Generative AI
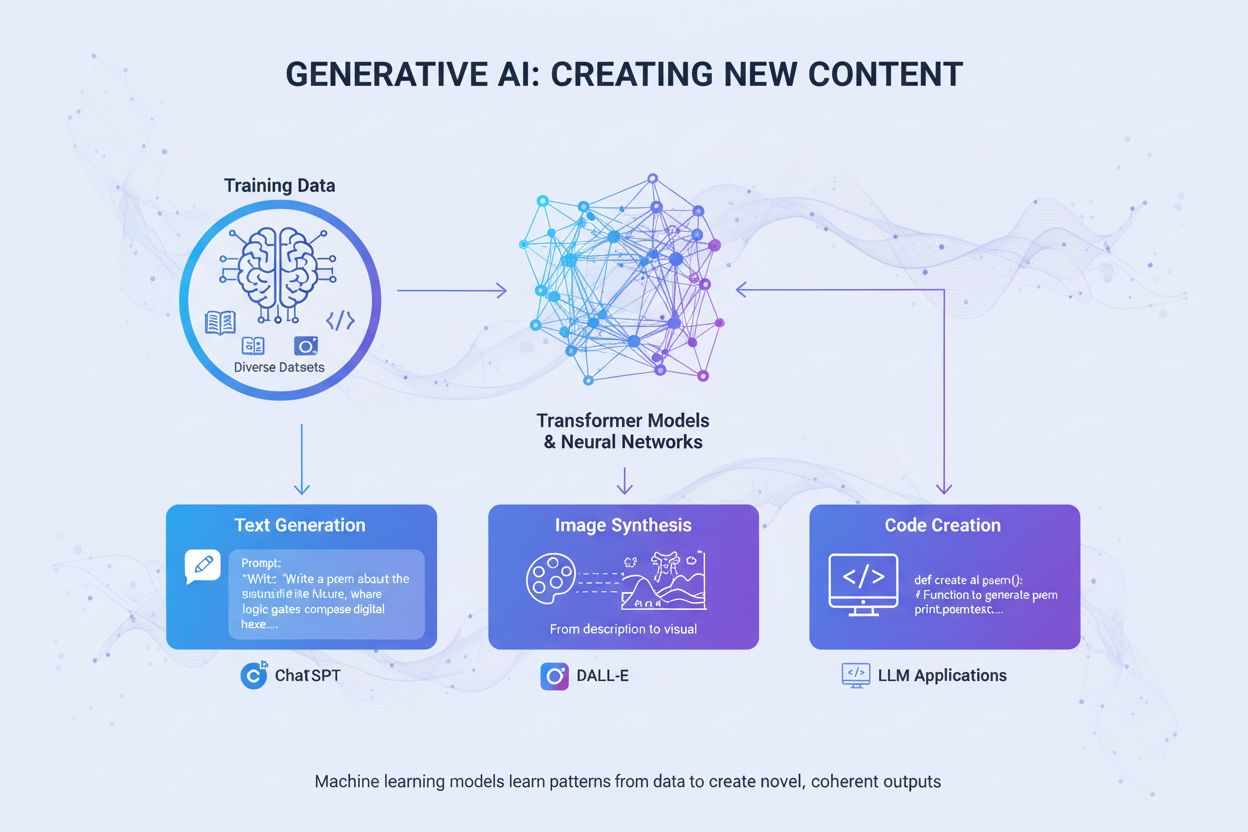
Generative AI creates new content from training data using neural networks. Learn how it works, its applications in ChatGPT and DALL-E, and why monitoring AI vi...
An AI-generated image is a digital image created by artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models rather than by human artists or photographers. These images are produced by training neural networks on vast datasets of labeled images, enabling the AI to learn visual patterns and generate original, realistic visuals from text prompts, sketches, or other input data.
An AI-generated image is a digital image created by artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models rather than by human artists or photographers. These images are produced by training neural networks on vast datasets of labeled images, enabling the AI to learn visual patterns and generate original, realistic visuals from text prompts, sketches, or other input data.
An AI-generated image is a digital image created by artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models rather than by human artists or photographers. These images are produced through sophisticated neural networks trained on vast datasets of labeled images, enabling the AI to learn visual patterns, styles, and relationships between concepts. The technology allows AI systems to generate original, realistic visuals from various inputs—most commonly text prompts, but also from sketches, reference images, or other data sources. Unlike traditional photography or manual artwork, AI-generated images can depict anything imaginable, including impossible scenarios, fantastical worlds, and abstract concepts that have never existed in physical reality. The process is remarkably fast, often producing high-quality images in seconds, making it a transformative technology for creative industries, marketing, product design, and content creation.
The journey of AI image generation began with foundational research in deep learning and neural networks, but the technology only became mainstream in the early 2020s. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), introduced by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, were among the first successful approaches, using two competing neural networks to generate realistic images. However, the real breakthrough came with the emergence of diffusion models and transformer-based architectures, which proved more stable and capable of producing higher-quality outputs. In 2022, Stable Diffusion was released as an open-source model, democratizing access to AI image generation and sparking widespread adoption. Shortly after, DALL-E 2 from OpenAI and Midjourney gained significant attention, bringing AI image generation into mainstream consciousness. According to recent statistics, 71% of social media images are now AI-generated, and the global AI image generator market was valued at $299.2 million in 2023, with projections to grow at 17.4% annually through 2030. This explosive growth reflects both technological maturation and widespread business adoption across industries.
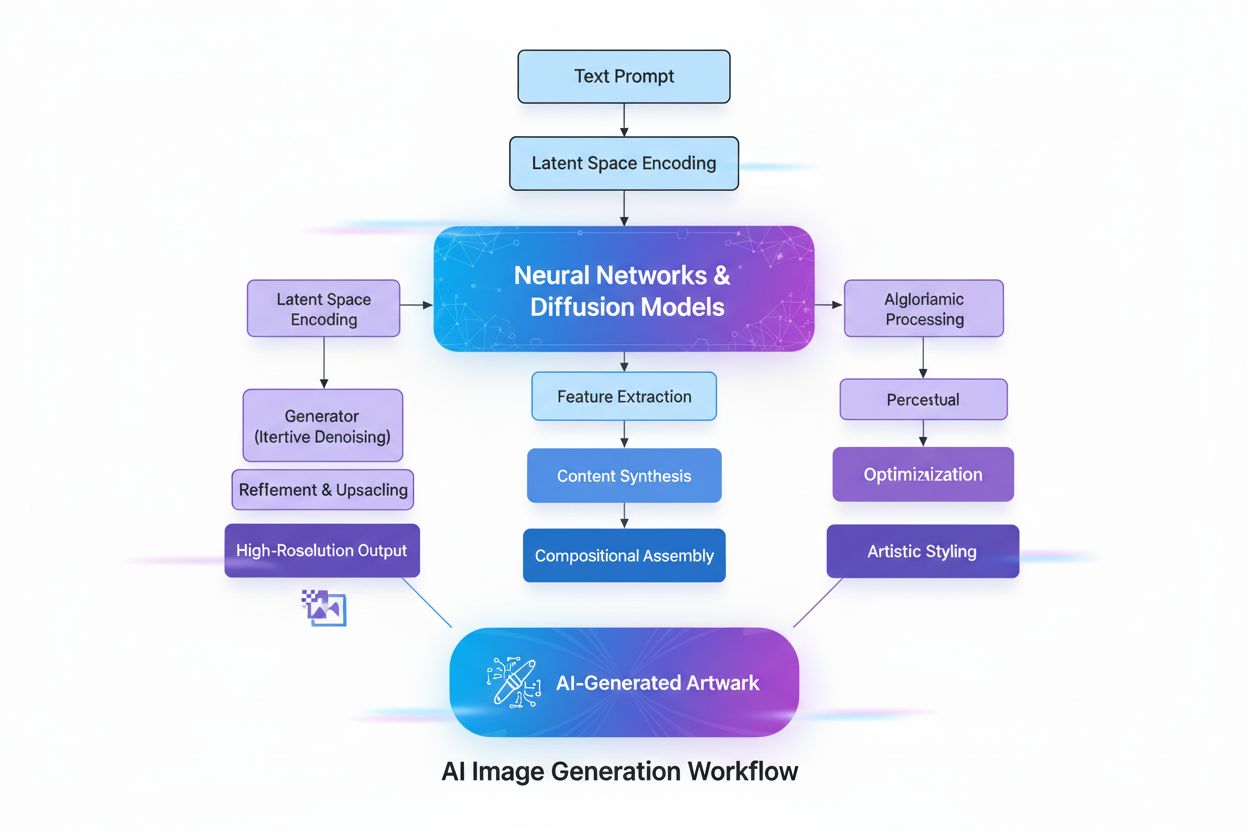
The creation of AI-generated images involves several sophisticated technical processes that work in concert to transform abstract concepts into visual reality. The process begins with text understanding using Natural Language Processing (NLP), where the AI converts human language into numerical representations called embeddings. Models like CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training) encode text prompts into high-dimensional vectors that capture semantic meaning and context. For example, when a user inputs “a red apple on a tree,” the NLP model breaks this down into numerical coordinates representing “red,” “apple,” “tree,” and their spatial relationships. This numerical map then guides the image generation process, acting as a rulebook that tells the AI what components to include and how they should interact.
Diffusion models, which power many modern AI image generators including DALL-E 2 and Stable Diffusion, work through an elegant iterative process. The model starts with pure random noise—essentially a chaotic pattern of pixels—and gradually refines it through multiple denoising steps. During training, the model learns to reverse the process of adding noise to images, essentially learning to “denoise” corrupted versions back to their original form. When generating new images, the model applies this learned denoising process in reverse, starting from random noise and progressively transforming it into a coherent image. The text prompt guides this transformation at each step, ensuring the final output aligns with the user’s description. This step-by-step refinement allows for exceptional control and produces remarkably detailed, high-quality images.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) employ a fundamentally different approach based on game theory. A GAN consists of two competing neural networks: a generator that creates fake images from random input, and a discriminator that attempts to distinguish real images from fake ones. These networks engage in an adversarial game where the generator continuously improves to fool the discriminator, while the discriminator becomes better at detecting fakes. This competitive dynamic drives both networks toward excellence, ultimately producing images that are nearly indistinguishable from real photographs. GANs are particularly effective for generating photorealistic human faces and performing style transfer, though they can be less stable to train than diffusion models.
Transformer-based models represent another major architecture, adapting the transformer technology originally developed for natural language processing. These models excel at understanding complex relationships within text prompts and mapping language tokens to visual features. They use self-attention mechanisms to capture context and relevance, enabling them to handle nuanced, multi-part prompts with exceptional accuracy. Transformers can generate images that closely match detailed textual descriptions, making them ideal for applications requiring precise control over output characteristics.
| Technology | How It Works | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best Use Cases | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffusion Models | Iteratively denoise random noise into structured images guided by text prompts | High-quality detailed outputs, excellent text alignment, stable training, fine control over refinement | Slower generation process, requires more computational resources | Text-to-image generation, high-resolution art, scientific visualizations | Stable Diffusion, DALL-E 2, Midjourney |
| GANs | Two competing neural networks (generator and discriminator) create realistic images through adversarial training | Fast generation, excellent for photorealism, good for style transfer and image enhancement | Training instability, mode collapse issues, less precise text control | Photorealistic faces, style transfer, image upscaling | StyleGAN, Progressive GAN, ArtSmart.ai |
| Transformers | Convert text prompts into images using self-attention and token embeddings | Exceptional text-to-image synthesis, handles complex prompts well, strong semantic understanding | Requires significant computational resources, newer technology with less optimization | Creative image generation from detailed text, design and advertising, imaginative concept art | DALL-E 2, Runway ML, Imagen |
| Neural Style Transfer | Fuses content from one image with artistic style from another | Artistic control, preserves content while applying style, interpretable process | Limited to style transfer tasks, requires reference images, less flexible than other methods | Artistic image creation, style application, creative enhancement | DeepDream, Prisma, Artbreeder |
The adoption of AI-generated images across business sectors has been remarkably rapid and transformative. In e-commerce and retail, companies use AI image generation to create product photography at scale, eliminating the need for expensive photo shoots. According to recent data, 80% of retail executives expect their businesses to adopt AI automation by 2025, and retail companies spent $19.71 billion on AI tools in 2023, with image generation representing a significant portion. The AI image editing market is valued at $88.7 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach $8.9 billion by 2034, with enterprise users accounting for approximately 42% of all spending.
In marketing and advertising, 62% of marketers use AI to create new image assets, and businesses using AI for social media content generation report 15-25% increases in engagement rates. The ability to rapidly generate multiple creative variations enables A/B testing at unprecedented scale, allowing marketers to optimize campaigns with data-driven precision. Cosmopolitan magazine made headlines in June 2022 by releasing a cover entirely created by DALL-E 2, marking the first time a major publication used AI-generated imagery for its cover. The prompt used was: “A wide angle shot from below of a female astronaut with an athletic female body walking with swagger on Mars in an infinite universe, synthwave, digital art.”
In medical imaging, AI-generated images are being explored for diagnostic purposes and synthetic data generation. Research has shown that DALL-E 2 can generate realistic X-ray images from text prompts and even reconstruct missing elements in radiological images. This capability has significant implications for medical training, privacy-preserving data sharing between institutions, and accelerating the development of new diagnostic tools. The AI-driven social media market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2031, up from $2.1 billion in 2021, reflecting the technology’s central role in content creation across digital platforms.
The rapid proliferation of AI-generated images has raised significant ethical and legal concerns that the industry and regulators are still grappling with. Copyright and intellectual property issues represent perhaps the most contentious challenge. Most AI image generators are trained on massive datasets of images scraped from the internet, many of which are copyrighted works created by artists and photographers. In January 2023, three artists filed a landmark lawsuit against Stability AI, Midjourney, and DeviantArt, claiming the companies used copyrighted images to train their AI algorithms without consent or compensation. This case exemplifies the broader tension between technological innovation and artist rights.
The question of ownership and rights to AI-generated images remains legally ambiguous. When an AI-generated artwork won first place at the Colorado State Fair’s fine arts competition in 2022, submitted by Jason Allen using Midjourney, significant controversy erupted. Many argued that since AI generated the artwork, it shouldn’t qualify as original human creation. The U.S. Copyright Office has indicated that works created entirely by AI without human creative input may not qualify for copyright protection, though this remains an evolving legal area with ongoing litigation and regulatory development.
Deepfakes and misinformation represent another critical concern. AI image generators can create highly realistic images of events that never occurred, enabling the spread of false information. In March 2023, AI-generated deepfake images depicting the fake arrest of former President Donald Trump spread across social media, created using Midjourney. These images were initially believed by some users to be real, demonstrating the technology’s potential for malicious misuse. The sophistication of modern AI-generated images makes detection increasingly difficult, creating challenges for social media platforms and news organizations attempting to maintain content authenticity.
Bias in training data is another significant ethical issue. AI models learn from datasets that can contain cultural, gender, and racial biases. The Gender Shades project led by Joy Buolamwini at MIT Media Lab revealed significant biases in commercial AI gender classification systems, with error rates for darker-skinned females being substantially higher than for lighter-skinned males. Similar biases can manifest in image generation, potentially perpetuating harmful stereotypes or underrepresenting certain demographics. Addressing these biases requires careful dataset curation, diverse training data, and ongoing evaluation of model outputs.
The quality of AI-generated images depends significantly on the quality and specificity of the input prompt. Prompt engineering—the art of crafting effective text descriptions—has become a critical skill for users seeking optimal results. Effective prompts share several characteristics: they are specific and detailed rather than vague, include style or medium descriptors (such as “digital painting,” “watercolor,” or “photorealistic”), incorporate atmosphere and lighting information (like “golden hour,” “cinematic lighting,” or “dramatic shadows”), and establish clear relationships between elements.
For example, instead of simply requesting “a cat,” a more effective prompt would be: “a fluffy orange tabby cat sitting on a windowsill at sunset, warm golden light streaming through the window, photorealistic, professional photography.” This level of detail provides the AI with specific guidance about appearance, setting, lighting, and desired aesthetic. Research shows that structured prompts with clear hierarchies of information produce more consistent and satisfactory results. Users often employ techniques like specifying artistic styles, adding descriptive adjectives, including technical photography terms, and even referencing specific artists or art movements to guide the AI toward desired outputs.
Different AI image generation platforms have distinct characteristics, strengths, and use cases. DALL-E 2, developed by OpenAI, generates detailed images from text prompts with advanced inpainting and editing capabilities. It operates on a credit-based system, with users purchasing credits for individual image generations. DALL-E 2 is known for its versatility and ability to handle complex, nuanced prompts, making it popular among professionals and creatives.
Midjourney focuses on artistic and stylized image creation, favored by designers and artists for its unique aesthetic sensibilities. The platform operates through a Discord bot interface, requiring users to input prompts via the /imagine command. Midjourney is particularly known for producing visually appealing, painterly images with complementary colors, balanced lighting, and sharp details. The platform offers subscription tiers ranging from $10 to $120 per month, with higher tiers providing more monthly image generation allowances.
Stable Diffusion, developed through collaboration between Stability AI, EleutherAI, and LAION, is an open-source model that democratizes AI image generation. Its open-source nature allows developers and researchers to customize and deploy the model, making it ideal for experimental projects and enterprise implementations. Stable Diffusion operates on a latent diffusion model architecture, enabling efficient generation on consumer-grade graphics cards. The platform is competitively priced at $0.0023 per image, with free trials available for newcomers.
Google’s Imagen represents another significant player, offering text-to-image diffusion models with unprecedented photorealism and deep language understanding. These platforms collectively demonstrate the diversity of approaches and business models in the AI image generation space, each serving different user needs and use cases.
The AI image generation landscape is evolving rapidly, with several significant trends shaping the future of the technology. Model improvement and efficiency continues at a breakneck pace, with newer models producing higher resolution outputs, better text alignment, and faster generation times. The AI image generator market is projected to grow at 17.4% annually through 2030, indicating sustained investment and innovation. Emerging trends include video generation from text, where AI systems extend image generation capabilities to create short video clips; 3D model generation, enabling AI to create three-dimensional assets directly; and real-time image generation, reducing latency to enable interactive creative workflows.
Regulatory frameworks are beginning to emerge globally, with governments and industry bodies developing standards for transparency, copyright protection, and ethical use. The NO FAKES Act and similar legislation propose requirements for watermarking AI-generated content and disclosing when AI was used in creation. 62% of global marketers believe required labels for AI-generated content would have a positive effect on social media performance, suggesting industry recognition of transparency’s importance.
Integration with other AI systems is accelerating, with image generation becoming embedded in broader AI platforms and workflows. Multimodal AI systems that combine text, image, audio, and video generation are becoming increasingly sophisticated. The technology is also moving toward personalization and customization, where AI models can be fine-tuned to specific artistic styles, brand aesthetics, or individual preferences. As AI-generated images become more prevalent across digital platforms, the importance of brand monitoring and citation tracking in AI responses grows correspondingly, making tools that track how brands appear in AI-generated content increasingly valuable for businesses seeking to maintain visibility and authority in the age of generative AI.
AI-generated images are created entirely by machine learning algorithms from text prompts or other inputs, while traditional photography captures real-world scenes through a camera lens. AI images can depict anything imaginable, including impossible scenarios, whereas photography is limited to what exists or can be physically staged. AI generation is typically faster and more cost-effective than organizing photo shoots, making it ideal for rapid content creation and prototyping.
Diffusion models work by starting with pure random noise and gradually refining it through iterative denoising steps. The text prompt is converted into numerical embeddings that guide this denoising process, progressively transforming the noise into a coherent image that matches the description. This step-by-step approach allows for precise control and produces high-quality, detailed outputs with excellent alignment to the input text.
The three primary technologies are Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), which use competing neural networks to create realistic images; Diffusion Models, which iteratively denoise random noise into structured images; and Transformers, which convert text prompts into images using self-attention mechanisms. Each architecture has distinct strengths: GANs excel at photorealism, diffusion models produce highly detailed outputs, and transformers handle complex text-to-image synthesis exceptionally well.
Copyright ownership of AI-generated images remains legally ambiguous and varies by jurisdiction. In many cases, the copyright may belong to the person who created the prompt, the developer of the AI model, or potentially no one if the AI operates autonomously. The U.S. Copyright Office has indicated that works created entirely by AI without human creative input may not qualify for copyright protection, though this remains an evolving legal area with ongoing litigation and regulatory development.
AI-generated images are widely used in e-commerce for product photography, in marketing for creating campaign visuals and social media content, in game development for character and asset creation, in medical imaging for diagnostic visualization, and in advertising for rapid concept testing. According to recent data, 62% of marketers use AI to create new image assets, and the AI image editing market is valued at $88.7 billion in 2025, demonstrating significant enterprise adoption across industries.
Current AI image generators struggle with generating anatomically correct human hands and faces, often producing unnatural features like extra fingers or asymmetrical facial elements. They also depend heavily on training data quality, which can introduce biases and limit diversity in generated outputs. Additionally, achieving specific details requires careful prompt engineering, and the technology sometimes produces results that lack natural appearance or fail to capture nuanced creative intent.
Most AI image generators are trained on massive datasets of images scraped from the internet, many of which are copyrighted works. This has led to significant legal challenges, with artists filing lawsuits against companies like Stability AI and Midjourney for using copyrighted images without permission or compensation. Some platforms like Getty Images and Shutterstock have banned AI-generated image submissions due to these unresolved copyright concerns, and regulatory frameworks are still being developed to address data transparency and fair compensation.
The global AI image generator market was valued at $299.2 million in 2023 and is projected to grow at a 17.4% compound annual growth rate through 2030. The broader AI image editing market is valued at $88.7 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach $8.9 billion by 2034. Additionally, 71% of social media images are now AI-generated, and the AI-driven social media market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2031, demonstrating explosive growth and mainstream adoption.
Start tracking how AI chatbots mention your brand across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms. Get actionable insights to improve your AI presence.

Generative AI creates new content from training data using neural networks. Learn how it works, its applications in ChatGPT and DALL-E, and why monitoring AI vi...
Learn what AI content generation is, how it works, its benefits and challenges, and best practices for using AI tools to create marketing content optimized for ...

Learn what user-generated content for AI is, how it's used to train AI models, its applications across industries, and the importance of authentic data for mach...
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and analyze our traffic. See our privacy policy.