Testing Content Formats for AI Citations: Experiment Design
Learn how to test content formats for AI citations using A/B testing methodology. Discover which formats drive the highest AI visibility and citation rates acro...

Structural elements such as tables, lists, clear sections, and hierarchical headings that improve how artificial intelligence systems parse, understand, and extract information from content. AI-friendly formatting increases extraction accuracy, reduces processing costs, and significantly improves the likelihood of content being cited in AI-generated responses.
Structural elements such as tables, lists, clear sections, and hierarchical headings that improve how artificial intelligence systems parse, understand, and extract information from content. AI-friendly formatting increases extraction accuracy, reduces processing costs, and significantly improves the likelihood of content being cited in AI-generated responses.
AI-friendly formatting refers to the strategic organization and presentation of content in ways that optimize how artificial intelligence systems parse, understand, and extract information from text. Unlike human readers who can intuitively navigate poorly structured content through context and visual scanning, AI models process text sequentially through tokenization, breaking content into discrete units that must be interpreted based on their position and relationship to surrounding tokens. This fundamental difference means that the way content is structured directly impacts extraction accuracy, semantic understanding, and the efficiency with which language models can identify and retrieve relevant information. When content is formatted with AI systems in mind—using clear hierarchies, semantic signals, and logical chunking—it dramatically improves how well LLM optimization occurs, enabling models to allocate their computational attention more effectively and produce more accurate, relevant responses. The importance of AI-friendly formatting has grown exponentially as large language models have become central to search, content discovery, and information retrieval, making it a critical consideration for anyone creating content that will be consumed by or processed through AI systems.

Large language models interpret structured content through a sophisticated process that begins with tokenization, where text is converted into numerical representations that the model can process through its neural network layers. The model’s attention mechanisms—the mathematical processes that determine which parts of the input text are most relevant to understanding any given section—work significantly more efficiently when content is properly structured, as clear formatting signals help the model quickly identify relationships between concepts and prioritize important information. Token efficiency becomes a critical factor in this process; when content is well-organized with clear headings, lists, and semantic chunking, the model requires fewer tokens to achieve the same level of understanding, which translates to faster processing, lower computational costs, and more accurate outputs. Structured content provides explicit semantic clarity through formatting cues that help the model distinguish between different types of information—such as definitions, examples, lists, and supporting details—without requiring the model to infer these relationships from context alone. Research in transformer architecture has demonstrated that models achieve higher accuracy rates when processing hierarchically organized information, as the attention mechanism can more effectively track dependencies and relationships across longer passages. Additionally, when content is semantically chunked into logical units, the model’s ability to maintain context and coherence improves substantially, reducing the likelihood of hallucinations or misinterpretations that can occur when processing dense, unstructured text.
| Format Type | AI Parsing Difficulty | Extraction Accuracy | Processing Speed | Token Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Markdown | Low | 95%+ | Fast | Excellent |
| Structured Tables | Very Low | 96%+ | Very Fast | Excellent |
| HTML | Medium | 75-85% | Medium | Good |
| High | 60-70% | Slow | Poor | |
| Plain Text | High | 50-60% | Slow | Poor |
| JSON/Structured Data | Very Low | 98%+ | Very Fast | Excellent |
The foundation of AI-friendly formatting rests on several key structural elements that work together to create content that AI systems can parse with maximum accuracy and efficiency. Heading hierarchies (H1, H2, H3) establish clear information architecture that helps models understand the relative importance and relationships between different sections, functioning as semantic signals that guide the model’s attention mechanisms toward key concepts. Bulleted and numbered lists break complex information into discrete, easily parseable units that reduce cognitive load on the model and improve extraction accuracy by clearly delineating individual points or steps. Tables and structured data provide the most explicit form of semantic organization, allowing models to understand relationships between data points through their spatial arrangement and column/row structure. Emphasis formatting (bold, italics) highlights critical terms and concepts, helping models identify key vocabulary and important distinctions without requiring complex inference. Short paragraphs (typically 2-4 sentences) improve comprehension by limiting the scope of each semantic unit, making it easier for the model to maintain context and accurately interpret relationships between ideas. Semantic chunking—the practice of organizing content into logical, self-contained units that represent complete thoughts or concepts—enables models to process information more effectively by creating natural boundaries that align with how meaning is constructed. Each of these elements serves a specific function in the AI parsing process, and their combined use creates content that is not only more useful to AI systems but also more accessible and valuable to human readers.
Tables represent one of the most powerful tools for AI-friendly formatting, offering a level of structured extraction accuracy that far exceeds unstructured prose. Research has demonstrated that when information is presented in tabular format, AI models achieve extraction accuracy rates exceeding 96%, compared to significantly lower rates when the same information is embedded in paragraph text, making tables the gold standard for content that needs to be reliably processed by AI systems. The effectiveness of tables stems from their explicit representation of relationships and categories; by organizing data into rows and columns with clear headers, tables eliminate ambiguity about how different data points relate to one another, allowing models to understand context and meaning without requiring complex inference. Context preservation is particularly strong in tabular formats because the column headers and row labels provide consistent semantic anchors that help the model maintain understanding of what each data point represents, even when processing large amounts of information. Tables also facilitate more efficient token usage, as the structured format allows models to represent complex relationships in fewer tokens than would be required to describe the same information in prose form. For content creators, this means that any information involving comparisons, specifications, timelines, or categorized data should be presented in table format whenever possible to maximize AI comprehension and citation likelihood. The combination of high accuracy, efficient token usage, and clear context preservation makes structured data in tabular format an essential component of any AI-friendly content strategy.
Markdown has emerged as the optimal formatting language for AI-friendly content creation, offering a unique combination of simplicity, machine-readability, and universal compatibility that makes it ideal for systems designed to be processed by both humans and artificial intelligence. Unlike proprietary formats or complex markup languages, Markdown uses lightweight markup conventions—simple symbols like # for headings, - for lists, and ** for emphasis—that are intuitive for humans to read and write while remaining completely unambiguous for machine parsing. The format’s machine-readable nature means that AI systems can reliably identify and extract structural information without requiring complex parsing logic or format-specific training, making Markdown content more consistently interpretable across different AI platforms and models. Markdown’s future-proof design ensures that content created in this format today will remain accessible and parseable by AI systems for decades to come, unlike proprietary formats that may become obsolete or require migration as technology evolves. The format’s interoperability across platforms—from documentation systems to content management platforms to AI training datasets—means that Markdown content can be easily repurposed, shared, and integrated into various workflows without format conversion or loss of structural information. Compared to HTML, which requires more complex syntax and can include styling information that adds noise to the semantic content, or to plain text, which lacks any structural signals, Markdown strikes an optimal balance between human readability and machine interpretability. For organizations seeking to create content that will perform well across AI systems while remaining accessible to human readers, adopting Markdown as a standard formatting language provides immediate and long-term benefits.
Lists represent a fundamental building block of AI-friendly formatting, dramatically improving both how AI systems comprehend content and how frequently that content gets cited in AI-generated responses. When information is presented as numbered or bulleted lists rather than embedded in paragraph text, AI models can more easily identify, extract, and cite individual points, leading to measurable increases in citation frequency and content visibility across AI platforms. Semantic chunking through lists creates natural boundaries between ideas, allowing the model to process each item as a discrete unit of meaning while maintaining clear relationships to the overall topic, which improves both comprehension accuracy and the model’s ability to selectively cite relevant portions of the content. Hierarchical list structures—where main points are supported by sub-points and further details—mirror how human cognition organizes complex information, making it easier for AI models to understand relationships between concepts and to identify which information is most relevant to specific queries. Lists also create what might be called “citation-ready snippets”; when a model encounters well-formatted list items, it can easily extract and cite individual points without requiring complex inference about where one idea ends and another begins. The organizational clarity provided by lists extends beyond simple comprehension to improve the model’s ability to reason about the information, make connections to related concepts, and generate more accurate and nuanced responses. Organizations that restructure their content to emphasize lists and hierarchical organization consistently see improvements in AI citation rates, content visibility in AI Overviews, and overall discoverability through AI-driven search and discovery systems.
Implementing AI-friendly formatting requires a systematic approach that integrates structural optimization into content creation workflows from the initial planning stages through final publication. Begin by establishing a heading hierarchy that clearly reflects your content’s information architecture, using H1 for the main topic, H2 for major sections, and H3 for subsections, ensuring that this hierarchy is consistent across all content and accurately represents the logical relationships between ideas. Incorporate schema markup (such as JSON-LD structured data) to provide explicit semantic information that helps AI systems understand not just the structure of your content but also its meaning and context, particularly for specialized domains like products, articles, events, or organizations. Create TL;DR sections or executive summaries at the beginning of longer content pieces, formatted as concise lists or short paragraphs, that allow AI models to quickly grasp the essential information and improve the likelihood of accurate citations in AI-generated responses. Implement a consistent metadata strategy that includes descriptive titles, clear introductions, and relevant keywords naturally integrated into headings and opening sentences, providing AI systems with multiple signals about content meaning and relevance. Break complex information into semantic chunks by using lists, tables, and short paragraphs rather than dense blocks of text, ensuring that each section represents a complete thought or concept that can be understood independently. Establish templates and guidelines for your content team that standardize the use of formatting elements, making AI-friendly formatting a default practice rather than an afterthought, and regularly audit existing content to identify opportunities for structural improvement. Test your formatted content with AI systems (such as ChatGPT, Claude, or Perplexity) to verify that the structure is being interpreted correctly and that key information is being accurately extracted and cited.

The formatting of content directly influences how frequently it appears in AI-generated responses and how prominently it is cited across different AI platforms, making structural optimization a critical factor in content visibility and discoverability in the age of AI-driven search. AI Overviews (Google’s AI-generated summaries that appear at the top of search results) preferentially cite content that is well-structured and easy to parse, meaning that properly formatted content is significantly more likely to be selected for inclusion in these high-visibility summaries. Similarly, platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other conversational AI systems demonstrate measurably higher citation frequency for content that uses clear formatting, lists, and structured data, as these elements make it easier for the model to identify, extract, and attribute specific information. The relationship between formatting and visibility creates a compounding effect: content that is cited more frequently in AI responses gains increased exposure, which drives more traffic and signals to search engines that the content is authoritative and relevant, further improving its visibility in both traditional and AI-driven search results. Research tracking AI citation patterns shows that well-formatted content receives 2-3 times more citations in AI-generated responses compared to poorly formatted content covering the same topics, representing a substantial competitive advantage in AI-driven discovery. This impact extends beyond simple citation counts to affect how content is presented; AI systems are more likely to feature well-formatted content prominently in their responses, often using the original formatting (lists, tables, emphasis) in their output, which increases both visibility and credibility. For content creators and organizations, understanding and optimizing for AI citation patterns through proper formatting has become as important as traditional SEO optimization, representing a fundamental shift in how content strategy must be approached.
While traditional SEO has long focused on keyword optimization, meta tags, and link building to improve visibility in search engine results, AI-friendly formatting represents an evolution in content strategy that prioritizes structural clarity and semantic meaning over keyword density and algorithmic manipulation. Traditional SEO approaches often resulted in content that was optimized for search engine crawlers but remained difficult for humans to read, with keyword stuffing, awkward phrasing, and poor organization that prioritized ranking signals over user experience. In contrast, AI-friendly formatting creates content that is simultaneously optimized for both human readers and AI systems, as the structural clarity that helps AI models understand content also makes the content more accessible, scannable, and valuable to human audiences. The shift from keyword-focused to structure-focused optimization reflects a fundamental change in how search and discovery work; modern AI systems understand meaning and context far more effectively than earlier search engines, making the explicit semantic signals provided by good formatting more valuable than implicit keyword signals. However, traditional SEO principles remain relevant and important; keywords still matter for initial content discovery and relevance matching, and link building continues to influence authority and ranking, meaning that effective modern content strategy must integrate both traditional SEO and AI-friendly formatting approaches. The evolution from AI-driven search represents not a replacement of SEO but rather an expansion of content optimization to include structural and semantic considerations alongside traditional ranking factors. Organizations that successfully navigate this transition are those that recognize that good content strategy is not about choosing between SEO and AI optimization, but rather about creating content that is fundamentally well-structured, clearly written, and genuinely valuable to both human readers and AI systems.
A growing ecosystem of tools and platforms has emerged to support the creation and optimization of AI-friendly formatted content, making it increasingly easy for organizations to implement these practices across their content workflows. Markdown editors like Obsidian, Notion, and VS Code provide intuitive interfaces for creating well-structured content while maintaining the simplicity and machine-readability that makes Markdown ideal for AI processing, and many of these tools include features specifically designed to help users maintain consistent formatting and hierarchy. Documentation platforms such as Gitbook, ReadTheDocs, and Confluence have built-in support for Markdown and structured content creation, making them ideal for organizations that need to maintain large bodies of technical or reference content that will be processed by AI systems. AI-native writing tools like Claude’s interface, ChatGPT’s custom instructions, and specialized platforms designed for content optimization increasingly include features that help users understand how their content will be interpreted by AI systems and provide real-time feedback on formatting effectiveness. Content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, with plugins such as Yoast SEO and Rank Math, are evolving to include AI-friendly formatting recommendations alongside traditional SEO guidance, helping content creators optimize for both human readers and AI systems simultaneously. Schema markup generators and structured data tools make it easier to add semantic information to content without requiring deep technical knowledge, enabling content creators to enhance their content’s interpretability by AI systems. Analytics and monitoring tools now include features that track how content performs in AI-generated responses and AI Overviews, providing data-driven insights into which formatting approaches are most effective for improving visibility and citation frequency. The integration of AI-friendly formatting support across these diverse tools and platforms means that organizations can adopt these practices without requiring specialized expertise or significant workflow disruption, making AI-friendly formatting an increasingly standard and accessible component of modern content strategy.
Traditional web formatting focuses on visual presentation and user experience through CSS styling, while AI-friendly formatting prioritizes semantic structure and machine-readability. AI-friendly formatting uses clear hierarchies, lists, tables, and semantic chunking that help AI models understand content meaning, whereas traditional formatting may look good visually but provide minimal structural signals to AI systems. The best approach combines both: content that is visually appealing and semantically structured.
No—in fact, AI-friendly formatting typically improves human readability. Clear headings, organized lists, short paragraphs, and well-structured tables make content easier for humans to scan and understand. The structural elements that help AI systems parse content also help human readers quickly find relevant information and understand relationships between ideas.
The most critical elements are: hierarchical headings (H1, H2, H3) that establish information architecture, tables with clear headers for structured data, numbered and bulleted lists for discrete points, and semantic chunking into logical units. Research shows that tables achieve 96%+ extraction accuracy, while short paragraphs and emphasis formatting also significantly improve AI comprehension.
Markdown is superior for AI processing because it uses lightweight, unambiguous markup that is easy for models to parse without requiring complex format-specific logic. HTML includes styling information and complex nesting that adds noise to semantic content. Markdown's simplicity and machine-readability make it the optimal format for content intended to be processed by AI systems.
Yes, absolutely. You can restructure existing content by adding clear headings, breaking dense paragraphs into lists, converting data into tables, and implementing semantic chunking. Many tools can help automate this process, and even manual restructuring typically takes less time than creating new content while providing immediate improvements in AI citation rates.
AI-friendly formatting reduces processing costs by improving token efficiency. Well-structured content requires fewer tokens to convey the same information compared to dense, unstructured prose. Research shows that Markdown-formatted content uses 3-5 times fewer tokens than equivalent PDF content, directly reducing API costs and improving response speed.
Schema markup is not required but is highly recommended. While clear formatting alone helps AI systems understand content, schema markup (JSON-LD structured data) provides explicit semantic information that further improves comprehension and citation likelihood. Schema markup is particularly valuable for specialized content types like products, articles, events, or organizations.
Track metrics including: citation frequency in AI-generated responses (using tools like AmICited), appearance in AI Overviews and chatbot responses, extraction accuracy rates, and traffic from AI-driven discovery. Compare these metrics before and after implementing AI-friendly formatting to quantify the impact on visibility and discoverability.
Track how AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews reference your brand and content. Discover which of your pages get cited most frequently and optimize your content strategy based on real AI citation data.

Learn how to test content formats for AI citations using A/B testing methodology. Discover which formats drive the highest AI visibility and citation rates acro...
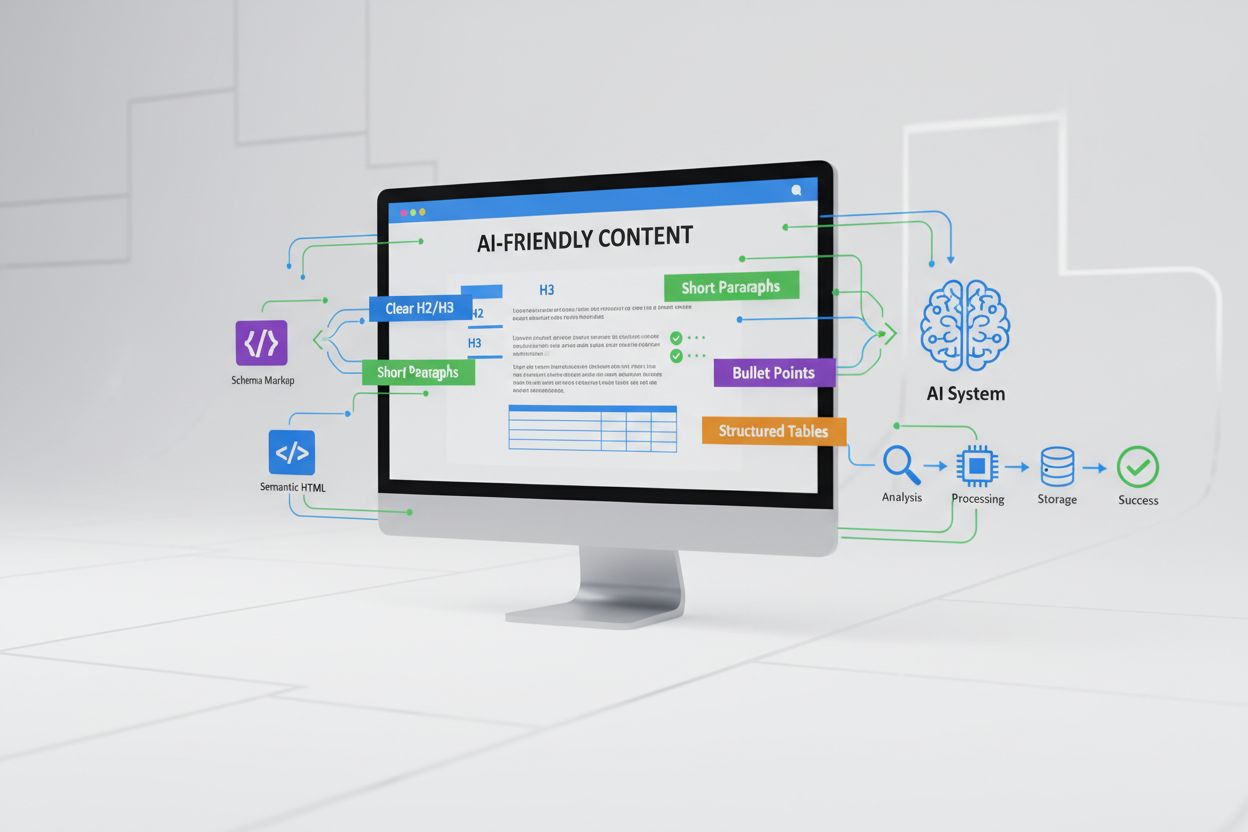
Learn what AI-scannable format means and how to structure content with clear headings, short paragraphs, and bullet points for better AI visibility and citation...

Learn to create comparison content optimized for AI citations. Use structured tables, schema markup, and fact-dense formatting to get cited in ChatGPT, Perplexi...