this entity is the same as this recognized entity in the knowledge graph.” This cross-platform consistency builds entity authority that AI systems use to verify expertise and determine citation worthiness.
The most effective way to implement AI Entity Markup is using JSON-LD format, which Google explicitly recommends because it separates schema from HTML content, making it easier to implement and maintain at scale. Place your JSON-LD in the <head> section of your page:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Your Company Name",
"url": "https://www.yourcompany.com",
"logo": "https://www.yourcompany.com/logo.png",
"description": "Your company description",
"foundingDate": "2020",
"sameAs": [
"https://www.linkedin.com/company/your-company",
"https://twitter.com/yourcompany",
"https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/your-company",
"https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Your_Company"
],
"contactPoint": {
"@type": "ContactPoint",
"contactType": "customer service",
"email": "support@yourcompany.com"
}
}
The real power of schema comes from connecting related entities using @id properties, which creates a web of relationships that AI systems can traverse to understand context. By referencing the same @id across multiple pages, you build a content knowledge graph that AI systems can use for more sophisticated reasoning. Critical rule: only mark up content that’s actually visible on the page. If users can’t see the information, don’t include it in schema. AI systems cross-reference schema with page content, and discrepancies damage your credibility. This means FAQ answers in schema must appear somewhere on the page, prices must match displayed prices, and author information must be verifiable on your site.
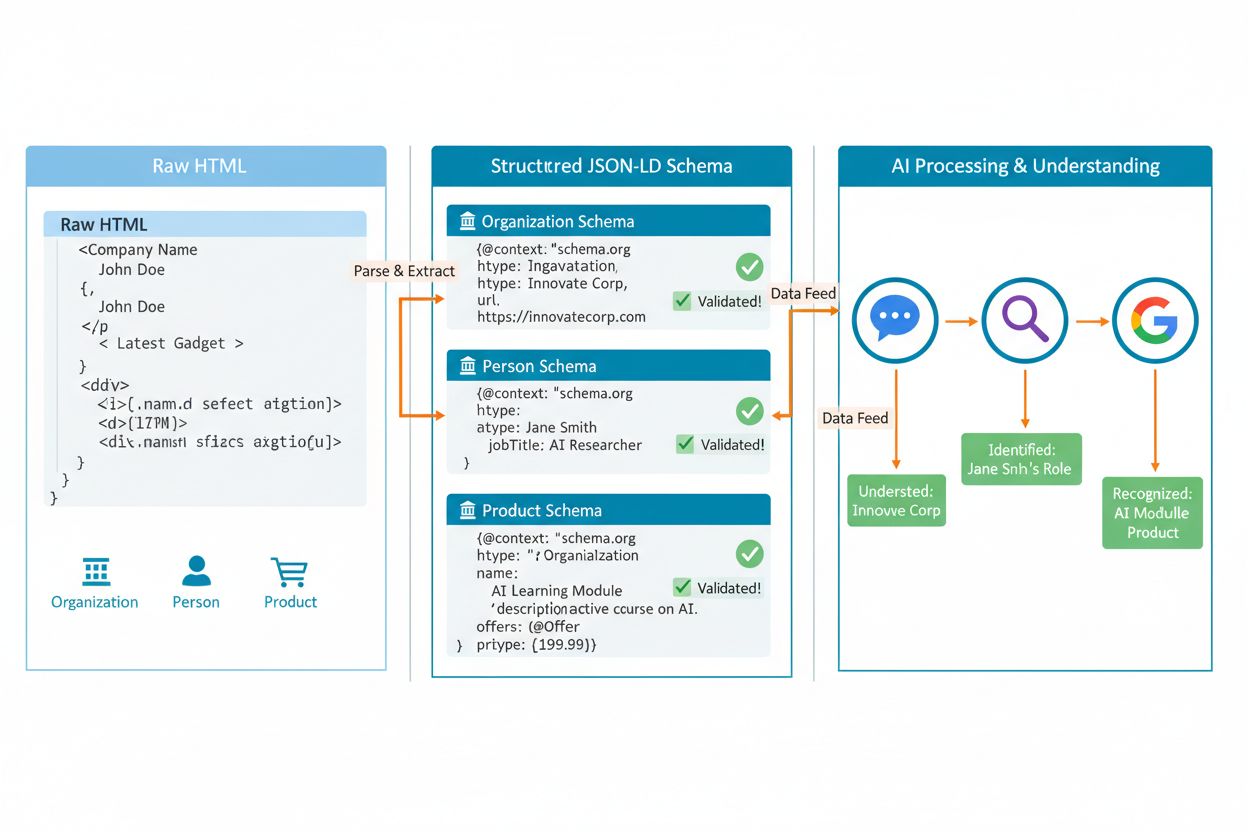
While traditional schema markup was designed primarily to help search engines display rich snippets and improve click-through rates, AI Entity Markup is fundamentally about enabling AI systems to understand, verify, and cite your content with confidence. Traditional SEO markup might help you get a star rating in search results; AI Entity Markup helps you get cited as an authoritative source in AI-generated answers. This distinction matters enormously in a zero-click search world where users see summarized answers from multiple sources combined into a single AI-generated result.
The impact on brand authority is profound. When your brand appears in an AI-generated response, it signals credibility and expertise even when users don’t click through to your site. Being featured in an AI Overview builds awareness and authority at scale, reaching users earlier in their buyer journey during research and exploration phases. Traditional SEO focuses on keywords and rankings; AI Entity Markup focuses on entity relationships and knowledge graph integration. A brand implementing proper entity markup across its website creates a semantic data layer that enables AI systems to understand not just what you say, but who you are, what you stand for, and how you connect to key topics. This clarity strengthens E-E-A-T signals—Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—which determine how AI systems recognize and cite your brand.
Unlike traditional SEO where you can track rankings and clicks, AI citation measurement is still evolving, but several approaches provide reliable insights. The most straightforward method is manual sampling: query ChatGPT, Claude, and Perplexity monthly with questions your target buyers would ask, documenting whether you’re being cited, in what context, and with what sentiment. Google Search Console now includes AI Overview data under the “Web” search type, allowing you to monitor impression patterns and detect visibility shifts. Tools like AmICited.com specifically monitor how AI systems reference your brand across GPTs, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews, providing dedicated tracking for AI citation performance.
Expected results typically appear within 90 days of systematic optimization. Foundation work—implementing Organization schema with sameAs properties and Article schema on key content—can show measurable citation improvements within 4-8 weeks. Authority-building through cross-platform presence and entity linking takes 3-6 months to fully compound. Sites with comprehensive structured data see up to 30% higher visibility in AI Overviews, while proper entity linking drives stronger engagement metrics including improved click-through rates. The ROI extends beyond citations: structured data also improves traditional search visibility through rich snippets, increases CTR by up to 35%, and strengthens overall content discoverability across multiple AI platforms.
The emerging llms.txt standard, introduced by Answer.AI in 2024, proposes a simple text file format for providing AI systems with curated access to your most important content. While adoption remains limited—as of mid-2025, only about 951 domains had published llms.txt files—the specification is elegant and may gain traction as AI systems evolve. However, traditional schema markup remains the proven, widely-supported approach for AI visibility. The broader trend is clear: AI systems are increasingly built on knowledge graphs, and entities and their relationships form the nodes and edges that underpin these systems. Brands that invest now in comprehensive, semantically rich structured data will have significant competitive advantages not just in today’s AI Overviews and chatbots, but across every AI-powered discovery platform that emerges.
The semantic data layer you build through proper entity markup becomes foundational infrastructure for how AI understands and represents your brand for years to come. As of 2025, over 45 million web domains have implemented Schema.org structured data—only about 12.4% of all registered domains. That gap represents a massive opportunity for forward-thinking brands willing to do the technical work. The question isn’t whether AI systems will rely more heavily on structured data in the future; they already do. The question is whether your content will be part of that structured, citable ecosystem or invisible to the AI systems that increasingly mediate how people discover information.
Traditional schema markup was designed primarily for search engines to display rich snippets and improve click-through rates. AI Entity Markup is specifically optimized for how AI systems parse, interpret, and cite content. While traditional markup helps with search visibility, AI Entity Markup helps you get cited as an authoritative source in AI-generated answers and summaries.
Start with Organization schema on your homepage with comprehensive sameAs properties, then Article schema on key content pages. FAQPage schema should be next—it's the most directly useful for AI extraction. After that, add HowTo schema to guides and SoftwareApplication schema to product pages.
Foundation work can show measurable citation improvements within 4-8 weeks. Authority-building through cross-platform presence and entity linking takes 3-6 months to fully compound. Most brands see measurable citation improvements within 90 days of systematic optimization.
Only incorrectly implemented markup harms performance. Google's guidelines are clear: use relevant schema types that match visible content, keep prices and dates accurate, and don't mark up content users can't see. Always validate with Google's Rich Results Test before publishing.
While all major AI systems benefit from structured data, they may use it differently. ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews all prefer content with clear semantic structure, but implementation details vary. Proper entity markup improves visibility across all AI platforms.
Entity markup transforms ambiguous text into verifiable, machine-readable facts that AI systems can confidently extract and cite. LLMs grounded in knowledge graphs achieve 300% higher accuracy compared to those relying on unstructured data. Sites with comprehensive structured data see up to 30% higher visibility in AI Overviews.
Entity markup creates connections between your content and knowledge graphs like Google's Knowledge Graph and Wikidata. These connections enable AI systems to understand entity relationships and context. By implementing proper entity linking through sameAs properties, you integrate your brand into the broader knowledge graph ecosystem.
For most sites, schema markup should be your priority—it's proven and widely supported. llms.txt is still an emerging standard with limited adoption by AI crawlers. If you're a developer-focused company with significant documentation, creating llms.txt might be worthwhile as future-proofing, but don't let it distract from comprehensive schema implementation.
Track your brand mentions across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and other AI systems. Understand how AI systems cite your content and optimize your visibility.

Learn how to build entity visibility in AI search. Master knowledge graph optimization, schema markup, and entity SEO strategies to increase brand presence in C...
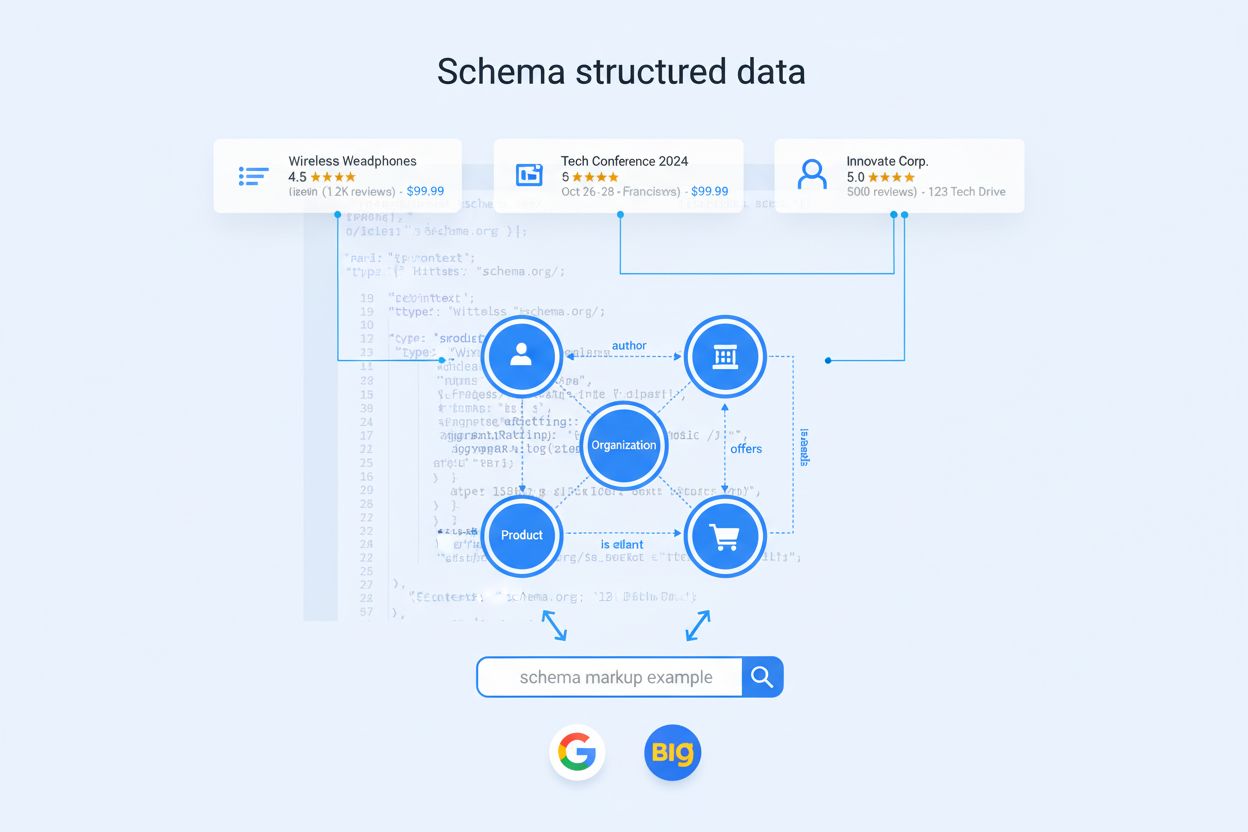
Schema markup is standardized code that helps search engines understand content. Learn how structured data improves SEO, enables rich results, and supports AI s...

Discover which schema markup types boost your visibility in AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini. Learn JSON-LD implementation strategies for ...